Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Heart failure in children and adolescents: an update on diagnostic approaches and management
- Amit Agrawal, Dalwinder Janjua, Abdulrahman Ahmed Alsayed Ali Zeyada, Ahmed Taher Elsheikh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):178-190. Published online June 19, 2023
-
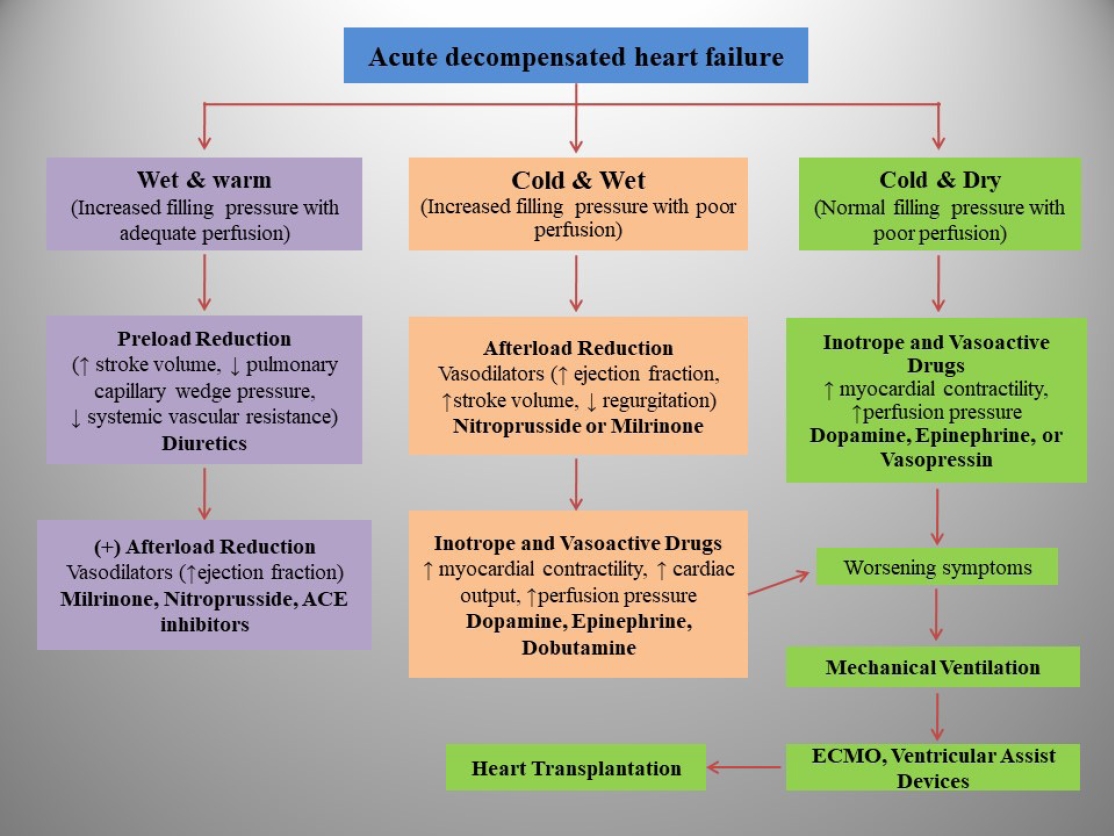
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) is a clinical syndrome featuring various symptoms (shortness of breath, ankle swelling, fatigue) and signs (pulmonary crackles, peripheral edema).
· Congenital heart diseases are the most common underlying etiology of PHF, whereas myocarditis and primary cardio-myopathies are common in children without structural ab-normalities.
· PHF pathophysiology is complex and multifactorial and varies by etiology and age.
· PHF management includes decongestive therapy, treatment of underlying causes, preventing progression, and managing pulmonary or systemic obstructions.
· Drugs should be chosen based on pharmacodynamics, clinical manifestations, hemodynamic state, and renal function.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia in children and adolescents: a single center experience
- Myung Chul Hyun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(12):390-394. Published online December 22, 2017
-
Purpose Atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT) is less common in pediatric patients than in adult patients. Thus, data for pediatric AVNRT patients are insufficient. Hence, we aimed to analyze the patient characteristics, treatment, and any recurrences in pediatric AVNRT patients.
Methods We reviewed the records of 50 pediatric AVNRT patients who had undergone radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) between January 1998 and December 2016...
- Case Report
- A pediatric case of Brugada syndrome diagnosed by fever-provoked ventricular tachycardia
- Geena Kim, Ye-Chan Kyung, I-Seok Kang, Jinyoung Song, June Huh, Young Keun On
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(8):374-378. Published online August 25, 2014
-
Brugada syndrome is a rare channelopathy associated with the
SCN5A gene that causes fatal ventricular arrhythmias. This case of Brugada syndrome, in which ventricular tachycardia (VT) was provoked by high fever, is the first report in a Korean child. The boy had retinoblastoma of his left eye diagnosed at 16 months of age. After chemotherapy, he contracted a catheter-related infection...
- Original Article
- Orthostatic symptoms does not always manifest during tilt-table test in pediatric postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome patients
- Tae-Eon Huh, Jung Sook Yeom, Young-Soo Kim, Hyang-Ok Woo, Ji Sook Park, Eun Sil Park, Ji-Hyun Seo, Jae-Young Lim, Chan-Hoo Park, Ki-Jong Park, Hee-Shang Youn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(1):32-36. Published online January 29, 2013
-
Purpose Chronic day-to-day symptoms of orthostatic intolerance are the most notable features of postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS). However, we have encountered patients with such symptoms and excessive tachycardia but with no symptoms during the tilt-table test (TTT). We aimed to investigate whether POTS patients with chronic orthostatic intolerance always present orthostatic symptoms during the TTT and analyze the factors underlying...
- Results of radiofrequency catheter ablation in children and adolescent with tachyarrhythmia
- Young Beom Chang, Seung Hyun Lee, Eun Young Kang, Kyoung-Suk Rhee, Chan Uhng Joo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(11):1085-1090. Published online November 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) has become an effective therapeutic modality for treating pediatric tachyarrhythmias. Using conventional RFCA catheters, ablation of parahisian accessory pathways may be difficult and have high risk for heart block. We reviewed the efficacy and complications of the RFCA in children and adolescent with arrhythmias including parahisian accessory pathways. Methods : We studied 48 patients... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Repeated Ventricular Tachycardia Caused by Cardiac Rhabdomyomas in an Infant with Tuberous Sclerosis
- Hee Jung Joo, Min Seob Song, Tae Gyu Hwang, Chul Ho Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(9):913-917. Published online September 15, 2003
-
Cardiac rhabdomyomas are relatively uncommon and associated with tuberous sclerosis in 40-50% cases. We report a 10-month-old infant with tuberous sclerosis who presented with ventricular arrythmias and status epilepticus. There were hypopigmented macules on the body, periventricular calcifications, renal cyst and cardiac rabdomyomas just below the aortic valve. The patient required resection of left ventricular subaortic masses due to sustained... -
- Original Article
- Role of Transesophageal Pacing in Evaluation of Palpitation in Infants and Children
- Su-Jeong Ryu, Jae Kon Ko, Young Hwue Kim, In Sook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(1):51-55. Published online January 15, 2003
-
Purpose : We intended to find out the role of transesophageal atrial pacing in evaluation of infants and children with palpitation of unknown origin. Methods : We tried transesophageal atrial pacing study in 69 infants and children with palpitation, in whom tachycardia wasn't documented in electrocardiogram and reviewed retrospectively the records of transesophageal pacing and medical records of theses patients to... -
- Clinical Features and ECG Findings of Supraventricular Tachycardia in Pediatric Patients
- Chang Hwan Jang, Myung Chul Hyun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(9):1012-1018. Published online September 15, 2001
-
Purpose : Supraventricular tachycardia(SVT) is the most frequent symptomatic arrhythmia in children. We performed this study to disover the SVT mechanisms, age at SVT onset, symptoms and ECG findings of SVT and effect of adenosine on SVT. Methods : We studied 57 patients(male : 30, female : 27, age : 1 day-15.8 years) who had been admitted or transferred due to SVT from January,... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Ventricular Tachycardia after Chloral Hydrate Ingestion
- Hye Kyung Lee, Yoon Seop Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(10):1390-1394. Published online October 15, 2000
-
Chloral hydrate is widely used as a sedative or hypnotic, especially in pediatric patients, but cardiac arrhythmia following chloral hydrate administration has rarely been reported in literature up to date. The most common cardiac arrhythmia is ventricular extrasystole. We describe a 17- year-old Down syndrome patient who developed a life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia developed after chloral hydrate administration of 100mg/kg body... -
- Original Article
- Treatment of Tachycardia by Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation in Children and Adolescents
- Sung Jae Lee, Mi Jin Jung, Sung Ho Kim, Walter C. Schueller, Gil Hyun Kim, Hak Soo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(2):210-215. Published online February 15, 2000
-
Purpose : RFCA has been proven to be an effective and safe tool for treating different kinds of tachycardia in adults. This study was designed to analyze the efficacy of this method in children and adolescents. Methods : Seventy-eight patients referred to Gachon Medical School, Gil Hospital for ablation of supraventricular(SVT) and ventricular tachycardia(VT) between January 1997 and February 1999 were... -
- Short-term Result of Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation in Pediatric Patients with Paroxysmal Tachycardia
- Hee Suk Jang, Hee Jung Cho, Myung Chul Hyun, Sang Bum Lee, Young Keun Cho, Chang Ho Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(2):203-209. Published online February 15, 2000
-
Purpose : To find out the efficacy, safety and early complication of radiofrequency catheter ablation(RFCA) in pediatric patients with paroxysmal tachycardia, we compared short-term results of RFCA in pediatric patients to adult patients. Methods : We studied 25 patients(11 pediatric patients, 14 adult patients), who underwent RFCA due to paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia(PSVT) or idiopathic ventricular tachycardia(VT) from November 1997 to August... -
- Atrial Ectopic Tachycardia in Infant
- Myung Ja Yoon, Chung Il Noh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(5):646-653. Published online May 15, 1998
-
Purpose : Atrial ectopic tachycardia(AET) in older children and adult is characterized by being chronic, incessant and intractable. However, the nature of infantile AET is not defined yet. The purpose of this study was to evaluate our experience of infantile AET. Methods : We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 13 infants(mean onset age, 2.8±2.3 months) diagnosed at Seoul National University... -
- Effucact of Adenosine Triphosphate in Infants and Children with Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Yae Kyung Suh, Chung Il Noh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(3):355-363. Published online March 15, 1992
-
Acute tachyarrhythmia in infancy and childhood may be life-threatening if it is not treated promptly and accurately. The selection of a safe and effective pharmacologic agent is work in hand. We tried ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to pediatric patients with acute epidsodes of supraventricular tachycardia for therapeutic or diagnostic purpose and determined the safety and effectiveness of the drug. ATP was given... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Broad QRS Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia That is Difficult to Differentiate from Ventricular Tachycardia
- Hung Ki Min, Hyun Hi Kim, Jong Wan Kim, Kyung Tai Whang, Sung Hoon Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(2):257-262. Published online February 15, 1992
-
A narrow QRS paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is a common dysrrhythmia and medical emergency in childhood. We experienced a case of broad QRS type paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia which was induced by transesophageal pacing technique and the morphology of the QRS complex was similar to that of ventricular tachycardia. So, We report this with a brief review and its related literatures. -
- Original Article
- Clinical study of supraventricular tachycardia in children.
- Eui Kyung Chung, Yun Seok Suh, Joo Won Lee, Soon Kyum Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(6):796-804. Published online June 30, 1991
-
Supraventricular tachycardia is the most symptomatic dysrhythmia encountered in infants and children. Recognition of the dysrhythmias is of great clinical importance, since increasing number of infants will develop congestive heart failure and occasionally circulatory collapse. Retrospective study was done in 17 patients with supraventricular tachycardia, who were admitted to our hospital from 1983 to 1989. The results were as follows: 1) 47 percent of our patients with... -
- Clinical Characteristics of Ventricular Tachycardia on 24 hour ECG in Children.
- Ki Soo Kim, Young Hwue Kim, Chung Il Noh, Jung Yun Choi, Yong Soo Yoon, Chang Yee Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1989;32(7):958-964. Published online July 31, 1989
-
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is uncommon, but is in increasing tendency probably due to better case detection and longer survival of the patients with complex congenital heart disease. Widespread use of 24 hour ECG has contributed a lot to better understanding of ventricular tachycardia. Fourteen cases of ventricular tachycardia diagnosed by 24 hour ECG at Seoul National Children’ s Hospital from Feb. 1986 to Sep.... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Chronic Atrial Tachycardia Managed with Digoxin and Reserpine.
- Young Hee Kim, Young Ju Choi, Sang Il Rhee, Sang Woo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(1):79-83. Published online January 31, 1984
-
An 1 8/12 year old girl had chronic, repetitive left atrial tachycardia and it was unresponsive to usual antiarrythmic drugs. The chief complaints were cyclic lethargy and irritability, occasionally associated with cyanosis and sweating. Her heart rate showed marked variation, depending upon the time of the day and her state of consciousness. ECG showed supraventricular tachycardia with ectopic pace-maker, proposed by... -
- A Case of Chronic Atrial Tachycardia.
- Seung Won Park, Moo Young Oh, In Soon Park, Chul Ho Kim, Soon Yong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(9):905-908. Published online September 30, 1983
-
We report a case of chronic atrial tachycardia in a 8 year-old boy. One year 3 month duration of chronic precordial palpitation is the only complaint on admission. Diagnosis was confirmed with characteristic EKG findings. Digitalis therapy was tried, but in vain. The clinical manifestations have been persistent during follow-up for 1 year 6 months since diagnosis. -
- A Case of Chaotic Atrial Tachycardia.
- Jung Hee Park, Eun Ai Lee, Joong Gon Kim, Keun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(2):180-182. Published online February 28, 1983
-
A 1.5 month-old male with rapid and irregular pulse rate had an uncommon form of atrial tachycardia. The electrocardiogram was compatable with the diagnosis of chaotic atrial tachycardia or multifocal atrial tachycardia. The patient was treated with digoxin. -
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









