|
Question: Is vitamin E a viable therapeutic option for managing neonatal hyperbilirubinemia?
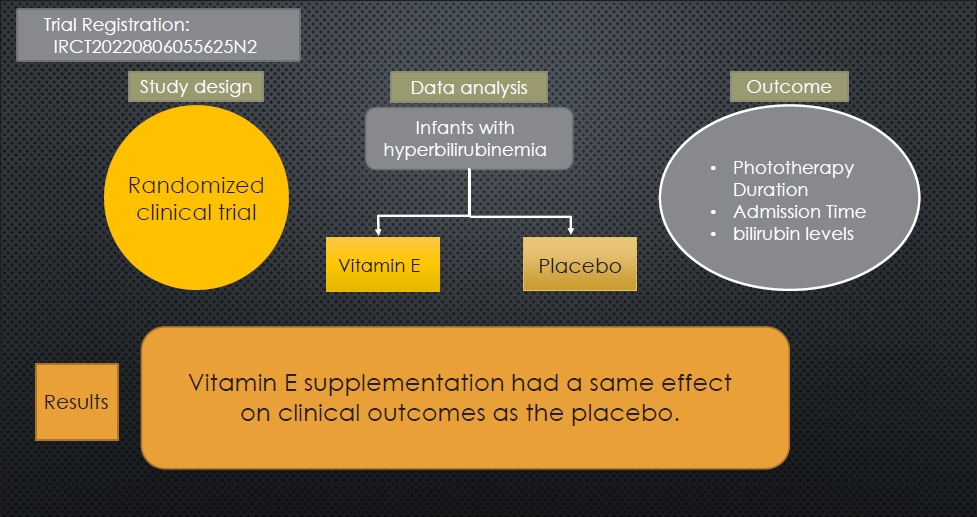
Finding: This randomized clinical trial examined the effects of oral vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin reduction (primary outcome), phototherapy duration, and length of hospital stay (secondary outcome) in 138 infants.
Meaning: Infants administered vitamin E versus placebo demonstrated similar reductions in bilirubin levels and length of hospital stay. |


