|
Questions: This study aimed to describe the survival of premature infants with critical congenital heart disease (CHD) and to identify the risk factors including the new modified version of the Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery (M-RACHS) associated with mortality.
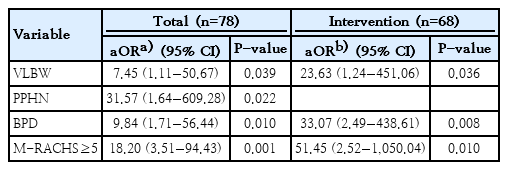
Finding: For premature infants with critical CHD, survival rate was 76.9% and very low birth weight (VLBW), persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), and M-RACHS 5 or more were associated with in-hospital mortality.
Meaning: VLBW, PPHN and BPD, as well as M-RACHS≥5, were risk factors for mortality among premature infants with critical CHD. |


