Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 60(7); 2017 |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Escherichia coli sequence type (ST) 131, a multidrug-resistant clone causing extraintestinal infections, has rapidly become prevalent worldwide. However, the epidemiological and clinical features of pediatric infections are poorly understood. We aimed to explore the characteristics of ST131 Escherichia coli isolated from Korean children with urinary tract infections.
Methods
We examined 114 uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) isolates from children hospitalized at Chung-Ang University Hospital between 2011 and 2014. Bacterial strains were classified into STs by partial sequencing of seven housekeeping genes (adk, fumC, gyrB, icd, mdh, purA, and recA). Clinical characteristics and antimicrobial susceptibility were compared between ST131 and non-ST131 UPEC isolates.
Results
Sixteen UPEC isolates (14.0%) were extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producers; 50.0% of ESBL-producers were ST131 isolates. Of all the isolates tested, 13.2% (15 of 114) were classified as ST131. There were no statistically significant associations between ST131 and age, sex, or clinical characteristics, including fever, white blood cell counts in urine and serum, C-reactive protein, radiologic abnormalities, and clinical outcome. However, ST131 isolates showed significantly lower rates of susceptibility to cefazolin (26.7%), cefotaxime (40.0%), cefepime (40.0%), and ciprofloxacin (53.3%) than non-ST131 isolates (65.7%, 91.9%, 92.9%, and 87.9%, respectively; P<0.001 for all). ESBL was more frequently produced in ST131 (53.3%) than in non-ST131 (8.1%) isolates (P<0.01).
Conclusion
ST131 E. coli isolates were prevalent uropathogens in children at a single medical center in Korea between 2011 and 2014. Although ST131 isolates showed higher rates of antimicrobial resistance, clinical presentation and outcomes of patients were similar to those of patients infected with non-ST131 isolates.
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is one of the most common bacterial infections and Escherichia coli is the most common bacterial species causing UTI in children1). Infants and children diagnosed with UTI usually present with fever only, and absence of urinary symptoms such as dysuria and frequency. Therefore, UTI is an important disease that should be considered in pediatric febrile illness without focus1,2). Although febrile UTIs in children might be upper UTIs, antimicrobial therapy has mostly been performed successfully in developed countries. However, extended spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) has emerged as a major global public health concern because infections due to ESBL-containing pathogens continue to be associated with significant morbidity and mortality worldwide3,4).
ESBL can spread between bacteria in hospitals and communities via transmissible genetic elements or specific bacterial clones. Recently, the sequence type (ST) 131 E. coli strain emerged as a major clone harboring drug-resistance potential such as that provided by ESBL in various types of extraintestinal infections worldwide. Therefore, it is very important to continuously monitor and promptly identify the regional epidemiology of this virulent strain of E. coli5,6).
In the past decade, many studies have been performed to identify the clinical, epidemiological, and microbiological characteristics of ST131 in adults7,8,9). However, limited data are available regarding extraintestinal infections caused by ST131 strains in children. In this study, we aimed to determine the characteristics of ST131 UPEC strains isolated from Korean children with UTI.
This was a prospective study conducted from March 2011 to December 2014. All subjects were children who were younger than 18 years, had been admitted to Chung-Ang University Hospital with diagnosis of community-acquired UTI. Informed consent was submitted by the parents/guardians of all subjects, and by the children older than 8 years when they were enrolled.
Urine samples were collected from midstream urine in toilet-trained children and by catheterization in others. UTI was defined as the presence of both positive urine culture (>105 colony-forming units [CFUs]/mL) and pyuria (>5 white blood cells [WBCs]/high-power field) with fever and/or urinary symptoms (i.e., urgency, frequency, and dysuria). UTI with fever or radiologic abnormality of kidney was defined as acute pyelonephritis (APN), and otherwise as cystitis. Asymptomatic bacteriuria, defined as significant growth of E. coli (>105 CFUs/mL) without fever or any urinary symptoms, were excluded in this study.
Clinical data were obtained from the medical records of the patients and entered into standardized case report forms. Inappropriate antimicrobial therapy was defined as the use of antimicrobials nonsusceptible to the isolated E.coli. Clinical success was defined as the resolution of fever with an improvement in urinalysis at day 7. Otherwise, patients were regarded as treatment failure. Recur was defined as 2nd episode of UTI after the completion of antimicrobial therapy for 1st episode of UTI. The present study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Chung-Ang University College of Medicine (approval number: 10-013-02-03).
All UPEC isolates were identified on the basis of typical morphology, lactose fermentation, positive spot indole test, and VITEK 2-GN cards (bioMérieux, Marcy l'Etoile, France). The isolates were stored at -80℃ until further use. Extraction and purification of bacterial whole-cell DNA from UPEC colonies were performed as described in the instruction manual of the QIAamp Kit (QIAGEN GmbH, Hilden, Germany).
Multiple polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays for gadA, chuA, and yjaA genes and the TSPE4.C2 DNA fragment were performed. The PCR mixture composition and thermal cycling conditions have been previously described10). PCR products were electrophoresed on agarose gels and photographed under ultraviolet transillumination. We could identify the 373-, 281-, 216-, and 158-base pair (bp) bands for gadA, chuA, yjaA, and TSPE4.C2, respectively. On the basis of the results of the PCRs, chuA– TSPE4.C2–, chuA– TSPE4. C2+, chuA+ yjaA+, and chuA+ yjaA– strains were classified as belonging to groups A, B1, B2, and D, respectively. The glutamate decarboxylase-alpha (gadA) gene of E. coli was used as an internal amplification control.
The MLST scheme used the following seven housekeeping genes: adk, fumC, gyrB, icd, mdh, purA, and recA. PCR amplification for each gene was performed using the same reaction mixture, primers, and conditions as described previously10). Because this study focused on ST131, we first screened the UPEC isolates on the basis of adk and fumC. If allele typing of adk and fumC identified allele 53 (adk53) and allele 40 (fumC40), respectively, further allele typing for gyrB, icd, mdh, purA, and recA was performed to confirm ST131. If the isolate had alleles other than adk53 or fumC40, the MLST procedure was stopped and the isolate was assigned to non-ST131. However, in the case of UPEC isolates with ESBL, we continued to analyze the alleles of other MLST genes to identify the full range of allele types of MLST for the isolates.
The sequencing reactions were carried out using a BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit (Applied Biosystems Inc., Foster City, CA, USA) with each forward primer. The reaction products were separated and detected using an Applied Biosystems 3730xl automated sequencer (Applied Biosystems Inc.), and the data were analyzed using the Sequencing analysis v3.3 software (Applied Biosystems Inc.). The allelic profile was summarized by assigning a ST via a web database (http://mlst.warwick.ac.uk/mlst/dbs/Ecoli/). The eBURST v3 software (available at http://www.mlst.net) was used to estimate the relationships between the isolates and to assign the strains to a clonal complex (CC)11).
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of all isolates to ampicillin, amoxicillin-clavulanate, piperacillin-tazobactam, cefazolin, cefotaxime, cefepime, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX), amikacin, gentamicin, ciprofloxacin, ertapenem, meropenem, imipenem, and tigecycline was performed using a VITEK 2 automated system (bioMérieux, Marcy l'Etoile, France). In addition, each isolate was tested using a VITEK 2 system with the ESBL test panel (bioMérieux) included in the NO45 card (bioMérieux). In vitro antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed by the broth microdilution method and the results were interpreted using the 2010 Clinical Laboratory Standard Institute breakpoints. Isolates resistant to antibiotics of three or more different classes were classified as multidrug resistant (MDR).
All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 22.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). The prevalence of virulence genes and antibiotic resistance patterns were compared between the 2 groups using Pearson chi-square test and Fisher exact test. Continuous variables were compared with the Student t test and Mann-Whitney U test. A P value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
A total of 114 subjects were enrolled in the study; the median age was 5.7 months (range, 0.5–227.6 months), and the male to female ratio was 1.53:1. Ninety-five of subjects (83.3%) presented with fever and 21 (18.4%) presented with urologic symptoms. APN and cystitis were diagnosed in 101 (88.6%) and 13 (11.4%), respectively. The mean serum WBC count was 14,942.5±5,606.2/mm3 and mean C-reactive protein (CRP) level was 48.2±49.3 mg/L. Kidney ultrasonography (US), dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scan, and voiding cystourethrography (VCUG) were performed in 99 (86.8%), 92 (80.7%), and 14 subjects (12.3%), respectively. Radiological abnormalities were found in 40 subjects (40.4%) in US, 23 (25.0%) in DMSA scan, 5 (35.7%) in VCUG. The number of subjects with abnormality in any of the three radiologic modalities was 53 (52.4%).
Cystitis were all treated only with oral 3rd generation cephalosporins such as cefpodoxime (n=4), cefdinir (n=1), and cefixime (n=8). In all APNs, cefotaxime was injected empirically, and continued to the end of admission in most cases (n=90, 89.1%). Among the 16 UTIs caused by ESBL-producing E.coli, 8 cases were treated definitively with another antibiotic agent, which was carbapenem (n=6, 75.0%) or piperacillin-tazobactam (n=2, 25.0 %). Treatment failure or recurrence did not occur in the study subjects.
One UPEC isolate from each subject was analyzed for phylogenetic grouping and MLST. In the phylogenetic grouping, gadA was amplified in all the UPEC isolates. Group B2 was the most common one at 83% (n=95), followed by groups D (11%, n=13), A (3%, n=3), and B1 (2%, n=3) (Fig. 1). All ST131 isolates and most isolates with ESBL (87.5%) were in the B2 group.
In the MLST, a total of 15 UPEC isolates were assigned to both adk53 and fumC40. All these isolates were confirmed as ST131 with an allelic profile of 53-40-47-13-36-28-29. In the other 99 isolates, none were assigned to adk53 or fumC40. Additionally, isolates with ESBL (n=16) were all fully analyzed for MLST, with the following results: ST131 (n=8, 50.0%), CC14 (ST14 and ST1193; n=3, 18.8%), ST69 (n=2, 12.5%), ST38 (n=1, 6.3%), ST73 (n=1, 6.3%), ST95 (n=1, 6.3%).
UTIs caused by ST131 isolates (n=15) were compared with those caused by non-ST131 isolates (n=99) in terms of the clinical aspects (Table 1). The mean ages of subjects were 13.61±17.15 and 22.62±40.09 months (P=0.409), and sex ratios were 1.8 and 1.5 in ST131 and non-ST131 groups (P=0.759), respectively. Fever and urologic symptoms manifested in 80.0% and 20.0%, respectively, of ST131 group, which did not differ significantly from the findings for the non-ST131 group (P=1.000 and P=0.720, respectively). The proportion of APN was also similar in ST131 (n=13, 86.7%) and non-ST131 (n=86, 86.9%) groups (P=1.000). In addition, laboratory findings such as urine nitrite, pyuria, leukocytosis, and CRP elevation were not significantly different between the 2 groups (P>0.05, for all). The proportion of subjects with any radiologic abnormality was 61.5% (n=8) in the ST131 group and 51.1% (n=45) in the non-ST131 group (P=0.561). The proportion of abnormality in US, DMSA, and VCUG individually were also not significantly different in both groups (P>0.05, for all). Finally, in ST131 group, initial empirical antimicrobials were more inappropriate than in non-ST131 group (53.3% vs. 8.1%, respectively; P<0.001), but definitive antimicrobials were not significantly different between the 2 groups in terms of inappropriateness (20.0% vs. 7.1%, respectively; P=0.125).
The susceptibility rates of all UPEC isolates for antimicrobial agents tested were as follows: ampicillin, 28.9%; amoxicillin-clavulanate, 81.6%; piperacillin-tazobactam, 69.3%; cefazolin, 60.5 %; cefotaxime, 85.1%; cefepime, 86.0%; amikacin, 99.1%; gentamycin, 72.8%; TMP-SMX, 61.4%, ciprofloxacin, 83.3%; ertapenem, 100%; meropenem, 100%; imipenem, 100%; and tigecycline, 100%. A total of 27 isolates (23.7%) were susceptible to all antibiotics, while 30 isolates (26.3%) were classified as MDR pathogens, which included 16 (14.0%) ESBL-producing isolates.
UPEC isolates of the ST131 group showed significantly lower susceptibility to cefazolin (26.7%), cefotaxime (40.0%), cefepime (40.0%), and ciprofloxacin (53.3%) than those of the non-ST131 group (65.7%, 91.9%, 92.9%, and 87.9%; P<0.001 for all) (Fig. 2). Susceptibility to gentamycin and TMP-SMX was also lower in the ST131 group (46.7% and 33.3 %, respectively) than the non-ST131 group (76.8% and 65.7%, respectively), but those differences were not statistically significant (P=0.084 in gentamycin and P=0.070 in TMP-SMX). ST131 isolates produced ESBL more frequently (n=8, 53.3%) than non-ST131 isolates (n=8, 8.1%) (P<0.001).
In this study, we investigated the clinical and molecular biological features of UPEC strains isolated from Korean children. The conventional phylogenetic group B2 was the most common group (83.3%) and the proportion of ST131 isolates was 13.2%. The proportion of isolates producing ESBL was 14.0%, and half of them were assigned to ST131. Among the ST131 isolates, 53.3% were ESBL producers and 46.7% were resistant to quinolone. Beside the inappropriate empirical antimicrobial therapy, no clinical and prognostic factor differed between ST131 and non-ST131 UPEC isolates.
After a PCR strategy to assign E. coli isolates rapidly to 1 of the 4 phylogroups A, B1, B2, or D was developed in 2000, it has been used extensively12). Although the distribution of phylogenetic groups varies among countries, E. coli isolates causing extraintestinal infections were generally found to belong to groups B2 and D10,13). Recently, MLST was developed as an attractive sequence-based genotyping technique, which provides reproducibility, comparability, and transferability between laboratories. MLST is thus a powerful tool for both global and long-term surveillance14).The advent of next-generation sequencing and precision typing methods has expanded the understanding of the molecular epidemiology of ESBL-producing bacteria and revealed widespread dissemination of E. coli ST131 bearing CTX-M-156,7,8). This clone might be the “driving force” behind the current ESBL pandemic, and circulating CTX-M strains often harbor multiple coresistance genes such as those conferring resistance to TMP-SMX, aminoglycosides, and fluoroquinolones, thereby limiting therapeutic options15).
E. coli ST131 has been shown to carry a broad range of virulence and resistance genes on transferable plasmids, and has been globally disseminated. Recent reports indicate that this drug-resistant E. coli clonal group is responsible for community-acquired UTI and bacteremia, as well as a significant number of healthcare associated infections16,17). Among the ESBL producing E. coli isolates from various sources, 39%-57% belonged to the ST131 lineage in recent studies18,19). In Korea, ST131 was found to be the predominant ST; it represented 31%-36% of ESBL-producing E. coli strains, and was distributed in both community and hospital isolate9,20). ST131 isolates were significantly associated with ESBL, especially CTX-M-15, and the majority of them were MDR7,21). In a study of outpatients with acute cystitis wherein E. coli had been isolated, treatment failure was more common among patients infected with ST131 E. coli8). However, patients with bloodstream infection by ST131 E. coli isolates did not exhibit poorer treatment outcomes than those with non-ST131 isolates in the other study9).
Although numerous studies of ST131 E. coli in adults have been performed, the clinical and molecular biological data for children remain very limited. As UTIs are the most common bacterial infection in children, it is especially important to identify the clinical significance and epidemiology of ST131 E. coli in pediatric UTI. UPEC strains recently isolated from Korean children belonged to phylogenetic groups B2 (61.6%–68.1%) and D (12.8%–26.8%), comprising the majority of all isolated strains22,23). In a Taiwanese study of infants hospitalized for community-acquired UTIs caused by ESBL-producing E. coli, ST131 accounted for 65% of the 111 isolates6). In the current study, ST131 accounted for 13.2% of total UPEC and 50.0% of ESBL-producing UPEC strains.
In addition, E. coli ST131 isolates also had high rates of non-susceptibility to quinolones6,7). In contrast to ESBL, which is transmissible between UPEC strains by plasmids, quinolone resistance mainly develops in the bacterial chromosome. Therefore, a high resistance rate to quinolone in ST131 E. coli isolates supports the notion that this clone has highly drug-resistant characteristics. In this study, ST131 UPEC strains showed higher resistance to ciprofloxacin, that is, 46.7%, than non-ST131 strains (12.1%).
It is generally accepted that invasive infections by ESBL producers in children are associated with longer hospital stays, recurrence, frequent complications, and increased mortality24,25). However, a Taiwanese study reported that children with UTI caused by ST131 clones had similar risk factors, clinical features and outcomes as those with UTI caused by non-ST1316). Additionally, in our study, there was no significant difference between ST131 and non-ST131 UPEC cases in relation to radiologic abnormality, treatment failure, or recurrence although empirical antimicrobial therapy was more inappropriate in UTIs caused by ST131 E. coli, which produced ESBL more often. This finding might be due to the easy clearance of uropathogens from the infected site (urinary tract) by natural drainage (urination), despite inappropriate antimicrobial coverage. Additionally, previous studies showed that use of non-carbapenem antimicrobial therapy against ESBL-producing uropathogens did not affect the time to defervescence after the initiation of antimicrobial treatment, treatment failure, and relapse rate in pediatric UTIs26).
This study has several limitations. First, we screened ST131 using two (adk and fumC) of the 7 genes used in the MLST scheme rather than by sequencing all 7 genes. Although neither adk53 nor fumC40 was detected in non-ST131 isolates in this study, it is possible that a double locus variant (DLV) of ST131 was missed by this approach. This could result in underestimation of the influence of strains related to ST131. However, among a total of 18 DLVs of ST131 in the MLST database (http://mlst.warwick.ac.uk/mlst/dbs/Ecoli/) in January 2017, no DLV had different alleles both in adk and fumC from ST131. Second, the number of ST131 isolates was very small; therefore, the comparison with non-ST131 isolates was not statistically powerful. Finally, the types of fimH or ESBL that have been investigated in adult studies of ST131 were not analyzed in this study. Larger scale studies of pediatric ST131 infection should be performed based on the findings of this study.
In summary, this is the first study for molecular epidemiology and clinical characteristic of ST131 E. coli in Korean children. ST131 E. coli was a prevalent uropathogen in Korean children admitted at a single hospital between 2011 and 2014. The ST131 UPEC isolates in this study were highly drug-resistant and a high proportion produced. Although no change of clinical outcome was produced by ST131 isolates, the epidemiology and clinical implications of ST131 E. coli should be monitored in invasive and noninvasive pediatric infectious diseases.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Research Resettlement Fund (2015) for the new faculty of Seoul National University.
Notes
Conflict of interest:
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Montini G, Tullus K, Hewitt I. Febrile urinary tract infections in children. N Engl J Med 2011;365:239–250.


2. Lee HS, Lee KH. Clinical characteristics of fever without localizing sign in infants younger than 100 days of age in a single center. Pediatr Infect Vaccine 2016;23:128–136.

3. Ahn DH, Kim KW, Cho HK, Tchah H, Jeon IS, Ryoo E, et al. Febrile urinary tract infections caused by community-acquired extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing and-nonproducing bacteria: a comparative study. Pediatr Infect Vaccine 2015;22:29–35.

4. Koçak M, Büyükkaragöz B, Çelebi Tayfur A, Çaltik A, Köksoy AY, Çizmeci Z, et al. Causative pathogens and antibiotic resistance in children hospitalized for urinary tract infection. Pediatr Int 2016;58:467–471.


5. Smith SP, Manges AR, Riley LW. Temporal changes in the prevalence of community-acquired antimicrobial-resistant urinary tract infection affected by Escherichia coli clonal group composition. Clin Infect Dis 2008;46:689–695.


6. Cheng MF, Chen WL, Hung WY, Huang IF, Chiou YH, Chen YS, et al. Emergence of extended spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli O25b-ST131: a major community-acquired uropathogen in infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2015;34:469–475.


7. Colpan A, Johnston B, Porter S, Clabots C, Anway R, Thao L, et al. Escherichia coli sequence type 131 (ST131) subclone H30 as an emergent multidrug-resistant pathogen among US veterans. Clin Infect Dis 2013;57:1256–1265.



8. Can F, Azap OK, Seref C, Ispir P, Arslan H, Ergonul O. Emerging Escherichia coli O25b/ST131 clone predicts treatment failure in urinary tract infections. Clin Infect Dis 2015;60:523–527.


9. Cho SY, Kang CI, Cha MK, Wi YM, Ha YE, Chung DR, et al. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of bloodstream infections caused by extended-spectrum β-Lactamase-producing escherichia coli sequence type 131. Microb Drug Resist 2015;21:463–469.


10. Yun KW, Kim DS, Kim W, Lim IS. Molecular typing of uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from Korean children with urinary tract infection. Korean J Pediatr 2015;58:20–27.



11. Feil EJ, Li BC, Aanensen DM, Hanage WP, Spratt BG. eBURST: inferring patterns of evolutionary descent among clusters of related bacterial genotypes from multilocus sequence typing data. J Bacteriol 2004;186:1518–1530.



12. Clermont O, Bonacorsi S, Bingen E. Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group. Appl Environ Microbiol 2000;66:4555–4558.



13. Kim JM, Cho EY, Lee JH. Phylogenetic groups and virulence factors of Escherichia coli causing urinary tract infection in children. Pediatr Infect Vaccine 2015;22:194–200.

14. Tartof SY, Solberg OD, Manges AR, Riley LW. Analysis of a uropathogenic Escherichia coli clonal group by multilocus sequence typing. J Clin Microbiol 2005;43:5860–5864.



16. Rogers BA, Sidjabat HE, Paterson DL. Escherichia coli O25b-ST131: a pandemic, multiresistant, community-associated strain. J Antimicrob Chemother 2011;66:1–14.


17. Johnson JR, Johnston B, Clabots C, Kuskowski MA, Castanheira M. Escherichia coli sequence type ST131 as the major cause of serious multidrug-resistant E. coli infections in the United States. Clin Infect Dis 2010;51:286–294.


18. Tiruvury H, Johnson JR, Mariano N, Grenner L, Colon-Urban R, Erritouni M, et al. Identification of CTX-M β-lactamases among Escherichia coli from the community in New York City. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2012;72:248–252.


19. Gqunta K, Govender S. Characterization of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli ST131 isolates from Port Elizabeth. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2015;81:44–46.


20. Park SH, Byun JH, Choi SM, Lee DG, Kim SH, Kwon JC, et al. Molecular epidemiology of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli in the community and hospital in Korea: emergence of ST131 producing CTX-M-15. BMC Infect Dis 2012;12:149



21. Kang CI, Cha MK, Kim SH, Ko KS, Wi YM, Chung DR, et al. Clinical and molecular epidemiology of community-onset bacteremia caused by extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing escherichia coli over a 6-year period. J Korean Med Sci 2013;28:998–1004.



22. Lee JE, Lee YH, Nam CH, Kwak GY, Lee SY, Kim JH, et al. Clinical and phylogenetic characteristics of escherichia coli urinary tract infections. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis 2010;17:16–22.

23. Choi UY, Han SB, Lee SY, Kang JH, Kim SM, Ma SH. Regional differences in phylogenetic group of Escherichia coli strains isolated from children with urinary tract infection in Korea. Korean J Pediatr 2012;55:420–423.



24. Lukac PJ, Bonomo RA, Logan LK. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in children: old foe, emerging threat. Clin Infect Dis 2015;60:1389–1397.




Fig. 1
Phylogenetic grouping and distribution of ST131 isolates and ESBL producers. ST, sequence type; ESBL, extended spectrum beta-lactamase. A, B1, B2, and D indicate the conventional phylogenetic groups of Escherichia coli.
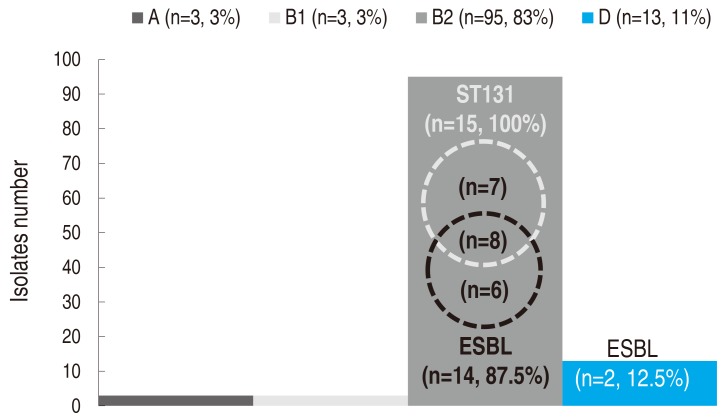
Fig. 2
Antimicrobial susceptibility, ST131 vs. non-ST131. Results of susceptibility testing with carbapenems and tigecycline were not included because all uropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates in the study showed 100% susceptibility, regardless of ST. ST, sequence type; AMX-CLV, amoxicillin-clavulanate; PIP-TAZ, piperacillin-tazobactam; TMP-SMX, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole; ESBL, extended spectrum beta-lactamase. *P<0.001.




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


