Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 61(3); 2018 |
|
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the clinical findings in pediatric rhabdomyolysis and the predictive factors for acute kidney injury (AKI) in Korean children.
Methods
Medical records of 39 Korean children, who were newly diagnosed with rhabdomyolysis from January 2008 to December 2015, were retrospectively analyzed. The diagnosis was made from the medical history, elevated serum creatinine kinase level >1,000 IU/L, and plasma myoglobin level >150 ng/mL. Patients with muscular dystrophy and myocardial infarction were excluded.
Results
The median patient age at diagnosis was 14.0 years (range, 3–18 years), and the male to female ratio was 2.5. The most common presenting symptom was myalgia (n=25, 64.1%), and 14 patients (35.9%) had rhabdomyolysis-induced AKI. Eighteen patients (46.2%) had underlying diseases, such as epilepsy and psychotic disorders. Ten of these patients showed rhabdomyolysis-induced AKI. The common causes of rhabdomyolysis were infection (n=12, 30.7%), exercise (n=9, 23.1%), and trauma (n=8, 20.5%). There was no difference in the distribution of etiology between AKI and non-AKI groups. Five patients in the AKI group showed complete recovery of renal function after stopping renal replacement therapy. The median length of hospitalization was 7.0 days, and no mortality was reported. Compared with the non-AKI group, the AKI group showed higher levels of peak creatinine kinase and myoglobin, without statistical significance.
Rhabdomyolysis is a syndrome characterized by skeletal muscle breakdown and leakage of muscle cell contents such as electrolyte, myoglobin, and other sarcoplasmic proteins into the circulation. It is caused by a wide variety of diseases such as trauma or direct injury, excessive muscle activity, hereditary muscle enzyme defects, infections, body temperature changes, drugs and toxins, and metabolic and endocrine disorders.1,2,3) The development of rhabdomyolysis is initiated by an increase in intracellular free ionized calcium due to either cellular energy depletion or direct plasma membrane rupture. The increased intracellular calcium activates several proteases, intensifies skeletal muscle cell contractility, induces mitochondrial dysfunction, and increases the production of reactive oxygen species, finally leading to the destruction of myofibrils and lysosomal digestion of muscle fiber contents.4) The exact incidence of rhabdomyolysis is unknown; however, morbidly obese patients, chronic users of lipid lowering agents, and postoperative patients are known to be at a high risk for the condition. The common presenting symptoms of rhabdomyolysis include myalgia, muscle weakness, and reddish brown urine associated with myoglobinuria; rhabdomyolysis is diagnosed by short-term elevations in serum creatinine phosphokinase (CK) in patients with symptoms. However, there is no consensus for serum level cutoff, and clinicians usually use five times the upper limit of normal as the cutoff. The diagnosis is confirmed by the measurement of myoglobin levels in serum or urine.5,6,7)
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common, severe complication of rhabdomyolysis, and roughly, 13%–46% of patients with rhabdomyolysis have been reported to develop AKI.3,6,8,9) Another report states that rhabdomyolysis accounts for 7% of all cases of AKI in USA.10) The renal injury in rhabdomyolysis is caused by fluid sequestration in the injured skeletal muscle, activation of the renin-angiotensin system and sympathetic nervous system, release of antidiuretic hormone, and renal vasoconstriction. As a result, it is thought that AKI is caused by salt and water conservation, and tubular damage by myoglobin-induced oxidative injury.8) Early recognition is important to prevent AKI, and the mainstay of treatment is aggressive intravenous fluid resuscitation with correction of electrolyte abnormalities. Adjunctive therapies including the alkalization of urine, diuretics, and continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) have been addressed; however, there is controversy regarding the benefits of these treatment modalities.
There are limited reports on the characteristics of and predictive factors for AKI in children with rhabdomyolysis. Our objectives were to (1) analyze the etiologies, clinical manifestations, and the prevalence of AKI and (2) establish the predisposing factors of AKI using the clinical and biochemical data in pediatric patients with rhabdomyolysis.
The medical records of 39 pediatric patients with rhabdomyolysis who attended Samsung Medical Center, a tertiary referral center located in Seoul, Republic of Korea, between January 2004 and December 2015 were retrospectively reviewed. All data were obtained from electronic medical records in accordance with the ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects established in the Helsinki Declaration of 1975 and revised in 2000. The Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Samsung Medical Center (approval number: 2016-03-158) approved this study. Obtaining of written informed consent was exempted from IRB. The clinical data including age, sex, associated symptoms and signs (fever, myalgia, muscle weakness, dark urine, and history of previous infection), the amount of fluid administered during admission, bicarbonate therapy, need for renal replacement therapy, length of hospital stay, and outcomes were collected from the electrical medical records. The laboratory data including initial serum hemoglobin, white blood cell count, platelet, blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, calcium, phosphorous, electrolyte, lactic dehydrogenase, alanine and aspartate aminotransferase levels, uric acid, CK, myoglobin, and urinalysis were also obtained from the medical records. The levels of serum CK and myoglobin were checked at admission and every 24 hours until the levels were normalized.
Rhabdomyolysis was diagnosed on the basis of medical history and laboratory findings including elevated serum CK levels >1,000 IU/L and serum myoglobin >150 ng/mL. The elevations in CK were not caused by myocardial infarction or inflammatory myopathies. The definition of AKI was based on the Kidney Disease Improvement Global Outcomes guideline.11) The estimated glomerular filtration rate was calculated using the modified Schwartz equation.12,13) Renal replacement therapy included peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, and CRRT.
Continuous data were presented as medians and interquartile ranges, and categorical data were presented as absolute frequencies. Continuous data were analyzed by Wilcoxon signed rank test while categorical data were analyzed by Fisher exact test to compare between the groups. A multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to assess the independent predictors for AKI. A receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve analysis was used to assess the sensitivity and specificity of the prediction of AKI. P value <0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed using SAS ver. 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
The demographic data are presented in Table 1. The median age of the patients at the time of diagnosis was 14 years, and the male to female ratio was 2.5:1. In total, 18 patients (46%) had underlying diseases, 4 of whom suffered from psychiatric diseases including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, autism, Tourette syndrome, schizophrenia, and depression, for which they were under medications. Four patients had neurologic problems including epilepsy, cerebral palsy, Sotos syndrome, and craniopharyngioma. One patient had a history of chronic vomiting, and failure to thrive was diagnosed as having duodenal obstruction after the development of rhabdomyolysis.
The most common presenting symptom was myalgia, and the number of children with dark urine was relatively small. The most common etiology was infection, and 14 children showed the symptoms and signs of viral infection before the development of rhabdomyolysis. The confirmed pathogens included adenovirus, parainfluenza type 1, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Exercise was the common etiology in older children aged above 10 years. Patients with trauma had a history of motor vehicle accidents and suicide attempt. Among four patients with ischemia, 3 patients underwent major surgeries including orthopedic surgery and cardiac surgery. Four patients had a history of medications including benzodiazepine that have been known to be associated with rhabdomyolysis.
Depending on the patient's condition, patients received the intravenous hydration with a total daily input of 1,600 to 3,000 mL/m2 as the initial treatment, and 3 patients subsequently underwent urine alkalization. The ratio of non-AKI to AKI was 1.7, and 8 patients proceeded to AKI Stage 3. Among 14 patients with AKI, 5 patients received CRRT. Among 5 patients with CRRT, four patients had underlying disease and received sodium bicarbonate therapy. The characteristics of each patient are shown in Table 2. The of hospital day was 7 days (range, 2–81 days). All patients recovered from AKI, and the long-term outcome of rhabdomyolysis was favorable.
Tables 3 and 4 show a comparison of clinical characteristics and laboratory findings between the groups of patients with and without AKI. The median peak blood myoglobin level was 2,945 ng/mL. Table 4 shows that the peak values of CK and myoglobin were higher in AKI group than in non-AKI group, without statistical significance. The degree of albuminuria detected by dipstick test at the time of initial diagnosis was significantly higher in AKI group than in non-AKI group. The ROC curve showed that the probability of AKI was high when the degree of proteinuria was high (Fig. 1). In case of constant albuminuria, the probability of AKI was high in the presence of underlying disease (Fig. 2).
Our results suggested that the etiologies and clinical manifestations of pediatric rhabdomyolysis were different from those of adults. A previous study conducted in adults reported that a single factor or combinations of alcohol, muscle pressure, traumatic muscle injury, metabolic disorder, and hypothermia might cause rhabdomyolysis in adult patients. In Korean adults, traumatic muscle injury was the most common cause of rhabdomyolysis.14) However, in pediatric studies, not only trauma but also infections were a common cause of rhabdomyolysis. A previous report stated that infection accounted for 59.5% of the causes of pediatric rhabdomyolysis. Wu et al.15) reported that viral myositis accounted for more than half of all cases of pediatric rhabdomyolysis, and physical exertion and seizure disorder were the second and third most frequent reasons, respectively. Kim et al.16) reported that respiratory tract infection (n=9, 15%) and seizure (n=7, 11.6%) were the most common cause of the rhabdomyolysis and this results were similar to our data.
Our findings were compatible with those of the previous study. It has been reported that approximately half of the patients with rhabdomyolysis present with the triad of myalgia, weakness, and dark urine, and pediatric patients usually presented with muscle pain, fever, and other symptoms associated with viral infection rather than dark urine. According to our results, the triad of symptoms is uncommon in pediatric rhabdomyolysis. In our study, the male to female ratio was 2.5:1, and this finding was similar to the previously reported data in which the male to female ratio ranged from 2:1 to 4:1.15,17,18) The male predominance might be associated with high muscle mass and high level of activity.
According to previous reports, the outcomes vary widely, and the incidence of AKI in pediatric patients with rhabdomyolysis varied from 5% to 50%.19,20) However, a retrospective study that included about 200 pediatric patients with rhabdomyolysis showed that the incidence of AKI was 5%, and suggested that the risk of AKI in children might be much lesser than that in adults. Another study conducted in Taiwanese children showed that the rate of AKI was 8.7%. In previous reports, AKI occurred in 25% of pediatric patients with rhabdomyolysis.16) However, in our study, the incidence of AKI in pediatric patients with rhabdomyolysis was 35.9%. This high incidence of AKI in rhabdomyolysis might be attributed to the characteristics of the tertiary hospital, in which the most of the patients had underlying diseases, especially neuropsychiatric illness, and were taking medications for the illness. These conditions might be associated with the high incidence of AKI caused by rhabdomyolysis.
Increased myoglobin and CK as a consequence of muscular cell death are the major laboratory findings, and there have been a few reports that evaluated the association between the levels of CK and myoglobin, and the development of AKI. In previous studies, the levels of CK and myoglobin have been used as an appropriate index for diagnosis and severity, and peak levels of CK were suggested as a predictive factor of AKI in adults. Kasaoka et al.21) reported that the peak value for blood myoglobin might be a good predictor of rhabdomyolysis-induced AKI in adults. The study in Taiwanese children with rhabdomyolysis also reported that serum CK and myoglobin are reliable predictors for the development of AKI.15) However, another study suggested that elevated levels of serum CK did not correlate with the severity of renal failure. In another study in adult patients with rhabdomyolysis, CK was not a specific or early predictor; however, peak CK level of 5,000 U/mL or higher was useful for screening purposes. However, this study had a limitation of delayed detection of AKI. Hence, the McMahon score system was used to help predict the development of AKI.22) Watanabe reported that AKI is more likely to develop in the presence of dehydration, metabolic acidosis, severe muscle damage, or multiple organ failure in children with rhabdomyolysis.20) In our study, 1 patient with duodenal obstruction suffered from vomiting and chronic dehydration; his body weight increased after the operation, and there was no evidence of rhabdomyolysis. Additionally, children with rhabdomyolysis caused by seizure are supposed to be at the highest risk of AKI. In our study, the peak values of myoglobin and CK were higher in AKI group than in non-AKI group, without statistical significance. Compared to the non-AKI group, the AKI group showed a higher degree of albuminuria at the time of initial diagnosis, which could reflect the severity of renal injury and could be a reliable predictor for the development of AKI. Our study suggested that AKI is more likely to develop in the presence of underlying diseases in children with rhabdomyolysis, and intensive management to prevent AKI is necessary in such children. In addition, 2 studies conducted in Spanish adult patients found that hypoalbuminemia, decrease in prothrombin time, and metabolic acidosis at the time of admission were independent risk factors for the onset of AKI. In another study, creatinine levels were also associated with AKI and its prognosis. However, this has not yet been confirmed in pediatric studies. Therefore, in order to find a better index for prediction of AKI, the association of AKI with the aforementioned factors should be evaluated in children.23,24)
In our study, CRRT was effective in reducing the value of serum CK and myoglobin, and patients who received CRRT showed complete recovery of renal function. According to the previous data, 66% of the patients with AKI caused by rhabdomyolysis died.16) In our study, there is a possibility that CRRT could affect the good prognosis. Recently, although there was a report that CRRT could improve myoglobin clearance, there is no consensus that CRRT could reduce the mortality rate in children with rhabdomyolysis. A few studies showed that CRRT was associated with reduced duration of the oliguria phase and reduced hospital stay; however, no significant differences were found in mortality rates when CRRT was compared with conventional therapy.25) There is insufficient evidence for the benefits of CRRT in the prevention of rhabdomyolysis-induced AKI. Prompt diagnosis and initial fluid management are necessary to prevent AKI in children with underlying diseases and rhabdomyolysis.
There are a few limitations to this study. This is a single, referral center study, and there is a possibility that children with morbidity were enrolled in the study. This condition could affect the clinical manifestations and outcomes. Additionally, this is a retrospective study, and the peak levels of CK and myoglobin might be incorrect.
In conclusion, the clinical manifestations of pediatric rhabdomyolysis are different from those of the condition in adults, and AKI is more likely to develop in the presence of a high degree of albuminuria and underlying diseases in children with rhabdomyolysis.
Notes
Conflicts of interest:
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
3. Melli G, Chaudhry V, Cornblath DR. Rhabdomyolysis: an evaluation of 475 hospitalized patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2005;84:377–385.


4. Giannoglou GD, Chatzizisis YS, Misirli G. The syndrome of rhabdomyolysis: pathophysiology and diagnosis. Eur J Intern Med 2007;18:90–100.


5. Gabow PA, Kaehny WD, Kelleher SP. The spectrum of rhabdomyolysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1982;61:141–152.


9. Ward MM. Factors predictive of acute renal failure in rhabdomyolysis. Arch Intern Med 1988;148:1553–1557.


10. Elsayed EF, Reilly RF. Rhabdomyolysis: a review, with emphasis on the pediatric population. Pediatr Nephrol 2010;25:7–18.


11. Kellum JA, Lameire N. KDIGO AKI Guideline Work Group. Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: a KDIGO summary (Part 1). Crit Care 2013;17:204



12. Schwartz GJ, Feld LG, Langford DJ. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in full-term infants during the first year of life. J Pediatr 1984;104:849–854.


13. Schwartz GJ, Gauthier B. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in adolescent boys. J Pediatr 1985;106:522–526.


14. Kim HY, Choi SO, Shin SJ, Kim YK, Han BG, Park SJ, et al. Analysis of 250 cases of rhabdomyolysis. Korean J Nephrol 1994;13:810–817.
15. Wu CT, Huang JL, Lin JJ, Hsia SH. Factors associated with nontraumatic rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure of children in Taiwan population. Pediatr Emerg Care 2009;25:657–660.


16. Kim JH, Goo MJ, Yeom JS, Park ES, Seo JH, Lim JY, et al. Clinical characteristics of acute renal failure of rhabdomyolysis in children. Korean J Pediatr 2007;50:277–283.

17. Chen CY, Lin YR, Zhao LL, Yang WC, Chang YJ, Wu KH, et al. Clinical spectrum of rhabdomyolysis presented to pediatric emergency department. BMC Pediatr 2013;13:134



18. Mannix R, Tan ML, Wright R, Baskin M. Acute pediatric rhabdomyolysis: causes and rates of renal failure. Pediatrics 2006;118:2119–2125.


19. Watemberg N, Leshner RL, Armstrong BA, Lerman-Sagie T. Acute pediatric rhabdomyolysis. J Child Neurol 2000;15:222–227.


20. Watanabe T. Rhabdomyolysis and acute renal failure in children. Pediatr Nephrol 2001;16:1072–1075.


21. Kasaoka S, Todani M, Kaneko T, Kawamura Y, Oda Y, Tsuruta R, et al. Peak value of blood myoglobin predicts acute renal failure induced by rhabdomyolysis. J Crit Care 2010;25:601–604.


22. Simpson JP, Taylor A, Sudhan N, Menon DK, Lavinio A. Rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury: creatine kinase as a prognostic marker and validation of the McMahon Score in a 10-year cohort: a retrospective observational evaluation. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2016;33:906–912.


23. Rodríguez E, Soler MJ, Rap O, Barrios C, Orfila MA, Pascual J. Risk factors for acute kidney injury in severe rhabdomyolysis. PLoS One 2013;8:e82992.



Fig. 1
Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) for proteinuria as a predictor of acute kidney injury caused by rhabdomyolysis.
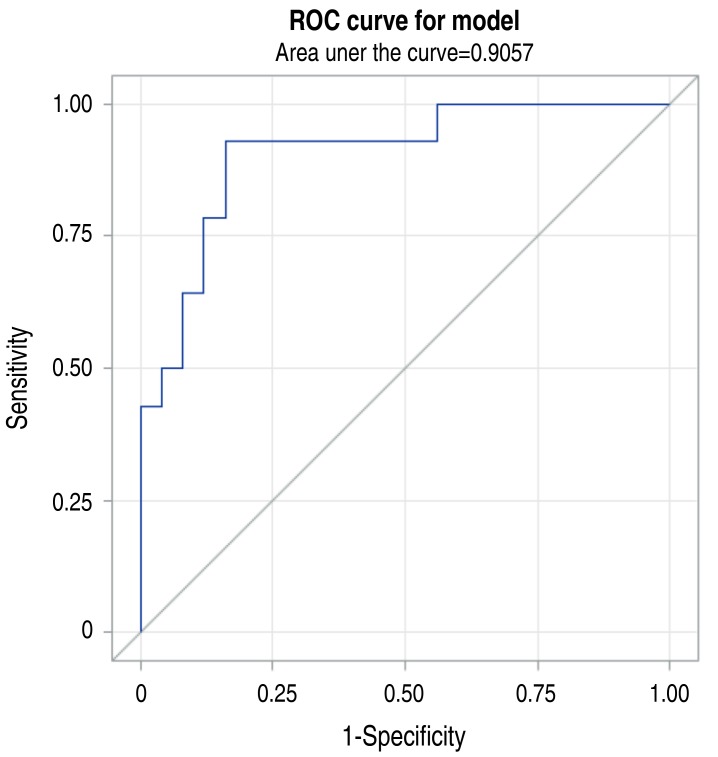
Fig. 2
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for underlying disease as a predictor of acute kidney injury caused by rhabdomyolysis.





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


