Article Contents
| Clin Exp Pediatr > Volume 66(2); 2023 |
|
Abstract
Background
Purpose
Methods
Results
Acknowledgments
Fig. 1.

Fig. 2.
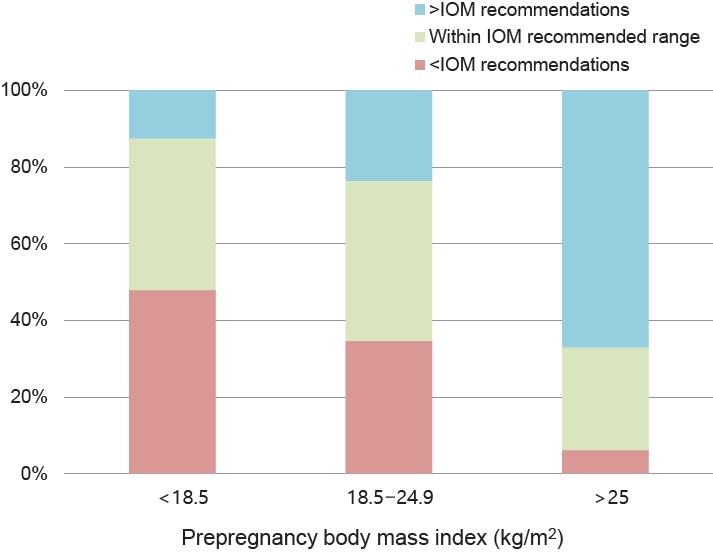
Table 1.
| Characteristic | Total study population (n=1,753) |
Prepregnancy BMI status |
P value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Underweight (Group 1)a) (n=232) | Normal (Group 2)a) (n=1,342) | Overweight/obese (Group 3)a) (n=179) | |||||
| Maternal factors | |||||||
| Gestational age (day) | 272.34±7.23 | 272.09±7.13 | 272.62±7.17 | 270.61±7.55 | 0.001b) | ||
| Maternal age (yr) | 33.85±3.81 | 33.09±3.88 | 33.84±3.70 | 34.95±4.28 | <0.001b) | ||
| Weight before the pregnancy (kg) | 55.76±8.64 | 46.47±3.48 | 54.98±5.13 | 73.69±8.97 | <0.001b) | ||
| Total weight gain (kg) | 13.44±4.50 | 13.19±4.51 | 13.52±4.48 | 13.12±4.62 | 0.178b) | ||
| BMI before the pregnancy (kg/m2) | 21.31±3.10 | 17.65±0.72 | 21.02±1.63 | 28.19±2.93 | <0.001b) | ||
| Height (cm) | 161.72±4.89 | 162.18±5.43 | 161.66±4.77 | 161.59±5.02 | 0.515b) | ||
| Baby factors | |||||||
| Birth weight (kg) | 3.19±0.37 | 3.08±0.35 | 3.19±0.37 | 3.33±0.39 | <0.001c) | ||
| Birth height (cm) | 49.32±10.99 | 48.77±1.75 | 49.41±12.51 | 49.32±2.21 | 0.005b) | ||
| Infant sex | 0.971d) | ||||||
| Male | 913 (52.08) | 120 (51.72) | 701 (52.23) | 92 (51.39) | |||
| Female | 840 (47.91) | 112 (48.72) | 641 (47.76) | 87 (48.60) | |||
| Delivery method | <0.001d) | ||||||
| NSVD | 970 (55.33) | 138 (59.48) | 757 (56.40) | 75 (41.89) | |||
| Cesarean section | 783 (44.66) | 94 (40.51) | 585 (43.59) | 104 (58.10) | |||
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
BMI, body mass index; NSVD, normal spontaneous vaginal delivery.
a) Underweight: prepregnancy BMI >18.5 kg/m2; normal: prepregnancy BMI 18.5–24.9 kg/m2; overweight/obese: prepregnancy BMI 25–29.9 kg/m2 or prepregnancy BMI >30 kg/m2.
b) Differences among groups were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test. Thus, any relationship between 2 of the 3 groups was significant.
Table 2.
| Prepregnancy maternal BMI |
Birthweight |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (95% CI) (kg) | P valued) | Crude β (95% CI)e) | P value | Adjusted β (95% CI)e,f) | P value | |
| Underweight (n=232)a) | 3.08 (3.03–3.12) | -0.037 (-0.053 to -0.020) | <0.001 | -0.036 (-0.051 to -0.021) | <0.001 | |
| Normal (n=1,342)b) | 3.19 (3.17–3.21) | 0.001h) | Ref | Ref | ||
| Overweight/Obese (n=179)c) | 3.33 (3.27–3.39) | 0.042 (0.024–0.061) | <0.001 | 0.054 (0.037–0.072) | <0.001 | |
| Prepregnancy maternal BMI |
BMI in childhood (4–6 yr old) |
|||||
| Mean (95% CI) (kg/m2) | P valued) | Crude β (95% CI)e) | P value | Adjusted β (95% CI)e,g) | P value | |
| Underweight (n=116)a) | 15.74 (15.45–16.03) | -0.049 (-0.075 to -0.023) | <0.001 | -0.041 (-0.066 to -0.015) | <0.002 | |
| Normal (n=267)b) | 16.52 (16.28–16.78) | <0.001h) | Ref | Ref | ||
| Overweight/Obese (n=89)c) | 17.69 (17.19–18.18) | 0.068 (0.039–0.096) | <0.001 | 0.059 (0.031–0.087) | <0.001 | |
d) Intergroup differences were analyzed using analysis of variance. Thus, any relationship between 2 of the 3 groups was significant.
e) β and 95% CI values were calculated using generalized linear regression with a log gamma function.
Table 3.
| Wight gain during the pregnancy |
Birth weight (n=1,753) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (95% CI) (kg) | P valuea) | Crude β (95% CI)b) | P value | Adjusted β (95% CI)b,c) | P value | |
| Low GWG (n=587) | 3.09 (3.06–3.12) | -0.037 (-0.050 to -0.024) | <0.001 | -0.027 (-0.039 to -0.015) | <0.001 | |
| Normal GWG (n=700) | 3.21 (3.18–3.24) | <0.001d) | Ref | Ref | ||
| Excess GWG (n=466) | 3.31 (3.28–3.35) | 0.068 (0.054–0.083) | <0.001 | 0.050 (0.036–0.064) | <0.001 | |
| Weight gain during the pregnancy |
BMI in childhood (4–6 yr old) |
|||||
| Mean (95% CI) (kg/m2) | P valuea) | Crude β (95% CI)b), P value | Adjusted β (95% CI)b,c) | P value | ||
| Low GWG (n=129) | 15.60 (15.25–15.95) | -0.52 (-0.077 to -0.026) | <0.001 | -0.035 (-0.057 to -0.013) | 0.002 | |
| Normal GWG (n=199) | 16.43 (16.15–16.71) | <0.001d) | Ref | Ref | ||
| Excess GWG (n=144) | 17.58 (17.25–17.91) | 0.068 (0.043–0.092) | <0.001 | 0.025 (0.005–0.045) | 0.015 | |
a) Differences among groups were analyzed using analysis of variance. Thus, any relationship between 2 of the 3 groups was significant.
b) β and their 95% CI were calculated using generalized linear regression with a log gamma function.
Table 4.
| Wight gain during the pregnancy |
Overweight/obese in childhood (4–6 yr old) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | OR (95% CI)b), P value | aOR (95% CI)b,c), P value | |
| Low GWG (n=129) | 21 (16.3) | 0.55 (0.32–0.97), 0.04 | 0.54 (0.29–0.99), 0.047 |
| Normal GWG (n=200) | 52 (26.0) | Ref | Ref |
| Excess GWG (n=144) | 63 (46.8) | 2.21 (1.40–3.49), 0.001 | 1.77 (1.09–2.88), 0.021 |





 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


