Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 55(11); 2012 |
Abstract
Purpose
We phylogenetically analyzed the Escherichia coli strains isolated from children with urinary tract infection (UTI) in 2 regions of Korea. Virulence factors (VFs) and antibiotic resistance of the strains were also determined to compare the possible differences.
Methods
A total of 138 E. coli strains were collected from the 2 regions; Gyeongin (78 strains) and Gyeongnam (60 strains). The phylogenetic groups were determined using the triplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method and multiplex PCRs were used to detect 7 VFs genes (fimH, papC, iutA, hlyA, sfa/focDE, afa/draBC, and kpsMT II). We also tested for antibiotic resistance.
Results
Phylogenetic groups, B2 (61.6%) and D (26.8%), comprised the majority of all isolated strains. Regional comparisons revealed that more B2 strains and fewer non-B2 (A+B1+D) strains were found in Gyeongnam, than in the Gyeongin region (P=0.033), and certain VFs were predominantly detected in Gyeongnam (P<0.05). Neither regional nor phylogenetic differences, in antibiotic resistance of the strains, were significant.
Escherichia coli are the most frequent causative organisms of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in children1). Following the introduction of Haemophilus influenza type b and pneumococcal vaccines, invasive bacterial infections that are caused by these pathogens have decreased2). In contrast, there have been some reports concerning the increase of invasive infections caused by E. coli strains2-4).
Four main phylogenetic groups of E. coli have been described: A, B1, B2, and D5). Phylogenetic analysis has shown that the extraintestinal pathogenic E. coli (ExPEC) strains, which cause UTI, typically belong to the groups B2 or D, while commensal strains belong predominantly to group A6). Phylogenetic research on E. coli strains has been preformed not only in the field of medical science, but also in veterinary medicine and public health science7-9). However, there are a few phylogenetic studies on ExPEC strains conducted in children, especially in Korea10,11).
As our pilot study, we phylogenetically analyzed the E. coli strains isolated from children with UTI in two regions of Korea. Virulence profiles and antibiotic resistance of the strains were also determined to compare for the possible differences.
A total of 138 E. coli strains were collected, between January 2005 and December 2006, from two regions in Korea; 78 strains from Gyeongin (Incheon St. Mary Hospital and Seoul Adventist Hospital), and 60 strains from Gyeongnam (Changwon Fatima Hospital). These strains were isolated from subjects aged <15 years and clinically suspected of having UTI12) on the basis of body temperature of >38.3Ōäā and pyuria with >5 white blood cells/high-power field. Urine was collected with sterile urine bags for infants and midstream catch for older children. Strains with urine cultures of Ōēź105 colony-forming units/mL of E. coli were isolated to be stored at -70Ōäā in tryptic-soy broth. De-identified samples of all strains, which were labeled only with the hospital of origin, were submitted to Incheon St. Mary Hospital for analysis. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Catholic University of Korea (IRB number: OCMC080T29).
The phylogenetic groups, A, B1, B2, and D, were identified by amplifying the chuA and yjaA genes, and the DNA fragment TspE4. C2 using polymerase chain reaction (PCR), according to the triplex method that has been described by Clermont et al.13). Briefly, chuA- TspE4. C2- strains were classified as group A, chuA- TspE4.C2+ strains as group B1, chuA+ yjaA- strains as group D, and chuA+ yjaA+ strains as group B2. Two separate multiplex PCRs were used to detect genes for seven virulence factors (VFs), as previously reported by Le Bouguenec et al.14). The first PCR included primer pairs of type-1 fimbriae (fimH), P fimbriae (papC), aerobactin (iutA), and hemolysin (hlyA). The second multiplex PCR was used to detect genes for S fimbriae (sfa/focDE), Dr adhesions (afa/draBC), and K-antigen (kpsMT II).
Antimicrobial susceptibilities were determined, using the broth dilution method with Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute criteria15). The following three antibiotics, which were used commonly in the treatment of children with UTI at outpatient clinics, were tested: amoxicillin/clavulanate, cefixime, and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (TMP/SMX)1). Strains with intermediate susceptibility were considered as resistant.
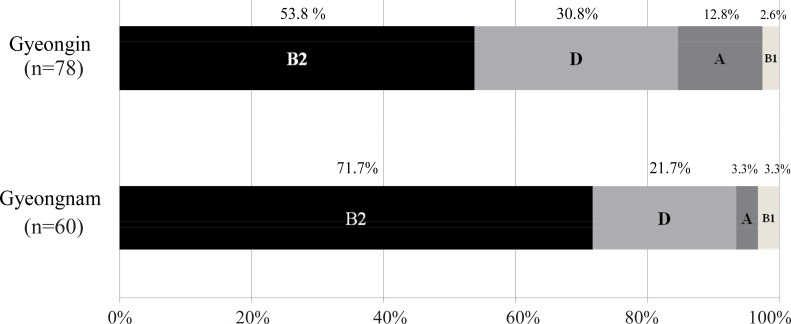
Of the 138 strains analyzed, those belonging to group B2 (61.6%) were the most prevalent, followed by groups D (26.8%), A (8.7%), and B1 (2.9%). Thus, groups B2 and D comprised the majority (88.4 %) of all isolated strains. Regional comparisons revealed that more B2 strains and fewer non-B2 (A+B1+D) strains were observed in Gyeongnam than in Gyeongin (P=0.033) (Fig. 1).
Across all 138 strains, fimH, papC, sfa/focDE, afa/draBC, kpsMT II, iutA, and hlyA were present in 92.8%, 55.8%, 17.4%, 11.6%, 69.6%, 47.8%, and 21.7%, respectively. In the comparison of phylogenetic groups, genes for all VFs, except afa/draBC, were more frequently found in the B2 strains than in the non-B2 (A+B1+D) strains (P<0.05). Regional comparisons showed that sfa/focDE (P=0.039) and kpsMT II (P=0.007) were predominantly detected in the Gyeongnam (Table 1).
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed that 72.5% strains were resistant to amoxicillin/clavulanate; 47.1%, to TMP/SMX; and 22.5%, to cefixime. Regional comparisons showed that more strains of Gyeongin were resistant to amoxicillin/clavulanate (P=0.341) and TMP/SMX (P=0.086) than those of Gyeongnam (Table 1). In the comparison of phylogenetic groups, more of the non-B2 (A+B1+D) strains were resistant to cefixime (P=0.646) and TMP/SMX (P=0.166) than that of the B2 strains. However, neither regional nor phylogenetic differences in antibiotic resistance of the strains were statistically significant.
Pathogenic E. coli strains cause a wide variety of intestinal or extraintestinal infections. In contrast to intestinal pathogenic E. coli strains, such as enteropathogenic E. coli or enterotoxigenic E. coli, the ExPEC strains do not cause disease within the intestinal tract, where they are adapted for peaceful coexistence with the host16). However, at the extraintestinal sites, these strains induce diverse infectious diseases, including UTI, bacteremia, neonatal meningitis, pneumonia, and intraabdominal infections16,17). On the basis of phylogenetical analysis, ExPEC strains typically belong to the groups B2 or D, and are thus, distinct from both the commensal and the intestinal pathogenic strains5,18).
Group B2 strains are known to posses more VFs than strains of the other groups, and group D strains are clinically remarkable because of their antimicrobial resistance16,19). Phylogenetic groups and VFs are unique microbiological features of the E. coli strains, but these features are obviously influenced by the host genetic factors (immune status, specific blood group antigens, and dietary intake), and socioenvironmental factors (climate, economic condition, and the extent of antibiotics usage)11,19,20).
The present study showed that a majority of the strains belonged to the group B2 or D, and that B2 strains and certain VFs were found predominantly in a particular region. The differences in the distribution of phylogenetic groups between nations have also been reported previously19,20). Among seven VFs detected, fimH was found to be present in nearly all the strains, which reflects an origin in a shared enterobacterial ancestor16). Most of the known extraintestinal VFs (papC, sfa/focDE, kpsMT II, and hlyA genes) were concentrated within groups B2 or D, whereas, the afa/draBC gene was more broadly distributed, which is consistent with the typically chromosomal versus plasmid location of these VFs21). With regard to the antibiotic resistance, neither regional nor phylogenetic differences were statistically significant. In general, antibiotic resistance of the strains is known to be associated negatively with virulence and positively with host compromise22). Our study, however, has certain limitations. A major limitation is that we could not include the host factors. Other limitations include the small sample size; the urine collection method; and the detection of genes, rather than gene expression.
In summary, we were able to confirm that the geographic location is an important determinant of the distribution of phylogenetic groups and VFs among these strains. Such regional differences should be considered, while conducting molecular epidemiological studies, on ExPEC strains in children.
References
1. Elder JS. Kliegman RM, Stanton BF, St. Geme JW, Schor NF, Behrman RE,Urinary tract infections. editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 2011;19th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders, :1829ŌĆō1834.

2. Herz AM, Greenhow TL, Alcantara J, Hansen J, Baxter RP, Black SB, et al. Changing epidemiology of outpatient bacteremia in 3- to 36-month-old children after the introduction of the heptavalent-conjugated pneumococcal vaccine. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2006;25:293ŌĆō300.


3. Weston EJ, Pondo T, Lewis MM, Martell-Cleary P, Morin C, Jewell B, et al. The burden of invasive early-onset neonatal sepsis in the United States, 2005-2008. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2011;30:937ŌĆō941.



4. Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Sanchez PJ, Faix RG, Poindexter BB, Van Meurs KP, et al. Early onset neonatal sepsis: the burden of group B Streptococcal and E. coli disease continues. Pediatrics 2011;127:817ŌĆō826.



5. Herzer PJ, Inouye S, Inouye M, Whittam TS. Phylogenetic distribution of branched RNA-linked multicopy single-stranded DNA among natural isolates of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 1990;172:6175ŌĆō6181.



6. Russo TA, Johnson JR. Proposal for a new inclusive designation for extraintestinal pathogenic isolates of Escherichia coli: ExPEC. J Infect Dis 2000;181:1753ŌĆō1754.


7. Baldy-Chudzik K, Mackiewicz P, Stosik M. Phylogenetic background, virulence gene profiles, and genomic diversity in commensal Escherichia coli isolated from ten mammal species living in one zoo. Vet Microbiol 2008;131:173ŌĆō184.


8. Nowrouzian F, Adlerberth I, Wold AE. P fimbriae, capsule and aerobactin characterize colonic resident Escherichia coli. Epidemiol Infect 2001;126:11ŌĆō18.



9. Orsi RH, Stoppe NC, Sato MI, Ottoboni LM. Identification of Escherichia coli from groups A, B1, B2 and D in drinking water in Brazil. J Water Health 2007;5:323ŌĆō327.


10. Yoo KH, Cho JJ, Lee SJ. Characterization of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. Korean J Urogenital Tract Infect Inflamm 2007;2:61ŌĆō65.
11. Lee JE, Lee YH, Nam CH, Kwak GY, Lee SY, Kim JH, et al. Clinical and phylogenetic characteristics of Escherichia coli urinary tract infections. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis 2010;17:16ŌĆō22.

12. Cheng CH, Tsau YK, Lin TY. Effective duration of antimicrobial therapy for the treatment of acute lobar nephronia. Pediatrics 2006;117:e84ŌĆōe89.


13. Clermont O, Bonacorsi S, Bingen E. Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group. Appl Environ Microbiol 2000;66:4555ŌĆō4558.



14. Le Bouguenec C, Archambaud M, Labigne A. Rapid and specific detection of the pap, afa, and sfa adhesin-encoding operons in uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol 1992;30:1189ŌĆō1193.



15. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Fifth informational supplement, M100-S15. 2005;Wayne: CLSI.
16. Johnson JR, Russo TA. Molecular epidemiology of extraintestinal pathogenic (uropathogenic) Escherichia coli. Int J Med Microbiol 2005;295:383ŌĆō404.


17. K├Čhler CD, Dobrindt U. What defines extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli? Int J Med Microbiol 2011;301:642ŌĆō647.


18. Johnson JR, Owens KL, Clabots CR, Weissman SJ, Cannon SB. Phylogenetic relationships among clonal groups of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli as assessed by multi-locus sequence analysis. Microbes Infect 2006;8:1702ŌĆō1713.


19. Duriez P, Clermont O, Bonacorsi S, Bingen E, Chaventre A, Elion J, et al. Commensal Escherichia coli isolates are phylogenetically distributed among geographically distinct human populations. Microbiology 2001;147(Pt 6): 1671ŌĆō1676.


20. Grude N, Potaturkina-Nesterova NI, Jenkins A, Strand L, Nowrouzian FL, Nyhus J, et al. A comparison of phylogenetic group, virulence factors and antibiotic resistance in Russian and Norwegian isolates of Escherichia coli from urinary tract infection. Clin Microbiol Infect 2007;13:208ŌĆō211.


Fig.┬Ā1
Two regions of Korea are compared in the distribution of phylogenetic groups of Escherichia coli strains isolated from children with urinary tract infection. Regional comparisons revealed that more B2 strains and fewer non-B2 (A+B1+D) strains are found in Gyeongnam than in Gyeongin (P=0.033).




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


