Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 55(11); 2012 |
Abstract
Purpose
Methods for quick and reliable detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae are needed for the diagnosis of pneumococcal disease and vaccine studies. This study aimed to show that sequential multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is more efficient than conventional culture in achieving S. pneumoniae-positive results.
Methods
Nasopharyngeal (NP) secretions were obtained from 842 pediatric patients admitted with lower respiratory infections at Severance Children's Hospital in Korea between March 2009 and June 2010. For identification and serotype determination of pneumococci from the NP secretions, the secretions were evaluated via multiplex PCR technique with 35 serotype-specific primers arranged in 8 multiplex PCR sets and conventional bacteriological culture technique.
Results
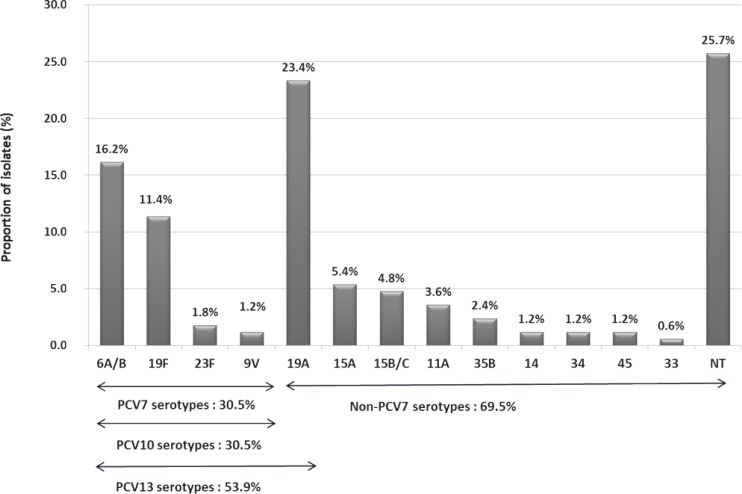
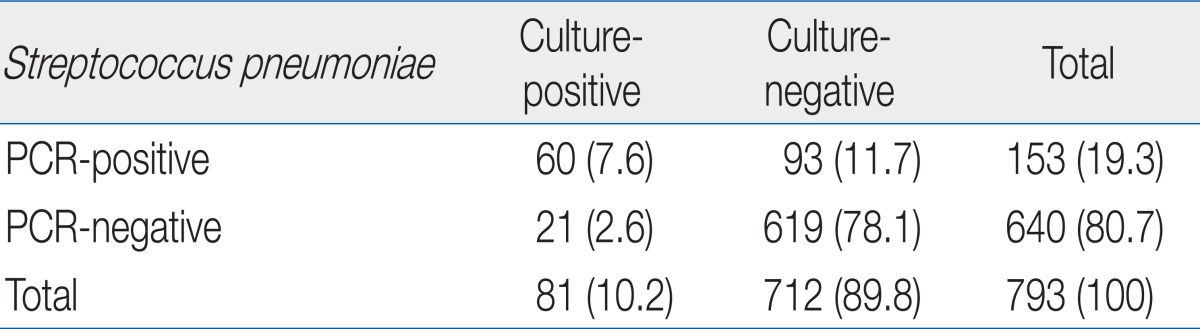
Among the results for 793 samples that underwent both bacterial culture and PCR analysis for pneumococcal detection, 153 (19.3%) results obtained by PCR and 81 (10.2%) results obtained by conventional culture technique were positive for S. pneumoniae. The predominant serotypes observed, in order of decreasing frequency, were 19A (23%), 6A/B (16%), 19F (11%), 15B/C (5%), 15A (5%), and 11A (4%); further, 26% of the isolates were non-typeable.
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a major pathogen, causing otitis media, sinusitis, pneumonia, bacteremia, and meningitis in children worldwide. It also offers some threat of mortality, mostly in developing countries1,2). The recent spread of antibiotic-resistant S. pneumoniae strains has caused considerable concern3,4). Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs), used since 2000, have been shown to reduce the incidence of vaccine-serotype invasive pneumococcal disease (IPD) and nasopharyngeal (NP) colonization of pneumococcus by the vaccine serotypes3,5-11). In spite of the availability of these efficient vaccines, pneumococcal infections remain a global problem due to the emergence of resistance and replacement by nonvaccine-serotype strains12,13).
Pneumococcal infections are traditionally diagnosed using bacterial culture combined with biochemical or immunochemical identification tests. However, conventional culture methods take at least 48 hours to obtain results, and antibiotic treatment prior to obtaining patient specimens or autolysis of pneumococci during transportation of samples may cause false-negative culture results. In addition, the current determination of serotypes by serological methods requires isolation of pneumococci, is time consuming and expensive, and the results are difficult to interpret. Rapid and precise methods of detection and serotyping of S. pneumoniae are needed to improve the diagnosis of IPD, but they are also essential for predicting the consequences of vaccinations on NP carriage. In this study we aimed to compare PCR with traditional culture isolation methods for detecting S. pneumoniae in NP aspirates and to improve the design of previously published protocols for sequential multiplex PCR-based serotyping of pneumococci according to the predicted distribution of pneumococcal serotypes in Korea.
A total of 842 NP secretions were collected from children (younger than 5 years of age) hospitalized with lower respiratory infections at Severance Children's Hospital in Seoul, Korea, from March 2009 to June 2010. The NP aspirates obtained by suction were divided into two samples: one was used for bacterial culture and the other for multiplex PCR-based serotyping. Informed consent was obtained from the parents or guardians of the patients prior to the collection of samples. The study was approved by the institutional review board of Severance Hospital.
A portion of each of the NP specimens was cultured on blood agar plates for 48 hours at 37℃ in an atmosphere enriched with 5% CO2. Isolates were identifiedas S. pneumoniaee by typical colony morphology, alpha-hemolysis, negative catalase reaction, Gram-positive staining, optochin disk sensitivity, and bile solubility.
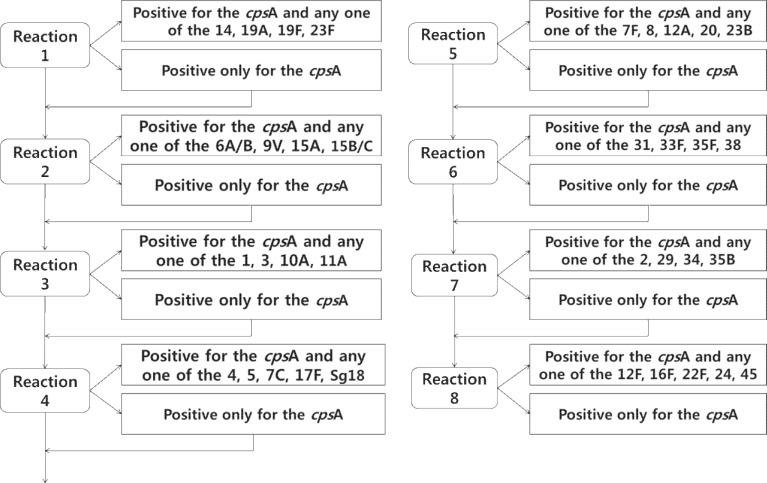
Nucleic acid from each NP specimen was extracted using a QIAamp Genomic DNA kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The extracted DNA suspension was kept frozen at -70℃ until further use. Thirty-five serotype-specific primer pairs were designed as described in published reports (Table 1)14-16). A primer pair targeting cpsA found in all 90 known pneumococcal serotypes was used as the positive control. The primers were grouped into eight sets for sequential testing (Fig. 1) based on the ranking of serotypes that are frequently detected in South Korea17-19). PCR for 35 serotypes were performedon all samples to check the status of co-colonization. PCR mixtures consisted of 12.5 µL 2× multiplex PCR Pre-Mix, 3.5 µL purified DNA, primers at concentration of 1 µm, and cpsA-f and cpsA-r primers at a concentration of 0.5 µm in a 25 µL reaction volume. Amplification conditions for all reactions were as follows: initial denaturation at 94℃ for 4 minutes; 30 cycles at 94℃ for 45 seconds, 54℃ for 45 seconds and 65℃ for 2 minutes 30 seconds; and a final extension cycle of 72℃ for 5 minutes. The PCR products were analyzed by gel electrophoresis on a 1.4% agarose gel at 120 volts for 45 minutes, stained with ethidium bromide, and visualized with ultraviolet transillumination.
Among the 842 total cases, 793 underwent simultaneous bacterial culture and PCR analysis for pneumococcal isolation, while 49 were only analyzed by PCR. Bacterial culture yielded positive results in 10.2% (81/793) cases and PCR in 19.3% (153/793). Both methods revealed identical results in 85.6% (679/793) of tests. Among 14.4% (114/793) that showed different results, 11.7% (93/793) showed negative results with culture and positive results with PCR, and 2.6% (21/793) showed positive results with culture and negative results with PCR (Table 2).
Among the total 842 specimens, 163 were positive by PCR analysis. In total, 163 PCR-positive samples and 4 co-colonization strains were analyzedfor serotyping. A total of 13 different S. pneumoniae serotypes could be identified, and 43 pneumococcal strains were non-typeable (26%). The most frequent serotypes were 19A (n=39, 23%) and 6A/B (n=27, 16%), followed by 19F (19, 11%), 15A (n=9, 5%), and 15B/C (n=8, 5%). These five serotypes together accounted for 61% of overall isolates. Among all isolates, 30.5% were the serotypes included in PCV7, and 69.5% were non-PCV7 vaccine types (Fig. 2).
In this study, multiplex PCR was used to detect pneumococci and to determine pneumococcal serotypes among 842 total cases. Of the total samples, 793 underwent simultaneous bacterial culture and PCR analysis, with a concordance of 85.6%. The detection rate of pneumococcal strains by multiplex PCR (19.3%) was higher than that by bacterial culture (10.2%). PCR analysis based on the amplification of cpsA or other pneumococcal genes has been shown to be sensitive and efficient in detecting pneumococcus in clinical samples16,20-23). Virolainen et al.20) found 18% of middle ear fluid specimens to be positive by culture and 30% by culture and PCR. Saha et al.16) showed that sequential multiplex PCR of 127 culture-negative cerebrospinal fluid samples yielded serotypes for 51 additional cases. Our results are consistent with those of previous studies in this field. In the present study, although 2.6% of samples showed positive results in culture but negative by PCR, these are thought to be the result of operator error and will likely be reduced by increased operator experience.
In addition to detection of pneumococci, accurate serotype determination is important for vaccine development. Presently the choice of vaccine strains depends on serotype prevalence patterns. Although serological determination by a quelling reaction of pneumococcal cells with antipolysaccharide sera is the currently used method for pneumococcal serotyping24,25), the high cost of antisera, the requirements for technical expertise, and subjectivity in interpretationof results are major shortcomings of the procedure14,16). Multiplex PCR has the potential to overcome these drawbacks and has been reported to have higher sensitivity and specificity than traditional quelling reaction methods14,16,26,27).
Because the serotype distribution among NP carriage isolates varies by geographic region, time, and age-group, we designed primers and modified the sequential multiplex PCR scheme based on the distribution of serotypes that were frequently isolated in Korea17-19). Among the serotypes identified in our study, the most common serotype was 19A, followed by: 6A/B, 19F, 15B/C, 15A, 11A, and in a small minority 35B, 23F, 14, 9V, 45 and 33. In Korea, PCV7 has been available since November 2003 and PCV10 and PCV13 were introduced in May 2010. Thus, our results, obtained from March 2009 to June 2010, represent the impact of PCV7 on NP carriage of pneumococcus. Several studies conducted in Korea prior to the use of PCV7 demonstrated that the proportion of PCV7 serotypes in invasive and noninvasive isolates, including carried strains, was 54 to 72% and 57 to 83%, respectively17-19,28,29). Our study revealed that PCV7 serotypes decreased to 30.5% of carried serotypes over the course of this study period, indicating a replacement phenomenon in NP carriage after the introduction of PCV7.
As PCV10 or PCV13 have only recently been introduced, there will likely be changes in serotype distribution among pneumococcal carriage isolates in the future. Surveillance of pneumococcal serotypes should be continued in order to monitor changes in serotype distribution necessary for the pneumococcal vaccine policy. To that end, our multiplex PCR system can be used as an accurate and rapid way of isolating and serotyping S. pneumoniae compared to conventional microbiology culturing. However, our study had an important limitation; 26% of total isolates were non-typeable because only 35 primer sets for pneumococcal serotyping were used in the protocol. In the future, new serotype-specific primers will need to be added, so that more serotypes may be detected. This will enhance detection and serotyping of S. pneumoniae when using multiplex PCR.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the MSD academic award grant from the Korean Pediatric Society. We gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance rendered by Ms. Kim Heui Og.
References
1. Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine for childhood immunization: WHO position paper. Wkly Epidemiol Rec 2007;82:93–104.

2. Hausdorff WP, Bryant J, Paradiso PR, Siber GR. Which pneumococcal serogroups cause the most invasive disease: implications for conjugate vaccine formulation and use, part I. Clin Infect Dis 2000;30:100–121.


3. Millar EV, O'Brien KL, Watt JP, Bronsdon MA, Dallas J, Whitney CG, et al. Effect of community-wide conjugate pneumococcal vaccine use in infancy on nasopharyngeal carriage through 3 years of age: a cross-sectional study in a high-risk population. Clin Infect Dis 2006;43:8–15.


4. Hanage WP, Huang SS, Lipsitch M, Bishop CJ, Godoy D, Pelton SI, et al. Diversity and antibiotic resistance among nonvaccine serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae carriage isolates in the post-heptavalent conjugate vaccine era. J Infect Dis 2007;195:347–352.


5. Tan TQ. Serious and invasive pediatric pneumococcal disease: epidemiology and vaccine impact in the USA. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2010;8:117–125.


6. Isaacman DJ, McIntosh ED, Reinert RR. Burden of invasive pneumococcal disease and serotype distribution among Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates in young children in Europe: impact of the 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine and considerations for future conjugate vaccines. Int J Infect Dis 2010;14:e197–e209.


7. Lin TY, Shah NK, Brooks D, Garcia CS. Summary of invasive pneumococcal disease burden among children in the Asia-Pacific region. Vaccine 2010;28:7589–7605.


8. Whitney CG, Pilishvili T, Farley MM, Schaffner W, Craig AS, Lynfield R, et al. Effectiveness of seven-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine against invasive pneumococcal disease: a matched case-control study. Lancet 2006;368:1495–1502.


9. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Invasive pneumococcal disease in children 5 years after conjugate vaccine introduction--eight states, 1998-2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2008;57:144–148.


10. Huang SS, Hinrichsen VL, Stevenson AE, Rifas-Shiman SL, Kleinman K, Pelton SI, et al. Continued impact of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on carriage in young children. Pediatrics 2009;124:e1–e11.



11. Ghaffar F, Barton T, Lozano J, Muniz LS, Hicks P, Gan V, et al. Effect of the 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on nasopharyngeal colonization by Streptococcus pneumoniae in the first 2 years of life. Clin Infect Dis 2004;39:930–938.


13. Dagan R, Givon-Lavi N, Leibovitz E, Greenberg D, Porat N. Introduction and proliferation of multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A clones that cause acute otitis media in an unvaccinated population. J Infect Dis 2009;199:776–785.


14. Pai R, Gertz RE, Beall B. Sequential multiplex PCR approach for determining capsular serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates. J Clin Microbiol 2006;44:124–131.



15. Bentley SD, Aanensen DM, Mavroidi A, Saunders D, Rabbinowitsch E, Collins M, et al. Genetic analysis of the capsular biosynthetic locus from all 90 pneumococcal serotypes. PLoS Genet 2006;2:e31



16. Saha SK, Darmstadt GL, Baqui AH, Hossain B, Islam M, Foster D, et al. Identification of serotype in culture negative pneumococcal meningitis using sequential multiplex PCR: implication for surveillance and vaccine design. PLoS One 2008;3:e3576



17. Lee TJ, Chun JK, Kim KH, Kim KJ, Kim DS. Serotype distribution of pneumococcus isolated from the ear discharge in children with otitis media in 2001-2006. Korean J Pediatr Infect Dis 2008;15:44–50.

18. Song JH, Baek JY, Cheong HS, Chung DR, Peck KR, Ko KS. Changes of serotype and genotype in Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates from a Korean hospital in 2007. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2009;63:271–278.


19. Choi EH, Kim SH, Eun BW, Kim SJ, Kim NH, Lee J, et al. Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 19A in children, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis 2008;14:275–281.



20. Virolainen A, Salo P, Jero J, Karma P, Eskola J, Leinonen M. Comparison of PCR assay with bacterial culture for detecting Streptococcus pneumoniae in middle ear fluid of children with acute otitis media. J Clin Microbiol 1994;32:2667–2670.



21. Kearns AM, Freeman R, Murphy OM, Seiders PR, Steward M, Wheeler J. Rapid PCR-based detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae DNA in cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Microbiol 1999;37:3434



22. Kontiokari T, Renko M, Kaijalainen T, Kuisma L, Leinonen M. Comparison of nasal swab culture, quantitative culture of nasal mucosal tissue and PCR in detecting Streptococcus pneumoniae carriage in rats. APMIS 2000;108:734–738.


23. Brugger SD, Hathaway LJ, Muhlemann K. Detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae strain cocolonization in the nasopharynx. J Clin Microbiol 2009;47:1750–1756.



24. O'Brien KL, Nohynek H. World Health Organization Pneumococcal Vaccine Trials Carriage Working Group. Report from a WHO Working Group: standard method for detecting upper respiratory carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2003;22:e1–e11.

25. Arai S, Konda T, Wad A, Matsunaga Y, Okabe N, Watanabe H, et al. Use of antiserum-coated latex particles for serotyping Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microbiol Immunol 2001;45:159–162.


26. Morais L, Carvalho Mda G, Roca A, Flannery B, Mandomando I, Soriano-Gabarro M, et al. Sequential multiplex PCR for identifying pneumococcal capsular serotypes from South-Saharan African clinical isolates. J Med Microbiol 2007;56(Pt 9): 1181–1184.


27. Dias CA, Teixeira LM, Carvalho Mda G, Beall B. Sequential multiplex PCR for determining capsular serotypes of pneumococci recovered from Brazilian children. J Med Microbiol 2007;56(Pt 9): 1185–1188.


28. Kim SM, Hur JK, Lee KY, Shin YK, Park SE, Ma SH, et al. Epidemiological study of pneumococcal nasal carriage and serotypes among Korean children. Korean J Pediatr 2004;47:611–616.
29. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Serotype distribution and antimicrobial susceptibility of invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates in Korea. Public Health Wkly Rep 2010;3:1–7.
Fig. 1
Scheme of sequential multiplex polymerase chain reaction-based pneumococcal serotyping showing the 8 reactions and the serotypes identified in each reaction.




 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


