Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 58(11); 2015 |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Kawasaki disease involves acute febrile systemic vasculitis that can cause a variety of symptoms by affecting various organs. Here, we aimed to evaluate the prevalence, causes, and prognosis of sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) occurring in children with Kawasaki disease.
Methods
Patients who were diagnosed with Kawasaki disease and received inpatient treatment in the Pediatrics Department at one of three university hospitals in Daegu city from February 2012 to September 2012 were enrolled in the study. The clinical features, hematological results, echocardiography results, audiometry results, and aspirin and salicylic acid serum levels of the patients were evaluated.
Results
Of the 59 children enrolled in the study, three showed mild bilateral SNHL on audiometry tests conducted after 48 hours of defervescence; these patients demonstrated normal patterns of recovery on follow-up tests 8 weeks later. Aspirin serum levels were significantly higher in the SNHL group after 48 hours of afebrile condition with high dose aspirin intake (P=0.034). However, no significant differences were found in other laboratory tests or for fever duration (P>0.05). Upon echocardiography, coronary artery abnormality was observed in 9 cases, but none of these patients showed hearing loss.
Conclusion
The results indicate that SNHL in children with Kawasaki disease might occur during treatment of the acute phase; this SNHL usually involves mild bilateral hearing loss and recovers naturally. However, this study suggests that determination of the causes and clinical implications of hearing loss in Kawasaki disease requires long-term follow-up studies with more cases.
Kawasaki disease is a type of systemic vasculitis that presents with acute inflammation, mainly in infants and children aged five or younger. Neither its etiology nor pathophysiology is clearly understood. The clinical manifestations of Kawasaki disease include five or more days of fever, bilateral conjunctival injection without exudates, lip and oral mucosal injection, nonpurulent cervical lymphadenopathy, polymorphous exanthem, and erythema and edema of the hand and foot1). In the acute phase of the disease, multiple organs are invaded and various symptoms may develop. In addition, arthritis, aseptic meningitis, aseptic pyuria, sensorineural hearing loss, hydrocholecystitis, and uveitis are often observed2).
The treatment of Kawasaki disease is conducted in most medical institutions according to the standardized protocol: High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin injection (2 g/kg) and the oral intake of a high dose of aspirin (80-100 mg/kg/day) within 10 days of the start of fever. The use of high-dose aspirin sometimes causes various side effects such as abdominal pain, acute hepatitis, hearing loss, tinnitus, gastric ulcer, gastrointestinal bleeding, and electrolyte abnormality3).
In this way, sensorineural hearing loss can develop due to the inflammatory reaction in the acute phase of Kawasaki disease, or from the side effects of the high-dose aspirin. In previous studies, various cases of sensorineural hearing loss duration, directionality, and severity have been reported in Kawasaki disease4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11). According to Magalhaes et al.8), and Alves et al.10), in Kawasaki disease, the patients with permanent sensorineural hearing loss showed anemia and thrombocytosis significantly more often, and had a longer duration of the increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate than patients with temporary hearing loss. In the meantime, Knott et al.4), and Sundel et al.7) suggested that the ototoxicity of the high-dose aspirin that was used for the treatment of the acute phase might cause sensorineural hearing loss.
In this study, the presence, causes, and prognosis of sensorineural hearing loss in children with Kawasaki disease were investigated.
In total, 59 of the Kawasaki disease inpatients (33 males and 26 females) from the Department of Pediatrics at three university hospitals in Daegu city (Kyungpook National University Medical Center, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, and Yeungnam University Hospital) from February 2012 to September 2012 agreed to participate in this study upon obtaining the approval of the Institutional Review Board. Their clinical manifestations, results of hematologic examination, echocardiography, audiometry, and the serum levels of aspirin and salicylic acid were monitored.
Kawasaki disease was diagnosed when a fever lasted five days or longer, and at least four of the five clinical manifestations are observed according to the 2004 American Heart Association criteria2,7). Incomplete Kawasaki disease cases that could not meet the criteria were excluded from this study. Cases of hearing loss risk factors including genetic defects, congenital malformations, use of ototoxic drugs such as diuretics or aminoglycoside antibiotics, and infection-like otitis media were also excluded. No patient had a history of hearing loss.
In the acute phase, a combination of intravenous immunoglobulin (GreenCross, 2 g/kg, 12 hours) injection and oral intake of high-dose (100 mg/kg/day, three times a day) aspirin (Rhonal, Kunwha Pharmaceutical, Seoul, Korea) were administered. When an afebrile condition was maintained for 48 hours, low-dose aspirin (3-5 mg/kg/day, once daily) replaced the previous high dose for an eight-week intake period.
A general blood test was conducted prior to beginning of treatment, two days after high-dose aspirin intake, at 48 hours of defervescence after high-dose aspirin intake, and at the fourth and eighth week of outpatient visits. The serum levels of aspirin and its metabolite, salicylic acid, were measured at 48 hours of defervescence after high-dose aspirin intake, and at the eighth week of outpatient visit while low-dose aspirin was administered.
Echocardiography was conducted by pediatric cardiologists before the acute phase treatments, before discharge, and at the fourth and eighth week of outpatient visits to check any coronary artery problems. Abnormal findings in the coronary arteries were defined according to the Japanese Ministry of Health criteria (1984)12): 3-mm diameter of the greater internal lumen of the coronary artery in children under the age of 5, or 4-mm diameter of the greater internal lumen of the coronary artery in children above the age of 5, or the region with greater than 1.5 times the internal diameter of an adjacent blood vessel, or irregularities in the coronary lumen. The sizes of coronary aneurysms were classified according to the American Heart Association criteria2), when the internal diameter of the coronary artery was 8 mm or greater, the case was classified as a giant aneurysm.
Patient's hearing was assessed at 48 hours of defervescence after high-dose aspirin intake and at the eighth week of outpatient visit, using pure tone audiometry in patients over three years of age (19 cases) and brainstem-evoked response audiometry in patients less than three years of age or in patients unwilling to cooperate (40 cases)4,8). The Clark classification was applied for determining the severity of hearing loss (Table 1)13).
Intake compliance was 100%; intake compliance (%)=[(amount to be taken-amount not taken)/amount to be taken]×100.
Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the two groups. A P value of <0.05 was determined as significant.
The group of 59 children was composed of 33 males (56%) and 26 females (44%). Of the 59 patients, three males showed sensorineural hearing loss, accounting for 5.1%. In terms of age (median months), sensorineural hearing loss was confirmed in hearing tests at 37 months (range, 16-126 months), and normal cases at 22 months (range, 3-102 months) showing no significant differences between the two groups (P=0.334) (Table 2).
All three cases with hearing loss showed 30 dB or lower mild bilateral sensorineural hearing loss in the tests conducted at 48 hours of defervescence, and showed a normal pattern of recovery on follow-up tests at the eight-week outpatient visit while taking low-dose aspirin (Fig. 1).
The serum levels of aspirin in the sensorineural hearing loss group measured at 48 hours of defervescence after high-dose aspirin intake and at the eighth week while taking low-dose aspirin were significantly higher than those of the normal group (P=0.034, P=0.026) (Table 3). However, the serum levels of the aspirin metabolite, salicylic acid, did not show a significant difference between the groups (P>0.05).
In terms of the total duration of fever (P=0.831), the duration of fever prior to beginning of treatment (P=0.454) (Table 4), and other laboratory tests (Table 5), no significant difference was observed between the groups (P>0.05).
In echocardiography, abnormality in the coronary artery was observed in nine patients (16%), but none showed hearing loss. Of these nine cases, none showed a giant aneurysm. All abnormalities in the coronary artery had spontaneously recovered by the followup echocardiography conducted at the eighth week of outpatient visit.
Kawasaki disease is an acute febrile systemic vasculitis of unknown etiology that occurs mostly in five-year-old or younger children. Some of the cases, about 20%-25%, show coronary artery complications such as a coronary aneurysm, and coronary artery stenosis or obstruction if left untreated2). Typically, Kawasaki disease is diagnosed when fever lasts more than five days and at least four of the five principal features are observed. For treatment during the acute phase of the disease, intravenous immunoglobulin and aspirin are used in combination, and consequently, the incidence of coronary artery complications significantly decreases to 2%-4%14,15). During the acute phase, various organs including the heart are affected, showing diverse symptoms. In particular, the incidence of central nerve system involvement in Kawasaki disease ranges from 1.1%16,17) to 30% 4,18), showing as aseptic meningitis, seizure, ataxia, transient facial paralysis, sensorineural hearing loss, and subdural effusion10). Although sensorineural hearing loss can cause serious problems in the language development period, the etiological and clinical manifestations are still not fully described, and insufficient attention has been paid to them.
In this study, sensorineural hearing loss during the Kawasaki disease's treatment period was confirmed; the hearing loss group and normal group were compared in terms of their clinical manifestations, general blood tests, and echocardiographic results; and the serum levels of aspirin and its metabolite (salicylic acid) were measured to find their association with sensorineural hearing loss. This is the first prospective study in South Korea in which the patients diagnosed with Kawasaki disease at the three university hospitals underwent uniform treatment and follow-up protocols.
Sensorineural hearing loss in patients with Kawasaki disease was first reported by a Japanese clinician in 198819). Since then, studies on the association have been conducted, but interpretations of the outcomes have varied20). Novo et al.5), Clausen et al.11), and Silva et al.18) reported cases of profound bilateral sensorineural hearing loss in patients with Kawasaki disease, despite the use of steroids for treatment, their hearing function was not improved. They reported that the sensorineural hearing loss might be caused by acute inflammatory reaction in the blood vessels of the middle ear, and their clinical manifestations were not same as those caused by aspirin ototoxicity5,18). In addition, it took 10 days to 5 years to recognize hearing loss in Kawasaki disease, and most cases occurred young children less than two years old5). Therefore, the early diagnosis and follow-up of sensorineural hearing loss in patients with Kawasaki disease is clinically very important.
Typically, sensorineural hearing loss after treatment with aspirin is known as 20 to 30 dB of mild hearing loss in both sides21). Aspirin ototoxicity is reversible within 72 hours upon stopping aspirin intake22). The minimum serum levels of aspirin that can cause a change in hearing thresholds are unknown, but there may be a significant correlation between the serum levels of aspirin and hearing threshold shifts21,23). Brien21) reported that the serum levels of salicylic acid appeared to be more closely associated with aspirin ototoxicity than the serum levels of aspirin. The action mechanism of aspirin on ototoxicity is not known exactly, but aspirin is understood to act on the outer hair cells of the cochlea to trigger morphological alterations24,25). It is thought that aspirin competitively combines with one of the proteins in the outer hair cells to reduce the electromotility of the outer hair cells, and deteriorates basilar membrane vibrations and sound transmission26,27). In addition, aspirin affects the blood vessels for the autonomic nerve in the cochlea to reduce its blood supply and to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, resulting in ototoxicity21).
In Sundel et al.7,9), the serum concentrations of aspirin and salicylic acid in patients with Kawasaki disease were measured, but no direct correlation between the drug's concentration and the change in the hearing threshold was confirmed. However, they described the importance of the serum level of salicylic acid in the expression of aspirin toxicity, and in particular, took notice that hypoalbuminemia during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease could have increased the serum level of salicylic acid. In Knott et al.4), some patients of Kawasaki disease with acute hearing loss showed patterns of bilateral high-frequency hearing loss that corresponded to those of hearing loss, due to aspirin ototoxicity. Considering some of them showed permanent sensorineural hearing loss, the hearing loss of patients with Kawasaki disease is somehow affected by aspirin toxicity, but this cannot be a complete explanation.
In this study, the hearing loss of three patients was confirmed after 48 hours of defervescence, after taking high-dose aspirin (100 mg/kg/day) for two days or longer, at the level of mild bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, less than 30 dB. However, these symptoms had recovered to normal at the eighth-week follow-up hearing test with low-dose aspirin intake. In this study, the clinical manifestations of transient mild bilateral sensorineural hearing loss were similar to those of aspirin toxicity.
Furthermore, the serum level of aspirin immediately before the first hearing test in sensorineural hearing loss patients was significantly high, but the serum level of salicylic acid did not show a significant difference. Unlike Sundel et al.7) and Knott et al.4), who described that the serum level of salicylic acid reflected the risk of ototoxicity more closely, the ototoxicity was considered more closely associated with aspirin concentration than its metabolite concentration in this study. In particular, one patient had a significantly high serum level of aspirin when he showed hearing loss, so it was strongly suspected that the occurrence of sensorineural hearing loss was associated with aspirin toxicity.
Nevertheless, the presence of anemia and thrombocytosis, and the increased aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase described in Magalhaes et al.8) and Alves et al.10) did not show a significant difference between the groups in this study.
In conclusion, sensorineural hearing loss in children with Kawasaki disease might occur during treatment in the acute phase of the disease, mostly involve mild bilateral hearing loss in the lower than 30-dB range and, spontaneously recovered. This was considered to be due to the side effects of high-dose aspirin, which was used for acute-phase treatments, but further studies with more cases may be necessary in the future.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a 2012 research grant from Korean Food and Drug Administration.
Conflicts of interest
Conflict of interest:
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Kawasaki T. Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children. Arerugi 1967;16:178–222.

2. Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Circulation 2004;110:2747–2771.


3. Matsubara T, Mason W, Kashani IA, Kligerman M, Burns JC. Gastrointestinal hemorrhage complicating aspirin therapy in acute Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 1996;128(5 Pt 1): 701–703.


4. Knott PD, Orloff LA, Harris JP, Novak RE, Burns JC. Kawasaki Disease Multicenter Hearing Loss Study Group. Sensorineural hearing loss and Kawasaki disease: a prospective study. Am J Otolaryngol 2001;22:343–348.


5. Novo A, Pinto S, Prior AC, Alvares S, Soares T, Guedes M. Kawasaki disease and sensorineural hearing loss: an (un)expected complication. Eur J Pediatr 2012;171:851–854.


6. Kara A, Besbas N, Tezer H, Karagoz T, Devrim I, Unal OF. Reversible sensorineural hearing loss in a girl with Kawasaki disease. Turk J Pediatr 2007;49:431–433.

7. Sundel RP, Cleveland SS, Beiser AS, Newburger JW, McGill T, Baker AL, et al. Audiologic profiles of children with Kawasaki disease. Am J Otol 1992;13:512–515.

8. Magalhaes CM, Magalhaes Alves NR, Oliveira KM, Silva IM, Gandolfi L, Pratesi R. Sensorineural hearing loss: an underdiagnosed complication of Kawasaki disease. J Clin Rheumatol 2010;16:322–325.


9. Sundel RP, Newburger JW, McGill T, Cleveland SS, Miller WW, Berry B, et al. Sensorineural hearing loss associated with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatr 1990;117:371–377.


10. Alves NR, Magalhaes CM, Almeida Rde F, Santos RC, Gandolfi L, Pratesi R. Prospective study of Kawasaki disease complications: review of 115 cases. Rev Assoc Med Bras 2011;57:295–300.


11. Clausen H, Howarth C, Giardini A. Kawasaki disease: always straight to the heart? BMJ Case Rep 2012;8 24 23:493–500. [Epub].
12. Research Committee on Kawasaki Disease. Report of subcommittee on standardization of diagnostic criteria and reporting of coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. Tokyo: Ministry of Health and Welfare, 1984.
14. Kato H, Koike S, Yamamoto M, Ito Y, Yano E. Coronary aneurysms in infants and young children with acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome. J Pediatr 1975;86:892–898.


15. Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Beiser AS, Burns JC, Bastian J, Chung KJ, et al. A single intravenous infusion of gamma globulin as compared with four infusions in the treatment of acute Kawasaki syndrome. N Engl J Med 1991;324:1633–1639.


16. Takagi K, Umezawa T, Saji T, Morooka K, Matsuo N. Meningoencephalitis in Kawasaki disease. No To Hattatsu 1990;22:429–435.

17. Terasawa K, Ichinose E, Matsuishi T, Kato H. Neurological complications in Kawasaki disease. Brain Dev 1983;5:371–374.


18. Silva CH, Roscoe IC, Fernandes KP, Novaes RM, Lazari CS. Sensorineural hearing loss associated to Kawasaki Disease. J Pediatr (Rio J) 2002;78:71–74.


19. Suzuki H, Yanagawa T, Kihira S. Two cases of hearing loss associated with Kawasaki disease. Clin Pediatr 1988;41:167–172.
20. Smith KA, Yunker WK. Kawasaki disease is associated with sensorineural hearing loss: a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 2014;78:1216–1220.


22. Myers EN, Bernstein JM. Salicylate ototoxicity; a clinical and experimental study. Arch Otolaryngol 1965;82:483–493.


23. Day RO, Graham GG, Bieri D, Brown M, Cairns D, Harris G, et al. Concentration-response relationships for salicylate-induced ototoxicity in normal volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1989;28:695–702.



24. Kakehata S, Santos-Sacchi J. Effects of salicylate and lanthanides on outer hair cell motility and associated gating charge. J Neurosci 1996;16:4881–4889.



25. Lue AJ, Brownell WE. Salicylate induced changes in outer hair cell lateral wall stiffness. Hear Res 1999;135:163–168.


Fig. 1
Pure-tone audiometry audiograms of a 126-month-old boy with Kawasaki disease who showed sensorineural hearing loss. (A) The patient showed mild bilateral hearing loss upon audiometry within 48 hours of defervescence, measuring 26.7 dB on the right side and 25 dB on the left side. (B) Eight weeks later, audiometry showed that the patient's hearing had returned to normal on both sides.
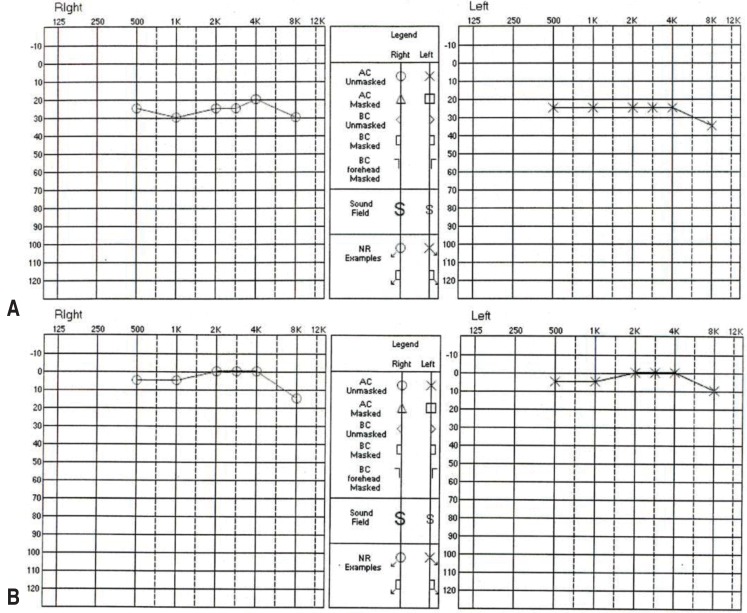
Table 1
Extent of hearing loss
| Degree of hearing loss | Decibels (dB) |
|---|---|
| Normal | 0-25 |
| Mild | 25-40 |
| Moderate | 41-55 |
| Moderate severe | 56-70 |
| Severe | 71-90 |
| Profound | >90 |
Adapted from Clark. ASHA 1981;23:493-50013).
Table 2
Characteristics of patients with Kawasaki disease
| Characteristic | Patients with hearing loss (n=3) | Patients without hearing loss (n=56) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mo) | 37 | 22 (33.5)† | 0.334 |
| Sex | |||
| Male:female | 3:0 | 30:26 |
Table 3
Serum concentrations (ng/mL) of aspirin and salicylic acid during aspirin treatment in patients with Kawasaki disease
Table 4
Duration of fever (days) in patients with Kawasaki disease
| Characteristic | Patients with hearing loss (n=3) | Patients without hearing loss (n=56) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total† | 5 | 6 (1.75)* | 0.831 |
| Before treatment‡ | 4 | 4 (1.00)* | 0.454 |



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


