|
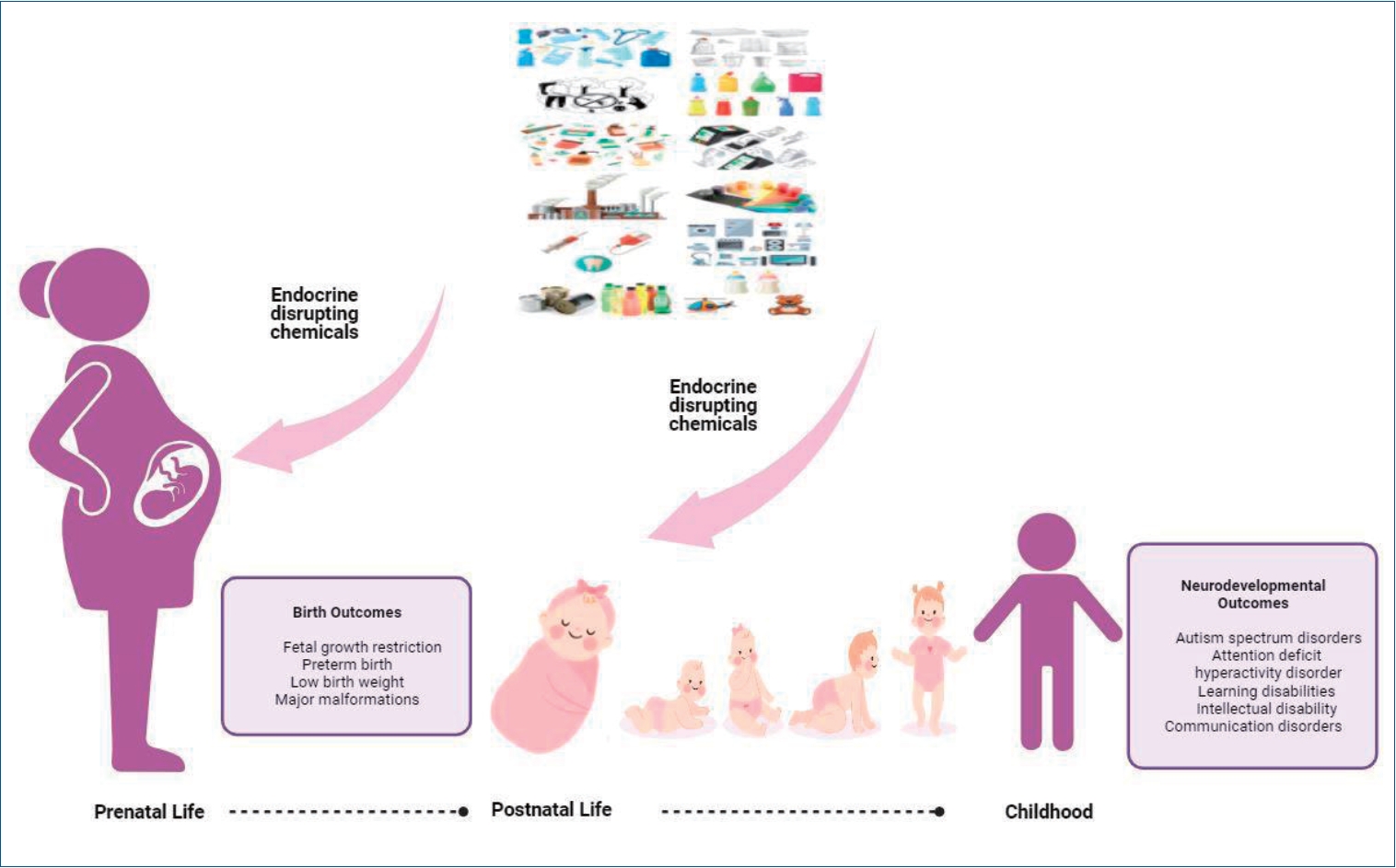
· Sensitivity to endocrine-disrupting chemical (EDC) exposure increases during critical developmental periods (in embryos, fetuses, and neonates).
· Pre- and postnatal exposure to EDCs is associated with fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, and low birth weight.
· Exposure to EDCs during fetal and early postnatal life can have lasting and lifelong neurodevelopmental outcomes, including autism spectrum, attention deficit hyperactivity, and other cognitive and behavioral disorders. |


