Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Risk factors for the occurrence and persistence of coronary aneurysms in Kawasaki disease
- Soo-kyeong Jeon, Geena Kim, Hoon Ko, Joung-Hee Byun, Hyoung Doo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(4):138-143. Published online November 22, 2018
-
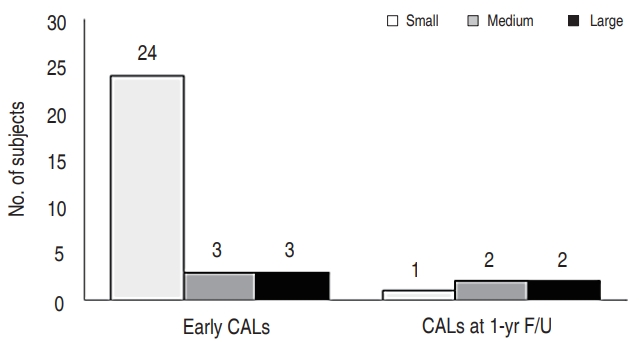
Purpose: Prognostic factors of coronary aneurysms in Kawasaki disease have been investigated in many studies. The aim of this study was to identify risk factors associated with early and late coronary artery outcomes in treated patients with Kawasaki disease. Methods: A total of 392 patients diagnosed with Kawasaki disease from January 2012 to December 2015 in Pusan National University Children’s Hospital...
- Case Report
- Giant coronary aneurysm caused by Kawasaki disease: consistency between catheter angiography and electrocardiogram gated dual-source computed tomography angiography
- Eun-Ha Hwang, Jung-Ki Ju, Min-Jung Cho, Ji-Won Lee, Hyoung-Doo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(12):501-504. Published online December 22, 2015
-
We present the case of a 5-year-old child with coronary complications due to Kawasaki disease; this patient unintentionally underwent both dual-source computed tomography (DSCT) coronary angiography and invasive coronary angiographic examination in 2 months. This case highlights the strong consistency of the results between DSCT coronary angiography and invasive coronary angiography. Compared to conventional invasive coronary angiography, DSCT coronary angiography...
- Original Article
- Detection rate and clinical impact of respiratory viruses in children with Kawasaki disease
- Ja Hye Kim, Jeong Jin Yu, Jina Lee, Mi-Na Kim, Hong Ki Ko, Hyung Soon Choi, Young-Hwue Kim, Jae-Kon Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(12):470-473. Published online December 20, 2012
-
Purpose The purpose of this prospective case-control study was to survey the detection rate of respiratory viruses in children with Kawasaki disease (KD) by using multiplex reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and to investigate the clinical implications of the prevalence of respiratory viruses during the acute phase of KD.
Methods RT-PCR assays were carried out to screen for the presence of respiratory syncytial...
- Epidemiology of Kawasaki disease in infants 3 months of age and younger
- Eun Jung Lee, Yong Won Park, Young Mi Hong, Joon Sung Lee, Ji Whan Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(6):202-205. Published online June 21, 2012
-
Purpose This study investigated the epidemiology of Kawasaki disease (KD) in infants ≤3-month-old.
Methods To study the epidemiology of KD in Korea, data for 27,851 KD patients were collected on a 3-year basis between 2000 and 2008 in a retrospective survey. From this, data for 609 KD patients ≤3-month-old were analyzed and compared with the data for KD patients >3-month-old.
Results The 609 KD patients...
- Epidemiologic study of Kawasaki disease in 6 months old and younger infants
- Yong Won Park, Ji Whan Han, In Sook Park, Chang Hwi Kim, Sung Ho Cha, Jae Sook Ma, Joon Sung Lee, Tae Chan Kwon, Sang Bum Lee, Chul Ho Kim, Heung Jae Lee, Yong Soo Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(12):1320-1323. Published online December 15, 2008
-
Purpose : The aim of this study was to investigate the epidemiologic status of Kawasaki disease (KD) in infants ≤6 months of age. Methods : For the epidemiologic study of KD in Korea, data from 22,674 KD patients were collected from 1997 to 2005 on a 3-year basis by a retrospective survey. From this survey, data of 1,739 KD patients ≤6... -
- Clinical application of D-dimer in Kawasaki Disease
- Jae Joon Han, Hong Ki Ko, Young Yoo, JungHwa Lee, Kwang Chul Lee, Chang Sung Son, Joo Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(2):205-208. Published online February 15, 2007
-
Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea Purpose : Vascular endothelial cell damage and alteration of a fibrinolytic system was suggested to play a role in the development of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease (KD). D-dimer is one of the markers of endothelial damage and fibrinolysis. We evaluated the clinical usefulness of D- dimer to differentiate KD... -
- Clinical and Epidemiologic Study of Kawasaki Disease in Children 8 Years of Age and Older
- Yong Won Park, Ji Whan Han, In Sook Park, Chang Hwi Kim, Sung Ho Cha, Jae Sook Ma, Tae Chan Kwon, Sang Bum Lee, Chul Ho Kim, Heung Jae Lee, Yong Soo Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(10):1139-1142. Published online October 15, 2005
-
Purpose : The aim of this study was to investigate the epidemiologic and clinical profiles of Kawasaki disease(KD) in children 8 years of age and older. Methods : For the epidemiologic study of KD in Korea, data of total 15,692 KD patients were collected from 1994 to 2002 on a 3 year basis, by the retrospective survey. Among them, data of... -
- Case Report
- Giant Coronary and Axillary Aneurysms in an Infant with Kawasaki Disease Associated with Thrombocytopenia
- Sei Young Seo, Jin Hee Oh, Jong-Hyun Kim, Ji-Whan Han, Kyung-Yil Lee, Dae Kyun Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(8):901-906. Published online August 15, 2005
-
Kawasaki disease (KD) is a leading cause of acquired heart disease in children. Yet the etiology of KD is still unknown and diagnosis depends on the exclusion of other diseases and the clinical manifestations meeting the defined criteria. Young infants frequently show atypical clinical courses and are frequently complicated with coronary aneurysms. Some cases show thrombocytopenia, which is known as... -
- A Case of Multiple Giant Coronary Aneurysms with Large Mural Thrombus due to Kawasaki Disease in a Young Infant
- Eun Na Choi, Jeoung Tae Kim, Yuria Kim, Byung Won Yoo, Deok Young Choi, Jae Young Choi, Jun Hee Sul, Sung Kye Lee, Dong Soo Kim, Young Hwan Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(3):321-326. Published online March 15, 2005
-
Kawasaki disease is an acute systemic vasculitis of unknown origin. Giant coronary aneurysm is one of the most serious complications, although peripheral artery vasculitis can produce life-threatening events. Myocardial ischemia and infarction can be caused by coronary artery stenosis, aneurysm, and stagnation of blood flow in coronary arteries which triggers thromboembolism. Atypical presentation in young infants often interferes with prompt... -
- A Case of Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection with Coronary Aneurysm
- Hee Jeong, Bong Seong Kim, Ok Ja Choi, Han Wook Yoo, So Duk Lim, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(6):687-693. Published online June 15, 2001
-
Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection(CAEBV) is a nonfamilial syndrome that shows a specific immunodeficiency for the Epstein-Barr virus(EBV). CAEBV is characterized by fever, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, hepatitis, interstitial pneumonitis, interstitial nephritis, and uveitis. Cardiovascular complications are rare in EBV infection. Patients with CAEBV show characteristically high titers of anti-viral capsid antigen(VCA) IgG antibody and anti-early antigen(EA) antibody, as well as relatively... -
- Original Article
- Clinical Analysis and Comparison of Kawasaki Disease between Patients Younger than One Year of Age and Those over One Year of Age
- Hee-Sun Chung, Kyung-Yil Lee, Ji-Whan Han, Sang-Won Cha, Dong-Joon Lee, Kyung-Tai Whang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(7):936-942. Published online July 15, 1999
-
Purpose : To identify the risk factors for coronary sequelae in Kawasaki disease, we analyzed and compared the clinical features and laboratory findings of Kawasaki disease in patients younger than one year of age with those over one year of age. Methods : A retrospective chart review was conducted of all children with Kawasaki disease who were admitted to the... -
- Survey of Harada Scoring of Occurrence of Coronary Aneurysm in Kawasaki Disease Compared to Current Criteria
- Chang Kyu Nam, Yong Wook Kim, Ki Bok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(7):928-935. Published online July 15, 1999
-
Purpose : Gamma-globulin is effective in preventing coronary aneurysm, the primary complication of Kawasaki disease(KD). However, in order to predict high-risk cases which absolutely require γ-globulin, because of its high expenses, Harada score(HS) was introduced in Japan in 1990. We attempted to compare HS scoring with the health insurance criteria currently used in Korea. Methods : Retrospective studies were performed on... -
- Lipid Profile and Its Association with Coronary Aneurysm in Kawasaki Disease
- Ju Sik Choi, Suk Min Choi, Kyu Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(6):835-840. Published online June 15, 1997
-
Purpose : The value of serum lipid in children after recovery of Kawasaki disease may be important because of the predilection of this disease for the coronary artery. Methods : We measured serum high density lipoprotein(HDL)-cholesterol, total cholesterol, triglycerides in 22 patients (mean age 38months, range 6 to 93 months) with Kawasaki disease during 10 days or less after onset and 2 months later... -
- Case Report
- Three Cases of Atypical Kawasaki Disease with Coronary Aneurysm
- Min-Young Park, Kwang-Sun Han, Sung-Yoon Cho, Byoung-Soo Cho, Sung-Ho Cha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(9):1315-1319. Published online September 15, 1993
-
Kawasaki disease is described by fever lasting five days or more, bilateral conjunctival injection, changes of lips and oral cavity, polymorphous exanthema, acute non-purulent cervical lymphadenopathy, and changes of extremities. Atypical Kawasaki disease is defined as fewer than 4 of 6 criteria described above including coronary artery abnormalities. Especially, atypical clinical manifestations of Kawasaki disease appear in infants younger than 6... -
- Original Article
- A comparative study of therapeutic effect of combined treatment with aspirin and intravenous gammaglobulin versus aspirin alone in Kawasaki disease.
- Sang Bong Lee, Eui Tak Oh, Kang Youl Bae, Hong Ja Kang, Woo Sik Chung, Kil Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(12):1664-1670. Published online December 31, 1991
-
We compared the therapeutic effect of intravenous gamma globulin plus aspirin with that of aspirin alone in reducing the coronary aneurysms and changes of clinical courses in 57 children with Kawasaki disease who were admitted in Dae Dong hospital from Jul. 1987 to Jun. 1990 These 57 cases were divided into two groups: Group A:High dose aspirin (100 mg/kg/day) during febrile stage and then... -
- A Clinical Observation of Kawasaki Disease at High Risk of Coronary Artery Aneurysm.
- Y.T Chung, M.Y Yeo, J.O Lee, B.H Lim, I.J Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(11):1540-1546. Published online November 30, 1991
-
Kawasaki disease is an acute febrile illness of unknown origin and its most serious complication is coronary aneurysms We compared the coronary arterial dilatated group with nondilatated group in clinical manifesta- tion laboratory test, electrocardiography in 90 children with Kawasaki disease, who were admitted to department of Pediatrics of Fatima Hospital from July 1985 to June 1990. The results were as follows. 1) Coronary arterial dilatation was... -
- A Comparative Study of Therapeutic Effect of Intravenous Gammaglobulin plus Aspirin Versus Aspirin Alone in Kawasaki Syndrome.
- Boung Yul Leem, Chong Sung Chung, Sung Ho Cha, Yong Mook Choi, Chang Il Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1989;32(10):1408-1415. Published online October 31, 1989
-
We compared the efficacy of intravenous gamma globulin plus aspirin with that of aspirin alone in reducing the frequency of coronary artery abnormahties and changes of clinical coures in children with acute kawasaki syndrome in the children of 44 cases who were admitted in K.H.U.H from Mar. 1986 to Fab. 1988. Group A: High dose aspirin (60〜90 mg/kg/D) during febrile stage and then switched... -
- A Clinical Study of Kawasaki Disease Complicating Coronary Aneurysm.
- Chong Sung Chung, Byung Yul Lim, Sung Ho Cha, Yong Mook Choi, Chang Il Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1989;32(9):1240-1247. Published online September 30, 1989
-
Kawasaki disease is an acute febrile illness of unknown origin and most frequently affects infants and children younger than age 5 years. Coronary aneurysms are most serious complication in Kawasai diseas and are developed in 15〜20% of patients. We studied 15 children Kawaski disease complicating coronary aneurysms, who were admitted to the Kyung Hee University Hospital during the period of January 1984 through January... -
- Two-Dimensional Echocardiographic Diagnosis of Cornary Aneurysms in Children with the Mucocutaneous Lymphnode Syndrome.
- Jun Hee Sul, Sung Kyu Lee, Dong Shik Chin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1987;30(12):1363-1367. Published online December 31, 1987
-
The two dimensional echocardiographic technique for detecting coronary artery aneurysms was performed in 62 cases with mucocutaneous lymphnode syndrome. Of 62 patients with MCLS, coronary artery aneurysms were detected as large echo-free space in 8 patients. It was found that coronary artery aneurysms usually developed during the acute stage of the illness, and regressed gradually thereafter. Most aneurysms disappeared in 6 months. Therefore, Echocardiography is... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome complicated by Coronary Aneurysm.
- Phil Joun Song, Chung Hye Chu, Kyoo Hwan Rhee, Yong Mook Choi, Chang Il Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(2):197-201. Published online February 28, 1984
-
We have recently experienced a case of mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome complicated by coronary aneurysm. He was suspected by two-dimensional echocardiographic examination and confirmed by the angiography of aorta. A brief review of related literatures was made. -
- Original Article
- Cardiac Involvement of Kawasaki Disease.
- Gu Soo Kim, Kyu Gap Hwang, Byung Kwan Sohn, Jung Yun Choi, Yong Soo Yun, Chang Yee Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(2):135-145. Published online February 28, 1984
-
Twenty-nine cases of Kawasaki disease, who were admitted to the Dept, of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Hospital, were evaluated on the incidence, clinical signs and laboratory findings of cardiovascular system. Among them two patients were excluded from the incidence of cardiac involvement: One with incomplete study died at home on 22nd day after the onset, and the other was referred because... -
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









