< Previous Next >
Article Contents
| Korean J Pediatr > Volume 59(5); 2016 |
|
Abstract
Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) in children is characterized by massive proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia. Minimal change nephrotic syndrome (MCNS) is the most common form of INS in children. The pathogenesis of MCNS still remains unclear, however, several hypotheses have been recently proposed. For several decades, MCNS has been considered a T-cell disorder, which causes the impairment of the glomerular filtration barrier with the release of different circulating factors. Increased levels of several cytokines are also suggested. Recently, a "two-hit" theory was proposed that included the induction of CD80 (B7-1) and regulatory T-cell (Treg) dysfunction, with or without impaired autoregulatory functions of the podocyte. In contrast to the well-established involvement of T cells, the role of B cells has not been clearly identified. However, B-cell biology has recently gained more attention, because rituximab (a monoclonal antibody directed against CD20-bearing cells) demonstrated a very good therapeutic response in the treatment of childhood and adult MCNS. Here, we discuss recent insights into the pathogenesis of MCNS in children.
Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) is a common chronic illness characterized by massive proteinuria and hypoalbuminemia in children1,2). Massive urinary loss of serum proteins can cause a hypercoagulable state, the dysregulation of fluid, electrolyte imbalance, and susceptibility to infections3). The International Study of Kidney Disease in Childhood reported that 84.5% of children with INS had minimal change nephrotic syndrome (MCNS), 9.5% had focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), 2.5% had mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis, and 3.5% had membranous nephropathy or other diseases leading to nephrotic-range proteinuria4). The pathological hallmark of MCNS is the effacement of foot processes in glomeruli, revealed by ultrastructural analysis, without any inflammatory injury or immune complex deposition2).
Eighty to ninety percent of children with INS respond to steroid treatment2). Unfortunately, 60%–80% of the children with steroid-responsive nephritic syndrome relapse, but they almost never develop end-stage renal disease (ESRD)2). Resistance to immunosuppressant therapy, including glucocorticoid and cyclosporin A, occurs in 50% of FSGS cases and 10% of MCNS cases, which is associated with progression to ESRD.
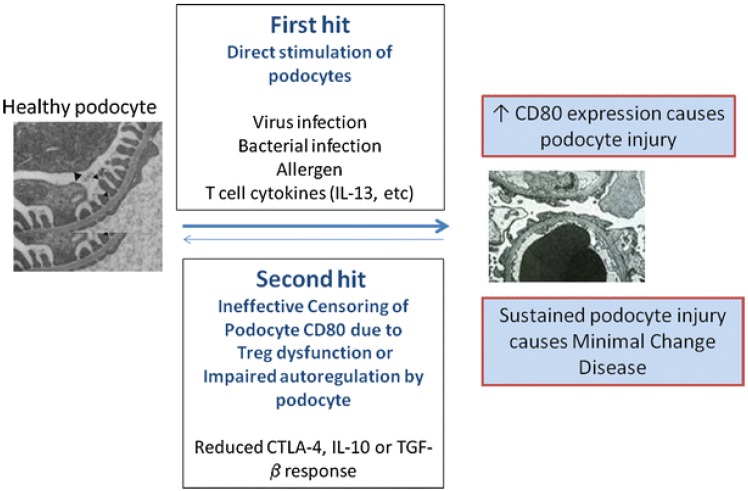
More than four decades ago, MCNS was considered as an exclusive systemic disorder of T cells and cell-mediated immunity5). Increased levels of various cytokines were also suggested as one aspect of the pathogenesis. Recently, Shimada et al.6) proposed a "two-hit" theory that included the induction of CD80 (or B7-1) and regulatory T-cell (Treg) dysfunction, with or without impaired autoregulatory function of the podocytes (Fig. 1). B-cell biology has also attained great attention, since rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against CD20-bearing cells, showed good therapeutic potential in the treatment of both childhood and adulthood MCNS7,8,9). However, the precise pathophysiology of MCNS still remains elusive. We hereby discuss immunological insights and recent findings on the pathogenesis of MCNS.
Approximately 40 years ago, Shalhoub5) proposed a major hypothesis that MCNS was caused by a circulating factor derived from dysfunctional T cells. This hypothesis was based on several findings, such as the presence of no immune complexes in glomeruli, a good response to steroids, and frequent remission after measles infection, which led to cell-mediated immuno-suppression5). For example, treatments of T-cell suppressive drugs, such as cyclosporin A and basiliximab (an anti-interleukin [IL]-2 receptor antibody), were effective in some patients with MCNS2,10).
In the last decades, it has been found that Tregs are a distinct subset of T-lymphocytes that play a pivotal role in maintaining immune homeostasis and tolerance to self-antigens11). The dysregulation of Tregs has been shown to be important in the pathogenesis of several autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus12). Recently, it has also been suggested that Tregs play an important role in the pathogenesis of MCNS13,14). Shimada et al.6) reported Treg dysfunction and/or impaired autoregulatory function by the podocyte have the potential to turn off CD80 expression once it is induced. Treg dysfunction could make transient massive proteinuria persistent, leading to podocyte injury, and eventually, MCNS6). Transient massive proteinuria is typically triggered by viral infections, bacterial infections, or allergen- or T-cell-mediated release of cytokines (e.g., IL-13, etc.)6).
The importance of the association between Tregs and nephrotic syndrome is highlighted by immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, and X-linked (IPEX) syndrome with concomitant nephrotic syndrome15). IPEX syndrome is a rare disorder of the immune regulatory system caused by mutations of FOXP3, which is a transcription factor responsible for the generation and maturation of Tregs, and the development of MCNS in IPEX syndrome can be explained by Treg dysfunction15). However, the reason behind children with MCNS having Treg impairment and/or podocyte autoregulation is still unknown.
Some studies have shown an association between various cytokines and proteinuria, and stated that glomerular permeability factors can be responsible for nephrotic syndrome in patients or in animal models of the proteinuric disease16). Accordingly, the increase in monocyte/macrophage cytokines, including IL-1, IL-12, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), was important in the initiation and recurrence of INS17). In rats with adriamycin-induced nephrotic syndrome, IL-1 produced by resident glomerular macrophages was associated with proteinuria18). In supernatants from children with MCNS, the levels of IL-1 were found to be elevated19).
IL-12, secreted by dendritic cells and macrophages, is also recognized as a T cell-stimulating factor20). It enhances the cytotoxic activity of natural killer cells and cytotoxic T-lymphocytes21). IL-12 levels were increased during the active clinical phase of MCNS in peripheral blood monocyte cultures (PBMC)22). On the contrary, some reports could not detect any IL-12 in serum, urine, and supernatants of PBMC from children with steroid sensitive nephritic syndrome (SSNS)23). Serum IL-12 levels were not significantly disparate between the active phase and remission phase of SSNS24).
TNF-α was increased in the blood and urine of children with NS, and mRNA expression was also increased in PBMC of these patients25,26). TNF-α has been found to induce glomerular injury in experimental MCNS25). IL-15 derived from mononuclear phagocytes following infections induced the differentiation of immature T-helper cells27). This cytokine mimics the stimulatory function of IL-2 on T cells and is believed to cause the release of the vascular permeability factor by PBMCs from nephrotic patients in combination with IL-1228).
In addition to these cytokines, other monocyte/macrophage-related cytokines are IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and IL-1829,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40). IL-6 expression in the urine and renal tissues was correlated with proteinuria in MCNS rats9). Also, serum IL-8 levels were higher in the initial nephrotic phase than in the remission phase in children with SSNS, and urinary concentrations of IL-8 were correlated with proteinuria in children with NS32,33). In contrast, however, Daniel et al.34) reported that serum IL-8 levels were decreased in cases of SSNS compared to healthy controls. IL-10 is mainly produced by monocytes, which have the capacity to reduce the release of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNF-α35). In the study by Matsumoto36), the release of IL-10 was lower in the supernatants of PBMC from patients with MCNS than from that of controls.
T-helper cells, cytotoxic T cells, natural killer cells, and macrophages secrete IFN-γ, which is shown to promote Th1 differentiation, eventually leading to cellular immunity and simultaneously inhibiting Th2 differentiation37). The concentration of IFN-γ was not increased in cases of relapse of children with SSNS38,39). Serum IFN-γ was significantly lower in the active phase of NS compared with the remission phase40).
IL-18 is produced by macrophages, and in combination with IL-12, it plays a pivotal role in cell-mediated immunity following infection41). Urinary levels of IL-18 correlated with disease activity in patients with MCNS42). Similarly, IL-18 levels in vitro were related to the disease activity in MCNS patients43). Serum levels of IL-18 correlated with both IL-4 and IL-13 in childhood SSNS40).
IL-2 promotes the differentiation of immature T cells into Tregs and is implicated in the "battle" against infections and prevention of autoimmune diseases44). IL-2 concentrations were significantly increased during relapse when than that during remission in children with SSNS34,38,45). The IL-2 mRNA expression was also significantly higher in the acute phase than in the remission phase of childhood INS46).
Th2 cytokines, such as IL-13, have been highlighted in the pathogenesis of MCNS39,47,48,49). CD4+ and CD8+ IL-13 mRNA expression increased during relapse than that during remission in children with SSNS39,47). IL-13 overexpression led to podocyte injury in MCNS rat models48). Serum IgE levels are elevated during relapse in SSNS and were correlated with IL-13 upregulation47).
Recent studies have identified that increased IL-13 expression can lead to podocyte injury and can induce a MCNS-like phenotype39,57,50). An increase in IL-13 production by CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells was shown to mediate SSNS39,47). Although no significant histologic changes were observed in the glomeruli of IL-13-transfected rats, they clinically exhibited substantial proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and hypercholesterolemia48). Electron microscopy revealed up to 80% effacement of podocyte foot processes, which progressed to nephrotic syndrome48). Notably, overexpression of IL-13 caused the downregulation of nephrin, podocin, and dystroglycan. These proteins are critical molecules in maintaining slit diaphragm (SD) integrity, and the concurrent upregulation of CD80, IL-4Rα, and IL-13Rα2 in IL-13-transfected rats48).
More recently, Park et al.51,52) reported that IL-13 significantly decreased zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) protein levels in human podocytes, whereas ZO-1 protein production was significantly increased in a rat model of puromycin aminonucleoside nephrosis. They demonstrated that IL-13 alters the expression of ZO-1, and such alterations in the content and distribution of ZO-1 may also be relevant to the pathogenesis of proteinuria in the MCNS model, which was significantly restored after treatment with a leukotriene receptor antagonist51). Therefore, these findings can further strengthen the hypothesis that IL-13 may increase podocyte permeability through the modulation of SD proteins, resulting in nephrotic-range proteinuria, namely MCNS, and also provide an explanation for the plausible connection among Th2 cytokines, MCNS, and atopy.
Increased IL-13 also induced the upregulation of CD80, IL-4Rα, and IL-13Rα2. CD80, a cell surface glycoprotein expressed on activated B lymphocytes, is a dendritic-associated receptor that acts as a costimulatory signaling molecule of the T cell when bound to CD28 expressed on T cells53). Exposure to low-dose lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was shown to upregulate CD80 in the podocytes of wild type and severe combined immunodeficient mice in vivo, which caused nephrotic-range proteinuria53). Mice lacking CD80 are protected from LPS-induced NS, which suggests a link between podocyte CD80 expression and proteinuria53). Tregs are known to inhibit the immune response by releasing soluble cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 (sCTLA-4), IL-10, and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, which can suppress CD80 expression on the antigen presenting cells (APCs). This leads to a blockade of the costimulatory activation of T cells54). Therefore, the immune response is initiated by the activation of CD80 on APCs, and over time, negatively regulated, with the Treg playing a pivotal role in this process.
In MCNS, it has been supposed that local mediators, such as podocyte-derived angiopoietin-like-4 (Angptl-4) and CD80, may be implicated in the pathogenesis of MCNS55). Theoretically, a number of cells within the human kidney may be able to secrete CD80, including podocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and tubular cells54). Overexpression of CD80 in podocytes has been observed in genetic, immune-mediated, drug-induced, and bacterial toxin-induced experimental kidney diseases with nephrotic syndrome56).
Urinary soluble CD80 was significantly increased in MCNS patients during relapse when compared with healthy controls and MCNS patients during remission or with FSGS56). Urinary CD80 correlated with disease activity. The urinary CD80/CTLA-4 ratio was more than 100 folds higher in patients with relapsed MCNS compared with those in remission. In addition, CD80 was observed in glomeruli by immunohistochemical staining in seven biopsy specimens of eight patients with MCNS during relapse56). Western blotting was also performed to distinguish between urinary soluble CD80 (MW 23 kDa) and membrane-associated CD80 (MW 53 kDa). Urinary CD80 was present as an approximately 53 kDa large protein, which suggests cell membrane-associated urinary CD8056). CD80 expression and CD80 protein secretion by podocytes were significantly increased in sera from patients with MCNS in relapse compared with sera from patients in remission53). Further studies addressed if CD80 and soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) levels are able to be reliably used to distinguish between MCNS and FSGS. However, urinary suPAR levels were not distinguishable between both diseases, while urinary CD80 levels were significantly increased in MCNS patients in relapse compared to those in remission and FSGS patients55).
LPS was capable of enhancing the expression of CD80 in podocytes, leading to nephrotic-range proteinuria53). CD80 was colocalized with the podocyte synaptopodin in human and murine kidney tissue specimens53). Activation of CD80 in cultured podocytes led to the reorganization of vital SD proteins, whereas LPS-signaling pathway through the toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 led to the reorganization of the podocyte actin cytoskeleton in vivo53). Therefore, CD80 may contribute to the pathogenesis of proteinuria by disrupting the SD structure53).
To depict pathogenetic pathways regulating and driving CD80 induction in podocytes, several studies were performed57,58). Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (polyIC) induced types I and II interferon signaling, nuclear factor kappa B activation, and the induction of CD80 expression, but dexamethasone blocked both basal and polyIC-stimulated CD80 expression, as did the inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B57). Intravenous injection of polyIC-LMW into mice resulted in significant albuminuria and led to increased urinary CD80 excretion58). Partial foot process fusion in glomeruli was seen by electron microscopy58).
It has been proposed that MCNS is a "two-hit" disorder6). The initial hit is the induction of CD80 on the podocyte, resulting in an alteration in shape with actin disruption that causes increased glomerular permeability and proteinuria6). The second hit is usually caused by the ineffective censoring of podocyte CD80 due to Treg dysfunction or impaired podocyte autoregulation and reduced CTLA-4, IL-10, or TGF-β response. CD80 expression may result from either direct binding of the podocyte by activated T-cell cytokines such as IL-13, or by activation of podocyte TLR by microbial products or allergens6). In normal circumstances, CD80 expression on podocytes is terminated by Treg cytokines or CTLA-4 and IL-10 by podocytes. However, if a second hit occurs in MCNS and abnormal censoring of podocyte CD80 expression continues due to a defective autoregulatory response by Tregs or by the podocyte itself, CD80 expression persists and results in MCNS6). An important experiment that has yet to be done is that of podocyte specific overexpression of CD80, which would clarify a direct effector role of CD80 in inducing proteinuria.
The implicated role of circulatory factors in the etiopathogenesis of MCNS has long been postulated. Vascular permeability factor, elaborated from concanavalin A-stimulated lymphocytes obtained from patients with MCNS, acts on systemic capillaries and on the glomerular permeability barrier59). The effects on the vasculature mimic the effects of IL-2 on permeability59). However, lymphocytes from MCNS patients with high vascular permeability factor activity revealed low amounts of IL-2, and immunoadsorption leading to the complete removal of IL-2 did not affect vascular permeability factor activity60). It became apparent that its secretion is increased by IL-2, IL-12, IL-15, and IL-18, whereas the addition of TGF-β to concanavalin A-stimulated MCNS T cells inhibited the release of the vascular permeability factor61).
In 1999, it was hypothesized that the vascular permeability factor 100KF, which has a role in MCNS, is closely related to hemopexin62). Plasma hemopexin was capable of inducing significant proteinuria and glomerular alterations, resembling MCNS63). Furthermore, it was shown that the mean titer of hemopexin is decreased during relapse, and compared to remission samples and other glomerulopathies, significant upregulation of hemopexin plasma activity and different hemopexin fragments were demonstrated during relapse64). It was concluded that active hemopexin could be present in an altered isoform64). Hemopexin-treated human podocytes showed marked actin reorganization after 30 minutes, which was reversible after four hours and led to the activation of protein kinase B, as well as RhoA. Moreover, Lennon et al.65) postulated a nephrin-dependent process, since these changes did not occur in nephrin-deficient podocytes.
Interestingly, a role for the glomerular secretion of Angptl-4 was proposed66). A podocyte-specific transgenic model (NPHS-Angptl-4) revealed a 500-fold increase in albuminuria in homozygous males over time, whereas adipose tissue-secreted Angptl-4 could not induce any proteinuria66). Electron microscopy showed a selective Angptl-4 signal in glomeruli and foot-process effacement in 5-month-old homozygous rats66). Glucocorticoid treatment reversed the sharp increase of Angptl-4 mRNA expression66). The initial enthusiasm was hampered due to the finding that Angptl-4 is increased in other diseases, leading to nephrotic-range proteinuria as well67). Angptl-4 is secreted in response to an elevation in the ratio of plasma free fatty acids to albumin, in terms of heavy proteinuria, reducing proteinuria but resulting in hypertriglyceridemia67).
In contrast to the well-established involvement of T cells in MCNS, the role of B cells is not yet certain. Despite an observed association between allergic diathesis and the onset of MCNS, an elevation of IgM, IgE, B-lymphocytes, and their subsets, surface IgM-, IgG-, and IgE-positive cells (Bγ, Bµ, and Bɛ) were already described in an earlier study68). In nephrotic patients, an increase in cytoplasmic Bγ (cBγ) was shown with an elevated cBγ/surface Bγ, which normalized during steroid treatment and increased again after withdrawal69). Recently, it was also shown that nuclear factor-related kappa B is upregulated during the relapse of MCNS, mainly in CD4+ T cells and B cells, and this induces the activation of AP1 signaling70).
B-cell biology, however, has attained more attention lately, since treatment with rituximab, a monoclonal antibody directed against CD20 bearing cells, has shown good therapeutic responses in the treatment of both childhood and adulthood MCNS7,71,72,73). Children with frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome had a significantly longer relapse-free period in the rituximab group compared to the control group7,8,73). Moreover, fewer patients with a significantly longer time to treatment failure were reported in the rituximab group7). Concurrent steroid treatment could be significantly reduced following rituximab initiation, while the rate of serious adverse events did not differ between both groups7). Subsequently, rituximab treatment has been licensed for the treatment of steroid-dependent and frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare in Japan74).
Here, we reviewed the pathogenesis of MCNS from an immunological perspective. Recent studies propose that the pathogenesis of MCNS could involve both lymphocytes and podocytes. Further studies are required to elucidate the exact pathophysiology of MCNS, and the development of novel drugs that target podocytes and immunosuppressants for lymphocytes are also needed.
Acknowledgments
Andreas Kronbichler was supported by the ERA-EDTA with a long-term fellowship (12 months) from August 2014 to August 2015. Jae Il Shin was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2011-0013789, 2013R1A1A1012112 and 2015R1C 1A1A01052984).
Conflicts of interest
Conflict of interest:
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
1. Oh J, Kemper MJ. Minimal change (steroid sensitive) nephrotic syndrome in children: new aspects on pathogenesis and treatment. Minerva Pediatr 2012;64:197–204.

4. Churg J, Habib R, White RH. Pathology of the nephrotic syndrome in children: a report for the International Study of Kidney Disease in Children. Lancet 1970;760:1299–1302.

5. Shalhoub RJ. Pathogenesis of lipoid nephrosis: a disorder of T-cell function. Lancet 1974;2:556–560.

6. Shimada M, Araya C, Rivard C, Ishimoto T, Johnson RJ, Garin EH. Minimal change disease: a "two-hit" podocyte immune disorder? Pediatr Nephrol 2011;26:645–649.


7. Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Mori R, Tuchida N, Kamei K, et al. Rituximab for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2014;384:1273–1281.


8. Ravani P, Rossi R, Bonanni A, Quinn RR, Sica F, Bodria M, et al. Rituximab in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter, open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 2015;26:2259–2266.



9. Zhao Z, Liao G, Li Y, Zhou S, Zou H. The efficacy and safety of rituximab in treating childhood refractory nephrotic syndrome: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep 2015;5:8219



10. Park SS, Hahn WH, Kim SD, Cho BS. Remission of refractory minimal change nephrotic syndrome after basiliximab therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 2009;24:1403–1407.


12. Grant CR, Liberal R, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D, Longhi MS. Regulatory T-cells in autoimmune diseases: challenges, controversies and--yet--unanswered questions. Autoimmun Rev 2015;14:105–116.


13. Araya C, Diaz L, Wasserfall C, Atkinson M, Mu W, Johnson R, et al. T regulatory cell function in idiopathic minimal lesion nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 2009;24:1691–1698.



14. Prasad N, Jaiswal AK, Agarwal V, Yadav B, Sharma RK, Rai M, et al. Differential alteration in peripheral T-regulatory and T-effector cells with change in P-glycoprotein expression in childhood nephrotic syndrome: a longitudinal study. Cytokine 2015;72:190–196.


15. Park E, Chang HJ, Shin JI, Lim BJ, Jeong HJ, Lee KB, et al. Familial IPEX syndrome: different glomerulopathy in two siblings. Pediatr Int 2015;57:e59–e61.


16. Pereira Wde F, Brito-Melo GE, Guimarães FT, Carvalho TG, Mateo EC, Simoes e. The role of the immune system in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: a review of clinical and experimental studies. Inflamm Res 2014;63:1–12.


17. Le Berre L, Bruneau S, Renaudin K, Naulet J, Usal C, Smit H, et al. Development of initial idiopathic nephrotic syndrome and posttransplantation recurrence: evidence of the same biological entity. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2011;26:1523–1532.


18. Bricio T, Molina A, Egido J, Gonzalez E, Mampaso F. IL-1-like production in adriamycin-induced nephrotic syndrome in the rat. Clin Exp Immunol 1992;87:117–121.




19. Saxena S, Mittal A, Andal A. Pattern of interleukins in minimalchange nephrotic syndrome of childhood. Nephron 1993;65:56–61.


20. Kalinski P, Hilkens CM, Snijders A, Snijdewint FG, Kapsenberg ML. IL-12-deficient dendritic cells, generated in the presence of prostaglandin E2, promote type 2 cytokine production in maturing human naive T helper cells. J Immunol 1997;159:28–35.



21. Trinchieri G. Interleukin-12: a proinflammatory cytokine with immunoregulatory functions that bridge innate resistance and antigen-specific adaptive immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 1995;13:251–276.


22. Matsumoto K, Kanmatsuse K. Increased IL-12 release by monocytes in nephrotic patients. Clin Exp Immunol 1999;117:361–367.



23. Stefanovic V, Golubovic E, Mitic-Zlatkovic M, Vlahovic P, Jovanovic O, Bogdanovic R. Interleukin-12 and interferon-gamma production in childhood idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 1998;12:463–466.


24. Yildiz B, Cetin N, Kural N, Colak O. CD19 + CD23+ B cells, CD4 + CD25+ T cells, E-selectin and interleukin-12 levels in children with steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Ital J Pediatr 2013;39:42



25. Bustos C, Gonzalez E, Muley R, Alonso JL, Egido J. Increase of tumour necrosis factor alpha synthesis and gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Eur J Clin Invest 1994;24:799–805.


26. Suranyi MG, Guasch A, Hall BM, Myers BD. Elevated levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the nephrotic syndrome in humans. Am J Kidney Dis 1993;21:251–259.


27. Benoit M, Desnues B, Mege JL. Macrophage polarization in bacterial infections. J Immunol 2008;181:3733–3739.


28. Matsumoto K, Kanmatsuse K. Interleukin-15 and interleukin-12 have an additive effect on the release of vascular permeability factor by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in normals and in patients with nephrotic syndrome. Clin Nephrol 1999;52:10–18.

29. Wang LM, Chi YJ, Wang LN, Nie L, Zou YH, Zhao TN, et al. Expression of interleukin-6 in rat model of doxorubicin-induced nephropathy. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 2010;12:912–914.

30. Assadi F. Neonatal nephrotic syndrome associated with placental transmission of proinflammatory cytokines. Pediatr Nephrol 2011;26:469–471.


31. Apostolopoulos J, Davenport P, Tipping PG. Interleukin-8 production by macrophages from atheromatous plaques. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1996;16:1007–1012.


32. Kanai T, Yamagata T, Momoi MY. Macrophage inflammatory protein-1beta and interleukin-8 associated with idiopathic steroidsensitive nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Int 2009;51:443–447.


33. Souto MF, Teixeira AL, Russo RC, Penido MG, Silveira KD, Teixeira MM, et al. Immune mediators in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: evidence for a relation between interleukin 8 and proteinuria. Pediatr Res 2008;64:637–642.


34. Daniel V, Trautmann Y, Konrad M, Nayir A, Scharer K. T-lymphocyte populations, cytokines and other growth factors in serum and urine of children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Clin Nephrol 1997;47:289–297.

35. Saraiva M, O'Garra A. The regulation of IL-10 production by immune cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2010;10:170–181.


36. Matsumoto K. Decreased release of IL-10 by monocytes from patients with lipoid nephrosis. Clin Exp Immunol 1995;102:603–607.




37. Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T, Hume DA. Interferon-gamma: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J Leukoc Biol 2004;75:163–189.


38. Neuhaus TJ, Wadhwa M, Callard R, Barratt TM. Increased IL-2, IL-4 and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) in steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol 1995;100:475–479.


39. Yap HK, Cheung W, Murugasu B, Sim SK, Seah CC, Jordan SC. Th1 and Th2 cytokine mRNA profiles in childhood nephrotic syndrome: evidence for increased IL-13 mRNA expression in relapse. J Am Soc Nephrol 1999;10:529–537.

40. Shalaby SA, Al-Edressi HM, El-Tarhouny SA, Fath El-Bab M, Zolaly MA. Type 1/type 2 cytokine serum levels and role of interleukin-18 in children with steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Arab J Nephrol Transplant 2013;6:83–88.

41. Kawakami K, Koguchi Y, Qureshi MH, Miyazato A, Yara S, Kinjo Y, et al. IL-18 contributes to host resistance against infection with Cryptococcus neoformans in mice with defective IL-12 synthesis through induction of IFN-gamma production by NK cells. J Immunol 2000;165:941–947.


42. Matsumoto K, Kanmatsuse K. Elevated interleukin-18 levels in the urine of nephrotic patients. Nephron 2001;88:334–339.


43. Matsumoto K, Kanmatsuse K. Augmented interleukin-18 production by peripheral blood monocytes in patients with minimalchange nephrotic syndrome. Am J Nephrol 2001;21:20–27.


44. Bluestone JA, Abbas AK. Natural versus adaptive regulatory T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 2003;3:253–257.


45. Lama G, Luongo I, Tirino G, Borriello A, Carangio C, Salsano ME. T-lymphocyte populations and cytokines in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 2002;39:958–965.


46. Shimoyama H, Nakajima M, Naka H, Maruhashi Y, Akazawa H, Ueda T, et al. Up-regulation of interleukin-2 mRNA in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 2004;19:1115–1121.

47. Cheung W, Wei CL, Seah CC, Jordan SC, Yap HK. Atopy, serum IgE, and interleukin-13 in steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 2004;19:627–632.


48. Lai KW, Wei CL, Tan LK, Tan PH, Chiang GS, Lee CG, et al. Overexpression of interleukin-13 induces minimal-change-like nephropathy in rats. J Am Soc Nephrol 2007;18:1476–1485.


49. Kim JE, Park SJ, Ha TS, Shin JI. Effect of rituximab in MCNS: a role for IL-13 suppression? Nat Rev Nephrol 2013;9:551



50. Wei CL, Cheung W, Heng CK, Arty N, Chong SS, Lee BW, et al. Interleukin-13 genetic polymorphisms in Singapore Chinese children correlate with long-term outcome of minimal-change disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2005;20:728–734.


51. Park SJ, Saleem MA, Nam JA, Ha TS, Shin JI. Effects of interleukin-13 and montelukast on the expression of zonula occludens-1 in human podocytes. Yonsei Med J 2015;56:426–432.



52. Kim BS, Park HC, Kang SW, Choi KH, Ha SK, Han DS, et al. Impact of cyclosporin on podocyte ZO-1 expression in puromycin aminonucleoside nephrosis rats. Yonsei Med J 2005;46:141–148.



53. Reiser J, von Gersdorff G, Loos M, Oh J, Asanuma K, Giardino L, et al. Induction of B7-1 in podocytes is associated with nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest 2004;113:1390–1397.



54. Garin EH, Diaz LN, Mu W, Wasserfall C, Araya C, Segal M, et al. Urinary CD80 excretion increases in idiopathic minimal-change disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 2009;20:260–266.



55. Cara-Fuentes G, Wei C, Segarra A, Ishimoto T, Rivard C, Johnson RJ, et al. CD80 and suPAR in patients with minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: diagnostic and pathogenic significance. Pediatr Nephrol 2014;29:1363–1371.


56. Garin EH, Mu W, Arthur JM, Rivard CJ, Araya CE, Shimada M, et al. Urinary CD80 is elevated in minimal change disease but not in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 2010;78:296–302.


57. Shimada M, Ishimoto T, Lee PY, Lanaspa MA, Rivard CJ, Roncal-Jimenez CA, et al. Toll-like receptor 3 ligands induce CD80 expression in human podocytes via an NF-κB-dependent pathway. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012;27:81–89.


58. Ishimoto T, Shimada M, Gabriela G, Kosugi T, Sato W, Lee PY, et al. Toll-like receptor 3 ligand, polyIC, induces proteinuria and glomerular CD80, and increases urinary CD80 in mice. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2013;28:1439–1446.


59. Lagrue G, Xheneumont S, Branellec A, Hirbec G, Weil B. A vascular permeability factor elaborated from lymphocytes. I. Demonstration in patients with nephrotic syndrome. Biomedicine 1975;23:37–40.

60. Heslan JM, Branellec AI, Pilatte Y, Lang P, Lagrue G. Differentiation between vascular permeability factor and IL-2 in lymphocyte supernatants from patients with minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol 1991;86:157–162.




61. Matsumoto K, Kanmatsuse K. Transforming growth factor-beta1 inhibits vascular permeability factor release by T cells in normal subjects and in patients with minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. Nephron 2001;87:111–117.


62. Cheung PK, Stulp B, Immenschuh S, Borghuis T, Baller JF, Bakker WW. Is 100KF an isoform of hemopexin? Immunochemical characterization of the vasoactive plasma factor 100KF. J Am Soc Nephrol 1999;10:1700–1708.


63. Cheung PK, Klok PA, Baller JF, Bakker WW. Induction of experimental proteinuria in vivo following infusion of human plasma hemopexin. Kidney Int 2000;57:1512–1520.


64. Bakker WW, van Dael CM, Pierik LJ, van Wijk JA, Nauta J, Borghuis T, et al. Altered activity of plasma hemopexin in patients with minimal change disease in relapse. Pediatr Nephrol 2005;20:1410–1415.


65. Lennon R, Singh A, Welsh GI, Coward RJ, Satchell S, Ni L, et al. Hemopexin induces nephrin-dependent reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol 2008;19:2140–2149.



66. Clement LC, Avila-Casado C, Mace C, Soria E, Bakker WW, Kersten S, et al. Podocyte-secreted angiopoietin-like-4 mediates proteinuria in glucocorticoid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Nat Med 2011;17:117–122.


67. Clement LC, Mace C, Avila-Casado C, Joles JA, Kersten S, Chugh SS. Circulating angiopoietin-like 4 links proteinuria with hypertriglyceridemia in nephrotic syndrome. Nat Med 2014;20:37–46.


68. Yokoyama H, Kida H, Tani Y, Abe T, Tomosugi N, Koshino Y, et al. Immunodynamics of minimal change nephrotic syndrome in adults T and B lymphocyte subsets and serum immunoglobulin levels. Clin Exp Immunol 1985;61:601–607.


69. Yokoyama H, Kida H, Abe T, Koshino Y, Yoshimura M, Hattori N. Impaired immunoglobulin G production in minimal change nephrotic syndrome in adults. Clin Exp Immunol 1987;70:110–115.


70. Audard V, Pawlak A, Candelier M, Lang P, Sahali D. Upregulation of nuclear factor-related kappa B suggests a disorder of transcriptional regulation in minimal change nephrotic syndrome. PLoS One 2012;7:e30523



71. Shin JI, Kronbichler A. Rituximab for patients with nephrotic syndrome. Lancet 2015;385:225–226.

72. Kronbichler A, Bruchfeld A. Rituximab in adult minimal change disease and focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nephron Clin Pract 2014;128:277–282.


Fig. 1
Two hit theory in podocyte immune disorder. IL, interleukin; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4; TGF, transforming growth factor. Adapted from Shimada et al. Pediatr Nephrol 2011;26:645-9, with permission of Springer6).



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link PubMed
PubMed Download Citation
Download Citation


