Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Global trends in importance of 24-hour movement behaviors to pediatric health: Implications for South Korea
- Eun-Young Lee, Reyana Jayawardena, Seiyeong Park, Justin Y. Jeon, Yeon-Soo Kim, Mark S. Tremblay
-
Cultivating a 24-hour movement behavioral profile conducive to health and well-being, marked by adequate levels of physical activity, limited screen time, and sufficient sleep, has emerged as an important avenue for promoting pediatric health. We aimed to provide evidence of this potential, this multiphase, multimethod, and integrative review comprehensively investigated the global trends in health promotion initiatives and status of... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.00178 [Accepted]
- Diet-related behaviors affecting health and substance use among children and adolescents
- Ji-Hyun Seo, Sochung Chung
-
Unhealthy diet-related behaviors and poor diet quality during childhood and adolescence are the main factors contributing to noncommunicable diseases such as obesity, dyslipidemia, diabetes, hypertension, and cardiometabolic syndrome. Unhealthy diet-related behaviors can become lifelong habits associated with mental health problems, including depression, anxiety, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and substance abuse issues such as smoking, drinking, and other chemical compounds. Children... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2023.01634 [Accepted]
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents: prevalence and associated factors
- Jee-Seon Shim, Jeong Mi Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):531-539. Published online September 24, 2024
-

Question: How prevalent is energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents and what are the associated factors?
Findings: The prevalence of energy drink consumption among Korean adolescents increased from 3.2% in 2014 to 12.2% in 2019. Energy drink consumption varies according to sociode-mographic and individual factors.
Meaning: Policies and educational strategies are needed to reduce energy drink consumption in adolescents.
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Parenting stress and interactive engagement behaviors in children with developmental delay
- Jung Sook Yeom, Rock Bum Kim, Jae Young Cho, Ji Sook Park, Eun Sil Park, Ji-Hyun Seo, Jae-Young Lim, Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(6):252-261. Published online May 19, 2023
-
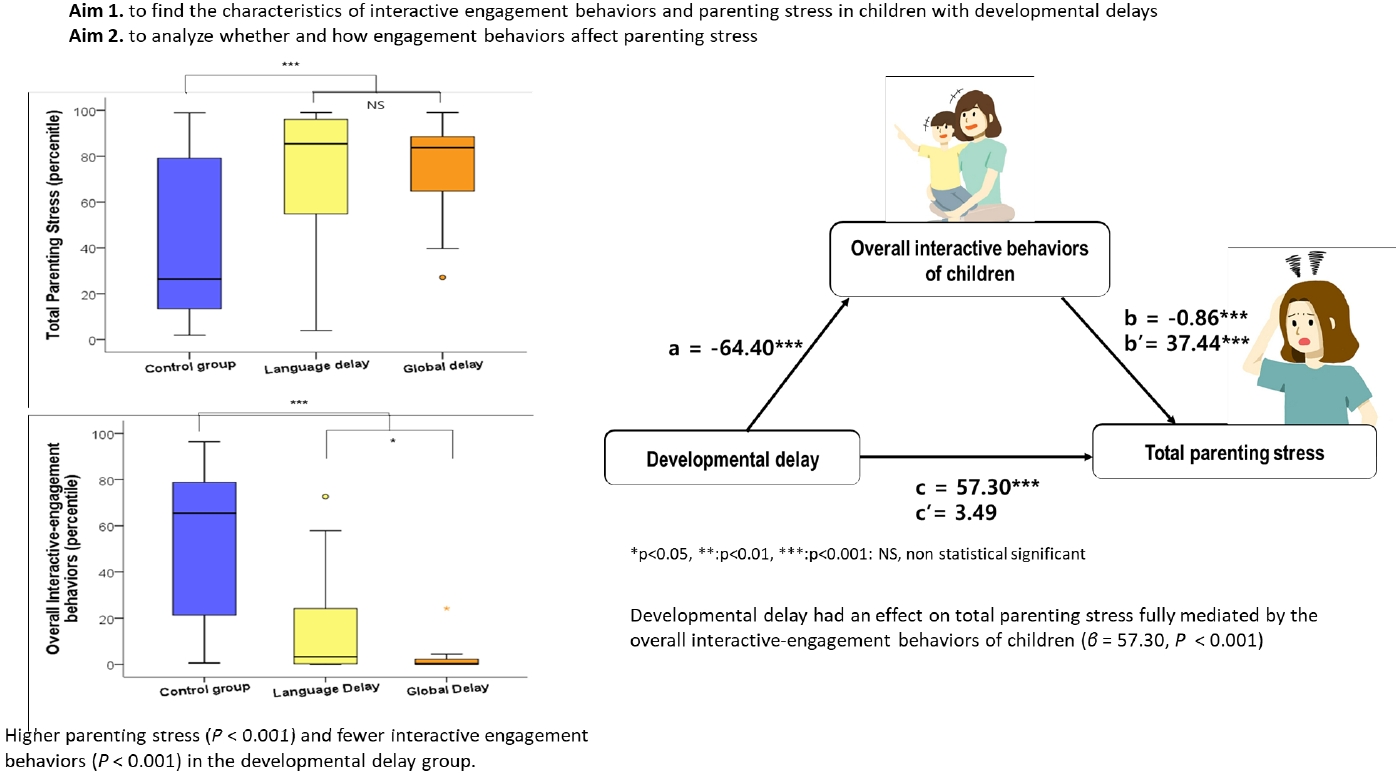
· Question: What level of parenting stress is experienced by parents of children with developmental delays (DDs) without autism spectrum disorder, and what factors contribute to it?
· Findings: Parents of children with DDs experienced high parenting stress that were significantly mediated by their children’s low interactive behaviors.
· Meaning: The interactive behaviors of children with DDs mediate parenting stress.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- A thickened formula reduces feeding-associated oxygen desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants
- Gayoung Lee, Juyoung Lee, Ga Won Jeon, Yong Hoon Jun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):32-37. Published online December 15, 2022
-
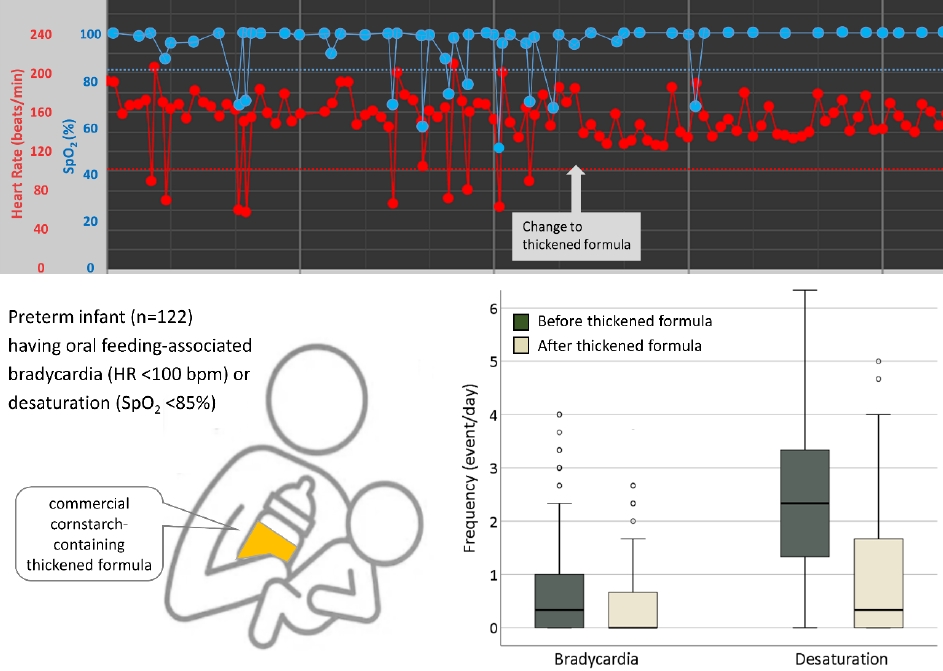
Question: Is a commercial thickened formula able to alleviate oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants?
Finding: Thickened formula feeding significantly reduced oral feeding-associated desaturation and bradycardia in preterm infants.
Meaning: Thickened formula feeding stabilizes oxygen saturation and heart rate during oral feeding among preterm infants with feeding difficulties.
- Review Article
- Other
- Behavioral insomnia in infants and young children
- Eun Kyeong Kang, Seung Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(3):111-116. Published online July 15, 2020
-

• Behavioral insomnia is common and affects a child’s daytime functioning and emotions.
• Diagnosing insomnia using the child’s sleep history, a sleep diary/log, and sleep questionnaires is important.
• Behavioral intervention, the main treatment, involves creating positive associations with sleep, establishing a consistent sleep schedule and bedtime routines, and the development of selfsoothing skills.
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Behavioral and intelligence outcome in 8- to 16-year-old born small for gestational age
- Kyung Hee Yi, Yoon Young Yi, Il Tae Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(10):414-420. Published online October 17, 2016
-
Purpose We investigated behavioral problems, attention problems, and cognitive function in children and adolescents born small for gestational age (SGA).
Methods Forty-six SGA children born at term and 46 appropriate for gestational age (AGA) children born at term were compared. Psychiatric symptoms were examined with reference to the Korean-Child Behavior Checklist, Korean-Youth Self Report, and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Rating Scale (ADHD-RS). Cognitive...
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Effects of early menarche on physical and psychosocial health problems in adolescent girls and adult women
- Jae-Ho Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(9):355-361. Published online September 21, 2016
-
The menarcheal age of Korean women has been rapidly decreasing for the last 50 years, and the average menarcheal age of women born in the 1990s is approaching 12.6 years. In addition, interest in early puberty has been increasing recently owing to the rapid increase in precocious puberty. Generally, out of concern for short stature and early menarche, idiopathic central...
- Current health issues in Korean adolescents
- Chang Ho Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(10):395-400. Published online October 31, 2011
-
During the adolescent period, they experience rapid physical, emotional, cognitive developments while they establish their lifestyle and habitual routines that strongly influence adult health and life. Recent rapid economic growth in Korea, and the earlier onset of physical, sexual, and psychological maturation of adolescents, has resulted in changes in the health status of adolescents from many years ago. Risk-taking behaviors...
- Excessive crying: behavioral and emotional regulation disorder in infancy
- Joon Sik Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(6):229-233. Published online June 30, 2011
-
In the pediatric literature, excessive crying has been reported solely in association with 3-month colic and is described, if at all, as unexplained crying and fussing during the first 3 months of life. The bouts of crying are generally thought to be triggered by abdominal colic (over-inflation of the still immature gastrointestinal tract), and treatment is prescribed accordingly. According to...
- Original Article
- The effect of sucrose on infants during a painful procedure
- Kyoung Hwa Joung, Soo Chul Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(8):790-794. Published online August 31, 2010
-
Purpose The purpose of this study was to test the efficacy of treating the pain among newborn infants associated with a medical procedure with sucrose with regard to overall physiological and behavioral stability.
Methods 103 newborn infants were enrolled in this study. The control group (n=63) did not receive any treatment. The experimental group (n=40) received 2 mL of 24% sucrose solution two...
- Review Article
- Diagnosis and therapy for functional urinary incontinence in childhood
- Ju Hyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(11):1147-1151. Published online November 15, 2008
-
Functional urinary incontinence, the absence of any neurologic or structural abnormality as a cause of urinary incontinence in children, is one of the most common clinical problems encountered in pediatric and urologic departments, and it can be socially and emotionally distressing for the affected children. The prevalence rates of functional urinary incontinence in school-aged children are not very high and... -
- Original Article
- The relationships among perception of physique, self-esteem, sociality, and behavioral characteristics in children
- Min-Ja Jung, Kyung-Lim Yoon, Kye-Shik Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(10):1052-1057. Published online October 15, 2008
-
This study was to examine the relations of perception of physique with self-esteem, sociality and problematic behaviors in children. Methods: Four hundred sixty five (231 boys and 234 girls) children were divided into three groups according to their height or body mass index according to the physical growth standard table had been presented in 2007 by the Korean Pediatric Society. The... -
- Effects of an intensive asthma education program on asthmatic children and their caregivers
- Kang Jin Seo, Gun Ha Kim, Byung Keun Yu, Yun Ku Yeo, Jong Hoon Kim, Eu Ddeum Shim, Mi Ri Yoon, Young Yoo, Ji Tae Choung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(2):188-203. Published online February 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Asthma is one of the most common chronic childhood disease. Education of asthmatic children and their families about asthma and its management may improve disease control, reduce symptoms, and improve school performance. The aim of the study was to evaluate the effects of an intensive asthma education program in asthmatic children and their families on outcome measure... -
- Health and risk taking behaviors of freshmen in college
- Hong Ki Ko, Jae Joon Han, Yoon Lee, Young Yoo, Kee Hyoung Lee, Ji Tae Choung, Sang Hee Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(10):1042-1049. Published online October 15, 2006
-
Purpose : This study was conducted to survey the preliminary data on risk behaviors and to identify the factors that prevent risk-behaviors in late adolescence. Methods : Freshmen(n=1,297) beginning the first semester in Korea University, Seoul, Korea completed self-administered risk behavior questionnaires, comprising 5 domains : demographics, smoking, drinking, drug abuse and sexual behavior. Results : The rate of smoking experience was... -
- Expression of Expanded Polyglutamine Disease Proteins in Drosophila (Drosophila Polyglutamine Disease Models)
- Sang Min Shin, Kyung Hoon Paik, Dong Kyu Jin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(4):425-432. Published online April 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Polyglutamine diseases are a group of diseases caused by the expansion of a polyglutamine tract in the protein. The present study was performed to verify if polyglutamine disease transgenic Drosophila models show similar dysfunctions as are seen in human patients. Methods : Polyglutamine disease transgenic Drosophila were tested for their climbing ability. And using genetic methods, the effects of... -
- Predisposing Factors of Risk Taking Behaviors in Korean Adolescents
- Jae Hee Soh, Yeon Kyeong Jung, Gi Young Jang, Young Kyoo Shin, Kee Hyoung Lee, Baik Lin Eun, Sang Hee Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(12):1364-1373. Published online December 15, 2001
-
Purpose : Risk-taking behaviors are defined as patterns of behavior initiated during adolescence which are responsible for the majority of negative health outcomes occurring during the rest of the life. The study was to explore the relationship between the risk-taking behaviors and their predisposing factors among adolescents. Methods : The study used a survey design with an anonymous self-report questionnaire administered to 1,076 students from... -
- Treatment of Self-Injurious Behavior Through Behavior Therapy.
- Bo In Chung, Jong Soo Kim, Jae Seung Yang, Bong Sun Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(5):585-597. Published online May 31, 1990
-
Three-step guided compliance training and movement suppression time-out technique were used to treat desruptive, self-injurious, and aggressive behaviors in an 8-years old tuberous sclerosis with severe mental retardation. In compliance training, the child’s compliance behavior to verval and/or gestural demand was reinforced with edible and/or social reinforcers and the noncomplied demand was forcefully carried out through physical prompting. Movement suppression time-out was enforced whenever any... -
- Neurobehavioral Response of Newborn Infants Following Delivery by Normal Labor and Cesarean Section under General and Spinal Anesthesia.
- Eun Ai Lee, Jung Hee Park, Yoon Ju Choi, Seung Ju Lee, Keun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1982;25(10):1032-1038. Published online October 31, 1982
-
Scanlon*s Early Neonatal Neurobehavioral Scale was administered to 110 babies delivered by normal labor and cesarean section. Fifty of the mothers had normal vaginal delivery, thirty of the mothers were induced into general anesthesia with thiopental sodium and thirty of the mothers received spinal anesthe- sia with tetracaine before cesarean section. The Scanlon*s scale involves an assessment of the infant*s state of wekefulness, varius reflexes, his... -
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









