Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Allergy
- Association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children: a systematic review and multicenter cohort study using a common data model
- Ji Eun Lim, Hye Min Kim, Ju Hee Kim, Hey Sung Baek, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):357-365. Published online June 14, 2023
-
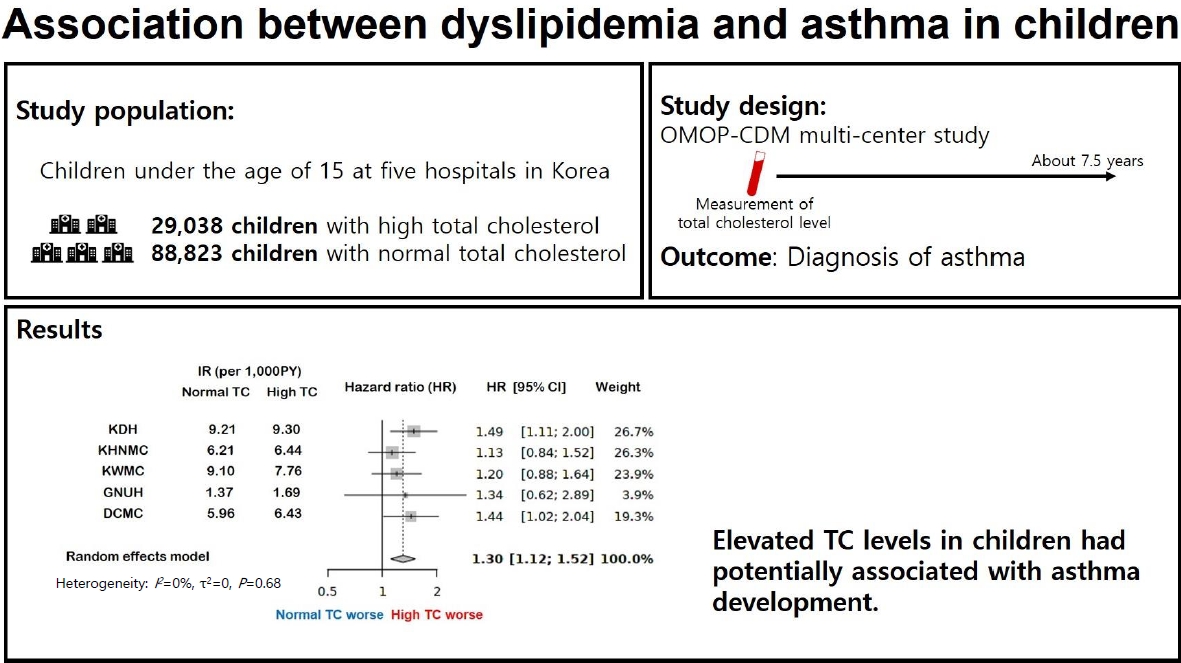
Question: Is dyslipidemia a risk factor for asthma in children?
Finding: This was a comprehensive systematic review and retrospective multicenter study of the association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children. In a multicenter cohort analysis using the Observational Medical Outcomes Partnership Common Data Model, elevated total cholesterol levels were associated with increased risk of asthma development.
Meaning: These findings suggest an association between dyslipidemia and asthma in children.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- A new perspective on cholesterol in pediatric health: association of vitamin D metabolism, respiratory diseases, and mental health problems
- Jeana Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):65-72. Published online December 9, 2021
-
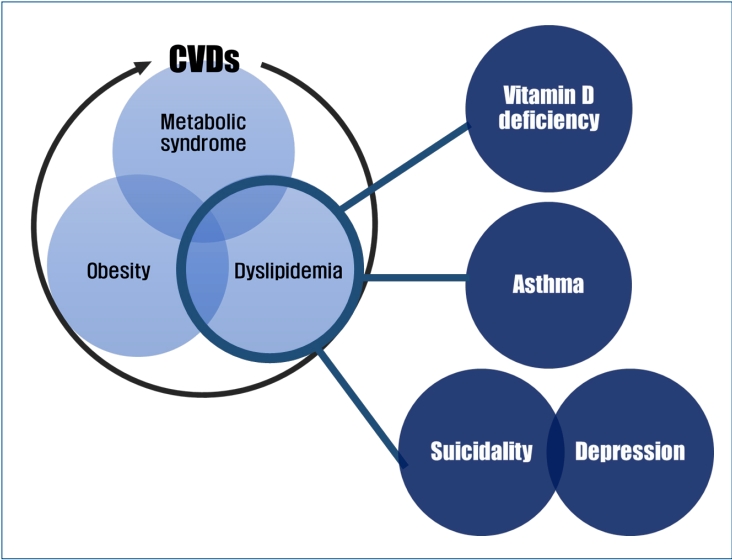
∙ Pediatric dyslipidemia is associated with several health problems besides cardiovascular diseases.
∙ There is a direct association between pediatric dyslipidemia and low serum vitamin D levels, asthma, and mental health problems regardless of body mass index.
∙ More large-scale nationally representative studies are needed to establish the appropriate cutoff points for the definition of dyslipidemia that is a prerequisite for further epidemiological studies in the Korean pediatric population.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Lipid accumulation product is a predictor of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in childhood obesity
- Bahar Özcabı, Salih Demirhan, Mesut Akyol, Hatice Öztürkmen Akay, Ayla Güven
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):450-455. Published online October 28, 2019
-

Background: Lipid accumulation product (LAP) is associated with the presence and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in adults.
Purpose: Here we evaluated the ability of LAP to predict NAFLD in obese children. Methods: Eighty obese children (38 girls; age 6–18 years) were included. Anthropometric measurements and biochemical values were obtained from the patients’ medical records. LAP was calculated as [waist...
- Gastroenterology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese and nonobese pediatric patients
- Eun Jeong Kim, Hyun Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(1):30-35. Published online September 17, 2018
-

Purpose: Obesity is risk factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). However, nonobese patients are also increasingly susceptible to NAFLD. The aim of this study was to compare the clinical characteristics of obese and nonobese pediatric patients with NAFLD. Methods: We retrospectively studied 68 patients who were diagnosed with NAFLD between January 2010 and October 2016 at 10–18 years of age....
- Case Report
- A case of Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome diagnosed by identification of mutations in the 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7) gene
- Mee Rim Park, Jung Min Ko, Chong-Keun Cheon, Gu-Hwan Kim, Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(11):1236-1240. Published online November 15, 2008
-
Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome (SLOS) is a rare, autosomal recessive disease caused by an inborn error in cholesterol synthesis. Patients with this disease suffer from multiple malformations due to reduced activity of 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase (DHCR7), which increases 7-dehydrocholesterol (7DHC) and 8-dehydrocholesterol (8DHC) concentrations and decreases cholesterol concentration in body fluids and tissue. The SLOS phenotypic spectrum ranges from a mild disorder with... -
- Original Article
- Changes of Lipid and Lipoprotein Compositions in Kawasaki Disease and its Impact on Cardiac Complications
- Sin Weon Yun, Ho Seok Lee, Dong Woon Kim, Kang Won Rhee, Young Soo Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(12):1370-1377. Published online December 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Delineation of serum lipid and lipoprotein values in children after Kawasaki disease(KD) is important because of the predilection of this disease for the coronary arteries. Methods : The KD group was composed of 51 patients who were hospitalized from Jan. 2002 to Dec. 2003. Control was 25 patients with non-KD febrile illness. The levels of total lipid, phospholipid,... -
- The Prevalence of Childhood and Adolescent Obesity in Jeju and Clinical Characteristics according to the Degree of Obesity
- Jung Ho Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(4):362-367. Published online April 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Recently, childhood obesity has increased and became a major health concern in Korea. The aim of this study is to examine the prevalence of childhood and adolescent obesity in Jeju and to analyze clinical characteristics according to the degree of obesity. Methods : A total of 3,643 students from April 2002 to August 2002 were studied. To examine the... -
- Alteration of Biochemical Profiles after High-Dose Intravenous Immunoglobulin Administration in Kawasaki Disease
- Ji-Won Lee, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(8):817-820. Published online August 15, 2003
-
Purpose : Intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) has been used as an immunomodulatory treatment for several immune-mediated diseases. The early effect of high-dose IVIG on biochemical profiles including lipids and proteins was evaluated in patients with Kawasaki disease(KD). Methods : Twelve children with KD(nine boys) were treated with IVIG of 2 g/kg over 12 hours. Serial sera were collected from the patients four times... -
- The Prevalent Rates of Abnormal Serum Aminotransferase Levels and Total Cholesterol Levels among Adolescents with Obesity
- Hyun Oh Jang, Chong Guk Lee, Yun Ju Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(12):1484-1490. Published online December 15, 2002
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study was to look at prevalences of abnormal serum aminotransferase levels and abnormal serum total cholesterol levels among adolescents with obesity in Seoul area. Methods : Body mass index[BMI(kg/m2)], serum aspartate aminotransferase(AST) alanine aminotransferase(ALT), and total cholesterol levels were measured in 26,876 adolescents(male : 13,287, female : 13,589) of first grade of high school in... -
- The Prevalence of Obesity and Underweight in Adolescents in Incheon Area and the Relationship between Serum Cholesterol Level and Obesity
- Myung Hyun Kim, Tae Wan Kim, Young Jin Hong, Byong Kwan Son, Soo Hwan Pai, Kyung Ja Chang, Soon Ki Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(2):174-182. Published online February 15, 2002
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study was to investigate the prevalence of obese and underweight adolescents in Incheon area and to examine the relationship between serum cholesterol level and obesity, then to assess the nutritional condition of adolescents. Methods : With a questionnaire regarding their demographic characteristics, blood samples were obtained from apparently healthy students aged 12 to 24 years... -
- Erratum
- Reference Values of Hematologic and Biochemical Parameters of Nutrition around Weaning Period
- Seung Joo Lee, Jeong Wan Seo, Jae Ock Park, Jae Hoon Shin, Hae Ran Lee, Ji Tae Chung, Hae Il Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(1):6-14. Published online January 15, 1999
-
Purpose : To determine the reference values of hematologic and biochemical parameters of nutrition around the weaning period. Methods : From February 1996 to March 1997, several nutritional laboratory values were evaluated in 130 healthy babies and 120 inpatients in the recovery stage of acute illness at six general hospitals. Results : Reference values in 9-month-old healthy babies(range : 6-12 months) were... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Familial Hypercholesterolemia with Diabetes Mellitus
- Yong Kyu Sohn, Kee Young Chang, Kee Hyoung Lee, Young Chang Tockgo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(6):862-866. Published online June 15, 1997
-
Familial Hypercholesterolemia is the most common hyperlipoproteinemia during the childhood, which occurs from the mutation of genes that regulates low-density lipoproteins(LDL), and is classified into two types, the homozygote presented abnormal genes from both parents and the heterozygote presented an abnormal gene from each parent. Type IIa familial hypercholesterolemia is characterized by, especially, increased level of LDL which is common type and normal level... -
- Original Article
- Lipid Profile and Its Association with Coronary Aneurysm in Kawasaki Disease
- Ju Sik Choi, Suk Min Choi, Kyu Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(6):835-840. Published online June 15, 1997
-
Purpose : The value of serum lipid in children after recovery of Kawasaki disease may be important because of the predilection of this disease for the coronary artery. Methods : We measured serum high density lipoprotein(HDL)-cholesterol, total cholesterol, triglycerides in 22 patients (mean age 38months, range 6 to 93 months) with Kawasaki disease during 10 days or less after onset and 2 months later... -
- The Change of Serum Cholesterol level in Children with Fever
- Mi Ja Park, Jae Yoon Kim, Jae Wook Ko, Don Hee Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1996;39(7):908-914. Published online July 15, 1996
-
Purpose : This study was undertaken to assess the change of the serum cholesterol level according to the duration of fever in children. Methods : A retrospective study presents data on fasting serum cholesterol assessed 346 children aged from 3 to 14 years, admitted to National Medical Center from Jan. 1992 to Jun. 1994 due to febrile disease. These patients were divided into three... -
- A Study on Nutritional Status of Iron and Lipids in Infants
- Kwang-Hea Choi, Son Moon Shin, Kee-Hwa Oh, Jung Sook Seo, Kwang-Soo Kim, Yung-Sun Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(3):297-305. Published online March 15, 1995
-
Purpose : This study was conducted to get baseline data to establish a guideline for the infant nutrition by observing the feeding practice and nutritional intake during infancy and evaluationg the nutritional status of iron and lipids at 12-month-old infants. Methods : This survery was cnducted from July to November, 1992. Subjects were healthy infants who were brought to Yeungnam University... -
- Serum Total Cholesterol and HDL Levels in Healthy Korean School Children: Do They Correlate with Obesity?
- Jae Geon Sim, Mi Za Chun, Moses Whang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(11):1579-1585. Published online November 15, 1994
-
Purpose : The cut-off value for hypercholesterolemia and normal HDL levels for Korean children are still not established despite increasing hypercholesterolemia with recent socioeconomic change. One of the aims of this study its to screen the serum total cholesterol and HDL levels in normal Korean school children, and another is to evaluate the relationships between serum lipid levels and obesity. Methods... -
- A Study on Evolution of Lipoportein(a) in Newborns
- Keun Haeng Cho, Young Sook Hong, Soo Won Lee, Soon Kyum Kim, Young Chang Tockgo, Han Kyeom Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(8):1078-1091. Published online August 15, 1994
-
Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is considered an additional, independent and largely genetically determined risk factor for the development of premature coronary heart disease. Furthermore abnormal plasma lipoprotein patterns have been associated with increased risk for developing coronary heart disease. Among these lipoproteins, an increased concentration of serum Apo B and decreased level of Apo A are considered as major risk factors, together... -
- Childhood Infection-associated Hypocalcemia
- Mi Reong Kim, Seoung Hwan Kim, Hee-Shang Youn, Chong-Hwa Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(2):223-231. Published online February 15, 1993
-
The causes of hypocalcemia in patients suffering from severe infection including sepsis are largely uncertain. So we measured serum albumin, total protein, cholesterol, PTH, and calcitonin of the infection-associated hypocalcemic chlidren and compared with those of normocalcemic children department of pediatrics of Gyeongsang National University Hospital. Hypocalcemic patients were compared to the decreased amount of serum albumin in the hypocalcemic... -
- The Normal Serum Total Cholesterol Level in Children
- Gyu Eun Whoang, Keun Su Rhee, Young Hun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(11):1559-1565. Published online November 15, 1992
-
The measurement of serum total cholesterol was made in 1 month to 16 years of age group (total 1505, male 700, female 805) to know the normal value on each age and sex group, and incidence of hypercholesterolemia in children. The results were as follows: 1) Serum total cholesterol levels were 163.12¡¾38.01 mg/dl in male, 165.69¡¾38.24 mg/dl in female, and 164.40¡¾38.12 mg/dl... -
- HDL Cholesterol, Copper, Ceruloplasmin, Zinc, Iron Values of the Blood in Newborn
- Kyeong Sang Kim, Chun Hang Lee, Hong Jin Lee, Won Ill Park, Kyung Ja Lee, Tae Hyon Yoon, Won Chan Tae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(8):1096-1101. Published online August 15, 1992
-
HDL choleaterol, copper, ceruloplasmin, zinc, and iron values of the blood of 85 newborns delivered at hallym University hospital from September, 1989 to February, 1991 were analysed. The results were as follows: 1) The mean value of HDL cholesterol in 50 normal newborns was 31.37¡¾9.47mg/dl, that of copper 80.54¡¾17.54ug/dl, that of ceruloplasmin 11.34¡¾6.37mg/dl, that of zinc 92.81¡¾79.74ug/dl, that of iron 198.98¡¾86.07 ug/dl. 2)... -
- The incidence of complications in severely obese children.
- Dong Hwan Lee, Chong Guk Lee, Chul Lee, Yong Seung Hwang, Sung Ho Cha, Yong Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(4):445-453. Published online April 30, 1991
-
The measurement of body weight, height and blood pressure, urine sugar, oral glucose tolerance test, S-GOT, S-GPT, cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol tests were made in 324 severely obese elementary, middle and high school students (218 boys and 106 girls) to know the incidence of complication in these children. . The results were as follow: 1) S-GOT or S-GPT were increased abnormally in 38.3% and fatty livers were... -
- A Case of Familial Hypercholesterolemia.
- J H You, H R Kil, J J Seo, Y H Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1989;32(9):1288-1294. Published online September 30, 1989
-
We experienced a case of familial hypercholesterolemia in 9 year-old boy with hypercholester- olemia, tendon xanthoma, foamy histicoytes in skin biopsy and biochemical abnormalities in family members, but without abnoramlity of cardiovascular system. Diagnosis was established by clinical characteristics, serum chemistry and lipoprotein- electrophotesis. A brief review of related literatures was done. -
- Quantitative Determination of Lipids in Breast Milk of Korean Woman.
- Sang Kie Kim, Chang Soo Ra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1986;29(7):765-772. Published online July 31, 1986
-
Human milk fat is the main energy sourse of the newborn infant. In addition to providing 50% of the total calories in Human milk, fats are essential to normal development because they provide fatty acids necessary for brain development are an integral part of all cell menbrance and are the sole vehicle for fat soluble Vitamin and Hormones in milk mature Human milk has... -
- A study on Serum Vitamin E and HDL-Cholesterol Level in Mother and Newborn.
- Jae Keun Yoon, Chul Wun Park, Hye Jin Suh, Im Ju Kang, Chung Chul Kim, Tae Ho Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(1):25-32. Published online January 31, 1984
-
A significant redistribution of cholesterol in lipoproteins following ingestion of large doses of vitamin E is documented. Especially vitamin E has been reported to increase serum high density lipoprotein(HDL) cholesterol. The inverse relationship between HDL-cholesterol and risk of develoing coronary disease was well known. Present study was undertaken to determine whether the corelation between vitamin E and HDL-cholesterol was significant in... -
- Lipoprotein Profiles in Minimal Change Nephrotic Syndrome.
- Yong Choi, Heui Jeen Kim, Hae Il Cheong, Jeong Kee Seo, Kwang Wook Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(3):237-246. Published online March 31, 1983
-
Data obtained from 59 hospitalized patients with minimal change nephrotic syndrome which was confirmed by kidney biopsy, were analyzed for serum albumin, serum lipids, 24hr urine protein, creatinine clearanee, HDL-eholesterol. In 38 of the patients, lipoproteins were analyzed. The following results were obained 1. Serum phospolipid (PL) was increased whenever serum total cholesterol (TC) was increased but to a lesser degree. The ratio of TC/PL were... -
- Studies on Total Cholesterol Level in Cerebrospinal Fluids of Tuberculous and Purulent Meningitis in Children.
- Son Sang See, Jong Woo Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1981;24(11):1057-1065. Published online November 15, 1981
-
The variations of total cholesterol level of the cerebrospinal fluids were investigated in 28 cases of meningeal diseases in children(15cases of tuberculous meningitis and 13cases of purulent meningitis) and 10 cases of healthy children as control. 1. The cholesterol was not detectable in the cerebrospinal fluids of the healthy children. 2. On admission, the stage II of tuberculous meningitis showed... -
- A study of Serum Triglyceride and Cholesterol in Korean Mothers and New born Infants.
- Sang Kee Park, Chang Soo Ra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1981;24(11):1028-1038. Published online November 15, 1981
-
-
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









