|
Question: Human milk has stronger antiviral, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties compared with formula milk. How dose breastfeeding affect respiratory syncytial virus infection in Korea?
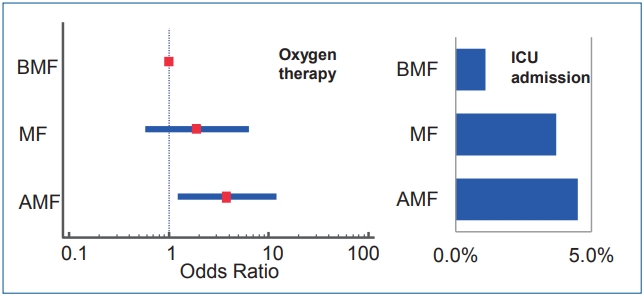
Finding: Breastfed infants required less oxygen therapy and possible intensive care unit admission than artificial formulafed infants during respiratory syncytial virus infection.
Meaning: This protective role of breast milk on RSV severity can be a supporting evidence for promoting breastfeeding in Korea. |


