Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Implication of microRNA as a potential biomarker of myocarditis
- Jin-Hee Oh, Gi Beom Kim, Heeyoung Seok
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):230-238. Published online March 2, 2022
-
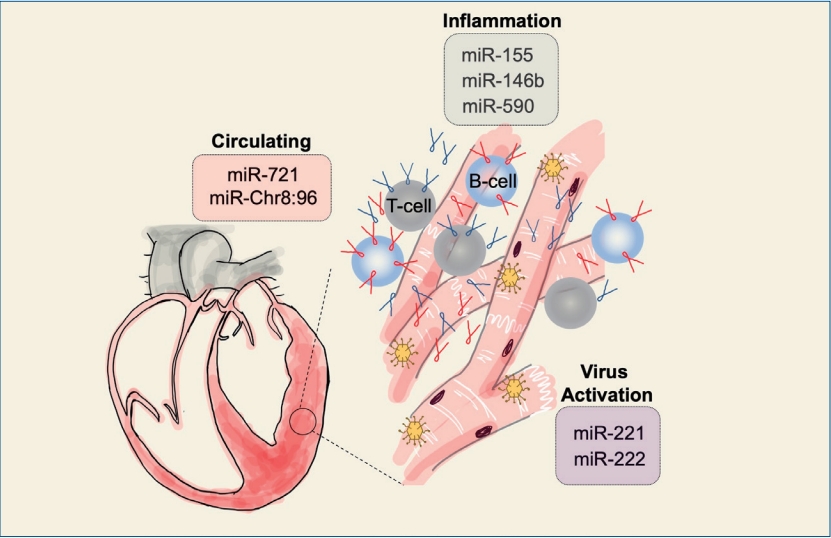
· Myocarditis was recently examined quantitatively as inflammation of the heart muscle based on endomyocardial biopsy, and its noninvasive diagnosis remains unsatisfactory.
· Additionally, numerous miRNAs (miR-155, miR-146b, miR-590, miR-221, miR-222, etc.) coupled with inflammation or viral activation have been examined in myocarditis patients or mouse models.
· The recent identification of mmu-miR-721 (has-miR-Chr8: 96), a myocarditis-specific microRNA, demonstrated its potential as an acute myocarditis biomarker.
- Critical Care Medicine
- The use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in children with acute fulminant myocarditis
- Silver Heinsar, Sainath Raman, Jacky Y. Suen, Hwa Jin Cho, John F. Fraser
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(5):188-195. Published online August 10, 2020
-
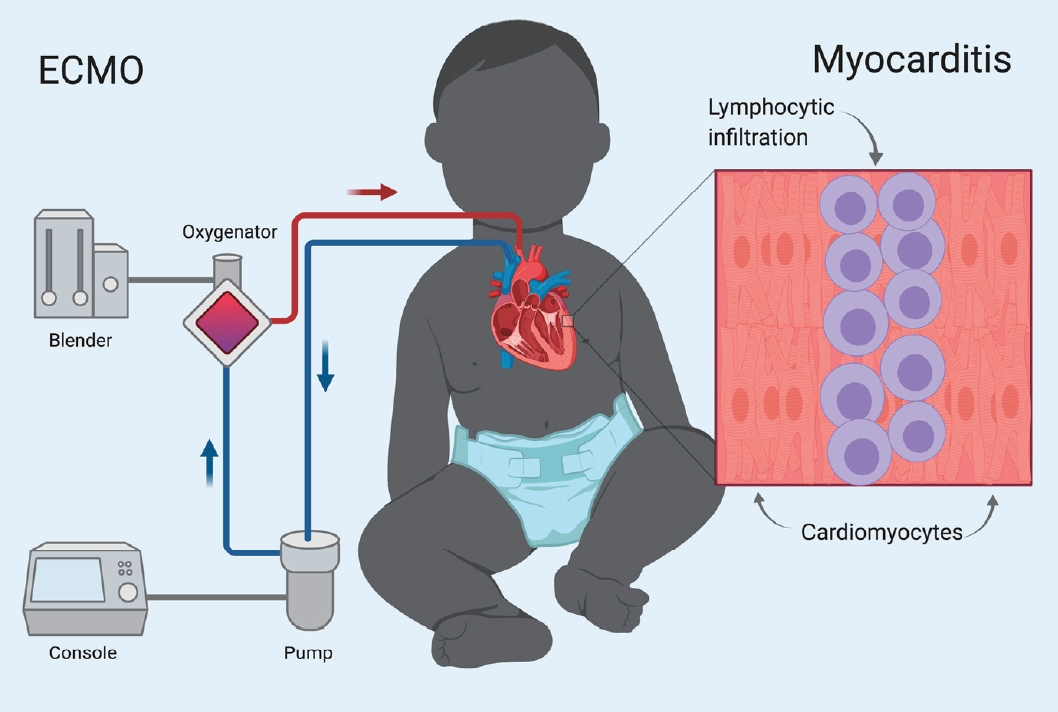
Acute fulminant myocarditis (AFM) occurs as an inflammatory response to an initial myocardial insult. Its rapid and deadly progression calls for prompt diagnosis with aggressive treatment measures. The demonstration of its excellent recovery potential has led to increasing use of mechanical circulatory support, especially extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Arrhythmias, organ failure, elevated cardiac biomarkers, and decreased ventricular function at presentation...
- Case Report
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Successfully treated infective endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus Aureus in extremely low birth weight infant - Sehwa Jung, Kyung Uk Jeong, Jang Hoon Lee, Jo Won Jung, Moon Sung Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(2):96-99. Published online February 29, 2016
-
Survival rates of preterm infants have improved in the past few decades, and central venous catheters play an important role in the intensive medical treatment of these neonates. Unfortunately, these indwelling catheters increase the risk of intracardiac thrombosis, and they provide a nidus for microorganisms during the course of septicemia. Herein, we report a case of persistent bacteremia due to...
- The first pediatric case of tularemia in Korea: manifested with pneumonia and possible infective endocarditis
- Jung Sook Yeom, Kyuyol Rhie, Ji Sook Park, Ji-Hyun Seo, Eun Sil Park, Jae-Young Lim, Chan-Hoo Park, Hyang-Ok Woo, Hee-Shang Youn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(10):398-401. Published online October 21, 2015
-
Tularemia is a potentially severe zoonotic disease caused by
Francisella tularensis . A lack of awareness about tularemia can be embarrassing and could result in delayed treatment because of improper diagnosis. The diagnosis of tularemia is difficult, because the infections are rare and the clinical spectrum is broad. As only 1 adult case has been reported in Korea thus far, pediatricians...
- Original Article
- Clinical features and short-term outcomes of pediatric acute fulminant myocarditis in a single center
- Eun Young Lee, Hae Lyoung Lee, Hyung Tae Kim, Hyoung Doo Lee, Ji Ae Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(11):489-495. Published online November 30, 2014
-
Purpose The aims of this study were to document our single-center experience with pediatric acute fulminant myocarditis (AFM) and to investigate its clinical features and short-term outcomes.
Methods We performed a retrospective chart review of all children <18 years old who were diagnosed with AFM between October 2008 and February 2013. Data about patient demographics, initial symptoms, investigation results, management, and outcomes between...
- Log-transformed plasma level of brain natriuretic peptide during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease is quantitatively associated with myocardial dysfunction
- Sunhee Bang, Jeong Jin Yu, Myung-Ki Han, Hong Ki Ko, Sail Chun, Hyung Soon Choi, Young-Hwue Kim, Jae-Kon Ko, In-Sook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(8):340-344. Published online August 31, 2011
-
Purpose Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) has been considered a biochemical marker for myocarditis in Kawasaki disease. We performed this study to determine its quantitative significance.
Methods We attempted to correlate log-transformed BNP concentrations (log-BNP) and clinical, laboratory, and echocardiographic variables in 81 children with Kawasaki disease. Stepwise multiple linear regression analysis was used to determine the variables independently associated with log-BNP concentration.
Results Serum C-reactive...
- Clinical outcome of acute myocarditis in children according to treatment modalities
- Hyun Jung Kim, Gyeong-Hee Yoo, Hong Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(7):745-752. Published online July 31, 2010
-
Purpose There is currently little evidence to support intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) therapy for pediatric myocarditis. The purpose of our retrospective study was to assess the effects of IVIG therapy in patients with presumed myocarditis on survival and recovery of ventricular function and to determine the factors associated with its poor outcome.
Methods We reviewed all consecutive cases of patients with myocarditis with...
- Review Article
- The myocarditis and cardiomyopathy in children
- Hong Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(11):1049-1054. Published online November 15, 2007
-
Myocarditis represent an important condition encountered by general pediatricians & general practitioners. Its presentation is varied, and therefore a high index of suspicion must be maintained when the possibility of myocarditis is raised. A progression from viral myocarditis to dilated cardiomyopathy has long been hypothesized. Treatment is initially aimed at achieving hemodynamic stability and is largely supportive. There is currently... -
- Case Report
- Surgical removal of a left ventricular thrombus caused by acute myocarditis
- Kyu Ha Lee, Min Jung Yoon, Mi Young Han, Sa Jun Chung, Soo Cheol Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(6):588-591. Published online June 15, 2007
-
Left ventricular thrombus is mainly caused by anterior myocardial infarction or severe cardiac wall dysfunction of the apex, and is rarely caused by a complication of acute myocarditis. A 12-year-old female who developed symptoms of motor dysphasia and incomplete hemiparesis of the right side was admitted to the hospital. The brain MRI taken on the day of her admission showed... -
- A case of constrictive pericarditis presenting with protein-losing enteropathy
- Jeong Mi Hong, Jae Young Lee, Soo Jin Kim, Gi Young Jang, Woo Sup Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(8):898-901. Published online August 15, 2006
-
Constrictive pericarditis represents a rare cause of protein-losing enteropathy in children. Reported is an 11-year-old girl with protein-losing enteropathy (PLE) as the principal manifestations of constrictive pericarditis. After total pericardiectomy, symptoms and signs of PLE disappeared. Doppler echocardiography including tissue Doppler imaging is a useful noninvasive initial diagnostic tool for differential diagnosis of diastolic heart failure. -
- Original Article
- The Clinical Significance of Soluble Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1(sICAM-1) and Soluble Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1(sVCAM-1) in Kawasaki Disease
- Kang Won Rhee, Sin Weon Yun, Dong Keun Lee, Eung Sang Choi, Byung Hoon Yoo, Mi Kyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(6):640-648. Published online June 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Kawasaki disease(KD) is known as an acute multi-systemic vasculitis with various immunologic abnormalities. Adhesion of leukocyte to endothelial cells is a key event in the sequence of inflammatory response. This study was performed to investigate the clinical significance of serum soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1(sICAM-1) and soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (sVCAM-1) in acute and subacute stages of typical... -
- A Clinical Study of Infective Endocarditis in Childhood
- Eun Na Choi, Jae Hun Kwon, Kyong Min Choi, Hwan Dae Hwang, Kyoung Mi Sin, Jae Young Choi, Jun Hee Sul, Dong Su Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(8):844-850. Published online August 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Advances in the treatment of congenital heart disease and a decline in the incidence of rheumatic fever has led to changes in the causative organisms and the clinical outcome of infective endocarditis(IE). We sought to analyze the clinical outcome, prognostic factors, causative organisms and corresponding antibiotic sensitivity in IE. Methods : Retrospective analysis of medical records of 104 children... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Streptococcal Toxic Shock Like Syndrome with Pleural Effusion
- Jinyoung Song, Keunha Ji, Heeseuk Kim, Jungwoo Rhoo, Dongwook Kim, Jongkook Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(2):200-204. Published online February 15, 2001
-
Streptococcal toxic shock like syndrome is a rapidly progressive and a fatal disease like staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome. In spite of the wide expansion and development of potent antibiotics, streptococcal infection still threatens human being. Recently we experienced a patient with toxic shock like syndrome who was suffered from fever and neck pain with rapid progression to hypotension and multiorgan... -
- A Case of Constrictive Pericarditis with Purulent Effusion in an Infant
- Kyoung Hee Kim, Yoon Ki Kang, Min Ho Kim, Chan Uhng Joo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(9):1279-1284. Published online September 15, 2000
-
Constrictive pericarditis is a rare disease of infancy and childhood, and is almost always caused by a tuberculosis or other infection. It is usually fatal, if untreated in acute phase. Early diagnosis of this condition is now facilitated by echocardiography and computerized tomography. Favorable outcome seems to depend on early diagnosis assured by echocardiography, early surgical treatment such as pericardiocentesis... -
- A Case of Candida Endocarditis with Vegetation on the Tricuspid Valve in a Preterm Infant
- Hye Young Han, Mi Jin Jung, Kwang Hoon Lee, Gil Hyun Kim, Hak Soo Lee, Guk Yang Park, Young Ha Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(6):832-836. Published online June 15, 2000
-
Fungal endocarditis is a rare disease in infants, but it has been reported with increasing frequency among premature infants requiring neonatal intensive care. Congenital heart disease, prolonged intravenous catheterization, the use of intravenous alimentation, broad-spectrum antibiotics administration and narcotic addiction are risk factors. Candida endocarditis is an unusual but severe complication of systemic candidiasis. Its occurrence has been related to... -
- Original Article
- Infective Endocarditis in Children : Review of 35 Cases over 11 Years(1987-1997)
- Jeong Jin Yu, Young Ho Kwak, Jung-Youn Hong, He Sun Jung, Jin Young Song, Hoan Jong Lee, Chung Il Noh, Jung Yun Choi, Yong Soo Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(4):526-534. Published online April 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Infective endocarditis(IE) is a serious complication in children with structural heart disease. We reviewed 35 cases of IE to identify the recent changes in the pattern of preexisting heart diseases, the spectrum of causative organisms and prognosis. Methods : The clinical records of children diagnosed as IE at the Seoul National University Children`s Hospital from January 1987 through December... -
- Comparison Study between Immunohistochemical Staining and Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay in Metalloproteinases and Tissue inhibitor of Metalloproteinases in Virus induced Myocarditis
- Young Mi Hong, Seung Sook Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(11):1524-1534. Published online November 15, 1999
-
Purpose : Most tissue disruption of extracellular matrix is mediated by extracellular proteinases. Matrix metalloproteinases(MMP) and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases(TIMP) are associated with wound healing and repair. There has been no study done on MMP and TIMP in myocarditis. Methods : Coxsackie B virus(4,000 plaque forming unit) was injected into Balb/c mice by intraperitoneal injection. Histopathological finding was observed... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Superior Mesenteric Artery Aneurysm associated with Marfan Syndrome
- Ick Ho Sung, Sang Hee Kim, Min Seop Song, Chul Ho Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(7):984-988. Published online July 15, 1998
-
Superior mesenteric artery aneurysm is very rare complication of Marfan syndrome, especially in children. A 11 years old male patient was admitted to the hospital because of fluctuating high fever and diagnosed as infective endocarditis and Marfan syndrome. During antibiotics therapy, fever was slowly decreased but abdominal pain was developed and pulsatile abdominal mass was palpable in the midline of... -
- Original Article
- The Study of Serum Troponin I and CK-MB in the Acute Stage of Kawasaki Disease
- Minshik Kim, Yoonae Chun, Youngok Lee, Namji Cho, Kyungsook Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(5):695-700. Published online May 15, 1998
-
Purpose : The pathogensis and etiologic agents are still unknown but clinical studies suggest that Kawasaki disease(KD) is an autoimmune disease caused by infectious agents associated with the early development of acute myocarditis and coronary artery abnormalities. The study investigates serum troponin I(cTnI) and creatine kinase(CK)-MB in the acute stage of KD before diagnosis the use of intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) treatment... -
- Case Report
- An autopsy Case of Nonbacterial Thrombotic Endocarditis
- Sun Hee Huh, Hae Yong Lee, Won Kyu Choi, Mee Kyung Namgoong, Jong Soo Kim, Mee Yon Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(6):888-893. Published online June 15, 1993
-
We experienced a case of nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis in a 25-day-old male neonate, who was suffered from ASD, MR and congestive heart failure. He was died suddenly during recovery phase. The Post diagnosis was nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis. We report with a brief review and its related literatures. -
- Original Article
- The Collaborative Clinical Analysis of 985 Cases of Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Carditis in Children for 10 Years(1978~1987) in Korea.
- Sung Ho Cha, Sang Young Jeong, Du Bong Lee, Kyong Su Lee, Sang Bum Lee, Tae Chan Kwon, Young Chang Tockgo, Chang Sung Sohn, Keun Chan Sohn, Young Jin Hong, Chan Young Kim, Chang Yee Hong, Yong Soo Yun, Jung Yun Choi, Chang Hwi Kim, Chul Ho Kim, Tae Ju Hwang, Jae Suk Ma, Chan Uhul Joo, Kyoo Hwan Rhee, Hahng Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1989;32(12):1621-1631. Published online December 31, 1989
-
Acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic carditis were still important disease of the acquired heart disease in children and adults, in spite of improving socioeconomic status in Korea. Recently, many outbreaks of acute rheumatic fever have been reported in the papers from developed countries. We should be aware of such outbreaks of acute rheumatic fever and should pay attention to their treatment of the patients... -
- A Clinical Observation on Infective Endocarditis in Childhood.
- Kyung Ae Yoon, Hoan Jong Lee, Young Yull Koh, Jung Yun Choi, Yong Soo Yun, Chang Yee Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1989;32(1):11-19. Published online January 31, 1989
-
Fifty.Six cases with infective endocarditis who were admitted to Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Hospital from January 1979 to December 1986 were reviewed. All the cases were confirmed bγ clinical findings, blood culture and echocardiographic findings. The incidence of infective endocarditis was 0.25/ 1,000 admissions. Male to female ratio was 1.2:1. All the cases had heart defect that was congenital heart disease in... -
- Experimental Diphtheritic Myocarditis with Special Reference to Ultrastructural Changes.
- Hyo Seop Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1986;29(12):1295-1308. Published online December 31, 1986
-
Myocardiopathy following diphtheria infection is one of the most serious and fatal complications, but its nature of the lesion remained in controversy, and even ultrastructural understanding on the direct effect of diphtheria toxin has not been clarified. The purpose of this experiment is to illustrate the full morphological spectrum of subclinical or EKG free diphtheritic myocardial injuries by administration of... -
- Clicical Syudy on Cardiac Involvement in Rheumatic Heart Disease in Children.
- Sung Ho Cha, Myeong Yeon lee, Jong Woo Bae, Byeong Soo Cho, Chang Il Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1986;29(11):1215-1224. Published online November 30, 1986
-
A clinical study was carried out to obtained the cardiac manifestations and echocardiographic findings from 25 cases of rheumatic carditis, those were undertaken echocardiography among 52 cases of rheumatic carditis from January 1973 to June 1985, admitted to Pediatric department of Kyung Hee university hospital. And compared with age matched 14 cases of control group. The following results were obtained: 1)... -
- A Study on Echocardiographic Findings of Rheumatic Carditis.
- Yong Sub Kim, Chan Yung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1985;28(4):345-342. Published online April 30, 1985
-
A clinical study was done about echocardiographic findings of 31 cases of rheumatic carditis among 56 cases of rheumatic fever admitted to Pediatric Department of Busan National University Hospital from July, 1982 for 2 years. The following results were obtained: 1)The incidence of rheumatic carditis was 55.4% among rheumatic fever and the peak age was 12~13 years old and the... -
- Diagnostic and Clinical Implications of Echocardiography in Staphylococcal Endocarditis.
- Kyu Chul Choi, Hyo Sup Joo, Ook Jung Kang, Kyoo Hwan Rhee, Chang Il Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(1):43-49. Published online January 31, 1984
-
We experienced two cases of staphylococcal infective endocarditis. The echocardiograms showed vegetations at the posterior leaflet of mitral valve and pulmonary arterial end of PDA, respectively. The serial two-dimensional echocardiograms revealed the fate of these vegetations on prolonged antimicrobial therapy. Also we reviewed the literatures. -
- Case Report
- A Case of Stomach Perforation during the Therapy of Rheumatic Carditis.
- Young Ju Lee, Man Jin Chung, Soon Ok Byun, Myung Hi Shin, Ji Sub Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(12):1241-1246. Published online December 31, 1983
-
We experienced acute stomach perforation in a 10 years old boy who suffered from rheum- atic carditis and treated with penicillin, aspirin and prednisolone. A brief review of literature was done. -
- A Case of Pericarditis as a Complication of Meningococcal Meningitis.
- Moo Young Oh, Seung Won Park, In Soon Park, Chul Ho Kim, Soon Yong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(8):799-802. Published online August 31, 1983
-
We report a case of pericarditis as a complication of meningococcal meningitis in a 10-month old male infant. Pericardial effusion developed on the 8th hospital day during penicillin treatment for meningococcal meningitis. He was treated successfully and recovered completely. A review of related literatures was made. -
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









