Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Change of voltage-gated potassium channel 1.7 expressions in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension rat model
- Hyeryon Lee, Kwan Chang Kim, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(9):271-278. Published online September 15, 2018
-

Purpose: Abnormal potassium channels expression affects vessel function, including vascular tone and proliferation rate. Diverse potassium channels, including voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels, are involved in pathological changes of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Since the role of the Kv1.7 channel in PAH has not been previously studied, we investigated whether Kv1.7 channel expression changes in the lung tissue of a monocrotaline...
- Clinical implications in laboratory parameter values in acute Kawasaki disease for early diagnosis and proper treatment
- Yu-Mi Seo, Hyun-Mi Kang, Sung-Churl Lee, Jae-Won Yu, Hong-Ryang Kil, Jung-Woo Rhim, Ji-Whan Han, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(5):160-166. Published online May 28, 2018
-
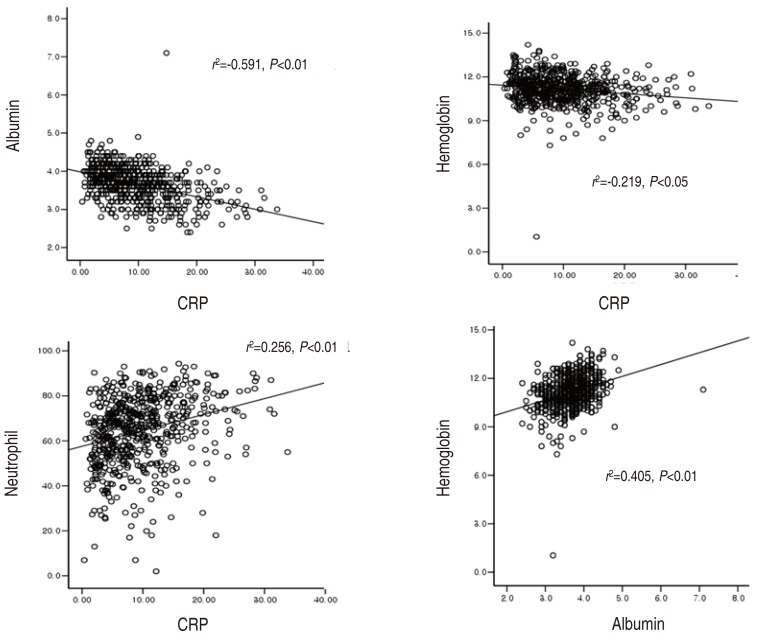
Purpose This study aimed to analyse laboratory values according to fever duration, and evaluate the relationship across these values during the acute phase of Kawasaki disease (KD) to aid in the early diagnosis for early-presenting KD and incomplete KD patients.
Methods Clinical and laboratory data of patients with KD (n=615) were evaluated according to duration of fever at presentation, and were compared between...
- C-reactive protein and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide discrepancy: a differentiation of adenoviral pharyngoconjunctival fever from Kawasaki disease
- Jung Eun Choi, Hee Won Kang, Young Mi Hong, Sejung Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(1):12-16. Published online January 22, 2018
-
Purpose To differentiate adenoviral pharyngoconjunctival fever (PCF) from acute Kawasaki disease (KD) using laboratory tests before results of virus-real time polymerase chain reaction and ophthalmologic examination are obtained.
Methods Baseline patient characteristics and laboratory measurements were compared between 40 patients with adenovirus infection and 123 patients with KD.
Results The patients with adenovirus infection were generally older than those with KD (median: 3.9 years vs....
- Pulmonology
- Clinical predictors of chest radiographic abnormalities in young children hospitalized with bronchiolitis: a single center study
- Ga Ram Kim, Min Sun Na, Kyung Suk Baek, Seung Jin Lee, Kyung Suk Lee, Young Ho Jung, Hye Mi Jee, Tae Hee Kwon, Man Yong Han, Youn Ho Sheen
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(12):471-476. Published online December 31, 2016
-
Purpose Chest radiography is often performed on patients hospitalized with typical clinical manifestations of bronchiolitis. We aimed to determine the proportion of subjects with pathologic chest radiographic findings and the clinical predictors associated with pathologic chest radiographic findings in young children admitted with the typical presentation of bronchiolitis.
Methods We obtained the following data at admission: sex, age, neonatal history, past history of...
- Gastroenterology
- Diagnostic value of the Vesikari Scoring System for predicting the viral or bacterial pathogens in pediatric gastroenteritis
- Dong Ho Shim, Dong Yeon Kim, Ky Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(3):126-131. Published online March 31, 2016
-
Purpose To evaluate the diagnostic value of the Vesikari Scoring System (VSS) as an early predictor of pathogens in children with acute gastroenteritis (AG).
Methods In this retrospective study, the VSS score, absolute neutrophil count (ANC), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were analyzed in 107 hospitalized children with AG, aged 6 months to 17 years. Patients were divided into nonspecific, viral, and bacterial...
- Serum procalcitonin as a diagnostic marker of neonatal sepsis
- In Ho Park, Seung Hyun Lee, Seung Taek Yu, Yeon Kyun Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(10):451-456. Published online October 31, 2014
-
Purpose We evaluated serum procalcitonin (PCT) as a diagnostic marker of neonatal sepsis, and compared PCT levels with C-reactive protein (CRP) levels.
Methods We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 269 neonates with a suspected infection, admitted to Wonkwang University School of Medicine & Hospital between January 2011 and December 2012, for whom PCT and CRP values had been obtained. Neonates were categorized...
- Predictive value of C-reactive protein in response to macrolides in children with macrolide-resistant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia - Young Ho Seo, Jang Su Kim, Sung Chul Seo, Won Hee Seo, Young Yoo, Dae Jin Song, Ji Tae Choung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(4):186-192. Published online April 30, 2014
-
Purpose The prevalence of macrolide-resistant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MRMP) has increased worldwide. The aim of this study was to estimate the proportion of MRMP in a tertiary hospital in Korea, and to find potential laboratory markers that could be used to predict the efficacy of macrolides in children with MRMP pneumonia.Methods A total of 95 patients with
M. pneumoniae pneumonia were enrolled in...
- Review Article
- Oxidative stress and the antioxidant enzyme system in the developing brain
- So-Yeon Shim, Han-Suk Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(3):107-111. Published online March 18, 2013
-
Preterm infants are vulnerable to the oxidative stress due to the production of large amounts of free radicals, antioxidant system insufficiency, and immature oligodendroglial cells. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a pivotal role in the development of periventricular leukomalacia. The three most common ROS are superoxide (O2•-), hydroxyl radical (OH•), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Under normal physiological conditions, a balance...
- Original Article
- Comparison of the accuracy of neutrophil CD64 and C-reactive protein as a single test for the early detection of neonatal sepsis
- Young Kwang Choo, Hyun-Seok Cho, In Bum Seo, Hyeon-Soo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(1):11-17. Published online January 31, 2012
-
Purpose Early identification of neonatal sepsis is a global issue because of limitations in diagnostic procedures. The objective of this study was to compare the diagnostic accuracy of neutrophil CD64 and C-reactive protein (CRP) as a single test for the early detection of neonatal sepsis.
Methods A prospective study enrolled newborns with documented sepsis (n=11), clinical sepsis (n=12) and control newborns (n=14). CRP,...
- Case Report
- A case of reactive arthritis after
Salmonella enteritis in in a 12-year-old boy - Peter Chun, Young Jin Kim, Young Mi Han, Young Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(7):313-315. Published online July 31, 2011
-
Reactive arthritis comprises a subgroup within infection-associated arthritides in genetically susceptible hosts. Researchers and clinicians recognize two clinical forms of reactive arthritis which occurs after genitourinary tract infection and after gastrointestinal tract infection. Chlamydia infection has been implicated as the most common agent associated with post-venereal reactive arthritis. Studies have proposed Shigella infection,
Salmonella infection, orYersinia infection as the...
- Original Article
- Influence of histologic chorioamnionitis and funisitis on the level of peripheral blood C-reactive protein at birth in preterm infants
- Do-Hyun Kim, Heun Ji Lee, Hee Sup Kim, Byoung Hoon Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(1):33-40. Published online January 15, 2010
-
Purpose : The objective of this study is to determine the change of C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in the peripheral blood of preterm infants at birth according to the stage of intrauterine inflammation. Methods : A total of 187 infants (<32 weeks of gestation) were divided into a “no histologic chorioamnionitis” [HCAM (-), n=85] group and a “histologic chorioamnionitis” [HCAM... -
- Outcome and risk factors of pediatric hemato-oncology patients admitted in pediatric intensive care unit
- Bo Eun Kim, Eun Ju Ha, Keun Wook Bae, Seongguk Kim, Ho Joon Im, Jong Jin Seo, Seong Jong Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(10):1153-1160. Published online October 15, 2009
-
Purpose : To evaluate the risk factors for mortality and prognostic factors in pediatric hemato-oncology patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU). Methods : We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of pediatric hemato-oncology patients admitted at the PICU of the Asan Medical Center between September 2005 and July 2008. Patients admitted at the PICU for perioperative or terminal... -
- Diagnostic value of various screening tests in neonatal sepsis
- Hyun Gon Je, Young Mi Jeoung, Soo Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(11):1167-1173. Published online November 15, 2006
-
Purpose : To evaluate various sepsis screening tests, individually and in combination, to formulate a guideline for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Methods : The study was a retrospective cohort study. It took place at the neonatal intensive care unit of the Paediatric Department, Il Sin Christian Hospital, Busan, Korea, over a period of 68 months from 1st, April, 2001 to... -
- Prediction of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Non-responders in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
- Gi Bum Lee, Ji-Won Lee, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(1):90-94. Published online January 15, 2004
-
Purpose : We evaluated the effects of intravenous immunoglobulin(IVIG) on the levels of laboratory indices examined serially according to the responsiveness to IVIG therapy in children with Kawasaki disease(KD). Methods : Children with KD(n=63) who had been treated with IVIG at a dosage of 2.0 g/kg were classified into two groups : the IVIG-resistant(consistent fever over 48 hours after initiation... -
- Clinical Significance of C-reactive Protein in Measles
- Sang-Lim Choi, Kyung-Yil Lee, Hyung-Shin Lee, Ja-Hyun Hong, Kyung-Tai Whang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(5):480-483. Published online May 15, 2003
-
Purpose : We evaluated clinical manifestations and laboratory findings in patients with measles according to C-reactive protein(CRP) concentration. Methods : A retrospective analysis was performed using the medical records of patients with measles at The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital from October 1999 to May 2000. We divided the patients with measles into four groups according to CRP... -
- C-Reactive Protein and Duration of Antibiotic Therapy in Neonatal Bacterial Infection
- Jae Il Yoo, Jin Hwa Jeong, Jeong Ho Lee, Jong Dae Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(7):901-908. Published online July 15, 1998
-
Purpose : To determine whether C-reactive protein(CRP) can be used as a parameter to assess the safety of discontinuing antibiotic therapy and allows a shorter course of therapy in neonates treated for suspected bacterial infection. Methods : We have experienced 193 cases of suspected neonatal bacterial infection at Pusan Maryknoll Hospital. CRP levels were measured daily by immunonephelometry. Infants with initial... -
- Plasma Fibronectin Concentration in the Premature,Fullterm Neonates and Infants
- Hyun Joo Lee, Kyung Hyo Kim, Gyoung Hee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(4):473-479. Published online April 15, 1997
-
Purpose : Plasma fibronectin has important role in the inflammatory response as non-specific opsonin and host defense. Plasma fibronectin concentration is different according to age and presence of infection. We performed this study to evalulate plasma fibronectin concentration in the healthy preterm, term neonates and infants and how that correlate with gestational age and birth weight and increased CRP concentration.... -
- Chronic Cough in Children
- Bin Cho, Joon Sung Lee, Kyung Tai Whang, Sung Hoon Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(8):1116-1123. Published online August 15, 1994
-
Chromic cough is a symptom frequently encountered by the pediatrician. Although most coughs are self-limited, chronic cough ofter proves to be a frustrating problem. This study was performed at Kangnam St. Mary's Hospital from January 1,1992 to December 31, 1992, and 83 children with chronic cough persisting for longer than 3 weeks was evaluated. We categorized these patients into 5... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Poststreptococcal Reactive Polyarthralgia
- Sung Ho Cha, Byong Soo Cho, Taekyu Hame
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(11):1635-1637. Published online November 15, 1993
-
Poststreptococcal reactive arthritis/arthralgia is characterized as an evidence of group A beta hemolytic streptococcal infection and does not fulfill the modified Jones criteria for a diagnosis of acute rheumatic fever. We had used to meet the patients with incomplete acute rheumatic fever who had more than 3 items of minor Jones criteria, or arthralgia or arthritis with one or two... -
- Original Article
- A Study of C-Reactive Protein in Acute Infectious Diseases in Children.
- H K Choi, Y H Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(6):762-771. Published online June 30, 1990
-
The C-reactive protein is an abnormal protein, which is reacted to various non-specific stmuli such as infection, tissue necrosis, trauma, neoplasm and granuloma formation. Hence, C-reactive protein was index of infection and its allied diseases. Serum C-reactive protein determination on total 207 patients with infectious disease and allied conditions were done in the pediatric ward of Chungnnam National Hospital during the period from Jan, 1988... -
- Serum C-Reactive Protein in Differential Diagnosis of Meningitis in Children.
- Hae Lim Chung, Hoan Jong Lee, Yong Seung Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1988;31(12):1588-1593. Published online December 31, 1988
-
CSF findings such as cell count, differential count, protein, glucose and serum CRP determined by capillary precipitin method evaluated in 90 patients of meningitis admitted to the pediatric ward of Seoul National University Children’s Hospital, in terms of differential diagnosis of meningitis. The results are as follows; 1) There was considerable overlap of CSF findings and hematQlogic values between bacterial, aseptic and tuberculous meningitis groups. 2) All 9... -
- Clinical Value of Urinary β₂ -Microglobulin in Patients with Urianry Tract Infection.
- Nak Uk Sung, Chang Ryul Kim, Jeh Hoon Shin, Woo Gill Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1987;30(9):1014-1020. Published online September 30, 1987
-
Urinary tract infection (UTI) in children is relatively common infectious disease and it may be the forerunner of severe renal diseases in adulthood. The site of infection is an important factor in the evaluation of the clinical course, treatment and prognosis of patients with UTI, because patients with bacteriuria of renal origin (pyelonephritis) are probably at risk of developing the renal parenchymal reduction seen... -
- Clinical Study of C-Reactive Protein in Neonatal Bacterial Infections.
- Kyung Shin Kim, Myung Sung Moon, Jin Choi, Keun Soo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(9):866-871. Published online September 30, 1983
-
Bacterial infections, such as sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia and urinary tract infection are frequent causes of death during neonatal period. Further more clinical symptoms of neonatal infections are often quite vague and the illnesses unexpectedly progress rapidly. The causative organisms are detected with difficulty in many instances. Therefore a quick, simple and.reliable laboratory test is obviously needed for easy recognization of neonatal bacterial... -
- Correlation between Body Temperature C-reactive Protein, Erythrocyte Sedimention Rate and Leukocytes in Infections of Infancy and Childhood.
- W H Choi, S H Kim, I K Paik, C M Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1981;24(5):451-458. Published online May 15, 1981
-
Body temperature and several laboratory tests including C-reactive protein, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, leukocyte count and the percentage of neurophil leukocytes were determined on total 372 cases(male:221, female:151) of infectious disease which were admitted to the pediatric department of presbyterian Medical Center, Daegu, Korea during the period of 1 year and 7 months from January 1978 to July 1979. Following results... -
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









