Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal sepsis-causing bacterial pathogens and outcome of trends of their antimicrobial susceptibility a 20-year period at a neonatal intensive care unit
- Woo Sun Song, Hye Won Park, Moon Youn Oh, Jae Young Jo, Chae Young Kim, Jung Ju Lee, Euiseok Jung, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):350-357. Published online December 9, 2021
-
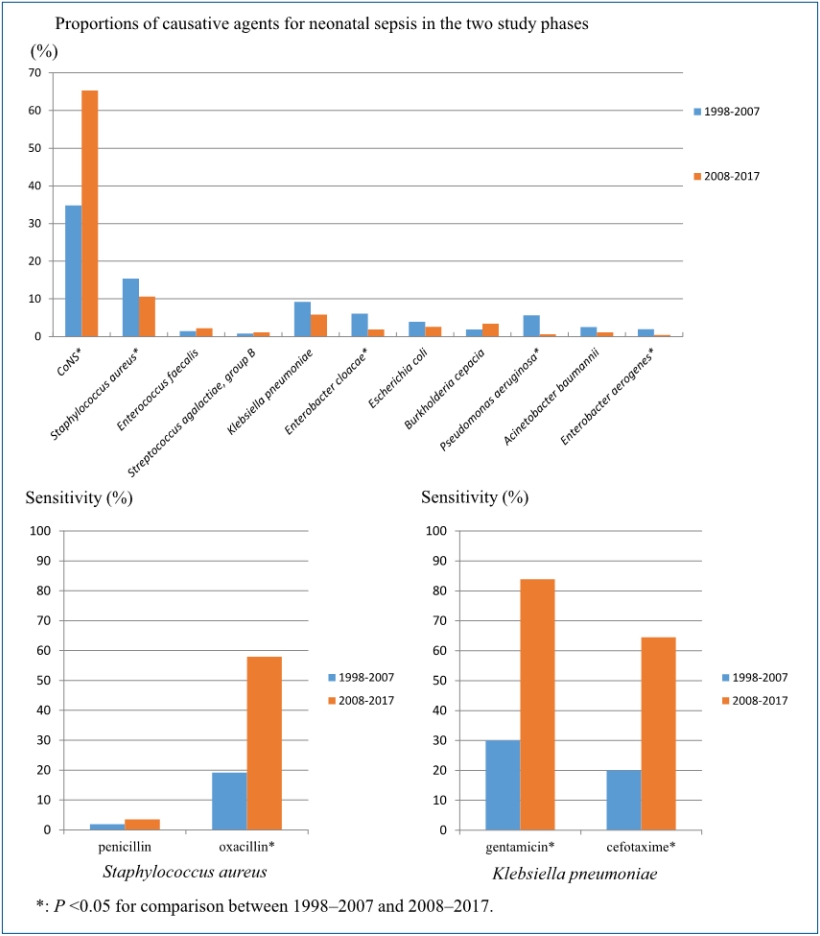
Question: What is prevalence of bacterial pathogens causing sepsis and their antimicrobial susceptibility over 20 years?
Finding: Coagulase-negative remains most common causative organism. The most common gram-negative organism was Klebsiella pneumonia. The susceptibility of staphylococcus aureus and K. pneumonia showed increased susceptability to oxacillin, cefotaxime and amikacin, gentamicin, respectively.
Meaning: Answers to the question asked is important in choosing antimicrobials and to monitor emergence of multidrug-resistant organisms.
- Case Report
- Necrotizing fasciitis and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome secondary to varicella in a healthy child
- Byung Ok Kwak, Min Jung Lee, Hye Won Park, Min Kyung Song, Sochung Chung, Kyo Sun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(12):538-541. Published online December 31, 2014
-
Varicella is usually considered to be a benign disease in healthy children; however, serious complications can occur such as necrotizing fasciitis and toxic shock syndrome. We describe a 38-month-old girl with necrotizing fasciitis and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome following varicella. She was previously healthy and vaccinated against varicella at 12 months of age. She had been diagnosed with varicella three...
- Original Article
- Kidney size estimation in Korean children with Technesium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid scintigraphy
- Min Jung Lee, Mi Kyung Son, Byung Ok Kwak, Hye Won Park, Sochung Chung, Kyo Sun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(1):41-45. Published online January 31, 2014
-
Purpose Renal size is an important indicator to determine adequate organ growth in children. The aim of this study was to estimate renal size with Technesium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scan and propose a simple formula for predicting renal length in normal Korean children.
Methods This study included 346 children (148 boys and 198 girls; age range, 1 month to 17 years) in whom...
- Case Report
- Hypokalemic periodic paralysis; two different genes responsible for similar clinical manifestations
- Hunmin Kim, Hee Hwang, Hae Il Cheong, Hye Won Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(11):473-476. Published online November 30, 2011
-
Primary hypokalemic periodic paralysis (HOKPP) is an autosomal dominant disorder manifesting as recurrent periodic flaccid paralysis and concomitant hypokalemia. HOKPP is divided into type 1 and type 2 based on the causative gene. Although 2 different ion channels have been identified as the molecular genetic cause of HOKPP, the clinical manifestations between the 2 groups are similar. We report the...
- Original Article
- The clinical manifestations, the short- and long-term outcomes of Bartter syndrome
- Hye Won Park, Joo Hoon Lee, Young Seo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(12):1231-1240. Published online December 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Bartter syndrome is a renal tubular defect in electrolyte transport characterized by hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis and other clinical signs and symptoms. The aims of this study were to analyze the clinical manifestations and the short- and long-term outcomes of Bartter syndrome. Methods : We retrospectively reviewed clinical history, laboratory finding of blood and urine, renal ultrasonography, and hearing... -
- Review Article
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome
- Hye Won Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(10):931-937. Published online October 15, 2007
-
The hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a rare disease of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, low platelet count and renal impairment. HUS usually occurs in young children after hemorrhagic colitis by shigatoxin-producing enterohemorrhagic E. coli (D+HUS). HUS is the most common cause of acute renal failure in infants and young children, and is a substantial cause of acute mortality and morbidity; however,... -
- Original Article
- Reference values for respiratory system impedance using impulse oscillometry in school-aged children in Korea
- Young Sun Wee, Hyoung Yun Kim, Da Wun Jung, Hye Won Park, Yoon Ho Shin, Man Yong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(9):862-867. Published online September 15, 2007
-
Purpose : The impulse oscillometry (IOS) is applicable to young children because it requires minimal cooperation and a non-invasive method to measure the mechanics of respiratory system. This study aimed to develop the reference values in school-aged children in Korea, using IOS which is a modification of forced oscillation technique (FOT). Methods : Measurements were performed in 92 previously untrained healthy... -
- The Prevalence of A985G Mutation in Medium Chain Acyl-Coenzyme A Dehydrogenase(MCAD) Gene in Neonates Determined from Guthrie Card
- Baeck Hee Lee, Hye Won Park, Moon Soo Park, Ho Jin Park, Yong Choi, Hae Il Cheong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(12):1645-1650. Published online December 15, 1997
-
Purpose : Medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase(MCAD) deficiency is an autosomal recessive disoder of β oxidation of fatty acids and characterized by episodic hypoglycemia, vomiting, convulsion, encephalopathy, apnea, and sudden death related to fasting or infection resembling Reye syndrome or sudden infant death syndrome. In acute stage, mortality rate is very high and survivors have significant risk of developmental disability and chronic somatic illness. However,... -
- Case Report
- A Pediatric Case of MELAS Syndrome Associated with Insulin-dependent Diabetes Mellitus
- Kyung Ran Park, Hye Won Park, Tae Sung Ko, Hae Il Cheong, Sei Won Yang, Young Seung Hwang, In Won Kim, Je Geun Chi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1996;39(10):1461-1465. Published online October 15, 1996
-
MELAS(mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and sroke like episodes) is a major subgroup of heterogeneous mitochondrial encephalopathy. Recent advances in molecular genetics revealed specific mutations in the mitochondrial DNA causing MELAS. We described clinical and molecular genetic findings of a 13-year-old boy with MELAS syndrome associated IDDM(insulin dependent diabetes mellitus). For molecular genetic studies, DNAs from peripheral blood nucleated cells were used. And the A→G... -
- Original Article
- Primary Distal Renal Tubular Acidosis in Children
- Byoung Chul Kang, Hye Won Park, Il Soo Ha, Hae Il Cheong, Yong Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1996;39(7):987-996. Published online July 15, 1996
-
Purpose : This study was designed to examine the clinical characteristics and the effect of treatment in children with primary distal renal tubular acidosis (dRTA). Methods : Medical records of 4 children diagnosed as dRTA at Seoul National University Children's Hospital were reviewed, and the clinical manifestations, laboratory findings, diagnostic criteria and effects of treatments were investigated. Results : All cases presented with growth retardation.... -
- Normal Values for Neonatal Periumbilical Skin Length
- Young Pyo Chang, Hyung Suk Lim, Hye Won Park, Woong Huem Kim, Hee Ju Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(7):924-927. Published online July 15, 1994
-
Malformations of umbilicus are feature of many dysmorphic syndromes and the measurement of periumbilical skin length should be considered as the basic step in the description of the umbilical malformations. So, we measured the periumbilical skin length in the 103 normal neonates and obtained the following results. 1) The means(+SD) of the periumbilical skin length were the 11.7mm(+3.0)in the cranial site... -
- A Clinical Observation on Lupus Nephritis in Children
- Kang Mo Ahn, Jae Sung Ko, Hye Won Park, Il Soo Ha, Hae Il Cheong, Yong Choi, Hee Joo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(6):842-849. Published online June 15, 1994
-
We reviewed the clinical features, histrologic patterns and clinical courses of 30 children with lupus nephritis retrospectively, and the results were summerized as follows; 1) The male to female ratio was 1:2.8, and the mean age at the onset was 108/12 years. 2) The clinical symptoms were diverse, and malaise, weight loss, anorexia, fever and malar rash were the most frequent findings. 3)... -
- Nephrotic Syndrome under 2 Years of Age
- Jae Sung Ko, Kang Mo Ahn, Hye Won Park, Il Soo Ha, Hae Il Cheong, Yong Choi, Kwang Wook Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(10):1395-1401. Published online October 15, 1993
-
There had been total 20 patients with early onset (4 months~2 years) primary nephrotic syndrome in the Deparment of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, during the period from March 1987 to February 1993. We analysed clinical courses, response to treatment, pathological findings and prognosis of the patients And the results were as follows; 1) The initial responders to steroid treatment... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Chronic Intestinal Pseudo-obstruction Syndrome
- Hye Won Park, Chul Ho Chang, Bum Soo Park, Jeong Kee Seo, Sung Hye Park, Je Geun Chi, Kyung Mo Yeon, Kui Won Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(10):1427-1434. Published online October 15, 1992
-
Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction is a clinical condition in which impaired intestinal propulsion causes recurrent symptoms of bowel obstruction in the absence of mechanical occlusion. In this paper a female neonate was presented with vomiting and abdominal distension in the first few days of life but passed normal meconium. Barium enema showed a microcolon and an abnormaly sited cecum. Malrotation of bowel... -
- Original Article
- A Clinical Aspect of the Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Hye Won Park, Tae Sun Ha, Il Soo Ha, Hae Il Cheong, Yong Choi, Kwang Wook Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(7):909-920. Published online July 15, 1992
-
We reviewed the medical records of 14 children (8 girls, 6 boys), diagnosed as hemolytic uremic syndrome at Seoul National University Children뭩 Hospital from 1981 to 1990. The age at presentation ranged from 1 month to 10 years, with a mean age of 2.7 years. Only eight (57.1%) of the children had diarrheal prodrome and five (35.7%) had grossly bloody... -
- A comparison between remission and nonremission groups of hepatitis B virus-associated membranous nephropathy in children.
- Kang Yong Park, Hye Won Park, Yon Ho Choe, Tae Sun Ha, Il Soo Ha, Yong Choi, Kwang Wook Ko, Hyun Soon Lee, Yong Il Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(11):1512-1518. Published online November 30, 1991
-
We analyzed medical records of 35 patients with Hepatitis B virus-associated Membranous Nephropathy proven by kidney biopsy at SNUCH from Jan. 1975 to Jun. 1990. Clinical presentation, laboratory and pathologic findings were compared between remission group (who are free of proteinuria and edema in current status) and nonremission group (who have either proteinuria or edema). Age at onset was younger in remission group (4.51 ±2.93... -
- A clinical study of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis in childhood.
- Tae Sun Ha, Hye Won Park, Ja Wook Koo, In Seok Lim, Hae Il Cheong, Yong Choi, Kwang Wook Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(3):363-370. Published online March 31, 1991
-
A retrospective analysis of clinical with findings in 24 children continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) who were admitted to the Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital from March, 1987 till August, 1990 was performed and the results were as follows; 1) The male to female ratio was 16:8, and the age distribution at the beginning of CAPD was from 59 days to 16.5... -
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









