|
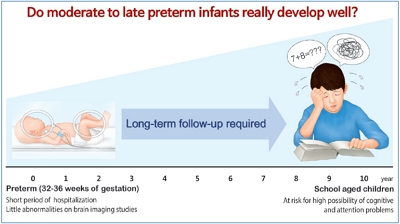
Question: Infants born at moderate to late preterm gestations are known to have little problem later on, but is that really true?
Finding: At school age, cognitive problem was observed in about a quarter of the children. In addition, more than half of the children was suspected of having attention problems.
Meaning: Moderate to late preterm infants are at risk of developing abnormal intelligence and attention problems at early school age, therefore they should not be neglected on longterm follow-up evaluation. |


