Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Risk factors for the occurrence and persistence of coronary aneurysms in Kawasaki disease
- Soo-kyeong Jeon, Geena Kim, Hoon Ko, Joung-Hee Byun, Hyoung Doo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(4):138-143. Published online November 22, 2018
-
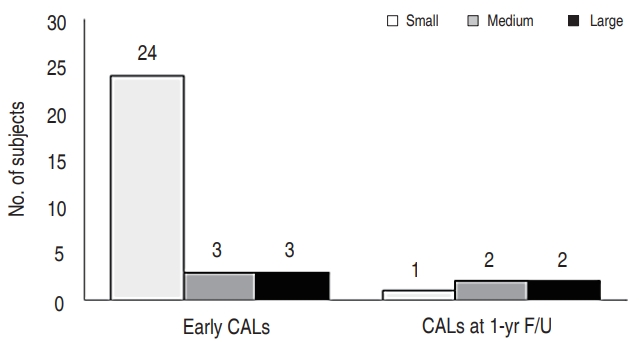
Purpose: Prognostic factors of coronary aneurysms in Kawasaki disease have been investigated in many studies. The aim of this study was to identify risk factors associated with early and late coronary artery outcomes in treated patients with Kawasaki disease. Methods: A total of 392 patients diagnosed with Kawasaki disease from January 2012 to December 2015 in Pusan National University Children’s Hospital...
- Case Report
- Giant coronary aneurysm caused by Kawasaki disease: consistency between catheter angiography and electrocardiogram gated dual-source computed tomography angiography
- Eun-Ha Hwang, Jung-Ki Ju, Min-Jung Cho, Ji-Won Lee, Hyoung-Doo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(12):501-504. Published online December 22, 2015
-
We present the case of a 5-year-old child with coronary complications due to Kawasaki disease; this patient unintentionally underwent both dual-source computed tomography (DSCT) coronary angiography and invasive coronary angiographic examination in 2 months. This case highlights the strong consistency of the results between DSCT coronary angiography and invasive coronary angiography. Compared to conventional invasive coronary angiography, DSCT coronary angiography...
- Percutaneous ultrasound-guided thrombin injection is effective even in infants with external iliac artery pseudoaneurysms
- Min-Jung Cho, Ung-Bae Jeon, Ki-Seok Choo, Hyoung-Doo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(4):199-201. Published online April 30, 2014
-
Iatrogenic pseudoaneurysms are extremely rare in children. Conventional management of pseudoaneurysms in adults has included surgical repair, ultrasound-guided compression, and more recently, endovascular embolization. However, in infants and children, there is little information regarding the applicability of such treatment modalities, which have been effective in adults, because of its rarity. Here, we present the case of a 6-month-old infant who...
- Original Article
- Detection rate and clinical impact of respiratory viruses in children with Kawasaki disease
- Ja Hye Kim, Jeong Jin Yu, Jina Lee, Mi-Na Kim, Hong Ki Ko, Hyung Soon Choi, Young-Hwue Kim, Jae-Kon Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(12):470-473. Published online December 20, 2012
-
Purpose The purpose of this prospective case-control study was to survey the detection rate of respiratory viruses in children with Kawasaki disease (KD) by using multiplex reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and to investigate the clinical implications of the prevalence of respiratory viruses during the acute phase of KD.
Methods RT-PCR assays were carried out to screen for the presence of respiratory syncytial...
- Epidemiology of Kawasaki disease in infants 3 months of age and younger
- Eun Jung Lee, Yong Won Park, Young Mi Hong, Joon Sung Lee, Ji Whan Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(6):202-205. Published online June 21, 2012
-
Purpose This study investigated the epidemiology of Kawasaki disease (KD) in infants ≤3-month-old.
Methods To study the epidemiology of KD in Korea, data for 27,851 KD patients were collected on a 3-year basis between 2000 and 2008 in a retrospective survey. From this, data for 609 KD patients ≤3-month-old were analyzed and compared with the data for KD patients >3-month-old.
Results The 609 KD patients...
- Case Report
- A sporadic case of Loeys-Dietz syndrome type I with two novel mutations of the
TGFBR2 gene - Jung Sook Ha, Yeo Hyang Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(6):272-275. Published online June 30, 2011
-
A recently recognized connective tissue disorder, Loeys-Dietz syndrome (LDS) is a genetic aortic aneurysm syndrome caused by mutations in the transforming growth factor-receptor type I or II gene (
TGFBR1 orTGFBR2 ). They have distinctive phenotypic abnormalities including widely spaced eyes (hypertelorism), bifid uvula or cleft palate, and arterial tortuosity with aortic aneurysm or dissection throughout the arterial tree. LDS is...
- Original Article
- Epidemiologic study of Kawasaki disease in 6 months old and younger infants
- Yong Won Park, Ji Whan Han, In Sook Park, Chang Hwi Kim, Sung Ho Cha, Jae Sook Ma, Joon Sung Lee, Tae Chan Kwon, Sang Bum Lee, Chul Ho Kim, Heung Jae Lee, Yong Soo Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(12):1320-1323. Published online December 15, 2008
-
Purpose : The aim of this study was to investigate the epidemiologic status of Kawasaki disease (KD) in infants ≤6 months of age. Methods : For the epidemiologic study of KD in Korea, data from 22,674 KD patients were collected from 1997 to 2005 on a 3-year basis by a retrospective survey. From this survey, data of 1,739 KD patients ≤6... -
- Review Article
- Pediatric cerebrovascular disease
- Ji Hoon Phi, Kyu-Chang Wang, Byung-Kyu Cho, Seung-Ki Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(12):1282-1289. Published online December 15, 2008
-
Recently, accumulated clinical experience and advanced neuroradiological techniques have led to a better understanding of pediatric cerebrovascular disease (CVD), which was once considered rare. Approximately 10% of pediatric neurosurgical patients have CVD; therefore, it is no longer uncommon to pediatricians and pediatric neurosurgeons. Furthermore, children with CVD tend to recover better than adults after stroke because the immature brain is... -
- Original Article
- Clinical application of D-dimer in Kawasaki Disease
- Jae Joon Han, Hong Ki Ko, Young Yoo, JungHwa Lee, Kwang Chul Lee, Chang Sung Son, Joo Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(2):205-208. Published online February 15, 2007
-
Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Korea University, Seoul, Korea Purpose : Vascular endothelial cell damage and alteration of a fibrinolytic system was suggested to play a role in the development of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease (KD). D-dimer is one of the markers of endothelial damage and fibrinolysis. We evaluated the clinical usefulness of D- dimer to differentiate KD... -
- Case Report
- A case of congenital ductus arteriosus aneurysm
- Sheng Wen Wang, Ji Eun Kim, Young Seok Lee, Young Ah Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(12):1363-1366. Published online December 15, 2006
-
Aneurysmal dilatation of the ductus arteriosis has been considered a rare but potentially fatal abnormality. The mechanism of ductal aneurysmal formation remains uncertain. Plain chest radiography has proven helpful in the diagnosis of ductus arteriosus aneurysm (DAA), before the application of transthoracic echocardiography. The transthoracic echocardiography is an important tool for the diagnosis and follow-up of DAA. We present a... -
- Original Article
- Clinical features and surgical results of ruptured sinus of valsalva aneurysm
- Tae Ho Lee, Dong Won Lee, Joon Yong Cho, Myung Chul Hyun, Sang Bum Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(3):287-291. Published online March 15, 2006
-
Purpose : Aneurysms of sinus valsalva are rare anormalies thought to be primarily congenital in origin, progressing into death by acute heart failure in cases of rupture. Surgical correction is the only method of treatment. With these clinical implications, we reviewed the clinical characteristics and surgical results of patients with ruptured sinus of valsalva aneurysm. Methods : Between January 1991... -
- Clinical and Epidemiologic Study of Kawasaki Disease in Children 8 Years of Age and Older
- Yong Won Park, Ji Whan Han, In Sook Park, Chang Hwi Kim, Sung Ho Cha, Jae Sook Ma, Tae Chan Kwon, Sang Bum Lee, Chul Ho Kim, Heung Jae Lee, Yong Soo Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(10):1139-1142. Published online October 15, 2005
-
Purpose : The aim of this study was to investigate the epidemiologic and clinical profiles of Kawasaki disease(KD) in children 8 years of age and older. Methods : For the epidemiologic study of KD in Korea, data of total 15,692 KD patients were collected from 1994 to 2002 on a 3 year basis, by the retrospective survey. Among them, data of... -
- Case Report
- Giant Coronary and Axillary Aneurysms in an Infant with Kawasaki Disease Associated with Thrombocytopenia
- Sei Young Seo, Jin Hee Oh, Jong-Hyun Kim, Ji-Whan Han, Kyung-Yil Lee, Dae Kyun Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(8):901-906. Published online August 15, 2005
-
Kawasaki disease (KD) is a leading cause of acquired heart disease in children. Yet the etiology of KD is still unknown and diagnosis depends on the exclusion of other diseases and the clinical manifestations meeting the defined criteria. Young infants frequently show atypical clinical courses and are frequently complicated with coronary aneurysms. Some cases show thrombocytopenia, which is known as... -
- A Life-Threatening Case of Tubular Esophageal Duplication Complicated with Aneurysm of the Aorta
- Yeon Kyung Jung, Gyeong Hoon Lee, Hai Lee Chung, Ki Sung Park, Kyung-Jae Jung, Chang Ho Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(6):655-659. Published online June 15, 2005
-
Esophageal duplication cysts are rare congenital lesions that occur as a result of a failure in the tubulation of the esophagus. They are most frequently single, tubular, or cystic. They may cause compressive symptoms or may be discovered incidentally on chest radiographs. They become symptomatic when complications develop. Symptoms often are related to the location of the duplication; esophageal lesions... -
- A Case of Multiple Giant Coronary Aneurysms with Large Mural Thrombus due to Kawasaki Disease in a Young Infant
- Eun Na Choi, Jeoung Tae Kim, Yuria Kim, Byung Won Yoo, Deok Young Choi, Jae Young Choi, Jun Hee Sul, Sung Kye Lee, Dong Soo Kim, Young Hwan Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(3):321-326. Published online March 15, 2005
-
Kawasaki disease is an acute systemic vasculitis of unknown origin. Giant coronary aneurysm is one of the most serious complications, although peripheral artery vasculitis can produce life-threatening events. Myocardial ischemia and infarction can be caused by coronary artery stenosis, aneurysm, and stagnation of blood flow in coronary arteries which triggers thromboembolism. Atypical presentation in young infants often interferes with prompt... -
- A Case of Tuberous Sclerosis associated with Abdominal Aneurysm
- Eun Jeong Lee, So Jeong Yim, Sun Mi Kim, Dae Chul Jeong, Jin Han Kang, Seung Yun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(5):583-587. Published online May 15, 2004
-
Tuberous sclerosis(TS) is known to be associated with multi-organ involvements, such as neurologic, renal and cardiac abnormalities. Abdominal aortic aneurysms in children and young adults are uncommon, however, some have been observed in patients with TS. We present an 8 month-old female patient with TS who developed aortic aneurysm and underwent successful surgical management. Since an aortic aneurysm is potentially... -
- Thrombolytic Therapy and Long Term Follow-up Study in a Child with Kawasaki Disease Complicated by Giant Coronary Aneurysm with Thrombosis
- Su Jung Moon, Su Ya Lee, Kyong Hee Na, Sun Young Park, Eun Young Kim, Kyoung Sim Kim, Yong Wook Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(3):302-307. Published online March 15, 2003
-
The long-term clinical issues in Kawasaki disease are concerned with the coronary artery lesions that result in aneurysmal formation, thrombotic occlusion, progression to ischemic heart disease, and premature atherosclerosis. We here report a 3 month old infant with Kawasaki disease complicated by giant coronary aneurysm with thrombosis. After urokinase(10,000 IU/kg) and heparin(400 IU/kg) were injected for two days as thrombolytic... -
- A Case of Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection with Coronary Aneurysm
- Hee Jeong, Bong Seong Kim, Ok Ja Choi, Han Wook Yoo, So Duk Lim, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(6):687-693. Published online June 15, 2001
-
Chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection(CAEBV) is a nonfamilial syndrome that shows a specific immunodeficiency for the Epstein-Barr virus(EBV). CAEBV is characterized by fever, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, hepatitis, interstitial pneumonitis, interstitial nephritis, and uveitis. Cardiovascular complications are rare in EBV infection. Patients with CAEBV show characteristically high titers of anti-viral capsid antigen(VCA) IgG antibody and anti-early antigen(EA) antibody, as well as relatively... -
- Langerhans` Cell Histiocytosis Associated wjth Secondary Aneurysmal Bone Cyst, One Case Report
- Yong-Koo Park, Kyung Nam Ryu, Won Leem
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(12):1626-1629. Published online December 15, 2000
-
Seconnday aneurysmal bone cyst is the disease that occurrs in the primary bone tumor and/or tumorus conditions Meticulous search is needed to make a correct diagnosis which dose not overlook the primary diseases. We have experinced an osteolytic lesion on the 7-year-old boy on his skull bone. Plain radiography of the skull revealed osteolytic lesion in the parieto-occipital bone. On... -
- Original Article
- Predicting of Aneurysm with Learning Vector Quantization in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
- Jae Hyun Kwon, Myung Kul Yum, Nam Su Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(1):78-84. Published online January 15, 2000
-
Purpose : We applied Learning Vector Quantization(LVQ) in the analysis of data from Kawasaki disease patients with coronary artery aneurysm in an attempt to achieve accurate predictions of outcome for individual patients. Methods : One hundred and seventy-five patients with Kawasaki disease were recruited. First, data of 75 patients(of which 60 patients had no aneurysm and 15 patients had aneurysm) were trained using the network.... -
- Clinical Analysis and Comparison of Kawasaki Disease between Patients Younger than One Year of Age and Those over One Year of Age
- Hee-Sun Chung, Kyung-Yil Lee, Ji-Whan Han, Sang-Won Cha, Dong-Joon Lee, Kyung-Tai Whang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(7):936-942. Published online July 15, 1999
-
Purpose : To identify the risk factors for coronary sequelae in Kawasaki disease, we analyzed and compared the clinical features and laboratory findings of Kawasaki disease in patients younger than one year of age with those over one year of age. Methods : A retrospective chart review was conducted of all children with Kawasaki disease who were admitted to the... -
- Survey of Harada Scoring of Occurrence of Coronary Aneurysm in Kawasaki Disease Compared to Current Criteria
- Chang Kyu Nam, Yong Wook Kim, Ki Bok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(7):928-935. Published online July 15, 1999
-
Purpose : Gamma-globulin is effective in preventing coronary aneurysm, the primary complication of Kawasaki disease(KD). However, in order to predict high-risk cases which absolutely require γ-globulin, because of its high expenses, Harada score(HS) was introduced in Japan in 1990. We attempted to compare HS scoring with the health insurance criteria currently used in Korea. Methods : Retrospective studies were performed on... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Superior Mesenteric Artery Aneurysm associated with Marfan Syndrome
- Ick Ho Sung, Sang Hee Kim, Min Seop Song, Chul Ho Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(7):984-988. Published online July 15, 1998
-
Superior mesenteric artery aneurysm is very rare complication of Marfan syndrome, especially in children. A 11 years old male patient was admitted to the hospital because of fluctuating high fever and diagnosed as infective endocarditis and Marfan syndrome. During antibiotics therapy, fever was slowly decreased but abdominal pain was developed and pulsatile abdominal mass was palpable in the midline of... -
- A Case of Slowly Progressing Aneurysm of Left Ventricle and Thoracic Aorta Due to Automobile Blunt Trauma
- Eun Ju Kim, Yu Sik Jeon,, Kyuchul Choeh, Jae Kyun Shin, Jeong Tae Ahn, Dong Man Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(2):259-263. Published online February 15, 1998
-
A five-year-old boy received a blunt trauma on chest by a kindergarten bus on Feb. 29, 1996. Pulmonary hemorrhage and pericardiac effusion were developed, followed by multi-organ failure threatening his life. All symptoms were improving when pansystolic harsh murmur(Ⅲ/Ⅵ) originating from a tiny ventricular rupture with a blood leak to the pericardial space was auscultated on the 12th day after the... -
- A Case of Systemic Fibromuscular Dysplasia with Renovascular Hypertension and Superior Mesenteric Arterial Aneurysm
- Jong-Woon Choi, Sang-Min Yoon, Young-Chae Joo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(6):872-876. Published online June 15, 1997
-
-
- Original Article
- Lipid Profile and Its Association with Coronary Aneurysm in Kawasaki Disease
- Ju Sik Choi, Suk Min Choi, Kyu Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(6):835-840. Published online June 15, 1997
-
Purpose : The value of serum lipid in children after recovery of Kawasaki disease may be important because of the predilection of this disease for the coronary artery. Methods : We measured serum high density lipoprotein(HDL)-cholesterol, total cholesterol, triglycerides in 22 patients (mean age 38months, range 6 to 93 months) with Kawasaki disease during 10 days or less after onset and 2 months later... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Peripheral Pulmonary Artery Aneurysm without Pulmonary Hypertension
- Kyeung Hee Moon, Woo Suk Juhng, Chan Uhng Joo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(2):284-287. Published online February 15, 1997
-
Aneurysm of the pulmonary artery is a rare entity. Aneurysm of the peripheral artery are even less common. An 14-year-old girl was admitted for the evaluation of cardiac murmur. There was a variable grade 2/6 systolic murmur along the left sternal border. The chest x-ray showed a round mass in the right perihilar region. Echocardiogram demonstrated a small muscular ventricular septal defect with mild... -
- Abstract= A Case of Right Coronary Arterial Occlusion with Normal Electrocardiogram in Atypical Kawasaki Diseases
- Yoon Kyung Lee, Jong Wan Kim, Kyung Tai Whang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1996;39(3):411-416. Published online March 15, 1996
-
Kawasaki disease is an acute febrile illness of unknown etiology that occurs predominantly in infants and early childhood. It had aroused intense interest because of the sequelae of coronary arteritis accompanied by coronary artery aneurysms and thrombotic occlusion, which may lead to ischemic heart disease or sudden death. Atypical Kawasaki disease is coined to describe patients who have coronary abnormalities,... -
- A Case of the Renal Artery Aneurysm Associated with the Dysplastic Kidney
- Tae Hee Park, Soo Hee Chang, Young Min Han, Soo Chul Cho, Dae Yeol Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(11):1571-1576. Published online November 15, 1995
-
Multicystic dysplastic kidney is the most frequent cause of abdominal mass in the neonate. It is frequently associated with contralateral genitourinary tract abnormalities and the most common abnormality is vesicoureteral reflux. Renal artery aneurysm is very rare in the children. Furthermore the case associated with the renal artery aneurysm has not been reported yet. We experienced a case of the left... -
- Pseudoaneurysm after Renal Biopsy; Angigraphic Diagnosis and Treatment by Superselective Embolization
- Sin Weon Yun, Keun Seop Jung, In Seok Lim, Chul Ha Kim, Dong Keun Lee, Byeong Heun You, Hyung Jin Shim, Young Ku Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(3):417-421. Published online March 15, 1995
-
The use of superselective embolization was assessed as a treatment for bleeding from arteriovenous fistulas and pseudoaneurysm after renal biopsy procedure. But unless it is sufficiently selective, the procedure results in loss of significant amount of renal parenchyme. We experienced one case of renal arterial pseudoaneurysm, which happened at 5days after percutaneous renal biopsy. Diagnosis of pseudoaneurysm was made by... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







