|
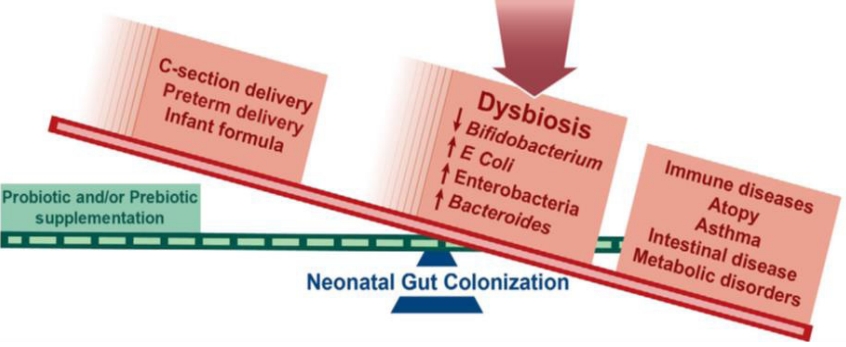
∙ Microbial colonization primarily occurs after birth but there may be some colonization in utero, although this remains highly controversial.
∙ Maternal factors during pregnancy affect the infant microbiota: diet, weight, gestational weight gain, and antibiotic usage.
∙ Microbes are passed from mother-to-infant during and after birth. Delivery mode, breastfeeding, early life antibiotic, and proton pump inhibitor treatment have the largest effects on microbial composition in early life.
∙ The early life gut microbiome plays an important role in the development of the immune system and metabolism. |


