Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Changes in frequency of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis and their viral causes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-center study
- Hyejin Na, Sanghoon Lee, Seo Hee Kim, Young Ok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):213-220. Published online March 19, 2024
-
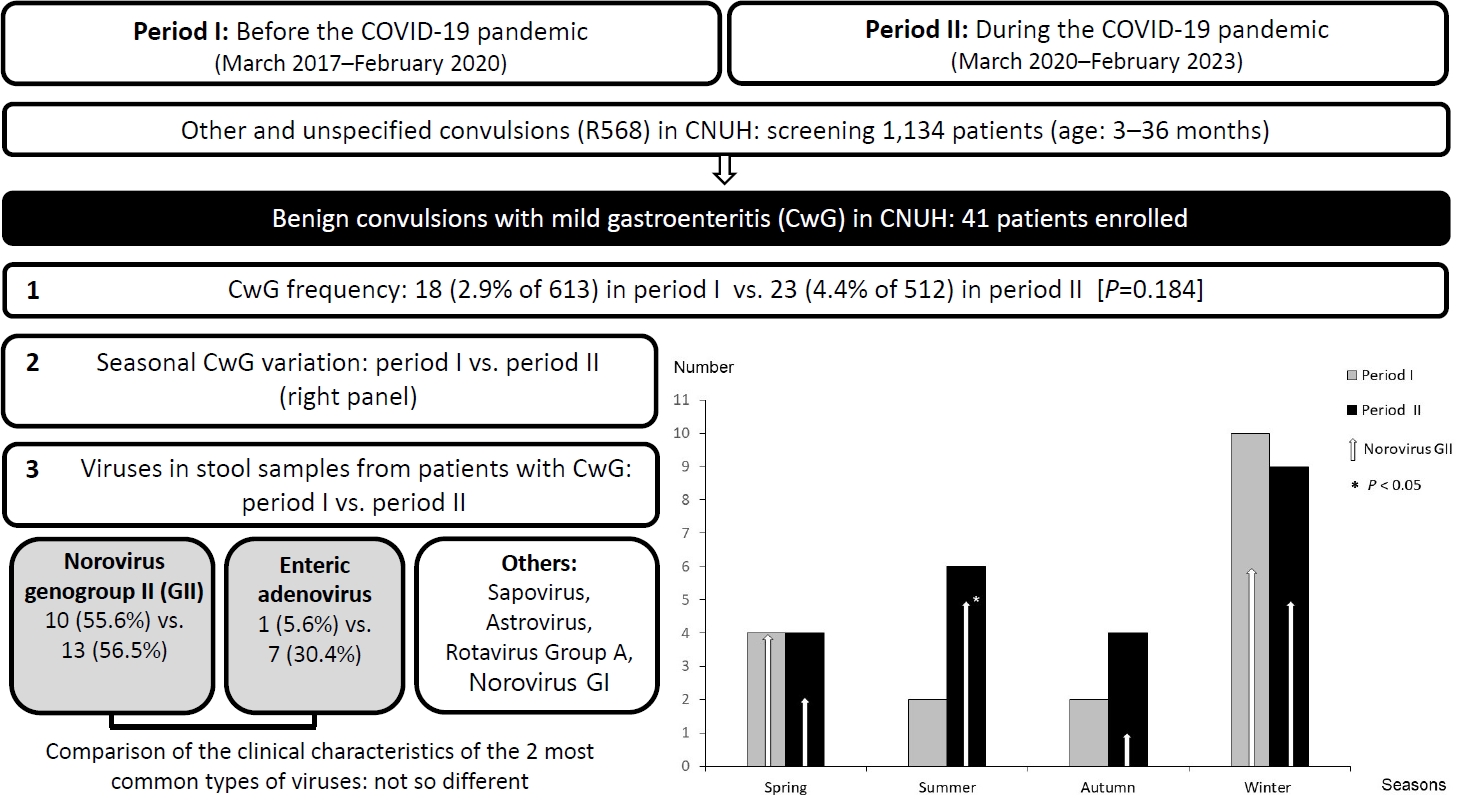
Question: Did coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) affect the frequency, seasonal variation, or virus type of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG)?
Findings: We compared 41 cases of CwG before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. After March 2020, frequency did not change significantly (18 patients vs. 23 patients), seasonal variation was lost, and number of cases of enteric adenovirus-associated CwG increased (1 cases vs. 7 cases).
Meaning: The COVID-19 pandemic affected CwG.
- Nutrition
- Effect of probiotics plus zinc supplementation on clinical outcomes of infants and children with acute infectious diarrhea: a randomized controlled trial
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Saad Jbraeil Sulaiman, Zaid Waad Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):203-212. Published online February 19, 2024
-

Question: Does zinc supplementation along with probiotics affect disease severity or clinical outcomes of children with acute diarrhea?
Findings: This study indicated that zinc supplementation and probiotics had no effect on clinical improvement or disease severity among pediatric patients with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Children who received probiotics plus zinc recovered faster than those who received probiotics only.
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Update on benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis
- Yeong Seok Lee, Ga Hee Lee, Young Se Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):469-475. Published online December 27, 2021
-
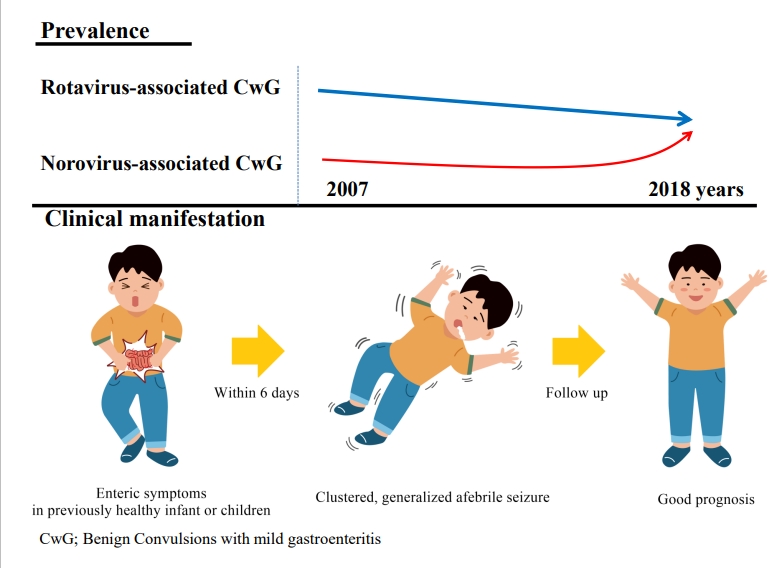
∙ The main pathogen for benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG) was previously rotavirus; however, cases associated with norovirus are increasing.
∙ CwG is characterized by clustered generalized seizures. Electroencephalography and magnetic resonance imaging show transiently abnormal findings in the acute phase that eventually normalize with progression. Its prognosis is good, and long-term treatment is unnecessary.
∙ There are many reports on the pathophysiological mechanism of CwG, which remains unclear.
- Gastroenterology
- Causes of acute gastroenteritis in Korean children between 2004 and 2019
- Eell Ryoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):260-268. Published online September 18, 2020
-
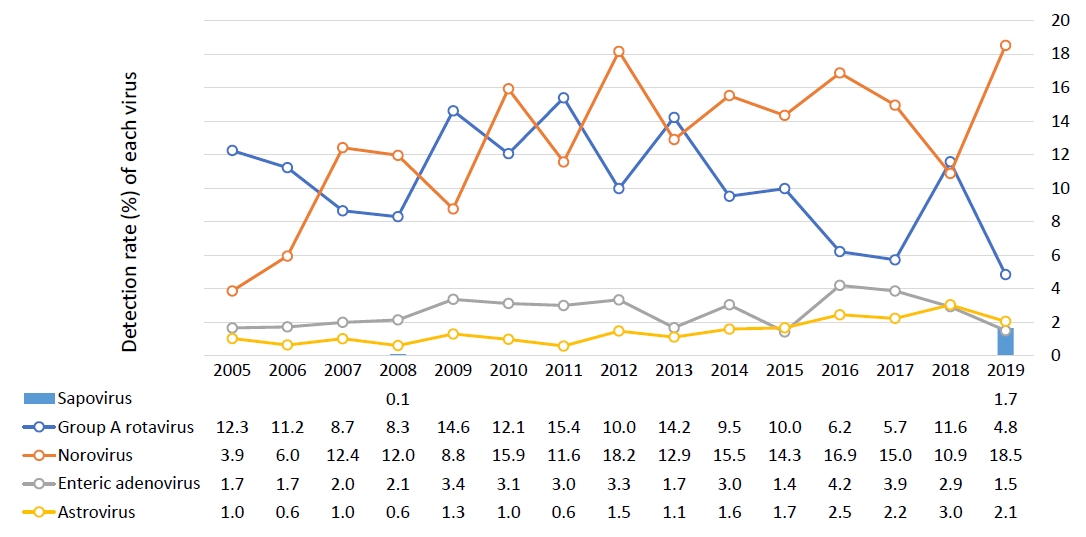
· Norovirus is the most common virus in Korean children with acute gastroenteritis.
· Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. are the most common cause of bacterial gastroenteritis in Korean children, with a detection rate of 3%–20%.
· Uncommon bacterial and parasitic gastroenteritis require attention because of increasing international exchange and overseas travel.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Diagnostic value of the Vesikari Scoring System for predicting the viral or bacterial pathogens in pediatric gastroenteritis
- Dong Ho Shim, Dong Yeon Kim, Ky Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(3):126-131. Published online March 31, 2016
-
Purpose To evaluate the diagnostic value of the Vesikari Scoring System (VSS) as an early predictor of pathogens in children with acute gastroenteritis (AG).
Methods In this retrospective study, the VSS score, absolute neutrophil count (ANC), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were analyzed in 107 hospitalized children with AG, aged 6 months to 17 years. Patients were divided into nonspecific, viral, and bacterial...
- Recent viral pathogen in acute gastroenteritis: a retrospective study at a tertiary hospital for 1 year
- Hye Il Jin, Yoo Mi Lee, You Jin Choi, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(3):120-125. Published online March 31, 2016
-
Purpose Viral gastroenteritis among children is mainly caused by rotavirus, norovirus, astrovirus, or adenovirus strains. However, changing socioeconomic conditions and a rotavirus vaccination program may be affecting the prevalence of these viral infections. Therefore, we aimed to elucidate the season-specific trends in viral infections for facilitating prophylaxis and surveillance in our region.
Methods We evaluated 345 pediatric patients (203 males, 142 females; age,...
- Review Article
- Benign convulsion with mild gastroenteritis
- Ben Kang, Young Se Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(7):304-309. Published online July 23, 2014
-
Benign convulsion with mild gastroenteritis (CwG) is a type of afebrile seizure that occurs in children. CwG is defined as a convulsion in a previously healthy child with no known central nervous system infection or encephalopathy, accompanying mild diarrhea without fever, electrolyte imbalance, or moderate to severe dehydration. Convulsions in CwG are characterized by multiple brief episodes of generalized or...
- Epidemiology of astrovirus infection in children
- Hye Sook Jeong, Ahyong Jeong, Doo-Sung Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(3):77-82. Published online March 16, 2012
-
Human astrovirus (HAstV) is a major cause of acute diarrhea among children, resulting in outbreaks of diarrhea and occasionally hospitalization. Improved surveillance and application of sensitive molecular diagnostics have further defined the impact of HAstV infections in children. These studies have shown that HAstV infections are clinically milder (diarrhea, vomiting, fever) than infections with other enteric agents. Among the 8...
- Original Article
- Clinical features of acute noroviral gastroenteritis in children : comparison with rotaviral gastroenteritis
- Pil-Joo Hwang, Ji Hee Kwak, Taek Jin Lee, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(4):453-457. Published online April 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Our aim was to describe the clinical features of noroviral gastroenteritis in children. Methods : This study included 22 children with noroviral gastroenteritis, as confirmed by stool RT-PCR, who were admitted to Bundang CHA Hospital between July 2006 and June 2008. Their medical records were reviewed and compared with those of 45 children with rotaviral gastroenteritis. Results : In the... -
- Isolation rate of 4 type virus of acute gastroenteritis in full-term neonates during neonatal period
- Soo Kyoung Moon, Jae In Lee, Hye Sun Yoon, Young Min Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(9):855-861. Published online September 15, 2007
-
Purpose : The most common causes of acute viral gastroenteritis in newborn period are rotavirus, astrovirus, norovirus and enteric adenovirus. This study was designed to investigate the clinical characteristics, clinical symptoms, isolation rate and distribution of these viruses in full-term neonates during neonatal period. We also studied the influence on the viral isolation rate by postnatal care place and feeding... -
- Clinical Study of Rotavirus Gastroenteritis in the Last 2 Years
- Hyoung Sik Kim, Myong Wan Jang, Cheol Hong Kim, Hyun Hee Lee, Hwang Jae Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(10):1116-1120. Published online October 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Although the rotavirus-related neonatal death occurred in western part of Kyeonggi Province recently, there were just a few reports about rotavirus gastroentertis in domestic since 2000. We proposed to investigate changes of epidemiology and clinical features of rotavirus gastroenteritis for the last 2 years. Methods : We selected 166 patients diagnosed as gastroenteritis from January, 2002 to July,... -
- Clinical Features of Benign Infantile Convulsions with Gastroenteritis
- Jung Sun Lee, Hae Oak Kwon, Young Mee Jee, Kyu Young Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(7):753-759. Published online July 15, 2005
-
Purpose : This study was performed to characterize clinical features of benign convulsions with gastroenteritis(CwG) in infants. Methods : We reviewed clinical features of 67 episodes in 64 patients with afebrile seizure accompanied gastroenteritis admitted to Dept. of Pediatrics Bundang CHA hospital from January 2001 to June 2004. Patients with meningitis, encephalitis/encephalopathy or apparent history of epilepsy were excluded. Results : There... -
- A Clinical Study on Benign Convulsions with Mild Gastroenteritis
- Jung Il Cho, Dong Wook Kim, Hyun Oh Jang, Jin Soo Moon, Seung Yeon Nam, Chong Guk Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(12):1306-1311. Published online December 15, 2004
-
Purpose : 'Benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis(BCwMG)' is afebrile seizures associated with gastroenteritis without dehydration or electrolyte imbalance in young children aged almost 6 months to 3 years. Because seizures can occur repeatedly, patients can be misdiagnosed with epilepsy. Therefore, understanding the characteristics of this disease is thought to be important. This study was carried out to investigate the clinical... -
- Detection of Cytokeratin-19 caused by Intestinal Epithelial Cell Damage in Childhood Diarrhea
- Ja Young Hwang, Se Young Seo, Seong Hoon Hahn, So Young Kim, Hyun Hee Kim, Won-Bae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(11):1193-1197. Published online November 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Acute gastroenteritis in infancy is a very common disease with a frequency of a billion diarrhea per year, leading to 3 to 5 million deaths. Since the etiology is not always clear, the treatment plan can be quite difficult to make. The laboratory examinations of stool culture, along with complete blood counts may sometimes be helpful to find... -
- Clinical Study of Benign Convulsion with Acute Gastroenteritis
- Jin Hyung Cho, Kim Eun Joo, Sung Koo Kim, Seon Hee Shin, Kon Hee Lee, Hae Sun Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(8):855-860. Published online August 15, 2004
-
Purpose : This study was performed to characterize clinical features of benign convulsions with acute gastroenteritis(CwG) in infants. Methods : We reviewed 83 consecutive seizures in 42 patients with CwG between January 1995 and December 2003. CwG was defined as convulsions having the following two characteristics : (a) seizures accompanied with symptoms of gastroenteritis without clinical signs of dehydration or electrolyte... -
- Fat Content in Stool of Children with Rotaviral Enteritis
- Joon Sup Song, So Chung Chung, Kyo Sun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(12):1212-1216. Published online December 15, 2003
-
Purpose : Rotavirus is a leading cause of severe gastroenteritis in infants and young children around the world. The aim of this study is to investigate the fat content in stools of patients with rotaviral enteritis compared to the stools of children who had no gastroenteritis. Methods : Seventy two patients who were admitted to Konkuk University Hospital, College of... -
- The Retrospective Study on Antibiotics Treatment in Acute Gastroenteritis
- Ji Hye Kim, Sung Hee Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(6):826-834. Published online June 15, 1997
-
Purpose : Most of the gastroenteritis due to viruses and some bacteria can be successfully managed by oral and/or intravenous fluid-electrolyte replacement and antibiotic therapy is unnecessary and even harmful. It is, however, not uncommon practice to prescribe antibiotics when acute gastroentritis is suspected. Therefore authors analysed the clinical courses of the patients treated for acute non-bacterial gastroenteritis in a university hospital to assess... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Ischemic Enteritis
- Ran Lee, Jeong Kee Seo, Kwi won Park, Jong Je Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(2):254-259. Published online February 15, 1997
-
Ischemic enteritis is caused by embolism or thrombosis of superior mesenteric artery and nonocclusive ischemia. Mesenteric venous thrombosis, drugs, and vasculitis are less frequent etiologic factors. In children, occlusion of microcirculation by fibrin thrombi initiated by endotoxemia may be an etiology. Severe abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea with evidence of gross or microscopic bleeding are common presenting symptoms. Angiography may be... -
- A Case of Non-IgE-mediated Serosal Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis in a Child with Chronic Asthma
- Yong Joo Kim, Ha Baik Lee, Hahng Lee, Eun Kyeong Hong, Hyun Chul Rhim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(12):1694-1700. Published online December 15, 1995
-
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis(EG) is a chronic disorder in which edsinophils constitute the predominant cell type in the inflammatory infiltrates of the gastrointestinaHGD tract. This disease was first described by Kaiiser in 1937. The clinical symptoms and signs are variable according to the extent of the eosinophilic infiltration(diffuse versus cir¡ⓒ cumscribed) and the depth of the eosinophilic reaction (mucosal, muscular, serosal). Some... -
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis in a Child
- Young Don Kim, Jung Hwa Choi, Young Tak Lim, Hee Ju Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(4):552-556. Published online April 15, 1995
-
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis is an uncommon disorder of the stomach, small bowel, and colon, characterized by eosinophilic infiltration of the gut wall and peripheral blood eosinophilia. The clinical features depend on the site of eosinophilic infiltration. Patients with eosinophilic gastroenteritis may develop an exudative ascites containing eosinophils. We experienced a case of eosinophilic gastroenteritis in a 9 year old boy who had... -
- Original Article
- Afebrile Convulsion Associated with Rotaviral Gastroenteritis in Childhood
- Yoon Kyeong Koh, Yong Hoon Park, Han Ku Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(4):501-506. Published online April 15, 1995
-
Rotavirus is an important pathogen of acute infantile gastroenteritis as well as is suspected of being one of the causative agents of benign convulsion. We evaluated the clinical and laboratory features noted in 9 young children with Rotazyme positive gastroenteritis and afebrile seizure retrospectly. Seventy-seven patients were admitted to the department of pediatrics in Yeungnam University Hospital with a history of... -
- Case Report
- Longterm Follow Up of A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis
- So Young Lee, Jeong Kee Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(1):104-109. Published online January 15, 1995
-
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis(EG) is a rare disease characterised histologically by eosinophilic infiltration of the gut wall. The clinical features depend on which layer and location are involved. Patients may be divided into three clinical groups as predominantly mucosal, muscle layer, or subserosal disease based on the histological site of eosinophilic infiltration of the bowel wall, although there is lften considerable overlap.... -
- A Case of Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis
- Moon Young Song, Jong Wan Kim, Joon Sung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(10):1457-1462. Published online October 15, 1994
-
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis is a rare disorder of unknown etiology characterized by protein losing enteropathy, peripheral eosinophilia and iron deficiency anemia secondary to gastrointestinal blood loss. It is often accompanied by signs of systemic allergy. This case of a 26-month-old male patient who developed scrotal edema and diarrhea for a month had peripheral eosinophilia ranged from 24 to 32% of total leukocyte,... -
- Original Article
- Role of Adenovirus in Diarrheal Children
- Gyung Ok Yu, Young Bae Moon, Dong Rak Choi, Duk Ha Kim, Hae Ran Lee, Chong Young Park, Hee Jung Kang, Kyu Man Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(2):205-211. Published online February 15, 1994
-
In order to investigate the role of adenovirus in diarrheal children, we evaluated 907 children with diarrhea and 193 children without diarrhea for a 22-month. Stools were tested for group A rotavirus antigen and for adenovirus types 40/41 (Ad 40/41) by using ELISA, cell technique and indirect immunofluorescent method. Adenovirus was detected in 10.1% of the diarrheal children and 3.1%... -
- Clinical Studies of Salmonelosis in Childhood
- Hong Shin Jeon, Young Jin Hong, Myung Ik Lee, Keun Chan Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(2):199-204. Published online February 15, 1994
-
During The last 11 years from Jan. 1980 to Dec. 1990, 72 cases of salmonellosis has been admitted to the Department of Pediatrics of National Medical Center and evaluated clinical difference between typhoid fever and salmonella gastroenteritis. The result were as follows: 1) The annual incidence of salmonella gastroenteritis in salmonellosis was increased in the latter half of the eighties. 2) Both... -
- A Study of Serum Transaminase Level and It's Correlation with Several Symptoms in Children with HRV Gastroenteritis
- Gang Youl Bae, Eui Tak Oh, Woo Sik Jung, Kil Seo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(8):1146-1155. Published online August 15, 1993
-
The retrospective study was taken to study the serum trasnsaminase level and it's correlation with several symptoms in human rotavirus gastroenteritis. 494 children, who admitted to the Department of Pediatrics in Dae Dong Hospital from January 1991 to December 1991 with chief complaints of waterdy diarrhea were included in studies. The 1 st stool specimen on admission was tested for rotavirus Ag... -
- Clincal Observations on Human Rotavirus (HRV) Gastroenteritis
- Seung Ryong Han, Seung Hyun Seo, Ki Sik Min, Jong Wan Kim, Kwang Nam Kim, Ki Yang Ryoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(2):226-233. Published online February 15, 1992
-
Clinical observations were made on 787 patients who were admitted to pediatric department of Kangdong Sacred Heart hospital because of watery diarrhea and vomiting between Jan. 1987 and Dec, 1989. ELISA study was done to detect HRV antigen for all patients. The results were as follows : 1) HRV antigen was detected in 492 patients (62.5%) by ELISA among 787 patients with watery... -
- A Study of Serum Transaminase Level and It's Correlation with Dehydration in Children with HRV Gastroenteritis.
- Tae Joon Park, Eung Sang Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(12):1662-1669. Published online December 31, 1990
-
The study was taken to study the serum transaminase level and it’s correlation with dehydration in Human Rotavirus gastroenteritis. 129 children, who admitted to the Department of Pediatrics in Chung-Ang University Hospital from January 1987 to December 1989 with chief complaints of fever, vomiting, and watery diarrhea were included in this studies. The stool specimen on admission was tested for Rotavirus Ag by ELISA method.... -
- Clinical Studies of Human Rotavirus Gastroenteritis.
- Eun Ok Rhee, Nam Joo Hwang, Yaung Sook Choi, Son Sang Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1989;32(10):1369-1376. Published online October 31, 1989
-
A clinical study of 92 HRV Antigen positive patients among 270 children admitted to the pediatric department of II Sin Christian Hospital because of diarrhea between Sept. 1st 1986 and Aug. 31st 1987 is reported. All cases were detected by the ELISA method. 1) All patients were under 2 year of age with the peak incidence being between 6 month and 1 year of age and... -
- A Clinical and Epidemiological study on Rotavirus Gastroenteritis in Children.
- Hye Kyung Chang, Chang Yeol Kim, Sung Hee Oh, Ha ik Lee, Kun Soo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1988;31(8):961-967. Published online August 31, 1988
-
We investigated the clinical and epidemiological characteristics of rotavirus gastroenteritis in children. The study included 1697 children with acute diarrhea who admitted to the Department of Pediatrics in Hanyang University Hospital from March 1983 through February 1987. The stool specimens were cultured to isolate Campylobacter, Shigella and salmonella and tested for rotavirus by ELISA. The results were 1) Rotavirus was isolated in 646 cases (38.1%) out of total... -
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









