Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Effects of probiotics combined with dietary and lifestyle modification on clinical, biochemical, and radiological parameters in obese children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized clinical trial
- Thushara Rodrigo, Samaranayake Dulani, Sumudu Nimali Seneviratne, Arjuna P. De Silva, Jerad Fernando, H. Janaka De Silva, Jayasekera , V. Pujitha Wickramasinghe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):304-311. Published online November 11, 2021
-
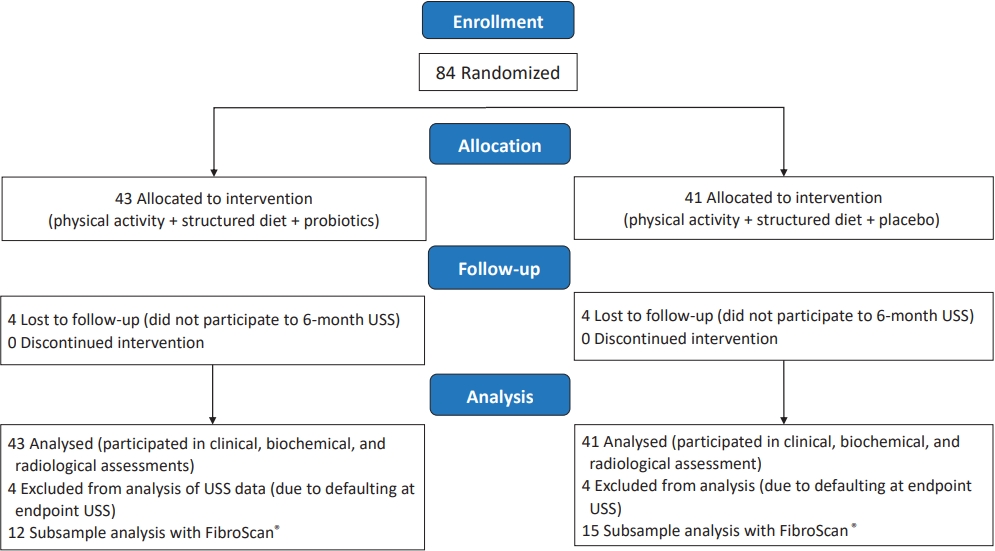
Question: Could probiotics be used as a therapeutic modality in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis?
Finding: There seem no added advantages over lifestyle modifications compared to Probiotics.
Meaning: There does not seem to be an advantage of probiotics over lifestyle modifications in improving obesity-associated metabolic derangement in children.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effectiveness of various nonpharmacological analgesic methods in newborns
- Pancham Kumar, Rakesh Sharma, Sukhdev Rathour, Sunidhi Karol, Mohit Karol
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):25-29. Published online August 16, 2019
-
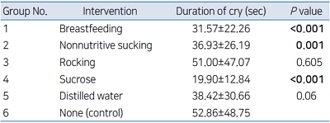
Question: Can nonpharmacological methods be used for neonatal pain management.
Finding: Nonpharmacological methods like Sucrose, breastfeeding etc have shown to significantly reduce the pain caused by intramuscular hepatitis B vaccination.
Meaning: Nonpharmacological methods are the safe and cheap potential modalities of analgesia which can be used during mild to moderate pain in newborns.
- Gastroenterology
- Association between Body Mass Index and Hepatitis B antibody seropositivity in children
- Yoowon Kwon, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(11):416-421. Published online August 12, 2019
-
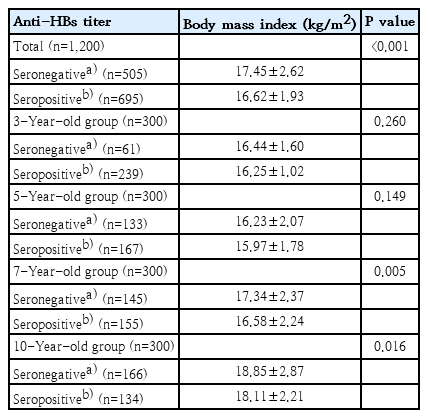
Background: The seropositivity rate of hepatitis B surface antigen (anti-HBs) antibodies is known to be ≥95% after hepatitis B virus vaccination during infancy. However, a low level or absence of anti-HBs in healthy children is discovered in many cases. Recent studies in adults reported that a reduced anti-HBs production rate is related to obesity.
Purpose: To investigate whether body mass index...
- Characteristics and prognosis of hepatic cytomegalovirus infection in children: 10 years of experience at a university hospital in Korea
- Chae-Yeon Min, Joo Young Song, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(8):261-265. Published online August 14, 2017
-
Purpose Studies on cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections in immunocompetent children are lacking, and minimal information is available in the medical literature on hepatic manifestations and complications of CMV. The aims of this study were to evaluate the clinical characteristics, laboratory data, and prognosis of children with CMV hepatitis, and to investigate its prevalence at a single medical center in Korea over a...
- Hepatitis associated with
Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in Korean children: a prospective study - Kyu Won Kim, Jae Jin Sung, Hann Tchah, Eell Ryoo, Hye Kyung Cho, Yong Han Sun, Kang Ho Cho, Dong Woo Son, In Sang Jeon, Yun Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(6):211-217. Published online June 22, 2015
-
Purpose Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) infection is a major cause of respiratory infection in school-aged children. Extrapulmonary manifestations of MP infection are common, but liver involvement has been rarely reported. The aim of this study was to determine the clinical characteristics of MP-associated hepatitis.Methods This prospective study included 1,044 pediatric patients with MP infection diagnosed serologically with MP IgM at one medical center...
- Case Report
- Two adolescent cases of Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
- Ji Hye Kim, Sung Hee Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(9):1038-1043. Published online September 15, 2009
-
Two adolescent cases of Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome, which has not been previously reported in Korean girls, presenting with right upper-quadrant abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever are reported here. A careful and thorough inquiry into the sexual history of the first patient, which was not done upon admission, led to a careful reassessment of the dynamic abdominal computed tomography scan revealing... -
- Autoimmune hepatitis-primary sclerosing cholangitis overlap syndrome in a 10-year-old girl with ulcerative colitis
- Jeana Hong, Mi Kyoung Song, Jae Sung Ko, Gyeong Hoon Kang, Woo Sun Kim, Jeong Kee Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(4):504-507. Published online April 15, 2009
-
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC), and primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) are chronic autoimmune liver diseases. Overlap syndrome is defined as a condition in which the clinical, biochemical, and histological features of these autoimmune diseases are overlapped. Thus, it is difficult to appreciate overlap syndrome as an actual diagnostic entity. Only a few cases of the overlap syndrome of... -
- Original Article
- Comparison of the seroconversion rate after primary hepatitis B vaccination and after revaccination of non-responders in full-term infants according to mother's HBsAg seropositivity
- Jang Hee Kang, Jae Won Moon, Seung Hyun Kong, Kwang Su Hwang, Ji Sun Mok, Hyeon Jung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(11):1165-1171. Published online November 15, 2008
-
Purpose : This study aimed to identify the true extent of non-responsiveness in full-term infants born from HBsAg-negative or HBsAg-positive mothers and vaccinated against hepatitis B virus (HBV) at 0, 1, and 6 months of age and to evaluate the effect of revaccination among non-responders. Methods : The study included 716 full-term infants born in 2004-2007. Of 716, 662 infants... -
- Review Article
- The epidemiology and present status of chronic hepatitis B in Korean children
- Byung-Ho Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(7):696-703. Published online July 15, 2008
-
Korea is now classified as an area of intermediate endemicity for hepatitis B virus (HBV), due to the implementation of universal HBV vaccination and national preventive programs for HBV infection. A national program of HBV vaccination was launched in Korea in 1988 for school-going children and was listed on a vaccination guideline in 1991. In 1995, universal vaccination for newborn... -
- Current status of hepatitis A virus infections in Korea
- Hee-Shang Youn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(7):690-695. Published online July 15, 2008
-
The age-specific anti-hepatitis A virus (HAV) seroprevalence rates in South Korea have changed markedly since the last 2030 years with an improvement in the socio-economic, housing, and environmental-sanitation conditions. These changes are characterized by very low anti-HAV seropositive rates among individuals less than 30 years of age; however, nowadays, most adolescents and young adults at an increased risk of developing... -
- Case Report
- Autoimmune hepatitis and thyroiditis associated with antituberculous medications : A case report
- Seong Keun Yu, Sara Kim, Jin Soo Moon, Han Seong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(5):528-532. Published online May 15, 2008
-
Drug-induced toxic hepatitis is a relatively common hepatic disease in children, and it is usually self-limiting upon cessation of the offending drugs. Antituberculous drugs are well known for inducing hepatitis. Some cases of drug-induced hepatitis with autoimmune features have been reported; in these cases, the offending drugs were usually methyldopa, nitrofurantoin, minocycline, and interferon. The authors report the first case... -
- Original Article
- A rise and fall in AST and ALT level in nonspecific reactive hepatitis
- Tai Sung Kim, Tae Hyung Hur, Sun Jeong Lim, Joong Hyun Bin, Seung Hoon Hahn, So Young Kim, Hyun Hee Kim, Wonbae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(4):396-400. Published online April 15, 2008
-
Purpose : The study was performed to assess the distribution of the diseases associated with nonspecific reactive hepatitis (NRH) for the past 10 years and to evaluate the change in the level of AST and ALT, and the difference by several variable factors. Methods : From January 1997 to December 2006, 646 patients had elevated liver enzymes among 22,763 patients admitted... -
- Review Article
- Acute liver failure in children
- Kyung Mo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(9):841-847. Published online September 15, 2007
-
Acute liver failure (ALF) is a very rare but devastating illness in children. Specific treatment to recovery is often not available, and the underlying cause of the liver failure is often unknown and diverse especially in children. Liver transplantation has increased the chance of survival; however it needs an optimal timing to reach the best result which is not familiar... -
- The management and treatment of chronic hepatitis B in Korean children
- Byung-Ho Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(9):823-834. Published online September 15, 2007
-
Interferon (IFN) alpha has been the first line therapy of chronic hepatitis B in children, but HBeAg seroconversion occurred in 26% of treated children compared to 11% of controls in multinational randomized controlled study. Recently, lamivudine was shown to be a potent inhibitor of Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reproduction both in HBeAg positive and in HBeAg negative (the pre-core mutant... -
- Original Article
- The outcome of perinatal prophylaxis for HBeAg positive mothers according to the maternal HBV-DNA levels at the delivery time
- On Jeong, Jong-Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(4):347-354. Published online April 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Perinatal hepatitis B viral infection is decreasing; however, 10% of babies to HBeAg positive mothers still become chronic carriers despite perinatal prophylaxis. Although, the cause of prophylaxis failure is still unclear, an importance of maternal HBV-DNA level at the delivery time has been suggested. This study was established to certify if it would be a useful predictable factor... -
- An epidemiologic study on the seropositive rate of hepatitis A virus among a selected group of children and adults in Busan
- Young Ok Kwon, Im Jeong Choi, Jin Wha Jung, Ji Hyun Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(3):262-267. Published online March 15, 2007
-
Purpose : The prevalence of hepatitis A virus (HAV) in a certain community reflects that community's living standards and hygienic conditions. And the pattern of HAV infection differs over time and geography. Recently, a shift in prevalence has been observed in cases from chilhood to adulthood. We studied the HAV antibody prevalence in the general population in Busan. Methods : From... -
- Diagnostic limitation and usefulness of 99mTc-DISIDA hepatobiliary scanning on neonatal cholestasis
- Jung Mi Kim, Byung-Ho Choi, You Cheol Jang, Ki Won Oh, Min Hyun Cho, Kyung Hee Lee, Jin-Young Park, Heng Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(7):737-744. Published online July 15, 2006
-
Purpose : To assess the usefulness of 99mTc-DISIDA scanning in the early evaluation of neonatal cholestasis and to verify the diagnostic value of this test in the differential diagnosis of biliary atresia. Methods : DISIDA scannings were performed and analyzed in 87 children(58 males and 29 females; age, 18-139 days, mean, 59.1 days) with neonatal cholestasis. Five groups according to the... -
- A study of the current(2003-2005) prevalence of anti-HBs and immunologic memory of hepatitis B vaccine in children from the central area of Korea
- Young Won An, Eun Hee Chung, Insoo Rheem
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(6):630-634. Published online June 15, 2006
-
Purpose : This study was conducted to assess the current(2003-2005) prevalence of anti-HBs and immunologic memory for Hepatitis B vaccine in children from the central area of Korea. Methods : Subjects were chosen from children and adolescents who received tests for hepatitis B surface antigen(HBsAg) and anti-HBs at Dankook University Hospital from March 2003 to May 2005. Among these, antibodies to... -
- Hepatitis Complicated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection in Children
- Seung Min Lee, Sung Moon Lee, Hann Tchah, In Sang Jeon, Eell Ryoo, Kang Ho Cho, Yong Han Seon, Dong Woo Son, Hee Joo Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(8):832-838. Published online August 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is relatively common in childhood. Its extrapulmonary manifestations have been reported so much, but hepatitis associated with it has been reported rarely in Korea. Methods : A clinical study was performed on 556 patients of M. pneumoniae pneumonia diagnosed serologically at Gil hospital from January 2001 to December 2004. We reviewed 65 cases among these patients,... -
- Comparison of Therapeutic Efficacy between Lamivudine and Alpha-Interferon in Korean Children with Chronic Hepatitis B at Two Years after the Initiation of Treatment
- Byung-Ho Choe, You Cheol Jang, Chang Hwan Jang, Ki Won Oh, Jun Hwa Lee, Cheol Woo Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(1):55-62. Published online January 15, 2005
-
Purpose : We compared the therapeutic efficacy of lamivudine and alpha-interferon in children with chronic hepatitis B two years after the initiation of treatment, so that we could verify the safety and long term efficacy of lamivudine in children. Methods : We prospectively studied 44 children(32 male and 12 female; age, 1-18 years, mean, 9 years) treated for chronic hepatitis B... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Aplastic Anemia following Hepatic Failure by Acute Hepatitis
- Hye Jin Ku, Young Tak Lim, Jae Hong Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(12):1356-1359. Published online December 15, 2004
-
Aplastic anemia following acute hepatitis or acute hepatic failure is an uncommon disease and has a poor prognosis. We experienced a case of aplastic anemia following acute hepatic failure in a 10- year-old girl. She was admitted because of jaundice and lethargy for 8 days. Laboratory findings revealed marked elevated serum transaminases and bilirubin levels, prolonged prothrombin time and partial... -
- A Case of Fulminant Hepatitis from Hepatitis A in a Child
- Young Min Kim, Jae Sun Kim, Sun Hwan Bae, Dong Hoon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(10):1106-1109. Published online October 15, 2004
-
Fulminant hepatitis from hepatitis A in children is rare and has a low survival rate. We report a case of fulminant hepatitis from hepatitis A in a 12-year-old girl. The patient was admitted because of a three day history of fever, epigastric pain and vomiting. On her second hospital day, she had insomnia, anxiety, dysthesia, continuous fever, vomiting and nausea.... -
- Medical Lecture Course
- Impact of Host Genetics on Susceptibility and Outcome of Viral Infections
- Eun Hwa Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(8):815-820. Published online August 15, 2004
-
The generation of a draft sequence of the human genome has lead to an opportunity to characterize human diversity, including the differences in host response to numerous pathogens. Host responses upon exposure to a pathogen can determine the wide spectrum of illness from subclinical or mild to severe diseases. Host factors, particularly genetic backgrounds, influence the pathogenesis of infectious diseases.... -
- Original Article
- Natural History of Chronic Hepatitis B in Children
- Yuria Kim, Seoung Yeon Baek, Ji Hyun Eom, Ki Sup Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(3):282-289. Published online March 15, 2004
-
Purpose : We investigated the spontaneous seroconversion rate of hepatitis B viral markers and predictive factors affecting seroconversion in children with chronic hepatitis B. Methods : The study population included 214 children diagnosed as chronic hepatitis B, with positive HBsAg, HBeAg and HBVDNA over six months, and all patients had a family history of chronic Hepatitis B. They were followed between... -
- Medical Lecture Course
- Perinatal Hepatitis B Virus Infection - Viral Factors in the Mechanism of Perinatal Immunoprophylaxis Failure -
- Jong-Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(2):123-130. Published online February 15, 2004
-
Perinatal hepatitis B virus(HBV) infection may occur despite combined immunoprophylaxis with hepatitis B immunoglobulin and vaccines. Although the mechanism of perinatal prophylaxis still has been obscure, it could be due to : in utero infection; host factors as the personal immunological differences of HLA or cytokine gene; viral factors as a high maternal HBV-DNA level or the presence of surface... -
- Original Article
- Study on Hepatitis B Virus Pre-S/S Gene Mutations in Children with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
- Byeong Hee Son, Yeong Hong Park, Woo Yeong Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(7):741-751. Published online July 15, 2001
-
Purpose : Hepatitis B virus(HBV) with various mutations has been reported. The aims of this study were to investigate the frequency and manifestation of HBV pre-S/S mutations in children with chronic hepatitis B infection. Methods : Sera from 17 children with chronic hepatitis B infection were analyzed by direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction amplification of HBV DNA. Results : Seventeen... -
- Hepatitis B Virus Pre-S Gene Mutations in Children with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection
- Jae Young Kim, Woo Yeong Chung, Chul Ho Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(9):1232-1240. Published online September 15, 2000
-
Purpose : The envelope of HBV consists of three polypeptides which are encoded in pre-S/S open reading frame. Three translation initiation sites are present within this pre-S/S open reading frame, i.e. pre-S1, pre-S2, and S, allowing the expression of large, middle and small HBs proteins. The pre-S1 is thought to carry the receptor binding site for viral entry into hepatocyte... -
- Mutations in Hepatitis B Virus Precore and Core Promotor in Children with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection - Comparison Between Vertical and Non-vertical Transmission -
- Jin Kuk Kim, Yeong Hong Park, Woo Yeong Chung, Chul Ho Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(6):779-791. Published online June 15, 2000
-
Purpose : The aims of this study were to investigate the frequencies and role of hepatitis B virus(HBV) precore and core promotor mutations in children with chronic hepatitis B infection. Methods : Sera from 46 children with chronic hepatitis B infection were analyzed by direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction product of HBV DNA. In this study, the patients were divided... -
- Effect of Liver Transplantation in Children with Fulminant Hepatitis
- Young Mee Seo, Bo Hwa Choi, Kyung Mo Kim, Kwang Min Park, Young Joo Lee, Sung Gyu Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(4):535-542. Published online April 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Liver transplantation(LT) is regarded as an important management option for fulminant hepatitis(FH), which is associated with considerable mortality under conservative management. The aim of this study was to evaluate the outcome of children with FH according to management. Methods : We reviewed medical records of patients presented with FH from January 1994 until April 1999. The children were... -
- Factors Predictive of Response to Interferon-α Therapy in Children with Chronic Hepatitis B
- Hong Kwon Kim, Bo Hwa Choi, Kyung Mo Kim, Kyung Hoon Kang, In Seok Lim, Eung Sang Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(4):514-519. Published online April 15, 2000
-
Purpose : The efficacy and safety of interferon-alpha(IFN-α) therapy in children with chronic hepatitis B(CHB) is similar to that of adults. However, little information is available about the predictive factors of response to this therapy in children. The aim of this study was to determine the predictive factors for responsiveness to IFN-α therapy in children with CHB. Methods : The basal... -
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









