Article category
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Article category
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Strategies for treating and managing chronic hepatitis C in children in the direct-acting antiviral era
- Suk-Jin Hong, Byung-Ho Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):46-47. Published online February 6, 2020
-

- Pulmonology
- Are alternative antibiotics needed for antibiotic-nonresponsive Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia?
- Eun-Ae Yang, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):44-45. Published online February 15, 2020
-
- Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Global prevalence of classic phenylketonuria based on Neonatal Screening Program Data: systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hamid Reza Shoraka, Ali Akbar Haghdoost, Mohammad Reza Baneshi, Zohre Bagherinezhad, Farzaneh Zolala
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):34-43. Published online February 6, 2020
-
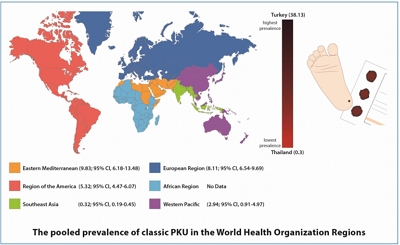
Question: What is the global prevalence of classic phenylketonuria based on Neonatal Screening Program Data?
Finding: The overall worldwide prevalence of the disease is 6.002 per 100,000 neonates. The highest prevalence (38.13) was reported in Turkey, while the lowest (0.3) in Thailand.
Meaning: This difference in the prevalence may be due to differences in the number of consanguineous marriages among the different regions, phenylalanine cutoff points, and sample sizes.
- Perspective
- General Pediatrics
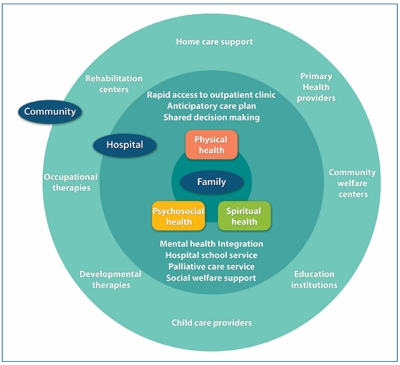
- Integrative care for children with medical complexity
- Jung Lee, Min Sun Kim, Hee Young Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(2):32-33. Published online November 14, 2019
-
- Clinical Note
- Allergy
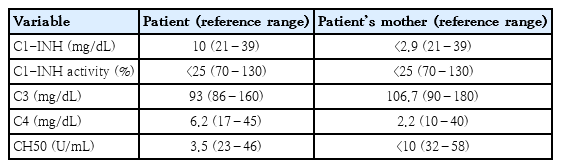
- Complement 4 levels of a 4-year-old girl with angioedema
- Soyoung Shin, Yoon Tae Lee, Kyung Yil Lee, Joonhong Park, Jae Ho Lee, Eun Ae Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):30-31. Published online November 8, 2019
-
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effectiveness of various nonpharmacological analgesic methods in newborns
- Pancham Kumar, Rakesh Sharma, Sukhdev Rathour, Sunidhi Karol, Mohit Karol
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):25-29. Published online August 16, 2019
-
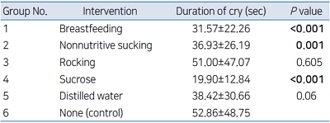
Question: Can nonpharmacological methods be used for neonatal pain management.
Finding: Nonpharmacological methods like Sucrose, breastfeeding etc have shown to significantly reduce the pain caused by intramuscular hepatitis B vaccination.
Meaning: Nonpharmacological methods are the safe and cheap potential modalities of analgesia which can be used during mild to moderate pain in newborns.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Comparative validity of microalbuminuria versus clinical mortality scores to predict pediatric intensive care unit outcomes
- Shifa Nismath, Suchetha S. Rao, B.S. Baliga, Vaman Kulkarni, Gayatri M. Rao
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):20-24. Published online August 12, 2019
-

Question: Does microalbuminuria predict mortality in pediatric intensive care unit?
Finding: Positive correlation was found between albumin-creatinine ratio and pediatric intensive care unit stay, organ dysfunction and need of inotropes. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for albumin-creatinine ratio was comparable to mortality scores.
Meaning: Microalbuminuria is a good predictor of outcome in pediatric intensive care unit and is comparable with mortality scores.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Hereditary angioedema in childhood
- Young Min Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):18-19. Published online January 15, 2020
-
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Prevention and management of pain in the neonatal intensive care unit
- Sung Shin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):16-17. Published online January 15, 2020
-
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Considerations for evaluating the effectiveness and long-term outcome of enzyme replacement therapy in Pompe disease
- Chong Kun Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):14-15. Published online August 7, 2019
-
- Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Neurobehavior
- Association between neonatal jaundice and autism spectrum disorders among children: a meta-analysis
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Salman Khazaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):8-13. Published online November 7, 2019
-
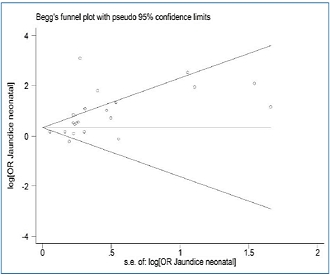
Autism spectrum disorder is a common neurodevelopmental disorder with an unknown etiology. The correlation between neonatal jaundice and the risk of developing autism spectrum disorder was investigated previously. Some studies showed significant associations, whereas others demonstrated no association. In this meta-analysis, we pooled the results of observational studies to examine the association between neonatal jaundice and the risk of autism...
- Review Article
- Pulmonology
- High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy in children: a clinical review
- Ji-Won Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):3-7. Published online October 28, 2019
-
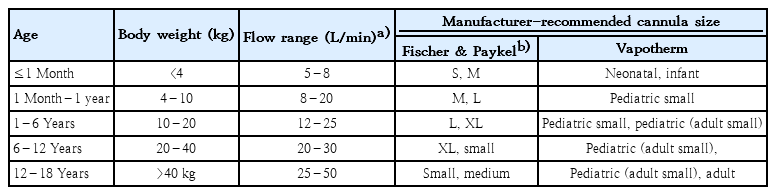
High-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) is a relatively safe and effective noninvasive ventilation method that was recently accepted as a treatment option for acute respiratory support before endotracheal intubation or invasive ventilation. The action mechanism of HFNC includes a decrease in nasopharyngeal resistance, washout of dead space, reduction in inflow of ambient air, and an increase in airway pressure. In preterm...
- Perspective
- Other
- The long journey toward improving children’s health: from ‘Korean Journal of Pediatrics’ to ‘Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics’
- Man Yong Han, Yeong Ho Rha, Chong-Woo Bae, Baik-Lin Eun; Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics Editorial Team
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):1-2. Published online January 15, 2020
-
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Lipid accumulation product is a predictor of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in childhood obesity
- Bahar Özcabı, Salih Demirhan, Mesut Akyol, Hatice Öztürkmen Akay, Ayla Güven
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):450-455. Published online October 28, 2019
-

Background: Lipid accumulation product (LAP) is associated with the presence and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in adults.
Purpose: Here we evaluated the ability of LAP to predict NAFLD in obese children. Methods: Eighty obese children (38 girls; age 6–18 years) were included. Anthropometric measurements and biochemical values were obtained from the patients’ medical records. LAP was calculated as [waist...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Hypoxia-inducible factor: role in cell survival in superoxide dismutase overexpressing mice after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia
- Ga Won Jeon, R. Ann Sheldon, Donna M Ferriero
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):444-449. Published online October 18, 2019
-
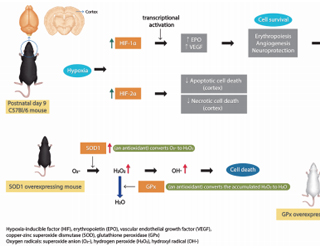
Background: Sixty percent of infants with severe neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy die, while most survivors have permanent disabilities. Treatment for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy is limited to therapeutic hypothermia, but it does not offer complete protection. Here, we investigated whether hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) promotes cell survival and suggested neuroprotective strategies.
Purpose: HIF-1α-deficient mice have increased brain injury after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia (HI), and the...
- Editorial
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Is there a simple and less invasive way to accurately diagnose acute pyelonephritis?
- Seong Heon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):442-443. Published online November 19, 2019
-
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Practical considerations when administering surfactants to preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome
- Heui Seung Jo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):440-441. Published online August 16, 2019
-
- Eosinophil count and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte count ratio as biomarkers for predicting early-onset neonatal sepsis
- Jang Hoon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):438-439. Published online July 9, 2019
-
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Reconsideration of urine culture for the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children: a new challenging method for diagnosing acute pyelonephritis
- Jun Ho Lee, Seonkyeong Rhie
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):433-437. Published online October 18, 2019
-
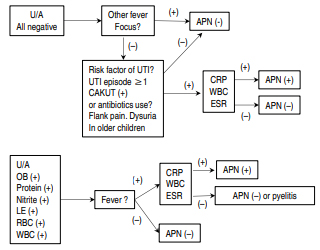
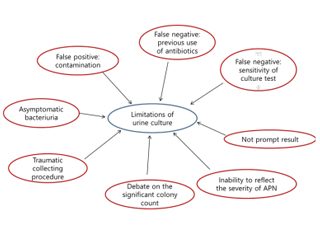
Acute pyelonephritis (APN) should be detected and treated as soon as possible to reduce the risk of the development of acquired renal scarring. However, in the medical field, urine culture results are not available or considered when the prompt discrimination of APN is necessary and empirical treatment is started. Furthermore, urine culture cannot discriminate APN among children with febrile urinary...
- Perspective
- Allergy
- Food allergy and food-induced anaphylaxis in children: an increasing critical public health issue
- Sooyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):431-432. Published online November 12, 2019
-
- Clinical note
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Gray-brown skin discoloration following phototherapy for hyperbilirubinemia due to anti-E alloimmunization
- Da Jeong Lee, Woo Sun Song, Seung Yeon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(11):428-430. Published online September 18, 2019
-

- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Clinical manifestations of BK virus infection in pediatric kidney transplant patients
- Yiyoung Kwon, Jeong Yeon Kim, Yeonhee Lee, Heeyeon Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(11):422-427. Published online September 5, 2019
-

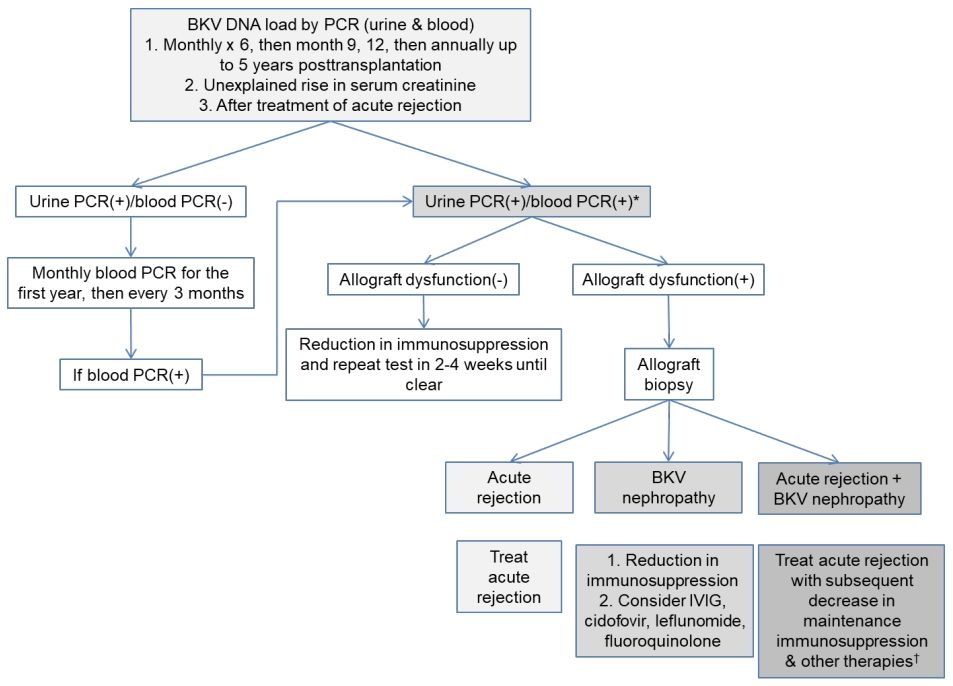
Background: Polyomavirus BK (BKV) infection is an important cause of graft loss in kidney transplant patients.
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to evaluate clinical findings and risk factors for BKV in pediatric patients after kidney transplantation. Methods: This retrospective single-center study included 31 pediatric kidney transplant recipients from January 2002 to December 2017. Two patients received 2 transplantations during the...
- Gastroenterology
- Association between Body Mass Index and Hepatitis B antibody seropositivity in children
- Yoowon Kwon, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(11):416-421. Published online August 12, 2019
-
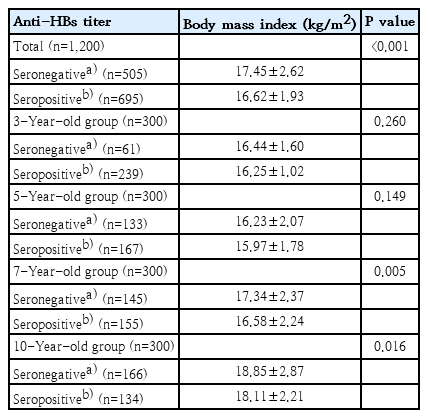
Background: The seropositivity rate of hepatitis B surface antigen (anti-HBs) antibodies is known to be ≥95% after hepatitis B virus vaccination during infancy. However, a low level or absence of anti-HBs in healthy children is discovered in many cases. Recent studies in adults reported that a reduced anti-HBs production rate is related to obesity.
Purpose: To investigate whether body mass index...
- Editorial
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Monitoring BK virus infection in pediatric kidney transplant recipients
- Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(11):414-415. Published online October 18, 2019
-
- Endocrinology
- Correlation between genetic heterogeneity and variability for response to growth hormone in Noonan syndrome
- Young-Lim Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(11):412-413. Published online July 9, 2019
-
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Controversy in the diagnosis and treatment of hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants
- Se In Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(11):410-411. Published online June 21, 2019
-
- Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Neurobehavior
- Evaluation of drug interventions for the treatment of sleep disorders in children with autism spectrum disorders: a systematic review
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Sara Ataei, Saeid Bashirian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(11):405-409. Published online October 2, 2019
-
A structured review study of drug interventions on sleep disorders in patients with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) has not been published to date. This systematic review aimed to investigate drug interventions for the treatment of sleep disorders in children with ASD. The Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus databases were searched until March 2019. Study quality was assessed using the...
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Influence of proton pump inhibitor therapy on intestinal inflammation assessed by fecal calprotectin in pediatric patients
- Su Yeong Kim, Na Mi Lee, Sin Weon Yun, Soo Ahn Chae, In Seok Lim, Eung Sang Choi, Dae Yong Yi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):400-404. Published online July 3, 2019
-
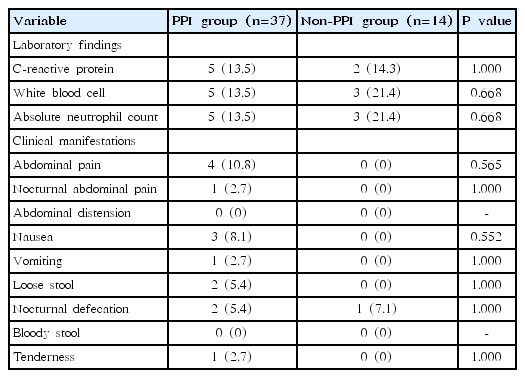
Background: An increase in the numbers of patients with gastrointestinal symptoms has recently been observed.
Purpose: To investigate the effects of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy on intestinal inflammation in children and adolescents as confirmed by clinical manifestations and objectively assessed by fecal calprotectin (FC) level measurement. Methods: Consecutive children (aged 3–18 years) who presented with gastrointestinal symptoms and were treated with...
- Endoscopic postdilatation application of Mitomycin C in children with resistant esophageal strictures
- Yasser K. Rashed, Mohamed El-Guindi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):395-399. Published online June 24, 2019
-
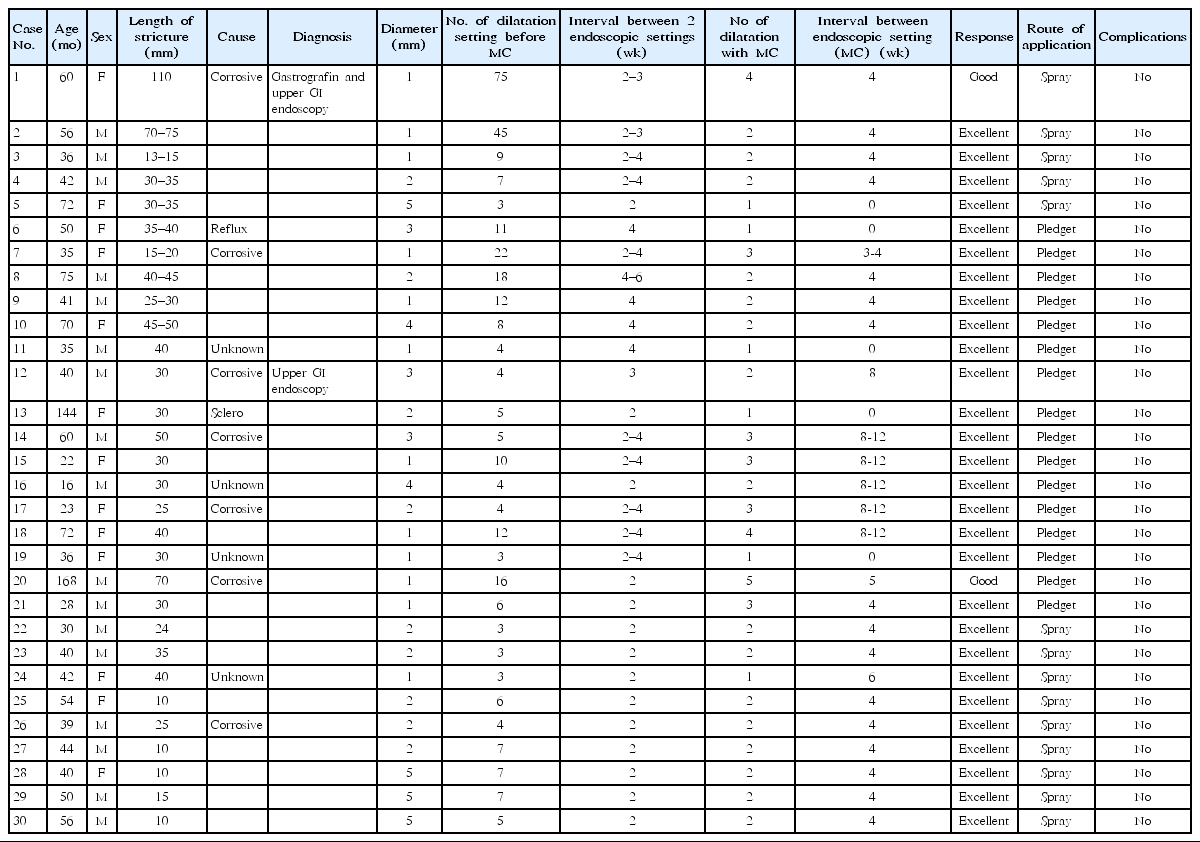
Background: The esophagus is the most common part of gastrointestinal (GI) tract at the risk of stricture. Benign disorders are the leading causes of narrowing. Caustic ingestion is the most common cause of esophageal stricture in children, especially in developing countries. Clinical responses to the topical application of Mitomycin C in various medical procedures have been reported.
Purpose: The study aimed...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Clinical impact of admission hypothermia in very low birth weight infants: results from Korean Neonatal Network
- Na Hyun Lee, Soo Kyung Nam, Juyoung Lee, Yong Hoon Jun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):386-394. Published online May 22, 2019
-
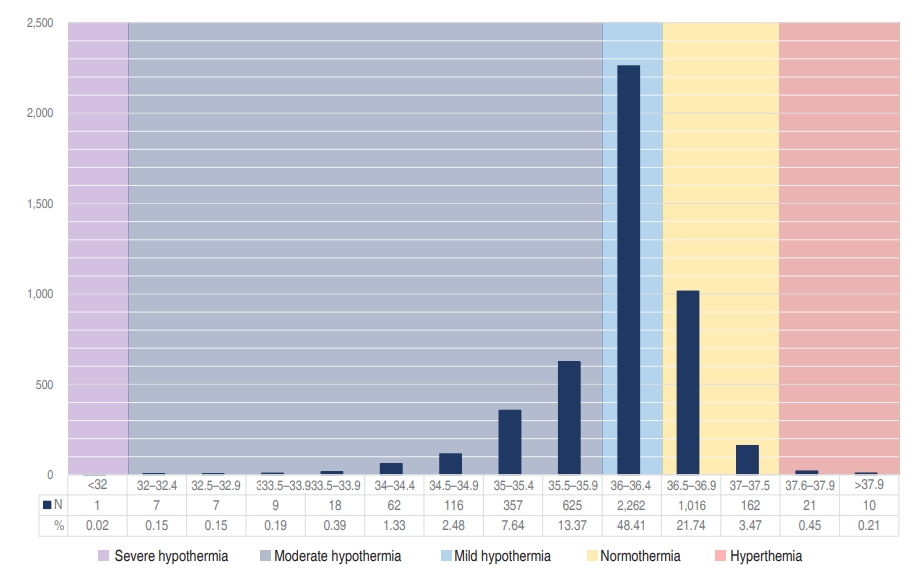
Background: Preterm infants have difficulty maintaining body temperature after birth. However, clinical guidelines advocate that neonatal body temperature should be maintained at 36.5°C–37.5°C.
Purpose: We aimed to investigate the incidence of admission hypothermia in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants and to determine the association of admission temperature with in-hospital mortality and morbidities. Methods: A cohort study using prospectively collected data involving...
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









