Most cited
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most cited
Most-cited articles are from the articles published during the last two years (2023 ~ ).
- Letter to the Editor
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Pentraxin 3 as a marker of early-onset neonatal sepsis
- Safaa ELMeneza, Iman El-Bagoury, Hind Rayes, Amira Hassan
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):312-314. Published online May 23, 2024
-

- Review Article
- Other
- Children’s health affected by parent’s behavioral characteristics: a review
- Sung Eun Kim, Jongin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):232-239. Published online August 21, 2023
-

· Parents’ occupational hazards, long working hours, and smoking behaviors should be modified adequately to minimize adverse health effects on their children.
· As of 2023, several diseases from fetal exposure to occupational hazards can be compensated with Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance in South Korea.
· A directed acyclic graph is recommended for medical research to control the effects of parents’ behaviors on children’s health.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin levels in infants with hyperbilirubinemia: a double-blind randomized clinical trial
- Mojtaba Cheraghi, Maziar Nikouei, Majid Mansouri, Siros Hemmatpour, Yousef Moradi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):249-256. Published online March 26, 2024
-
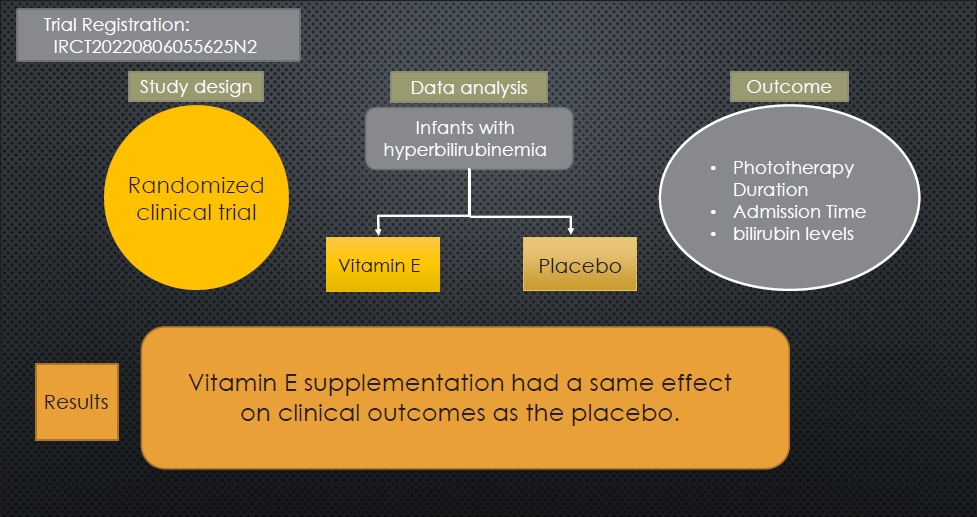
Question: Is vitamin E a viable therapeutic option for managing neonatal hyperbilirubinemia?
Finding: This randomized clinical trial examined the effects of oral vitamin E supplementation on bilirubin reduction (primary outcome), phototherapy duration, and length of hospital stay (secondary outcome) in 138 infants.
Meaning: Infants administered vitamin E versus placebo demonstrated similar reductions in bilirubin levels and length of hospital stay.
- Review Article
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients modified dietary intervention in the management of overweight/obese children and adolescents: a systematic review
- Jihyun Park, Oh Yoen Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):191-200. Published online July 11, 2023
-
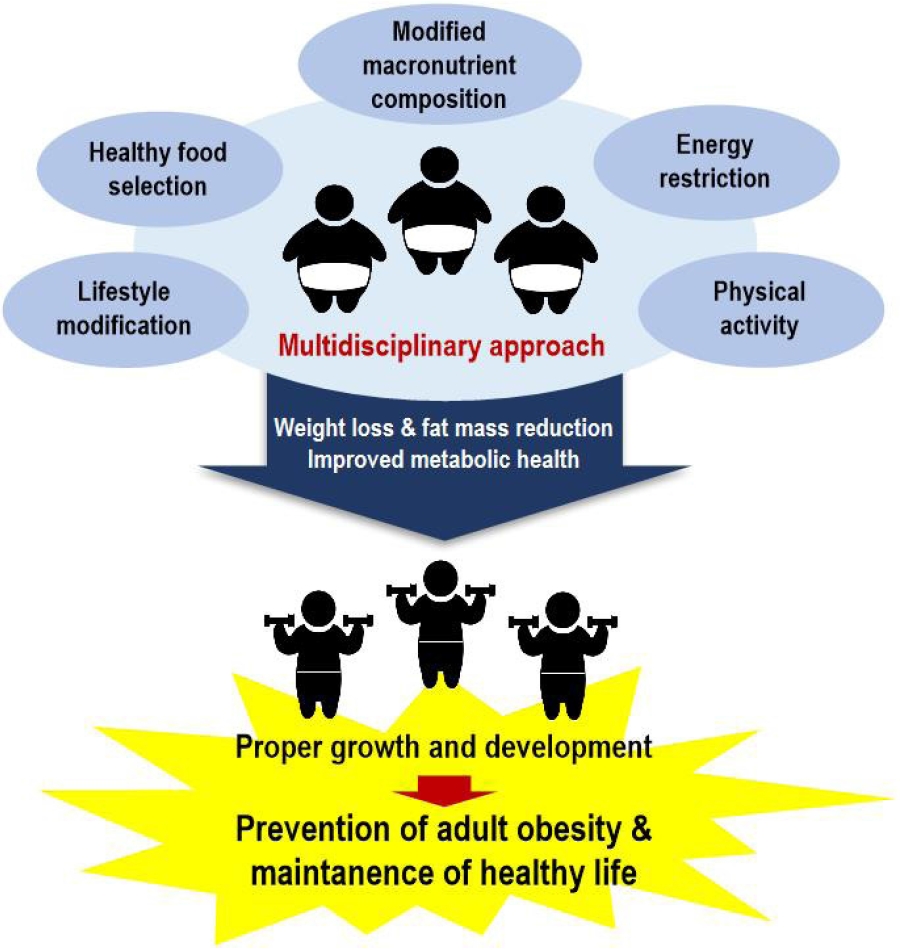
· Dietary macronutrient modifications affect the body composition of and metabolic markers in children and adolescents.
· Hypocaloric diets, regardless of macronutrient composition, are reportedly effective for weight loss in obese children.
· Future interventional studies with meta-analyses that include Korean children and adolescents are needed to provide basic information applicable to this population.
- Letter to the Editor
- Pulmonology
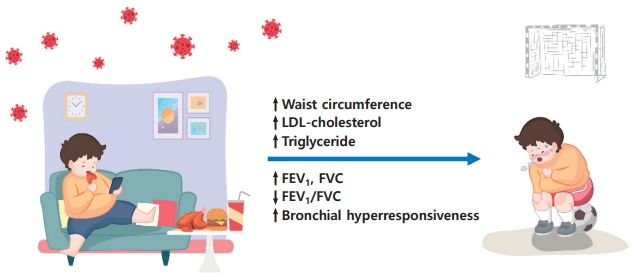
- Metabolic syndrome and pulmonary dysfunction in asthmatic children during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Jue Seong Lee, Sang Hyun Park, Yoon Lee, Seunghyun Kim, Wonsuck Yoon, Young Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):168-170. Published online February 19, 2024
-
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Comparative analysis of adolescent hypertension definitions for predicting early adulthood carotid artery intima-media thickness: Tehran lipid and glucose study
- Maryam Barzin, Shirin Yaghoobpoor, Maryam Mahdavi, Behnaz Abiri, Majid Valizadeh, Fereidoun Azizi, Pooneh Dehghan, Farhad Hosseinpanah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):694-703. Published online September 12, 2024
-
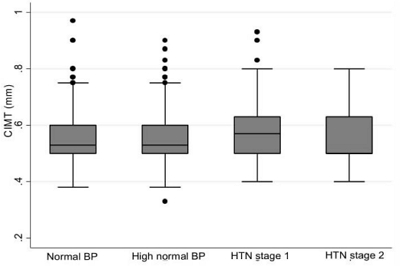
Question: What is the prevalence of HTN among adolescents enrolled in the TLGS according to 3 different accepted definitions (4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG). Also, what is the ability of each of these definitions in predicting early adulthood CIMT, as a surrogate for cardiovascular disease events?
Finding: The highest and lowest prevalence of stage 1 HTN was observed with the AAP-CPG (17.7%) and ESH (8.8%), respectively. Similarly, the highest and lowest prevalence of stage 2 HTN was noted with the AAP-CPG (1.5%) and ESH (0.8%), respectively. The highest to lowest predictive abilities belonged to the 4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG, respectively.
Meaning: Among the various definitions of pediatric HTN, the 4th report offered the best ability to predict a high CIMT during early adulthood, followed by the ESH and AAP-CPG.
- General Pediatrics
- Role of proper postnatal care in continued exclusive breastfeeding among young Indonesian mothers
- Wahyu Triadmajani, Shinta Prawitasari, Abdul Wahab
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):686-693. Published online September 12, 2024
-
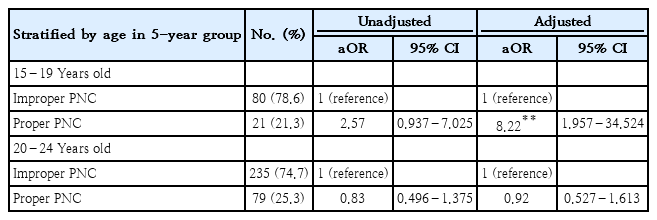
Question: Is proper postnatal care (PNC) associated with exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) practice among young Indonesian mothers?
Finding: Proper PNC elevates the likelihood of EBF among Indonesian adolescent mothers aged 15–19 years.
Meaning: Breastfeeding services should be provided during the early postnatal period to support EBF practice among adolescent mothers. High-quality PNC is a tailored intervention for vulnerable populations.
- Review Article
- Adolescence Medicine
- Diet-related behaviors affecting health and substance use among children and adolescents
- Ji-Hyun Seo, Sochung Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):664-671. Published online October 31, 2024
-
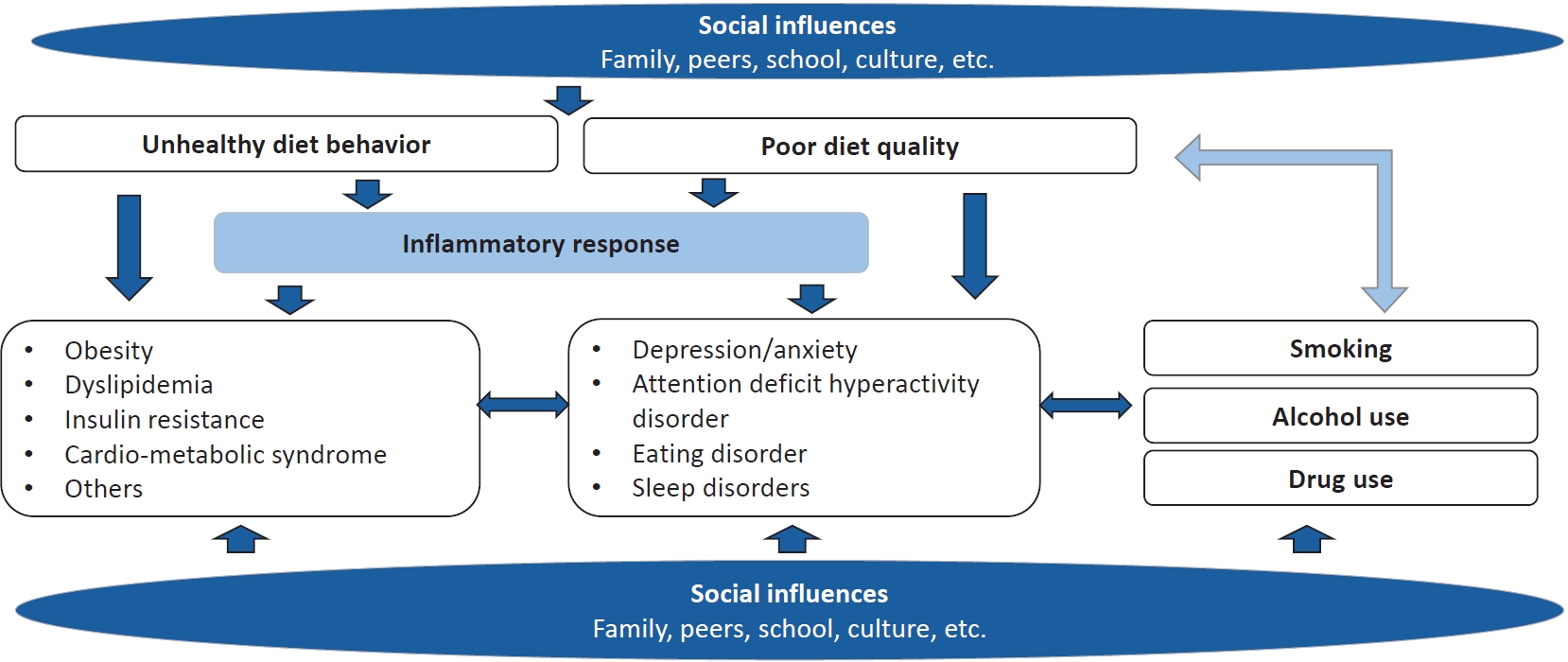
· Diet behaviors in children and adolescents are influenced by environmental and sociocultural factors.
· Unhealthy diet behaviors and poor diet quality are the main contributing factors to noncommunicable diseases and mental health problems during childhood and adolescence.
· Smoking and alcohol drinking in children and adolescents may be associated with unhealthy diet behavior or poor diet quality.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Strategies to support language development in neonatal intensive care unit: a narrative review
- Ju Sun Heo, Ee-Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):651-663. Published online November 6, 2024
-
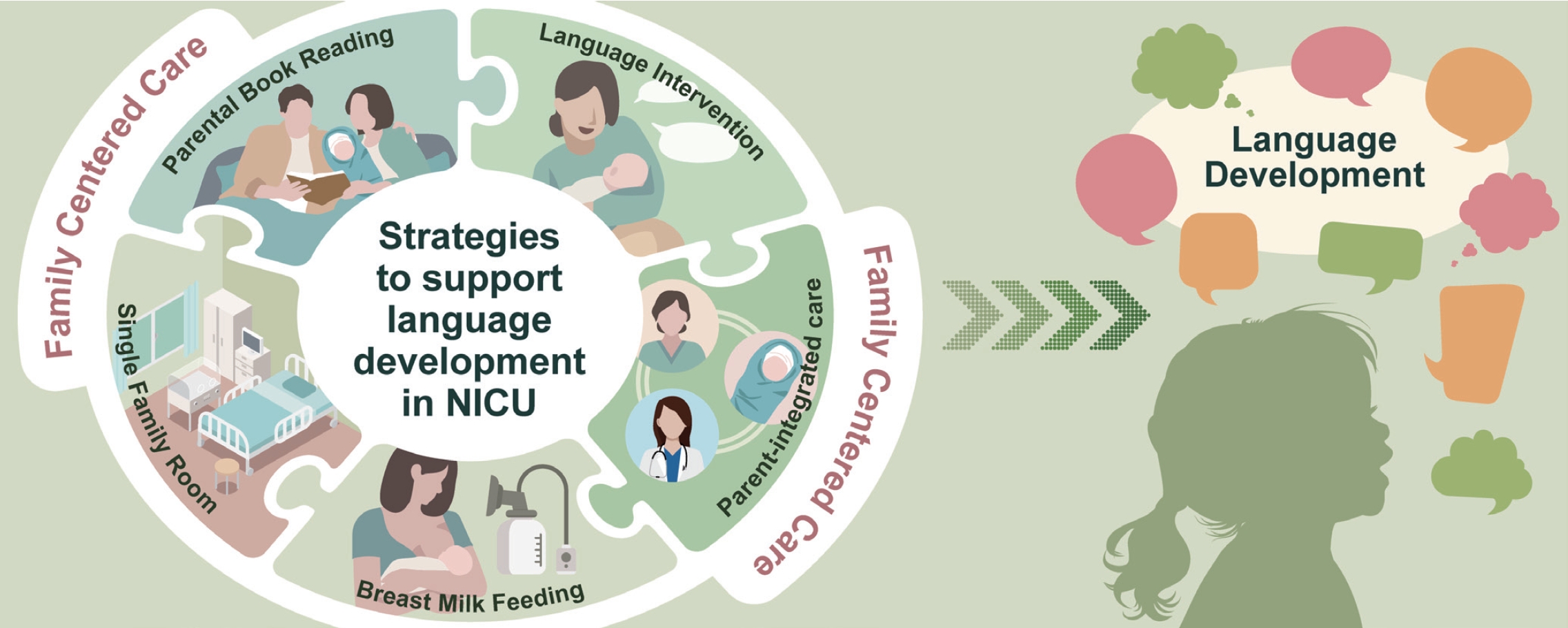
· Preterm infants often experience speech and language development delays during early childhood, impacting children's ultimate outcomes.
· Promoting breastfeeding, increasing parent-infant interactions in a single-family room, promoting a nurturing language environment by parental book reading and language interventions, and parent-integrated interventions in the neonatal intensive care unit could potentially enhance children's language development.
· Integrating these strategies through family-centered care is essential.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Comorbidities of allergic rhinitis in children
- Yong Ju Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):675-676. Published online July 31, 2024
-
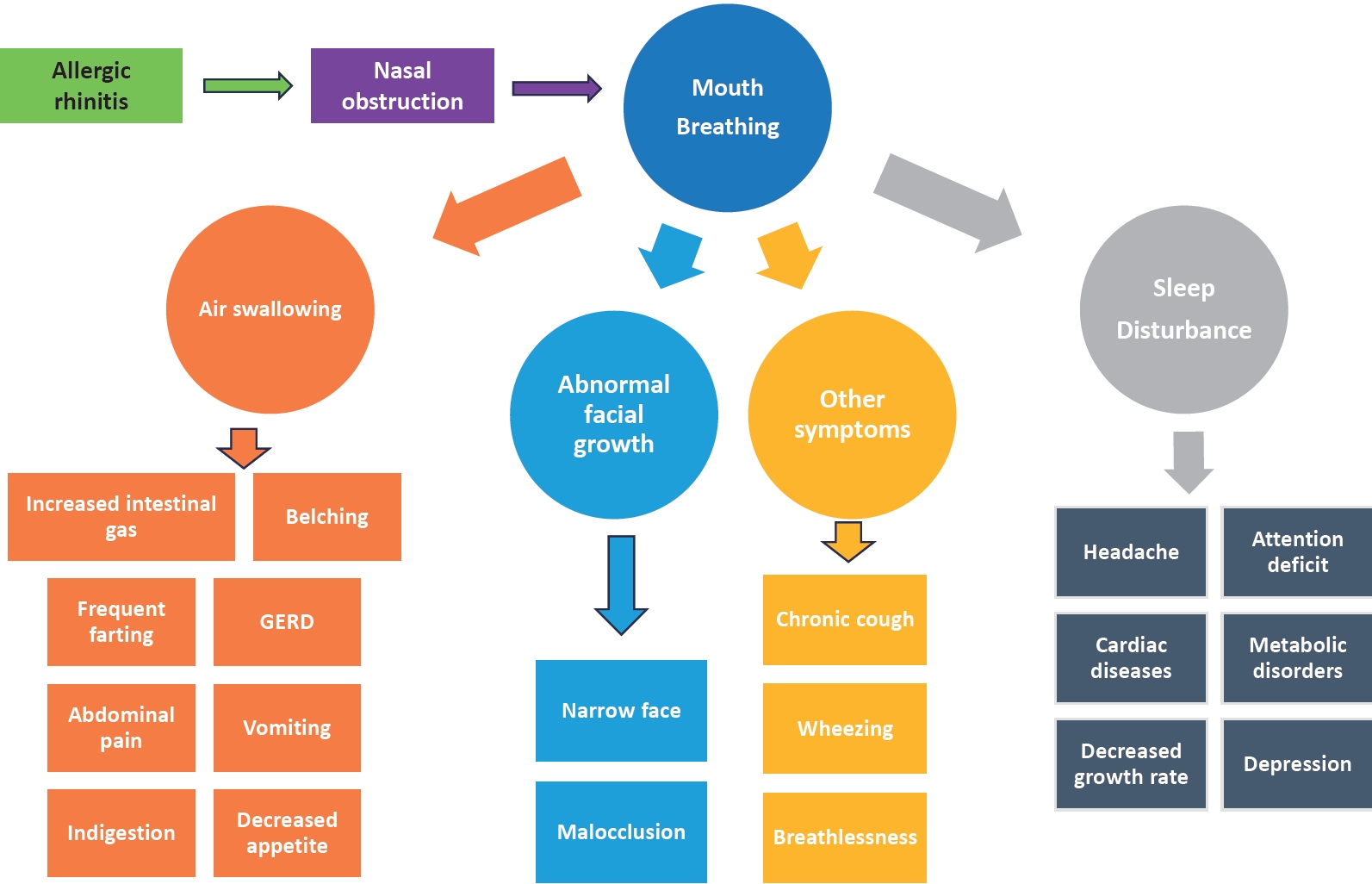
· Allergic rhinitis in children often goes undiagnosed or untreated, with significant systemic complications like sleep disorders, growth issues, and gastrointestinal symptoms linked to nasal obstruction.
· A patient-centered action plan that considers symptom severity, preferences, and comprehensive management of associated complications is essential for effective treatment.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Mortality of very low birth weight infants by neonatal intensive care unit workload and regional group status
- Sung-Hoon Chung, Chae Young Kim, Yong-Sung Choi, Myung Hee Lee, Jae Woo Lim, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim; the Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):619-627. Published online September 12, 2024
-

Question: How do structural and staffing characteristics of neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) influence the mortality rates of very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs)?
Findings: NICUs with higher staffing levels, particularly with more neonatologists, and those offering advanced care levels were associated with lower mortality rates. Additionally, regional disparities were observed, with some areas demon-strating significantly higher survival rates.
Meaning: Adequate staffing and equitable regional distribution of medical resources are crucial for improving survival outcomes in VLBWIs. Efforts to enhance NICU staffing and address regional healthcare disparities are essential for optimizing care quality and reducing mortality in this vulnerable population.
- Clinical Note
- Immunology
- Comparative analysis of rare periodic fever syndromes including the first Korean case of hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome
- Yoonsun Yoon, Hyun Seo Kim, Jung Ok Shim, JungHwa Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):550-552. Published online September 24, 2024
-

- Review Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effect of pesticide exposure on stunting incidence: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Sani Rachman Soleman, Yaltafit Abror Jeem, Muhammad Fathi Banna Al Faruqi, Mahdea Kasyiva, Vita Widyasari, Kuswati Kuswati, Nur Aini Djunet, Muflihah Rizkawati, Ety Sari Handayani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):510-518. Published online September 24, 2024
-

This review aimed to determine whether pesticide exposure is associated with stunting in children. The 13 included studies agree that pesticide exposure is not correlated with stunting incidence regardless of substance type (organophosphate and pyrethroid). Heterogeneity appeared with age covariate as potential confounding. The evidence of this study is challeng-ing, as the adverse effects of pesticides grossly occurred. The protection of children is warranted for preventing future neurodevelopment issues.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Protective effect of recombinant interleukin-10 on newborn rat lungs exposed to short-term sublethal hyperoxia
- Hyeon-Soo Lee, Young-Joon Ryu, Min-Jae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):540-549. Published online September 27, 2024
-

Lung injury is generated from the early stage of hyperoxia through the biologic effects of cell death and inflammatory response, which eventually leads to evolution of bronchopul-monary dysplasia. Therefore, a protective measure against hyperoxia-induced lung injury is needed. The present study observed that anti-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-10 had protective effects on newborn rat lungs from injury induced at the early stage of hyperoxia, by preventing cell death and down-regulating inflammatory response.
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Environmental changes surrounding congenital heart disease
- Eun-Young Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):332-338. Published online January 2, 2023
-
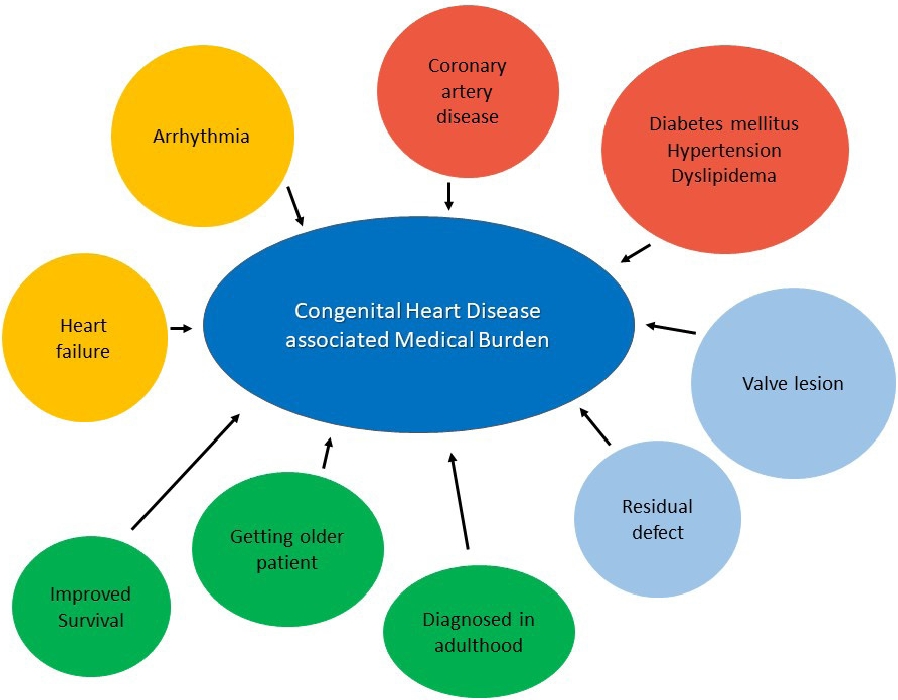
· As the number of patients with congenital heart disease increases, the medical burden increases.
· Various fusion imaging techniques using percutaneous procedures have been introduced.
· With advances in technology, convenient ambulatory devices have been introduced.
· A well-organized team approach is required to resolve advanced heart failure in patients with congenital heart disease.
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Arrhythmias in pediatric patients with COVID-19
- Ji-Eun Ban
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):348-349. Published online June 14, 2023
-
· Childrens with coronavirus disease 2019 less commonly display life-threatening arrhythmias, including premature atrial or ventricular beats, or conduction disturbances such as first-degree atrioventricular blocks.
· Life-threatening arrhythmias (e.g., nonsustained or sustained ventricular tachycardia, atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation, complete atrioventricular block) occur in children with sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection suffering from myocarditis or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C).
· Monitoring clinical status and assessing and managing arrhythmias are crucial in MIS-C.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
- SARS-CoV-2 fecal shedding pattern in pediatric patients with acute COVID-19 or COVID-19-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome
- Setareh Mamishi, Fatemeh Jalali, Sepideh Benvari, Babak Pourakbari, Mohammad Reza Abdolsalehi, Reihaneh Hosseinpour Sadeghi, Mohammad Shahbabaie, Amene Navaeian, Shima Mahmoudi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):366-368. Published online June 14, 2023
-
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Trends of vitamin D in asthma in the pediatric population for two decades: a systematic review
- Myongsoon Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):339-347. Published online June 14, 2023
-
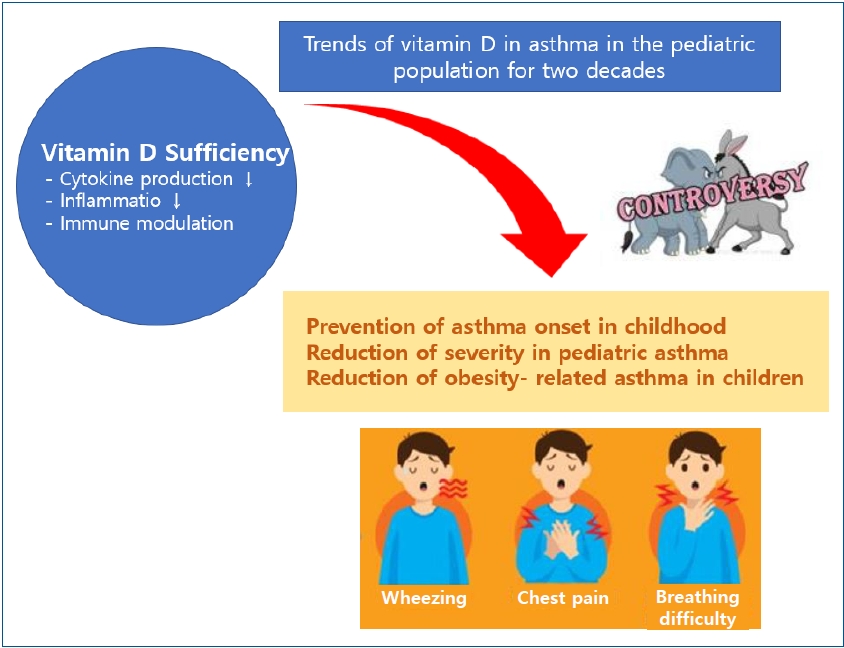
· Vitamin D may affect asthma via multiple mechanisms, including lung and optimal immune system functions.
· Many clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin D on asthma onset and aggravation. However, definitive clinical trials are lacking, and reports have detailed contradictory effects of vitamin D in children with asthma.
· Some exciting reports stated that obesity and vitamin D deficiency are associated with increased asthma symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Seroprevalence of maternal peripartum human T-cell lymphotropic virus type-1 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the Nigerian literature
- Abdulrasheed Usman, Muhammad Hamis Musa, Bukhari Isah Shuaib, Olayemi Balogun, Mukhtar Adeiza
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):307-316. Published online December 22, 2022
-
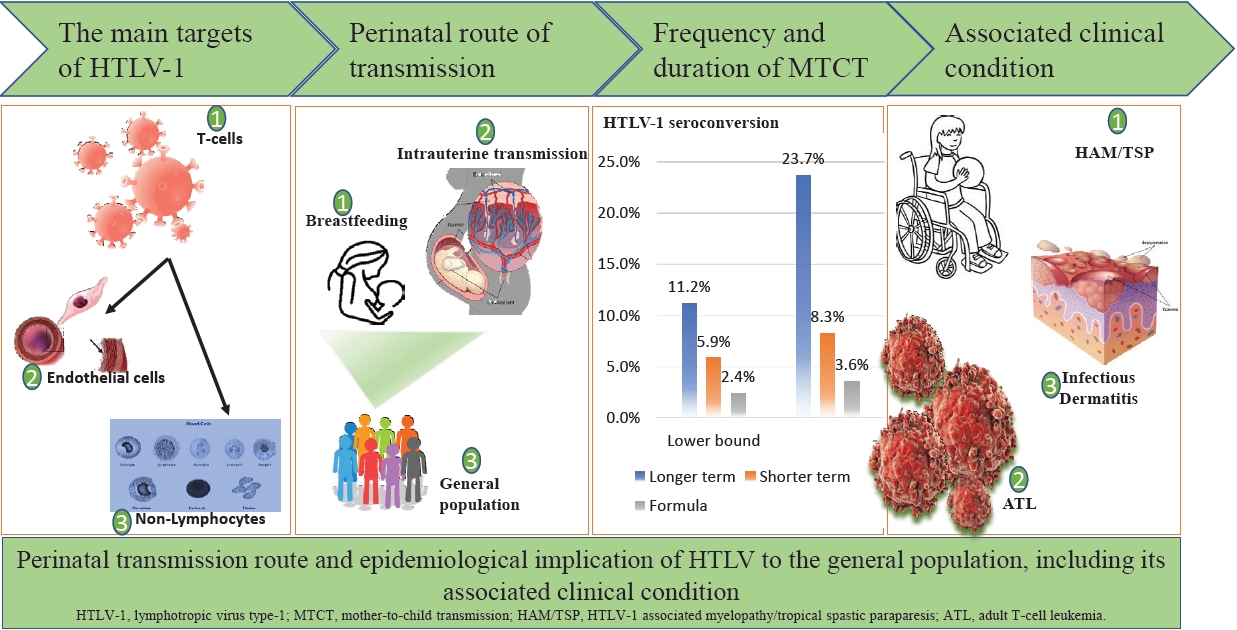
The peripartum period is an important transmission time for human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 (HTLV-1) infection, mainly via breastfeeding and partly through the placental tissues of carrier mothers. Although most HTLV-1–infected individuals are asymptomatic, fetal and childhood infections often result in several diseases with disappointing treatment outcomes. An estimated HTLV-1 burden in Nigeria among perinatal women must be determined to enable rational planning of a comprehensive health care intervention.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
- Chest x-ray findings in children with COVID-19: lesson learned from referral hospitals in Medan, North Sumatera, Indonesia
- Andrew Limavady, Eka Airlangga, Ririe Fachrina Malisie, Ayodhia Pitaloka Pasaribu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):317-319. Published online May 16, 2023
-
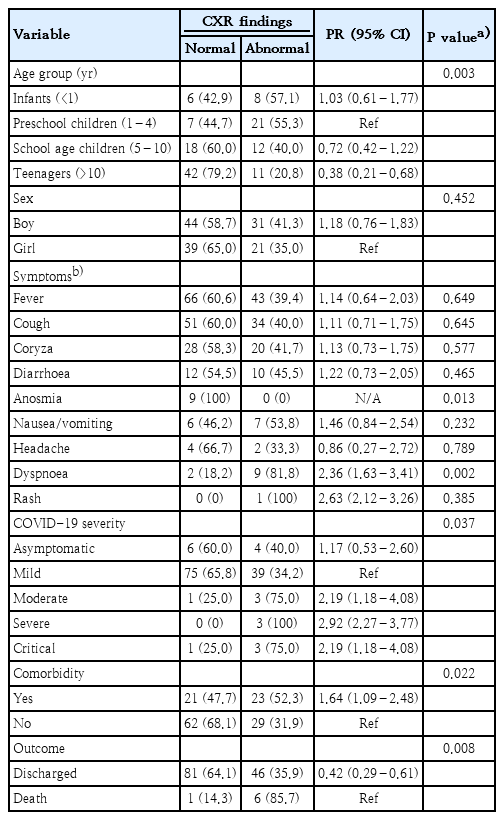
- Editorial
- Gastroenterology
- Gut microbiota’s impact on obesity
- Sujin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(7):294-295. Published online June 14, 2023
-

· An imbalance of the gut microbiota with a relative increase in Firmicutes versus Bacteroidetes is associated with the pathogenesis of obesity.
· Dysbiosis is associated with microbial genes associated with short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) production and increased colonic SCFA levels. SCFAs have also been shown to regulate appetite and satiety hormones, which can affect food intake and energy balance.
· A dietary high-fat intake is reportedly associated with increased plasma lipopolysaccharide. Altered Toll-like receptor-4 signaling leads to propagating the cascade of further inflammation and promoting insulin resistance.
- Perspective
- Other
- New public-centered child protection system in Korea
- We Sun Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):179-181. Published online April 18, 2023
-
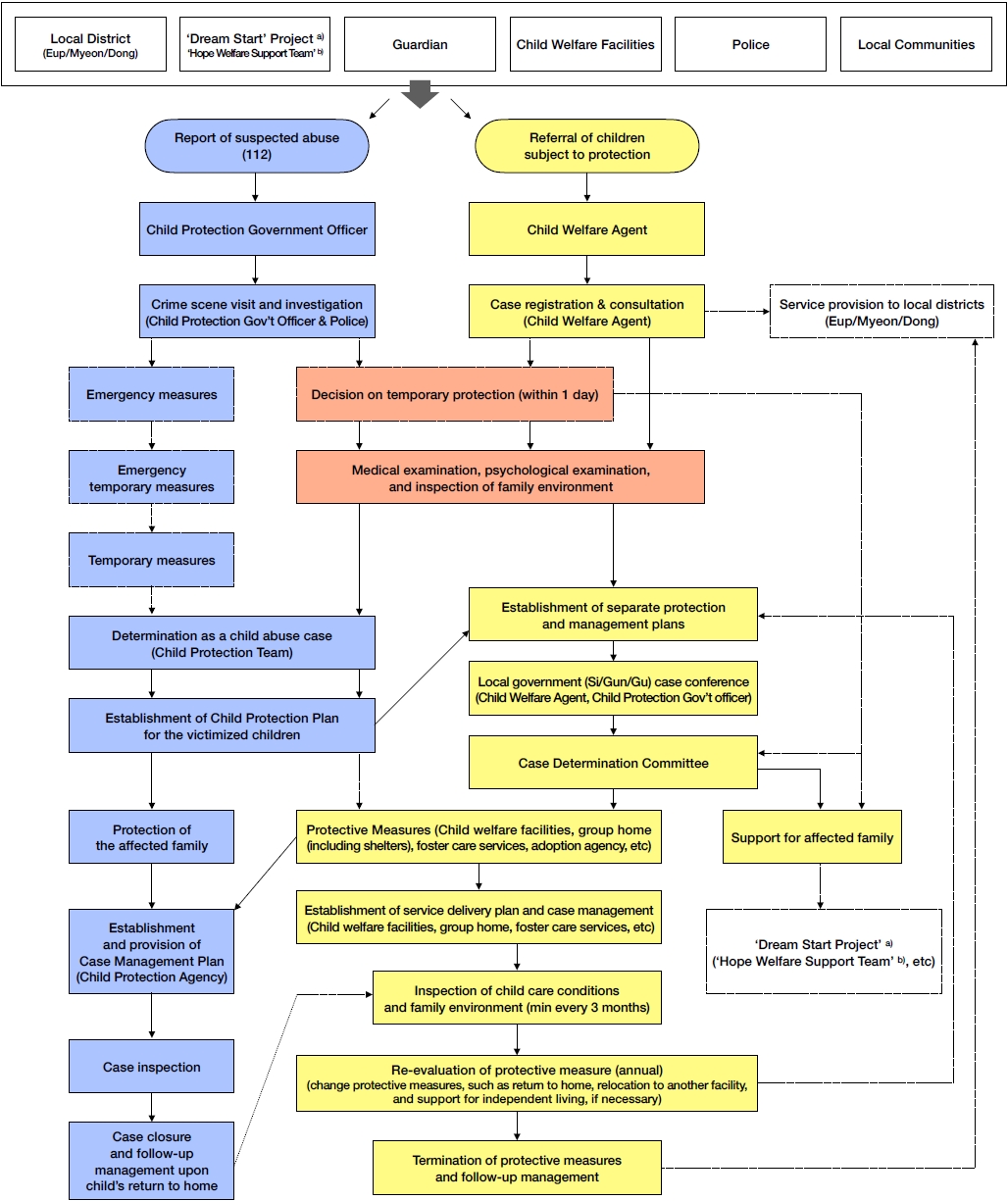
Korea’s child abuse response system was transformed under policy change in April 2020, from what was previously operated on a private-centered basis to a focus on the public sector with expanded role of local governments. Promising outcomes are expected with new system as greater governmental intervention will effectively protect at-risk children with acceleration in institutional collaboration and expertise in information management and administration.
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Understanding the usefulness of electroencephalography source localization
- Bo Lyun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):210-211. Published online April 18, 2023
-
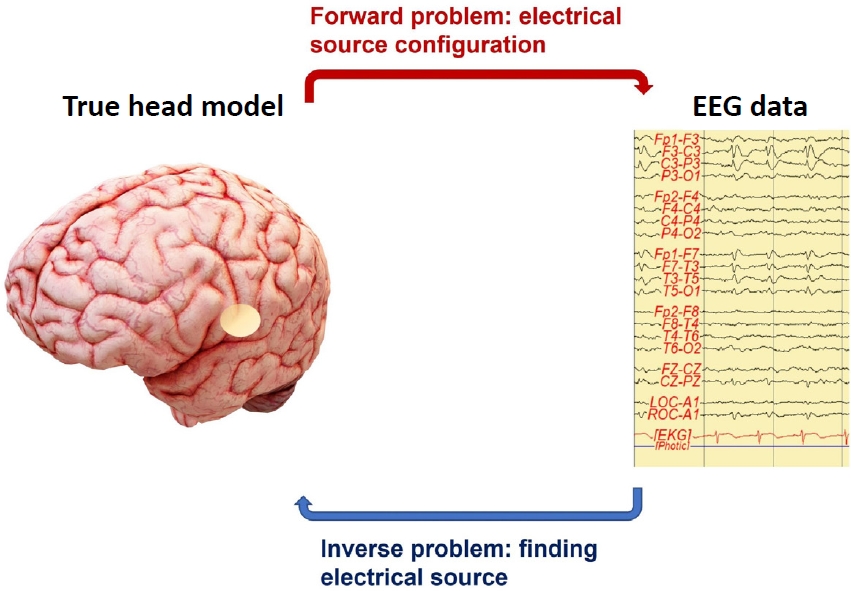
· Electroencephalography (EEG) records brain activity with high temporal resolution.
· EEG source localization, combined with other functional or structural imaging methods, provides information about brain network and connectivity in clinical neuroscience.
· EEG source localization identifies brain location from electrical current sources in several neuropsychiatric diseases such as epilepsy, attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder, and anxiety disorders.
- Infection
- Impact and role of vitamins as immunonutrition in children during COVID-19 pandemic
- Yoo Min Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(5):212-214. Published online April 18, 2023
-

· Vitamins have effector mechanisms in the innate and adaptive immune systems and potential roles in preventing and reducing the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
· Vitamins may be immunonutrients in the treatment of COVID-19 infections and prevention of patient deterioration due to critical illness, thus demonstrating the significance of a nutritious, well-balanced diet.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics of pediatric patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus common human coronaviruses: a national multicenter study
- In Suk Sol, Eun Lee, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Yong Ju Lee, Hye Yung Yum, Mi-Hee Lee, Mi Ae Chu, Hui Jeong Moon, Hyo-Bin Kim, Ju Hee Seo, Jung Yeon Shim, Ji Young Ahn, Yoon Young Jang, Hai Lee Chung, Eun Hee Chung, Kyunghoon Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Cheol Hong Kim, Yang Park, Meeyong Shin, Kyung Suk Lee, Man Yong Han, Soo-Jong Hong, Eun Kyeong Kang, Chang Keun Kim; on behalf of The Pneumonia & Respiratory Disease Study Group of Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):134-141. Published online December 22, 2022
-

Question: The clinical differences between severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and human coronaviruses (HCoV) in children remain unknown.
Finding: This study compared the clinical findings of children infected with SARS-CoV-2 versus HCoV. Its findings suggest that children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 have a milder clinical course than those with HCoV.
Meaning: The clinical course of children and adolescents with SARS-CoV-2 should be closely monitored during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic.
- Hematology
- Changes and correlations of T-cell coinhibitory molecule programmed death-1 and interferon-γ in pediatric immune thrombocytopenia
- Fady Mohamed El-Gendy, Amira M.F. Shehata, Esam Awad Abd El-Kawy, Mahmoud Ahmed El-Hawy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):127-133. Published online February 24, 2023
-

Question: What are the PD-1+ CD4+ T cells percentages and serum interferon gamma (IFN-γ) levels of pediatric patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)?
Finding: Compared with healthy controls, the PD-1+ CD4+ T cells percentages and IFN-γ levels were significantly higher in ITP patients before and 1 month after therapy.
Meaning: Our findings suggest that PD-1+ CD4+ T cells and IFN-γ are involved in the pathophysiological process of ITP.
- Editorial
- Emergency Medicine
- Current diagnosis and image-guided reduction for intussusception in children: teamwork approach
- Ji-Hyun Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):66-67. Published online September 1, 2022
-
· The successful and safe enema reduction of intussusception depends primarily on the experience and preference of the radiologists and the availability of resources.
· The establishment of a standardized manual or protocol for reduction and pre-reduction treatment of intussusception, along with the collaboration of pediatricians, radiologists, and surgeons, is expected to improve the treatment success rate.
- Letter to the Editor
- Critical Care Medicine
- Role of serum bilirubin-to-albumin ratio as a prognostic index in critically ill children
- You Min Kang, Ga Eun Kim, Mireu Park, Jong Deok Kim, Min Jung Kim, Yoon Hee Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Myung Hyun Son, Soo Yeon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):85-87. Published online December 5, 2022
-
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Lumbar puncture or not: when does febrile seizure require a neurodiagnostic evaluation?
- Seung Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(2):68-69. Published online December 9, 2022
-
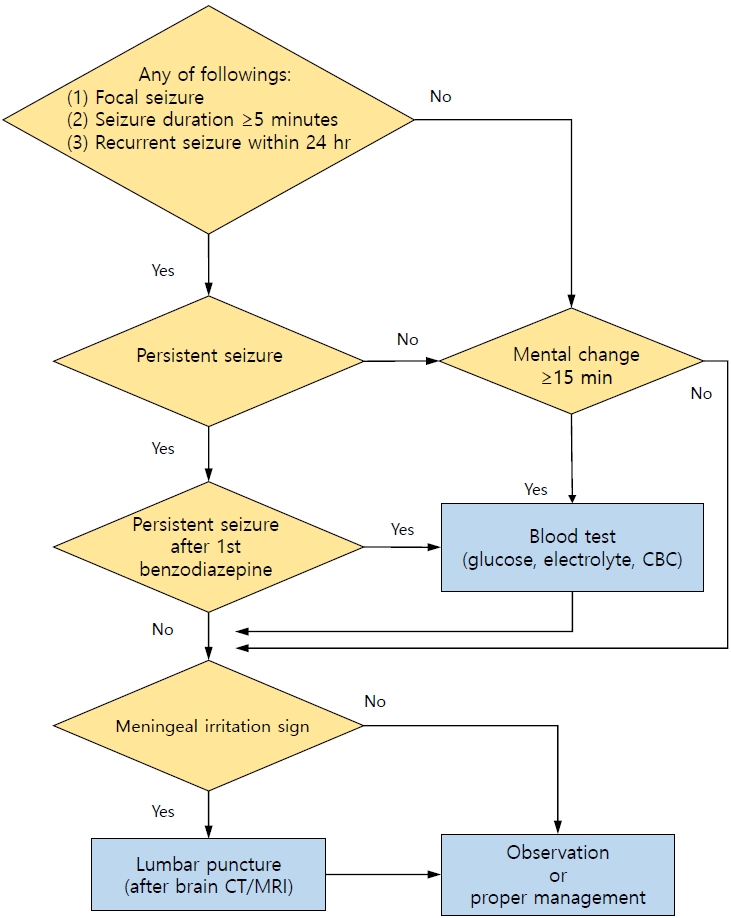
· A neurodiagnostic evaluation (lumbar puncture, blood tests, electroencephalography, and neuroimaging) is not indicated in most patients with simple febrile seizures.
· A lumbar puncture is indicated when a central nervous system infection is suspected in any patient with febrile seizures.
· Blood tests (glucose, electrolytes, and complete blood count) are indicated in patients with persistent seizure after benzodiazepine treatment, prolonged loss of consciousness, poor general condition, or signs of dehydration.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Applications of genomic research in pediatric endocrine diseases
- Ja Hye Kim, Jin-Ho Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):520-530. Published online June 14, 2023
-
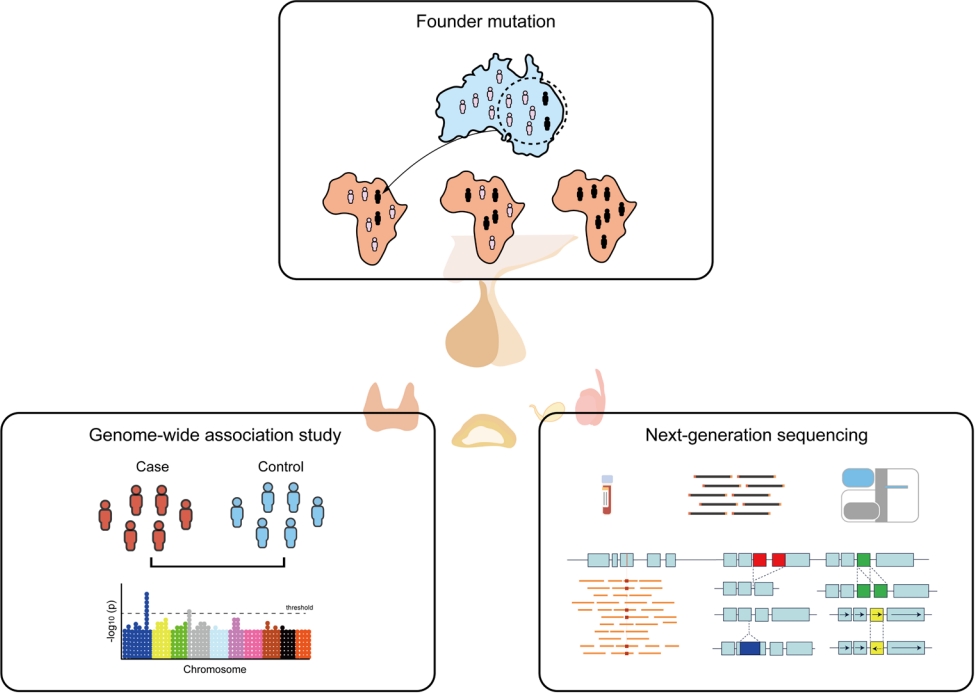
· Recent advances in molecular genetics have improved our understanding of pediatric endocrine disorders and are now used in mainstream medical practice.
· Genome-wide association studies can increase our understanding of the biological mechanisms of disease and inform new therapeutic options.
· The identification of founder mutations leads to the efficient localization of the genes underlying Mendelian disorders.
· Next-generation sequencing technologies benefit clinical practice and research of pediatric endocrinology.
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.












