|
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) is a clinical syndrome featuring various symptoms (shortness of breath, ankle swelling, fatigue) and signs (pulmonary crackles, peripheral edema).
· Congenital heart diseases are the most common underlying etiology of PHF, whereas myocarditis and primary cardio-myopathies are common in children without structural ab-normalities.
· PHF pathophysiology is complex and multifactorial and varies by etiology and age.
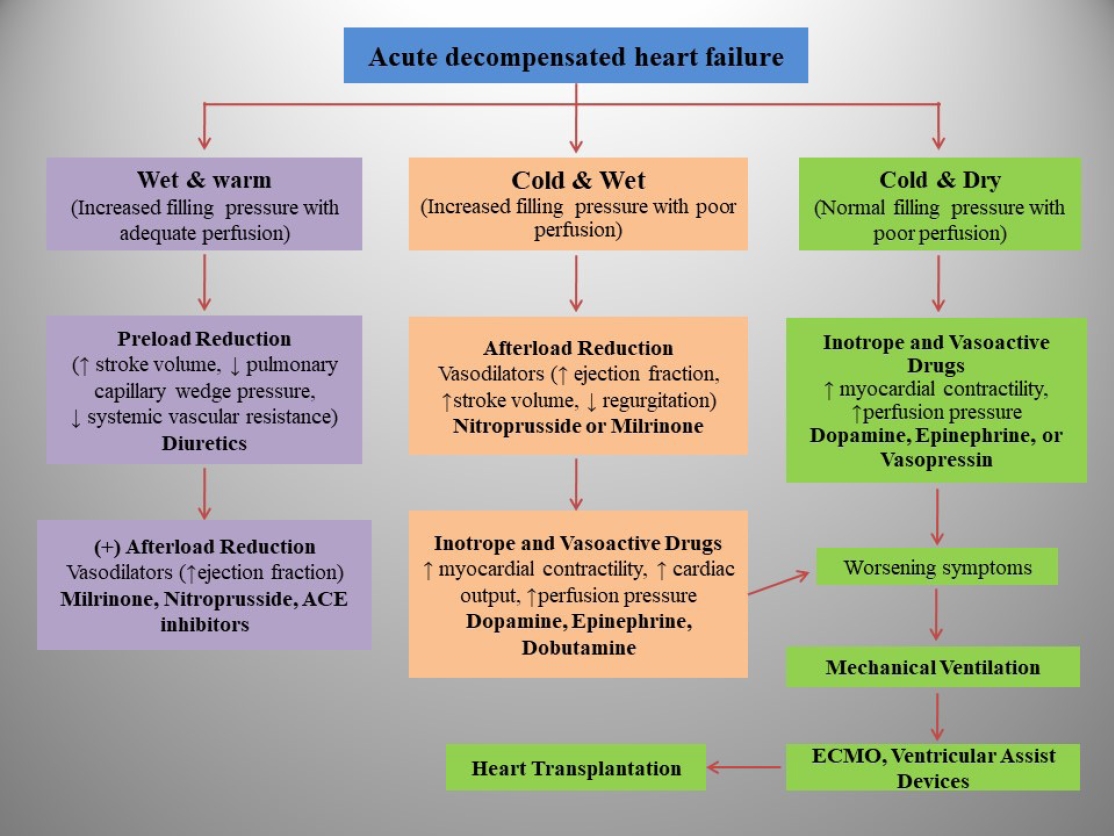
· PHF management includes decongestive therapy, treatment of underlying causes, preventing progression, and managing pulmonary or systemic obstructions.
· Drugs should be chosen based on pharmacodynamics, clinical manifestations, hemodynamic state, and renal function. |


