Infection
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Infection
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (64)
- Cardiology (81)
- Critical Care Medicine (15)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (65)
- Gastroenterology (76)
- General Pediatrics (58)
- Genetics and Metabolism (26)
- Hematology (20)
- Immunology (16)
- Infection (82)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (127)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (54)
- Neurology (96)
- Nutrition (33)
- Oncology (19)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (35)
- Rheumatology (4)
- Other (44)
- Perspective
- Infection
- COVID-19 in children: reasons for uneventful clinical course
- Sweni Shah, Ramachandran Meenakshisundaram, Subramanian Senthilkumaran, Ponniah Thirumalaikolundusubramanian
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):237-238. Published online June 18, 2020
-
- Review Article
- Infection
- Epidemiology and clinical features of coronavirus disease 2019 in children
- Soo-Han Choi, Han Wool Kim, Ji-Man Kang, Dong Hyun Kim, Eun Young Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):125-132. Published online April 6, 2020
-
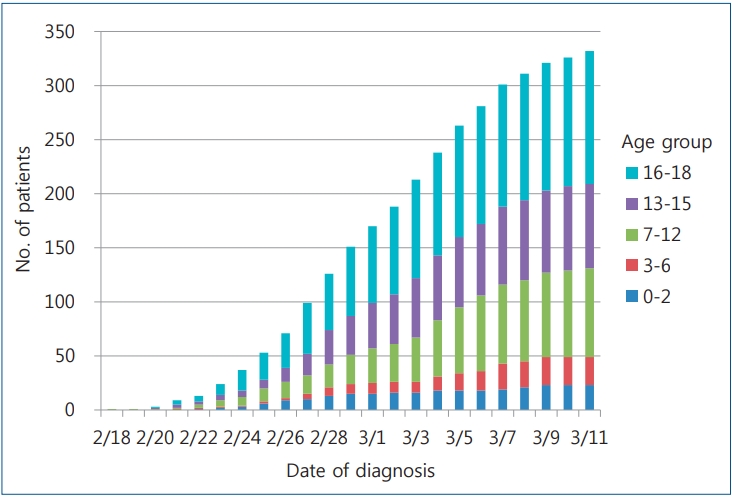
Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), which started in Wuhan, China, in December 2019 and declared a worldwide pandemic on March 11, 2020, is a novel infectious disease that causes respiratory illness and death. Pediatric COVID-19 accounts for a small percentage of patients and is often milder than that in adults; however, it can progress to severe disease in some cases. Even neonates...
- Epidemiology, virology, and clinical features of severe acute respiratory syndrome -coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2; Coronavirus Disease-19)
- Su Eun Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):119-124. Published online April 2, 2020
-

A cluster of severe pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan City, Hubei province in China emerged in December 2019. A novel coronavirus named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) was isolated from lower respiratory tract sample as the causative agent. The current outbreak of infections with SARS-CoV-2 is termed Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) by the World Health Organization (WHO). COVID-19...
- Central line-associated bloodstream infections in neonates
- Hye Jung Cho, Hye-Kyung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(3):79-84. Published online December 19, 2018
-
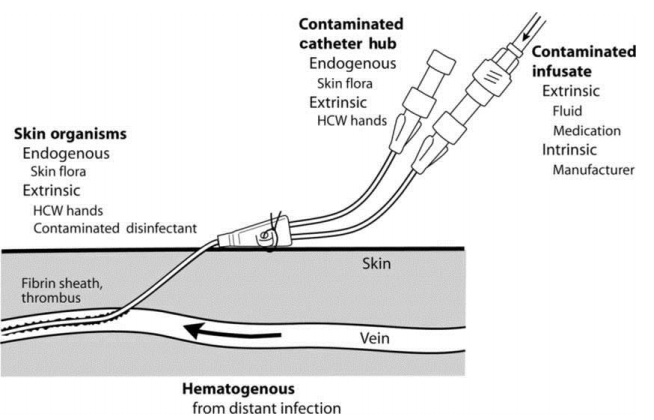
Newborn infants, including premature infants, are high-risk patients susceptible to various microorganisms. Catheter-related bloodstream infections are the most common type of nosocomial infections in this population. Regular education and training of medical staffs are most important as a preventive strategy for central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs). Bundle approaches and the use of checklists during the insertion and maintenance of central...
- Case Report
- Infection
- Scabies mimicking graft versus host disease in a hematopoietic cell transplant recipient
- Dongsub Kim, Soo-Han Choi, Dong Youn Lee, Juyoun Kim, Eunjoo Cho, Keon Hee Yoo, Hong Hoe Koo, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(11):371-373. Published online November 9, 2018
-
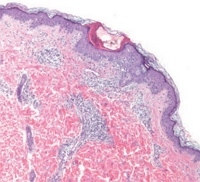
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the mite, Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis. Complex responses to scabies mites in the innate, humoral, and cellular immune systems can cause skin inflammation and pruritus. Diagnosis can be challenging because scabies resembles other common skin conditions. We report the first Korean case of scabies in a hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) recipient,...
- Original Article
- Infection
- A contact investigation after exposure to a child with disseminated tuberculosis mimicking inflammatory bowel disease
- Dongsub Kim, Sodam Lee, Sang-Hee Kang, Mi-Sun Park, So-Young Yoo, Tae Yeon Jeon, Joon-Sik Choi, Bora Kim, Jong Rim Choi, Sun Young Cho, Doo Ryeon Chung, Yon Ho Choe, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(11):366-370. Published online November 15, 2018
-
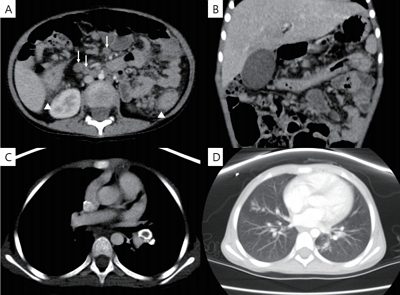
Purpose: Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the most important diseases that cause significant mortality and morbidity in young children. Data on TB transmission from an infected child are limited. Herein, we report a case of disseminated TB in a child and conducted a contact investigation among exposed individuals. Methods: A 4-year-old child without Bacille Calmette-Guérin vaccination was diagnosed as having culture-proven...
- Usefulness of the procalcitonin test in young febrile infants between 1 and 3 months of age
- In Sul Lee, Young Jin Park, Mi Hyeon Jin, Ji Young Park, Hae Jeong Lee, Sung Hoon Kim, Ju Suk Lee, Cheol Hong Kim, Young Don Kim, Jun Hwa Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(9):285-290. Published online September 15, 2018
-

Purpose: To study the usefulness of the procalcitonin (PCT) test in young febrile infants between 1 and 3 months of age. Methods: We evaluated the medical records of 336 febrile infants between 1 and 3 months of age who visited the Emergency Department or outpatient department of Samsung Changwon Hospital from May 2015 to February 2017, and analyzed the clinical characteristics...
- Clinical and laboratory profiles of hospitalized children with acute respiratory virus infection
- Eunjin Choi, Kee-Soo Ha, Dae Jin Song, Jung Hwa Lee, Kwang Chul Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(6):180-186. Published online June 25, 2018
-

Purpose Despite the availability of molecular methods, identification of the causative virus in children with acute respiratory infections (ARIs) has proven difficult as the same viruses are often detected in asymptomatic children.
Methods Multiplex reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays were performed to detect 15 common respiratory viruses in children under 15 years of age who were hospitalized with ARI between January 2013...
- Association between vitamin D and urinary tract infection in children
- Abolfazl Mahyar, Parviz Ayazi, Sara Safari, Reza Dalirani, Amir Javadi, Shiva Esmaeily
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(3):90-94. Published online March 19, 2018
-
Purpose The present study aimed to determine the relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) level and Urinary tract infections (UTIs) in children.
Methods In this case-control study, 70 children with UTI (case group) were compared with 70 healthy children (control group) in terms of serum 25(OH)D levels. The children were between 1 month and 12 years of age. Serum 25(OH)D levels were measured...
- Treatment-failure tularemia in children
- Arzu Karlı, Gülnar Şensoy, Şule Paksu, Muhammet Furkan Korkmaz, Ömer Ertuğrul, Rıfat Karlı
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(2):49-52. Published online February 28, 2018
-
Purpose Tularemia is an infection caused by
Francisella tularensis . Its diagnosis and treatment may be difficult in many cases. The aim of this study was to evaluate treatment modalities for pediatric tularemia patients who do not respond to medical treatment.Methods A single-center, retrospective study was performed. A total of 19 children with oropharyngeal tularemia were included.
Results Before diagnosis, the duration of symptoms in...
- Case Report
- Infection
- Acute pancreatitis in hand, foot and mouth disease caused by Coxsackievirus A16: case report
- Byungsung Park, Hyuckjin Kwon, Kwanseop Lee, Minjae Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(10):333-336. Published online October 20, 2017
-
Coxsackievirus A16 (CA16), which primarily causes hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD), is associated with complications, such as encephalitis, acute flaccid paralysis, myocarditis, pericarditis, and shock. However, no case of pancreatitis associated with CA16 has been reported in children. We report a case of CA16-associated acute pancreatitis in a 3-year-old girl with HFMD. She was admitted because of poor oral...
- Original Article
- Infection
- The impact of an educational intervention on parents' decisions to vaccinate their <60-month-old children against influenza
- Aery Choi, Dong Ho Kim, Yun Kyung Kim, Byung Wook Eun, Dae Sun Jo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(8):254-260. Published online August 14, 2017
-
Purpose Seasonal influenza can be prevented by vaccination. Disease prevention in children aged <60 months is of particular importance because of the associated familial and societal burden. Considering that caretakers make the decision to vaccinate their children, the identification of drivers and barriers to vaccination is essential to increase influenza vaccination coverage.
Methods A total of 639 parents participated in the pre- and...
- Editorial
- Infection
- Additional corticosteroids or alternative antibiotics for the treatment of macrolide-resistant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia - Eun-Ae Yang, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(8):245-247. Published online August 14, 2017
-
- Original Article
- Infection
- Uropathogenic
Escherichia coli ST131 in urinary tract infections in children - Ki Wook Yun, Mi-Kyung Lee, Wonyong Kim, In Seok Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(7):221-226. Published online July 31, 2017
-
Purpose Escherichia coli sequence type (ST) 131, a multidrug-resistant clone causing extraintestinal infections, has rapidly become prevalent worldwide. However, the epidemiological and clinical features of pediatric infections are poorly understood. We aimed to explore the characteristics of ST131Escherichia coli isolated from Korean children with urinary tract infections.Methods We examined 114 uropathogenic
E. coli (UPEC) isolates from children hospitalized at Chung-Ang University...
- Effects of clarithromycin treatment in scrub typhus in children: comparison with chloramphenicol and azithromycin
- Min Lee, June Kim, Dae Sun Jo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(4):124-127. Published online April 25, 2017
-
Purpose Chloramphenicol and tetracycline are not recommended for treating scrub typhus in pediatric patients because of potential side effects, such as aplastic anemia or tooth discoloration. While clarithromycin has recently been used in adults, few reports have been published on its effects in pediatric patients. We report the clinical profiles of pediatric scrub typhus and the effects of clarithromycin on scrub...
- Etiology and clinical characteristics of fever of unknown origin in children: a 15-year experience in a single center
- Yi-Seul Kim, Kyung-Ran Kim, Ji-Man Kang, Jong-Min Kim, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(3):77-85. Published online March 27, 2017
-
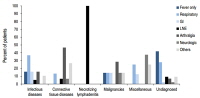
Purpose Fever is one of the most common symptoms in children. In previous studies, infectious disease was the most common cause of pediatric fever of unknown origin (FUO). The aim of this study is to investigate the etiology, clinical characteristics and prognosis of pediatric FUO in 21 century with more diagnostics available and to analyze the factors for certain disease categories.
Methods Among...
- Review Article
- Infection
- Recommended immunization schedule for children and adolescents: Immunization Guideline (8th edition) released by the Korean Pediatric Society in 2015
- Jong-Hyun Kim, Eun Hwa Choi, Su Eun Park, Yae-Jean Kim, Dae Sun Jo, Yun-Kyung Kim, Byung-Wook Eun, Jina Lee, Soo-Young Lee, Hyunju Lee, Ki Hwan Kim, Kyung-Hyo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(12):461-465. Published online December 31, 2016
-
This report includes the recommended immunization schedule table for children and adolescents based on the 8th (2015) and revised 7th (2012) Immunization Guidelines released by the Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society (KPS). Notable revised recommendations include: reorganization of the immunization table with a list of vaccines on the vertical axis and the corresponding age on the...
- Erratum
- Infection
- Erratum:
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in pediatric patients: an analysis of 15 confirmed consecutive cases during 14 years - Kyung-Ran Kim, Jong Min Kim, Ji-Man Kang, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(9):387-387. Published online September 21, 2016
-
- Case Report
- Infection
- Distinctive clinical features of HPeV-3 infection in 2 neonates with a sepsis-like illness
- Jung Sook Yeom, Ji Sook Park, Ji-Hyun Seo, Eun Sil Park, Jae-Young Lim, Chan-Hoo Park, Hyang-Ok Woo, Hee-Shang Youn, Ok Jeong Lee, Tae-Hee Han, Ju-Young Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(7):308-311. Published online July 31, 2016
-
We report a human parechovirus-3 (HPeV-3) infection in 2 neonates who had prolonged fever (>5 days) with palmar-plantar erythema. This distinctive rash was observed 4–5 days after fever onset, just before defervescence. Elevated aspartate aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase, and ferritin levels were characteristic laboratory findings in the 2 cases, suggesting tissue damage caused by hypercytokinemia. Case 1 was treated with intravenous...
- Original Article
- Infection
- Usefulness of interferon-γ release assay for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection in young children
- Ki Wook Yun, Young Kwang Kim, Hae Ryun Kim, Mi Kyung Lee, In Seok Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(6):256-261. Published online June 30, 2016
-
Purpose Latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) in young children may progress to severe active tuberculosis (TB) disease and serve as a reservoir for future transmission of TB disease. There are limited data on interferon-γ release assay (IGRA) performance in young children, which our research aims to address by investigating the usefulness of IGRA for the diagnosis of LTBI.
Methods We performed a tuberculin skin...
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in pediatric patients: an analysis of 15 confirmed consecutive cases during 14 years- Kyung-Ran Kim, Jong Min Kim, Ji-Man Kang, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(6):252-255. Published online June 30, 2016
-
Purpose Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia occurs in various immunocompromised patients. Despite the prophylaxis strategies in clinical practice, certain patients developP. jirovecii pneumonia. This study was performed to investigate pediatric cases withP. jirovecii pneumonia in a single center.Methods We identified pediatric patients younger than 19 years with microbiologically confirmed
P. jirovecii pneumonia from January 2000 to February 2014. A retrospective chart review...
- Case Report
- Infection
- Tuberculosis-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adolescent diagnosed by polymerase chain reaction
- Ju-Hee Seo, Jun Ah Lee, Dong Ho Kim, Joongbum Cho, Jung Sub Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(1):43-46. Published online January 22, 2016
-
We present a case of tuberculosis-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a 14-year-old girl. The patient presented with weight loss, malaise, fatigue, prolonged fever, and generalized lymphadenopathy. Laboratory investigation revealed pancytopenia (white blood cells, 2,020 cells/µL; hemoglobin, 10.2 g/dL; platelets, 52,000 cells/µL), hypertriglyceridemia (229 mg/dL), and hyperferritinemia (1,420 ng/mL). Bone marrow biopsy showed a hypocellular bone marrow with a large numbers of...
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











