- Review Articles
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal family-centered care: evidence and practice models
- Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):171-177. Published online June 14, 2023
-
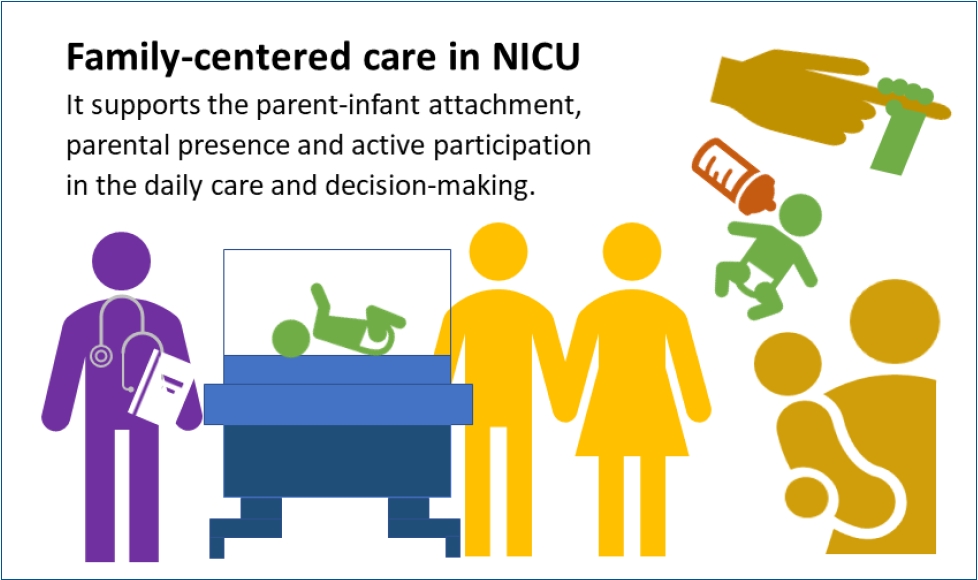
· Concrete evidence exists of early parent-infant attachment supported by family-centered care (FCC) in the neonatal intensive care unit.
· FCC involves the parents’ presence and participation in the infant’s care and decision-making.
· A private and comfortable space should be provided. A single-family room is ideal; however, a quiet space with a recliner can be a good alternative.
· Care culture changes and staff training are required.
- Cardiology
- Heart failure in children and adolescents: an update on diagnostic approaches and management
- Amit Agrawal, Dalwinder Janjua, Abdulrahman Ahmed Alsayed Ali Zeyada, Ahmed Taher Elsheikh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):178-190. Published online June 19, 2023
-
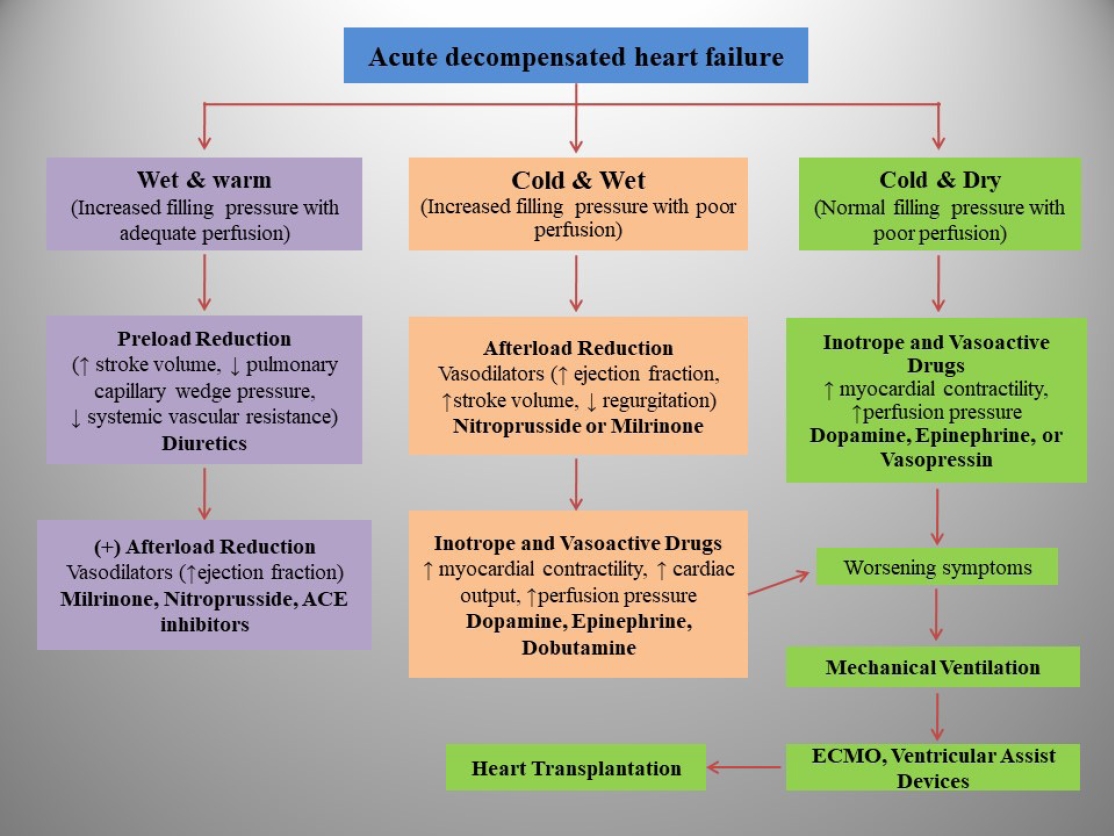
· Pediatric heart failure (PHF) is a clinical syndrome featuring various symptoms (shortness of breath, ankle swelling, fatigue) and signs (pulmonary crackles, peripheral edema).
· Congenital heart diseases are the most common underlying etiology of PHF, whereas myocarditis and primary cardio-myopathies are common in children without structural ab-normalities.
· PHF pathophysiology is complex and multifactorial and varies by etiology and age.
· PHF management includes decongestive therapy, treatment of underlying causes, preventing progression, and managing pulmonary or systemic obstructions.
· Drugs should be chosen based on pharmacodynamics, clinical manifestations, hemodynamic state, and renal function.
- Nutrition
- Macronutrients modified dietary intervention in the management of overweight/obese children and adolescents: a systematic review
- Jihyun Park, Oh Yoen Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):191-200. Published online July 11, 2023
-
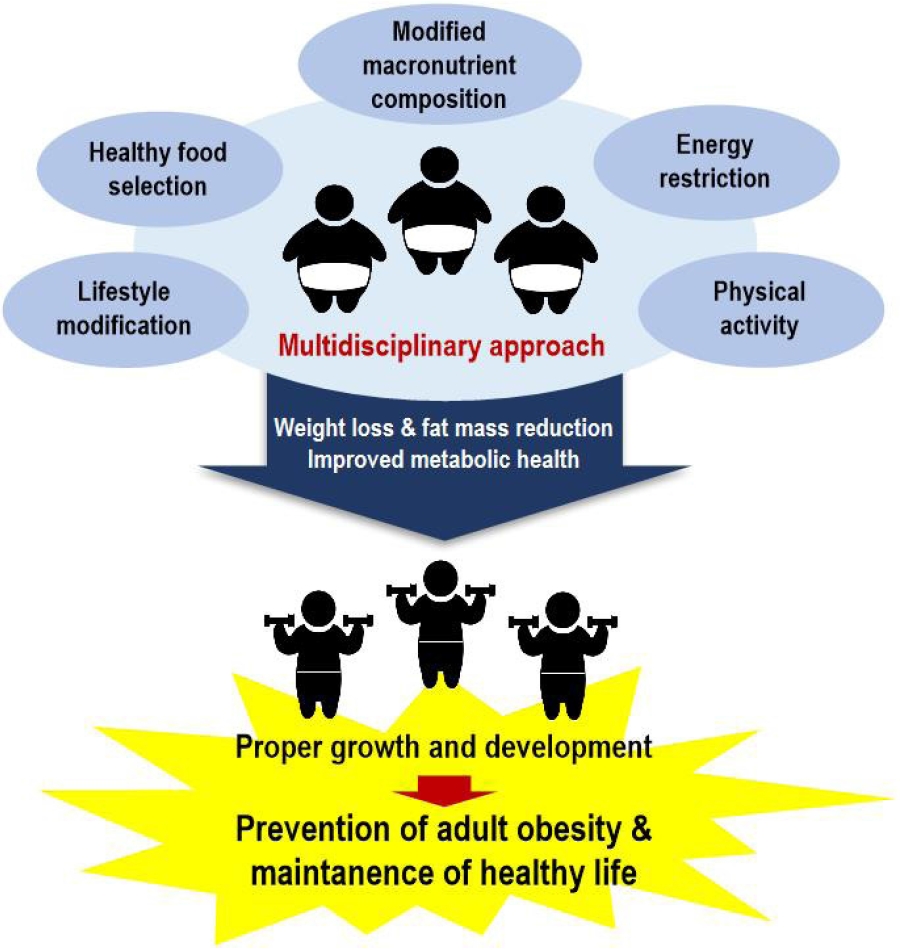
· Dietary macronutrient modifications affect the body composition of and metabolic markers in children and adolescents.
· Hypocaloric diets, regardless of macronutrient composition, are reportedly effective for weight loss in obese children.
· Future interventional studies with meta-analyses that include Korean children and adolescents are needed to provide basic information applicable to this population.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Trends in food allergen immunotherapy in Korea after changed national regulations
- Tae Won Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):201-202. Published online November 21, 2023
-
National regulations, academic guidelines, and clinical trends in food allergen immunotherapies (FA-AIT) differ among countries and have changed rapidly. Current officially approved FA-AIT are oral immunotherapy (OIT) using heated milk/egg in Korea and peanut OIT using standardized products in the United States and Europe. FA-AIT should be administered by specialist physicians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing severe allergic reactions inside and outside research settings.
- Original Articles
- Nutrition
- Effect of probiotics plus zinc supplementation on clinical outcomes of infants and children with acute infectious diarrhea: a randomized controlled trial
- Deldar Morad Abdulah, Saad Jbraeil Sulaiman, Zaid Waad Ahmed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):203-212. Published online February 19, 2024
-

Question: Does zinc supplementation along with probiotics affect disease severity or clinical outcomes of children with acute diarrhea?
Findings: This study indicated that zinc supplementation and probiotics had no effect on clinical improvement or disease severity among pediatric patients with acute diarrhea.
Meaning: Children who received probiotics plus zinc recovered faster than those who received probiotics only.
- Neurology
- Changes in frequency of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis and their viral causes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-center study
- Hyejin Na, Sanghoon Lee, Seo Hee Kim, Young Ok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):213-220. Published online March 19, 2024
-
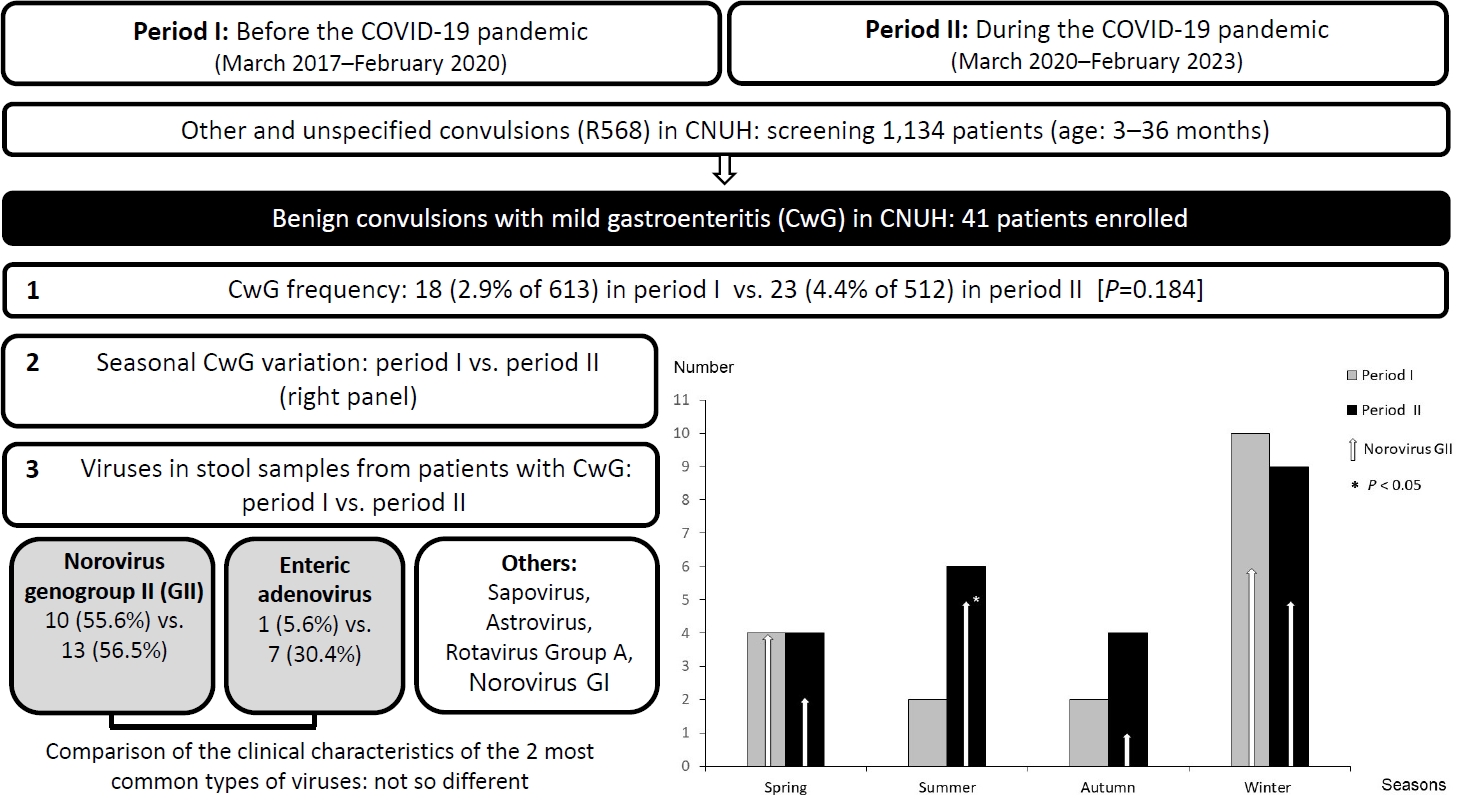
Question: Did coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) affect the frequency, seasonal variation, or virus type of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG)?
Findings: We compared 41 cases of CwG before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. After March 2020, frequency did not change significantly (18 patients vs. 23 patients), seasonal variation was lost, and number of cases of enteric adenovirus-associated CwG increased (1 cases vs. 7 cases).
Meaning: The COVID-19 pandemic affected CwG.
- Letter to the Editor
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
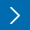
- Assessment of iron status and red cell parameters in healthy term small for gestational age neonates at birth
- Arif Hossain, Shorna Rahman, Shahana Akter, Ismat Jahan, Sanjoy Kumer Dey, Abdul Mannan, Mohammod Shahidullah
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):221-223. Published online March 19, 2024
-