Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Metabolic complications of obesity in children and adolescents
- Hyunjin Park, Jung Eun Choi, Seunghee Jun, Hyelim Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):347-355. Published online November 16, 2023
-
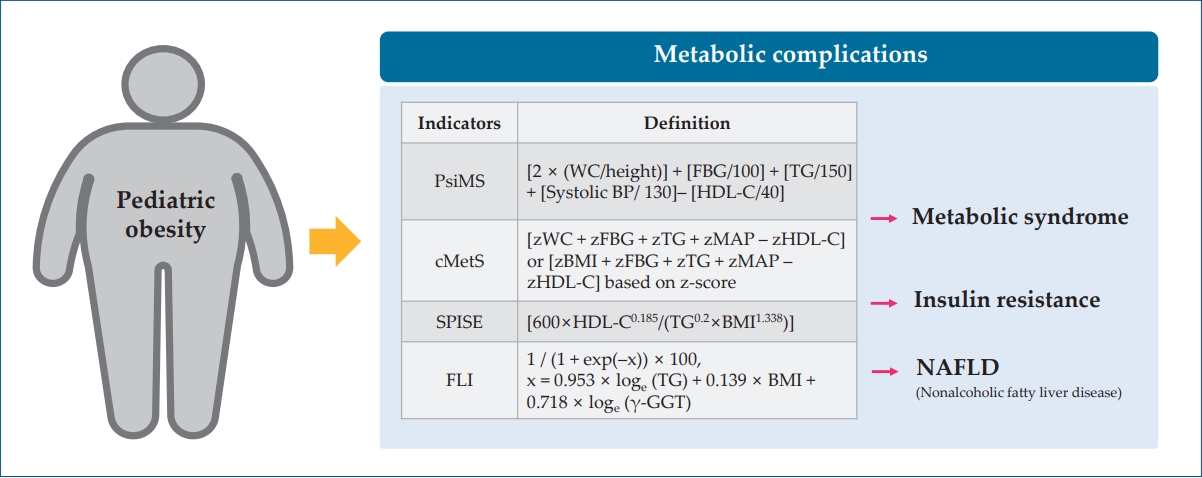
· Pediatric obesity increases the risk of metabolic complications (insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease) and long-term cardiovascular diseases.
· A new obesity definition and various indicators (continuous metabolic syndrome score, pediatric simple metabolic syndrome score, fatty liver index) have been proposed to evaluate children’s susceptibility to metabolic disorders.
· Laboratory and body composition tests in pediatric screenings can identify groups at high risk of metabolic complications of obesity.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hyperandrogenemia in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Ozlem Kara, Hanife Aysegul Arsoy, Murat Keskin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(9):395-402. Published online June 14, 2023
-

Question: Is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) a risk factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in adolescents?
Finding: The frequency of NAFLD did not increase in adolescents with PCOS. However, hyperandrogenemia was a risk factor for NAFLD.
Meaning: Adolescents with PCOS and hyperandrogenemia should be closely monitored for hepatic steatosis.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance in children
- Kyungchul Song, Ho-Seong Kim, Hyun Wook Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(12):512-519. Published online January 9, 2023
-

· The prevalence of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) increased from 8.2% in 2009 to 12.1% in 2018 in Korea.
· Laboratory tests, biomarkers, and imaging studies are used for the early detection of NAFLD.
· Insulin resistance is closely related to NAFLD.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Effects of probiotics combined with dietary and lifestyle modification on clinical, biochemical, and radiological parameters in obese children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized clinical trial
- Thushara Rodrigo, Samaranayake Dulani, Sumudu Nimali Seneviratne, Arjuna P. De Silva, Jerad Fernando, H. Janaka De Silva, Jayasekera , V. Pujitha Wickramasinghe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):304-311. Published online November 11, 2021
-
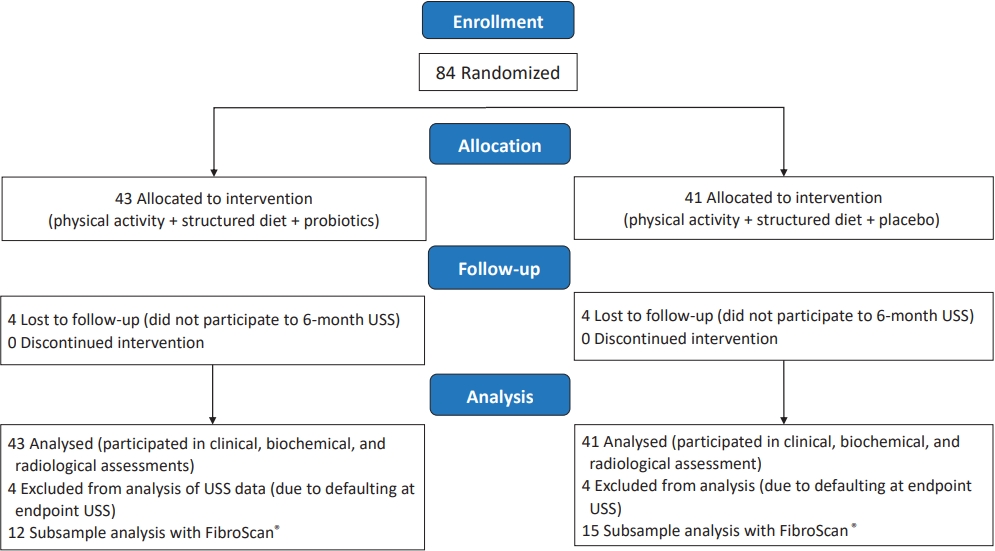
Question: Could probiotics be used as a therapeutic modality in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis?
Finding: There seem no added advantages over lifestyle modifications compared to Probiotics.
Meaning: There does not seem to be an advantage of probiotics over lifestyle modifications in improving obesity-associated metabolic derangement in children.
- Lipid accumulation product is a predictor of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in childhood obesity
- Bahar Özcabı, Salih Demirhan, Mesut Akyol, Hatice Öztürkmen Akay, Ayla Güven
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):450-455. Published online October 28, 2019
-

Background: Lipid accumulation product (LAP) is associated with the presence and severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in adults.
Purpose: Here we evaluated the ability of LAP to predict NAFLD in obese children. Methods: Eighty obese children (38 girls; age 6–18 years) were included. Anthropometric measurements and biochemical values were obtained from the patients’ medical records. LAP was calculated as [waist...
- Gastroenterology
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese and nonobese pediatric patients
- Eun Jeong Kim, Hyun Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(1):30-35. Published online September 17, 2018
-

Purpose: Obesity is risk factor for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). However, nonobese patients are also increasingly susceptible to NAFLD. The aim of this study was to compare the clinical characteristics of obese and nonobese pediatric patients with NAFLD. Methods: We retrospectively studied 68 patients who were diagnosed with NAFLD between January 2010 and October 2016 at 10–18 years of age....
- Clinical significance of serum alanine aminotransferase and lifestyle intervention in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Kyoung Ah Kwon, Peter Chun, Jae Hong Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(9):362-367. Published online September 21, 2016
-
Purpose This study aimed to investigate the clinical significance of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and the effect of lifestyle intervention on NAFLD.
Methods The clinical data of 86 children diagnosed with NAFLD were reviewed retrospectively. Forty-six patients belonged to the elevated ALT group and 40 to the normal ALT group. The clinical parameters of...
- Review Article
- Noninvasive diagnosis of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Hye Ran Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(2):45-51. Published online February 25, 2013
-
Because nonalcoholic steatohepatitis can progress towards cirrhosis even in children, early detection of hepatic fibrosis and accurate diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are important. Although liver biopsy is regarded as the gold standard of diagnosis, its clinical application is somewhat limited in children due to its invasiveness. Noninvasive diagnostic methods, including imaging studies, biomarkers of inflammation, oxidative stress,...
- Original Article
- The efficacy of aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index for assessing hepatic fibrosis in childhood nonalcoholic steatohepatitis for medical practice
- Earl Kim, Yunkoo Kang, Seungmin Hahn, Mi Jung Lee, Young Nyun Park, Hong Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(1):19-25. Published online January 29, 2013
-
Purpose Childhood obesity is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and it has become one of the most common causes of childhood chronic liver diseases which significant as a cause of liver related mortality and morbidity in children in the United States. The development of simpler and easier clinical indices for medical practice is needed to identify advanced hepatic fibrosis...
- Case Report
- A case of hepatopulmonary syndrome in a child with fatty liver disease secondary to hypopituitarism after craniopharyngioma resection
- Sun Ju Im, Hyun Seok Park, Hyoung Doo Lee, Jae Hong Park, Hee Ju Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(8):794-798. Published online August 15, 2007
-
Hepatopulmonary syndrome is a triad that includes: hepatic dysfunction, intrapulmonary vascular dilatation and abnormal arterial oxygenation. The incidence of intrapulmonary vascular dilatations, in adults with end-stage liver disease, has been reported to be 13% to 47%, however the incidence in children is unclear and the cases in Korean children have never been reported. The hepatopulmonary syndrome may occur as a... -
- Original Article
- Prevalence of the Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Children
- Sung Woog Hwang, Duk Hee Kim, Ho Seong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(1):13-20. Published online January 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Obesity is, along with metabolic syndrome, closely related with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. This study tried to evaluate the prevalence of nonalcoholic liver disease in obese children and verify the factors associated with the disease. Methods : Two hundred and seventy nine children who showed a body mass index of 95 percentile over the baseline in health examinations... -
- Prospective, Controlled Trial with Dipheny1-dimethy1-dicarboxylate in Children with Chronic Liver Diseses : The Effect on Lowering Serum Aminotransferase Levels
- Ji Eun Wunon, Sang Gil An, Ki Moon Cha, Yong Min Chung, Hee Sup Kim, Hann Tchah, Ho Jin Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(10):1378-1383. Published online October 15, 1995
-
Purpose : The prospective cotrolled study was performed to identify the effect of the dipheny1-dimethy1-dicarboxylate(PMC) on lowering serum transaminases in children with chronic liver diseases. Methods : The twenty patients were paticipated in this study who were followed up in the Department of Pediatrics of the Seoul Red Cross Hospital because of the elevated levels of serum alaine aminotransferase(ALT) and aspartate... -
-
- Clinical study on metabolic liver diseases in infancy and childhood.
- Jeong Lim Kim, Ki Sup Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(11):1477-1493. Published online November 30, 1991
-
The liver plays a central role in synthetic, degradative, and regulatory pathways involving the metabolism of carbohydrates, protein, lipid, mineral, and vitamins. There are many metabolic abnormalities or specific enzyme deficiencies that affect the liver. The clinical manifestations of metabolic diseases of the liver mimic infections, intoxications, and other systemic diseases. The comprehension of the pathogenesis on the inborn metabolic errors and early... -
- A Case of Congenital Hepatic Fibrosis with Hypersplenism.
- Hye Suk Hong, Yang Won Lee, Keon su Rhee, Young Hun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1987;30(12):1456-1460. Published online December 31, 1987
-
Congenital hepatic fibrosis is a relatively rare disease of liver in children and young adults, manifesting a heredofamilial tendency, that is characterized by hepatosplenomegaly, protal hypertension and frequent renal involvement. A generalized portal and interlobular fibrosis of liver are characteristic finding on microscopy, with relative preservation of hepatocyte and liver function. Recently, we have experienced a case of congenital hepatic fibrosis in a... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Congenital Hepatic Fibrosis.
- Son Moon Shin, Sang Il Lee, Joong Gon Kim, Hyo Seop Ahn, Hyung Ro Moon, Kwang Wook Ko, Je Geun Chi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1981;24(6):577-583. Published online June 15, 1981
-
Congenital hepatic fibrosis is a relatively rare liver disease in children and young adults,that is characterized by stony hard hepatomegaly and portal hypertension with relative preservation of liver function and underlying architecture. Since this Condition was first delineated by Kerr et al in 1961, approximately over 150 cases have been reported in the literature. However, congenital hepatic fibrosis was not... -
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









