Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Cytokine profile of Post–cardiopulmonary bypass in children
- Kantara Saelim, Kanokpan Ruangnapa, Jirayut Jarutach, Pongsanae Duangpakdee, Smonrapat Surassombatpattana, Pharsai prasertsan
-
Background: Open cardiac surgery involving cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) triggers a systemic inflammatory response that significantly affects clinical outcomes. However, the dynamics and specific roles of cytokine release after CPB in the pediatric population remain unclear.
Purpose: To evaluate the dynamics of cytokine levels and their association with low cardiac output syndrome (LCOS)-related outcomes. Methods: A prospective observational cohort study was conducted of 32 children who underwent elective open cardiac surgery... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.00836 [Accepted]
- Critical Care Medicine
- Serum amyloid A and proadrenomedullin as early markers in critically ill children with sepsis
- Nagwan Y. Saleh, Wafaa M. Abo El Fotoh, Mona S. Habib, Salem E. Deraz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(8):578-586. Published online February 26, 2025
-
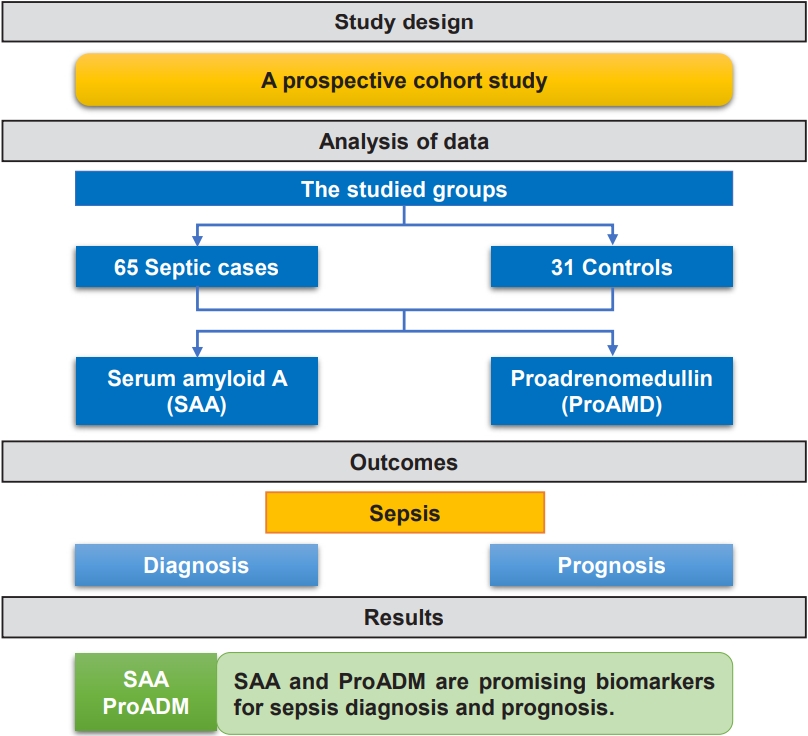
Question: Are serum amyloid A (SAA) and proadrenomedullin (proADM) levels early markers in critically ill children with sepsis?
Finding: This prospective case-control study included 65 critically ill children with sepsis admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit and 31 controls. SAA and proADM levels were significantly higher in patients versus controls.
Meaning: SAA and proADM are promising biomarkers for diagnosing and predicting outcomes in pediatric sepsis.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin levels can predict allergic disease development and atopic march in children
- Zak Callaway, Chang-Keun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):398-405. Published online February 3, 2025
-
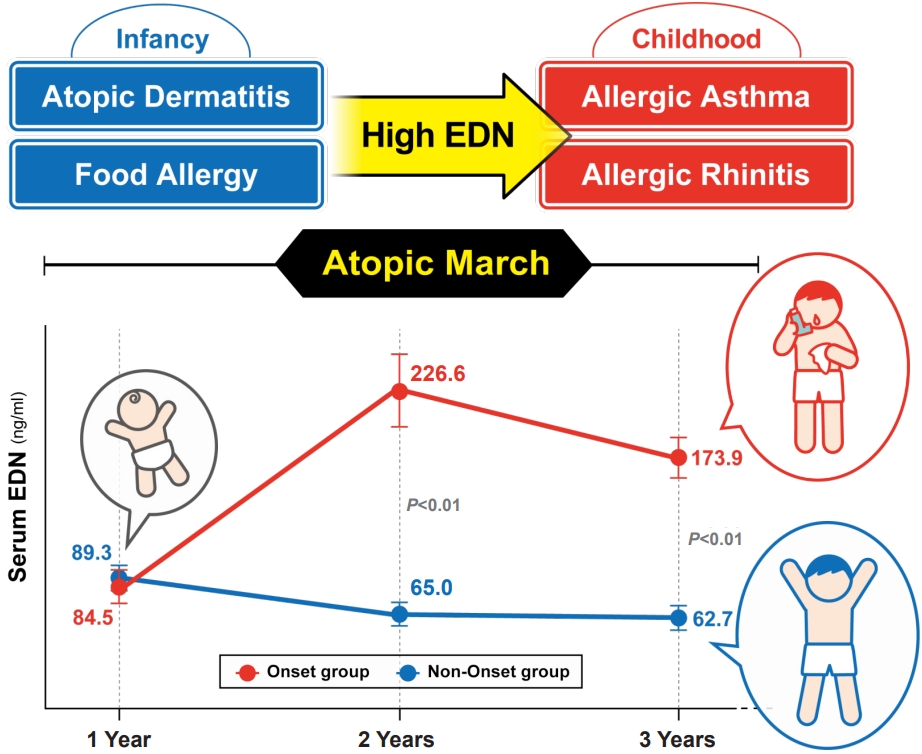
· Allergic march occurs in a subset of children, beginning with atopic dermatitis and progressing to food allergies, allergic rhinitis, and/or asthma. Its early diagnosis is important to slowing its progression.
· Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN), an excellent biomarker of eosinophil activity, is often elevated in allergic diseases.
· EDN levels have been used to predict allergic disease development and diagnose, treat, and monitor allergic diseases.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Differential roles of interleukin-6 and adrenomedullin in early diagnosis and mortality predictions in late-onset neonatal sepsis
- Emilly Henrique dos Santos, Gabriel Acca Barreira, Mariana Okay Saippa, Maria Carolina Pires Cruz, Karen Alessandra Rodrigues, Ronaldo Arkader, Thelma Suely Okay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):463-471. Published online December 23, 2024
-

Question: Can adrenomedullin (ADM) or interleukin-6 (IL-6) detect late-onset neonatal sepsis (LOS) at admission (area under the curve [AUC]>0.90) as an early diagnostic marker?
Finding: Only IL-6 consistently distinguished survivors from nonsurvivors (AUC>0.90) on admission and antibiotic treatment days 3 and 7. C-reactive protein level identified infections from day 3 but failed to predict outcomes (AUC<0.70).
Meaning: IL-6 level can improve LOS diagnosis and prognosis.
- Adolescence Medicine
- Relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and insulin resistance in excess-weight Latin children
- Mariano Nicolás Aleman, María Constanza Luciardi, Emilce Romina Albornoz, María Cristina Bazán, Adela Victoria Abregú
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):37-45. Published online December 21, 2023
-
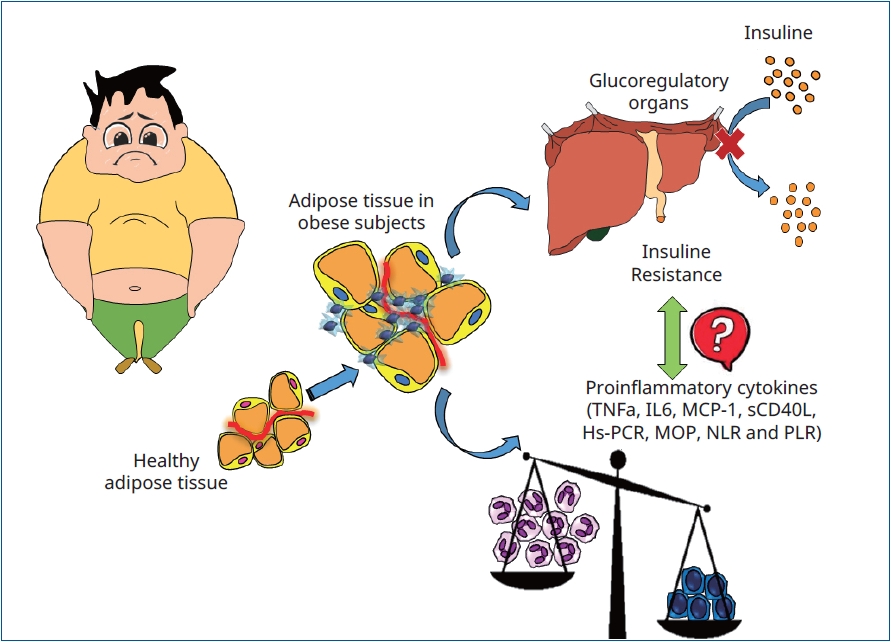
Question: What is the prevalence of insulin resistance (IR) in excess-weight Latin children, and can proinflammatory biomarkers predict it?
Finding: IR prevalence was elevated and tumor necrosis factor- α, interleukin-6, monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1, soluble CD40 ligand, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels were increased in excess-weight Latin children. However, none predicted IR status.
Meaning: These inflammatory biomarkers were unable to predict IR status. Therefore, further investigations are necessary.
- Review Article
- Other
- MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers for the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric diseases
- Hwal Rim Jeong, Il Tae Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):119-125. Published online May 24, 2023
-

MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression post transcriptionally, and MiRNA expression levels vary with developmental stages. MiRNAs play an important role in several biological processes in children, including growth, neuro-development, inflammation, and tumor formation. Research on miRNAs may uncover the molecular mechanisms underlying various pediatric diseases, leading to the development of novel biomarkers that aid in the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of these diseases.
- Cardiology
- Implication of microRNA as a potential biomarker of myocarditis
- Jin-Hee Oh, Gi Beom Kim, Heeyoung Seok
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):230-238. Published online March 2, 2022
-
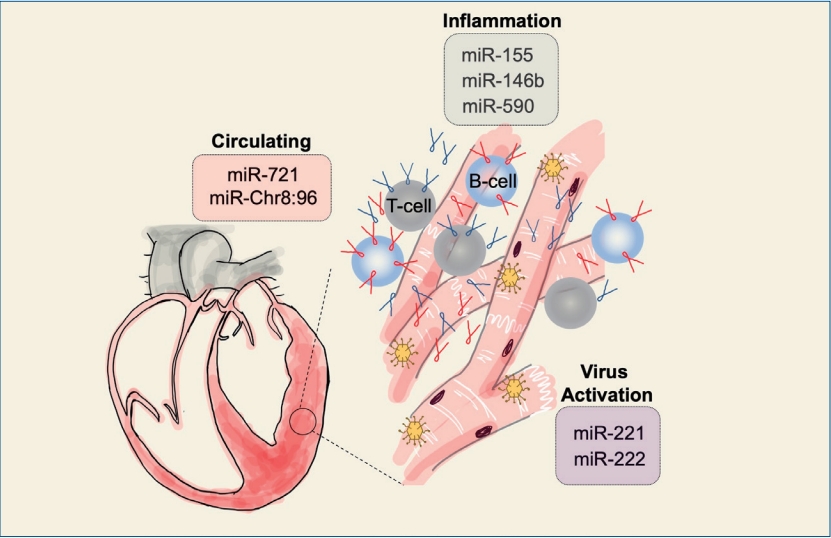
· Myocarditis was recently examined quantitatively as inflammation of the heart muscle based on endomyocardial biopsy, and its noninvasive diagnosis remains unsatisfactory.
· Additionally, numerous miRNAs (miR-155, miR-146b, miR-590, miR-221, miR-222, etc.) coupled with inflammation or viral activation have been examined in myocarditis patients or mouse models.
· The recent identification of mmu-miR-721 (has-miR-Chr8: 96), a myocarditis-specific microRNA, demonstrated its potential as an acute myocarditis biomarker.
- Neurology
- Promising candidate cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of seizure disorder, infection, inflammation, tumor, and traumatic brain injury in pediatric patients
- Seh Hyun Kim, Soo Ahn Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):56-64. Published online August 23, 2021
-
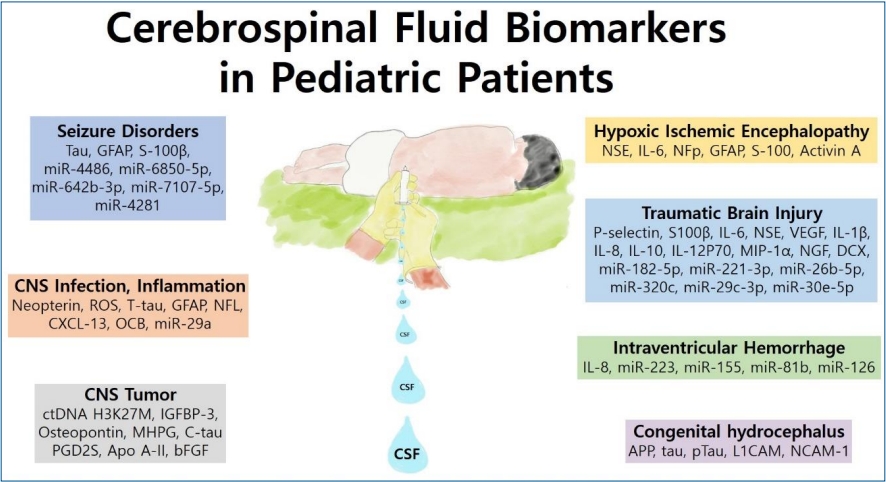
· Pediatric cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) components have been extensively evaluated as biomarkers of various neurologic diseases.
· Several promising candidate CSF biomarkers, including Tau, glial fibrillary acidic protein, neuron-specific enolase, S100β, and interleukins, have been studied in pediatric patients with seizure disorders, central nervous system infections, inflammation, tumors, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, traumatic brain injuries, intraventricular hemorrhage, and congenital hydrocephalus.
· Circulating microRNAs in the CSF are a promising class of biomarkers for various neurological diseases.
- Original Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Variation in clinical usefulness of biomarkers of acute kidney injury in young children undergoing cardiac surgery
- Hee Sun Baek, Youngok Lee, Hea Min Jang, Joonyong Cho, Myung Chul Hyun, Yeo Hyang Kim, Su-Kyeong Hwang, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(4):151-156. Published online February 5, 2020
-
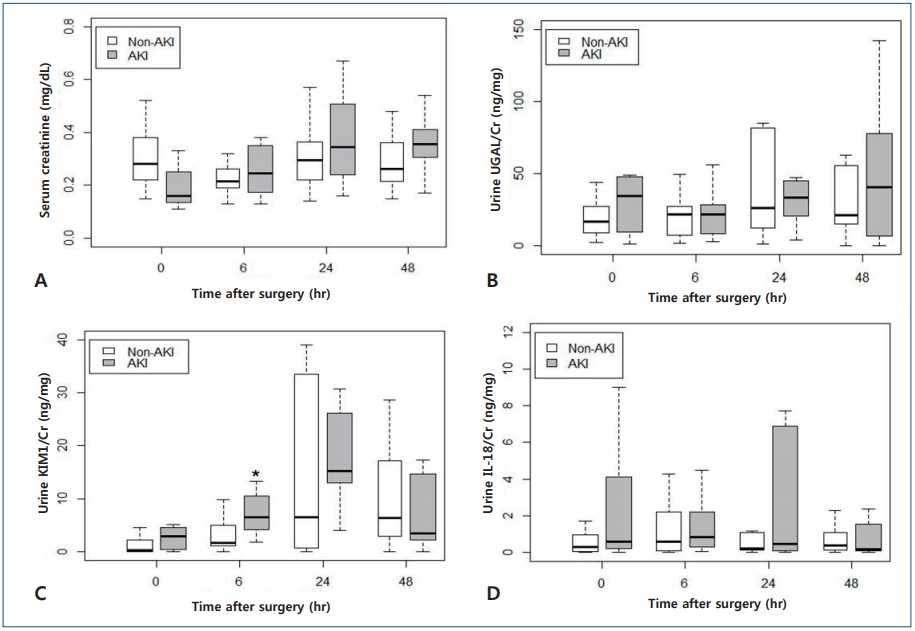
Question: Can clinical usefulness of biomarkers of acute kidney injury vary on the clinical circumstances?
Finding: In young children undergoing cardiac surgery, urine KIM-1/Cr level peaked at 24 hours with significant difference from baseline level and was significantly higher at 6 hours in the AKI group. However, urine NGAL/Cr and IL-18/Cr levels showed no specific trend with time for 48 hours after cardiac surgery.
Meaning: Urine KIM-1/Cr concentration could be considered a good biomarker for early AKI prediction after open cardiac surgery in young children.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Understanding of type 1 diabetes mellitus: what we know and where we go
- Chong Kun Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):307-314. Published online October 4, 2018
-

The incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) in children and adolescents is increasing worldwide. Combined effects of genetic and environmental factors cause T1DM, which make it difficult to predict whether an individual will inherit the disease. Due to the level of self-care necessary in T1DM maintenance, it is crucial for pediatric settings to support achieving optimal glucose control, especially...
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Diagnostic and prognostic value of proadrenomedullin in neonatal sepsis
- Sameh Samir Fahmey, Heba Mostafa, Noha Abd Elhafeez, Heba Hussain
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(5):156-159. Published online May 28, 2018
-
Purpose Sepsis is a major cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality. Early diagnosis is a major problem because of the lack of specific clinical signs. Therefore, a reliable diagnostic marker is needed to guide the use of antimicrobial agents. The objective of our study was to assess the value of proadrenomedullin (pro-ADM) in establishing the diagnosis and evaluating the prognosis of...
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Diagnostic accuracy of urinary biomarkers in infants younger than 3 months with urinary tract infection
- Nani Jung, Hye Jin Byun, Jae Hyun Park, Joon Sik Kim, Hae Won Kim, Ji Yong Ha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(1):24-29. Published online January 22, 2018
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of urinary biomarkers, such as neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (uNGAL) and β-2 microglobulin (uB2MG), in early detection of urinary tract infection (UTI) in infants aged <3 months with fever.
Methods A total of 422 infants aged <3 months (male:female=267:155; mean age, 56.4 days), who were admitted for fever, were retrospectively included in...
- Cardiology
- Subtle inflammation: a possible mechanism of future cardiovascular risk in obese children
- Watchareewan Sontichai, Prapai Dejkhamron, Peraphan Pothacharoen, Prachya Kongtaweelert, Kevalee Unachak, Nuthapong Ukarapol
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(11):359-364. Published online November 27, 2017
-
Purpose The risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) has been shown to be associated with systemic inflammation in obese adults with metabolic syndrome (MetS). The aims of this study were to evaluate the prevalence of MetS and its relation to inflammatory markers in obese Thai children.
Methods A cross-sectional study was conducted. Children with history of endogenous obesity, chronic diseases, drug ingestion, and any...
- Review Article
- The role of cytokines in seizures: interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-1Ra, IL-8, and IL-10
- Youngah Youn, In Kyung Sung, In Goo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(7):271-274. Published online July 19, 2013
-
Brain insults, including neurotrauma, infection, and perinatal injuries such as hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, generate inflammation in the brain. These inflammatory cascades induce a wide spectrum of cytokines, which can cause neuron degeneration, have neurotoxic effects on brain tissue, and lead to the development of seizures, even if they are subclinical and occur at birth. Cytokines are secreted by the glial...
- Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin: a novel biomarker for diagnosis and monitoring of asthma
- Chang-Keun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(1):8-12. Published online January 29, 2013
-
Asthma is associated with increased levels of eosinophils in tissues, body fluids, and bone marrow. Elevated levels of eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) and eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) have been noted in asthma patients. Higher levels of EDN and ECP are also associated with exacerbated asthmatic conditions. Thus, EDN, along with ECP, may aid the diagnosis and monitoring of asthma. Several groups...
- Case Report
- A case of isodicentric chromosome 15 presented with epilepsy and developmental delay
- Jon Soo Kim, Jinyu Park, Byung-Joo Min, Sun Kyung Oh, Jin Sun Choi, Mi Jung Woo, Jong-Hee Chae, Ki Joong Kim, Yong Seung Hwang, Byung Chan Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(12):487-490. Published online December 20, 2012
-
We report a case of isodicentric chromosome 15 (idic(15) chromosome), the presence of which resulted in uncontrolled seizures, including epileptic spasms, tonic seizures, and global developmental delay. A 10-month-old female infant was referred to our pediatric neurology clinic because of uncontrolled seizures and global developmental delay. She had generalized tonic-clonic seizures since 7 months of age. At referral, she could...
- Original Article
- Change of hemostatic markers according to the clinical state in Kawasaki disease
- Yong Beom Kim, You Sook Yoon, Sang Yun Lee, Hong Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(12):1247-1251. Published online December 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Pathologically, Kawasaki disease (KD) is associated with widespread vascular endothelial damage in the acute phase. The vasculitis induced endothelial injury leads to coagulation abnormalities. Abnormalities of endothelial function, platelet activation, and fibrinolysis are present during acute phase and long after the onset of KD. The aim of study is to evaluate the change of hemostatic markers in the... -
- Bone Mineral Density and Bone Markers in the Children with Epilepsy Taking on Chronic Anticonvulsants
- Soon Bum Lee, So Young Kang, Jeesuk Yu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(5):527-533. Published online May 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Long-term administration of anticonvulsants in children with epilepsy may cause short stature, hypocalcemia and low bone mineral density. This study was performed for the early detection of abnormal bone metabolism in children with epilepsy on taking anticonvulsants. Methods : Thirty children aged 5 to 16 years who were diagnosed with epilepsy were enrolled in this study. All had taken... -
- Alteration of Bone Metabolism Markers According to the Progression of Puberty
- Seong Yong Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(2):140-149. Published online February 15, 2004
-
Purpose : The object of this study is to evaluate bone metabolism in healthy adolescents according to the progression of puberty. Methods : Forty boys(13.9?.7 years) and 42 girls(12.1?.6 years) were classified by Tanner stage (TS) and bone age. Serum levels of osteocalcin(OC) and bone specific alkaline phosphatase(BALP) were measured as bone formation markers. Serum level of C-terminal telopeptide of type... -
- Changes of Bone Metabolism Markers and Bone Mineral Density with Improvement of Thyroid Function in Children and Adolescents with Hyperthyroidism
- Min Ho Jung, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang, Byung Churl Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(6):743-753. Published online June 15, 2002
-
Purpose : Dynamics of bone mineral density(BMD) and bone metabolism in children and adolescents with hyperthyroidism have not been thoroughly investigated. The aim of this study was to study how the improvement of thyroid function with antithyroid treatment influenced bone metabolism and BMD in children and adolescents with hyperthyroidism. Methods : Serum levels of osteocalcin(OC), bone-specific alkaline phosphatase(b-ALP), and carboxyterminal telopeptide... -
- Colonic Transit Time in Chronic Constipated Patients
- Je Eun Choi, Im Jeong Choi, Jung A Lee, Sung Mi Kim, Jin Hwa Jeong, Jeong Ho Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(7):752-757. Published online July 15, 2001
-
Purpose : In most instances, constipation is considered as idiopathic or functional. The total colonic transit time, traced by radio-opaque markers, makes possible the identification of the colon segment that has the motility alteration that causes constipation. We measured the total and segmental colonic transit time in children with chronic idiopathic constipation and compared the results with those without constipation... -
- The Utility of Serum Prealbumin as a Biochemical Marker for Nutritional Adequacy in Neonates
- Ji A Jung, Eun Ae Park, Jeong Wan Seo, Seung Joo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(5):605-610. Published online May 15, 2000
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study was to determine the utility of serum prealbumin as a biochemical marker for nutritional adequacy in neonates. Methods : From March 1998 to May 1999, 71 fullterm(54 AGA, 9 LGA, 8 SGA) and 46 preterm neonates were enrolled. The correlations among prealbumin, albumin, birth weight and gestational age were obtained. Serum concentrations of albumin... -
- Immunohistochemical Studies on Neuroendocrine Markers in Malignant Neuronal Tumors (Neuroblastoma and Ganglioneuroblastoma) in Children
- Woo Yeong Chung, Sun Kyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(10):1377-1388. Published online October 15, 1992
-
The authors studied 24 cases of malignant neuronal tumors, 14 neuroblastomas and 10 ganglioneuroblastomas, immunohistochemically, using antibodies to neuroendocrine markers including neuron specific enolase (NSE), somatostatin, chromogranin, β-endorphin, and adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH). The tissue specimens were obtained by biopsy or autopsy at Pusan National University Hopital and Pusan Paik Hospital from 1980 to 1989. The positive reactivity of markers in... -
-
- A Case of Mixed Gonadal Dysgenesis.
- Eun Young Choi, Min Sik Kim, Hey Sun Lee, Young Min Ahn, Kyung Joon Min
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1989;32(7):1023-1029. Published online July 31, 1989
-
The syndrome of Mixed Gonadal Dysgenesis is characterized by a unilateral testis, usually intra- abdominal a streak gonad on contralateral side, persistent Mullerian structures and ambiguous genitalia. These patients are chromatin negative and exhibit XO/XY mosaicism, probably resulting from a cytogenetic error very early in embryogenesis. The testis and the streak gonad should be removed because of the potential devlopement of a gonadoblastoma and the virilization... -
- Clinical Observation of Profiles of Serologic Markers in Hepatitis B.
- H Y Ahn, S T Kim, S G Cho, Y Y Choi, J S Ma, C Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1985;28(7):653-662. Published online July 31, 1985
-
Serologic markers of hepatitis B virus were detected by Enzymeimmunoassay in acute(88 cases in 68 patients) and chronic (19 cases in 6 patients) hepatitis B. 1)Positive rate of HBsAg was highest (acute 64.5%, chronic 89.4%) in 5 serologic markers and AntiHBe or AntiHBs were not detected in chronic cases. 2)18 serologic profiles (I~XXIII) were observed, of these common type was... -
- Hepatitis B Serologic Markers at Birth in Babies of HBsAg-Positive Mothers.
- Jeoung Wan Seo, Hye Seung Kim, Keun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1985;28(3):236-241. Published online March 31, 1985
-
It has been established that hepatitis B virus may be transmitted from mothers to infants in the perinatal period. A study was undertaken to identify HBsAg in neonates born to mothers who were asymptomatic carriers of HBsAg. From Jan. 1 ’83 to June 30 ’84, total 4,044 cases of pregnant women and 131 babies were studied for serologic markers of hepatitis... -
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











