Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Trends of vitamin D in asthma in the pediatric population for two decades: a systematic review
- Myongsoon Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):339-347. Published online June 14, 2023
-
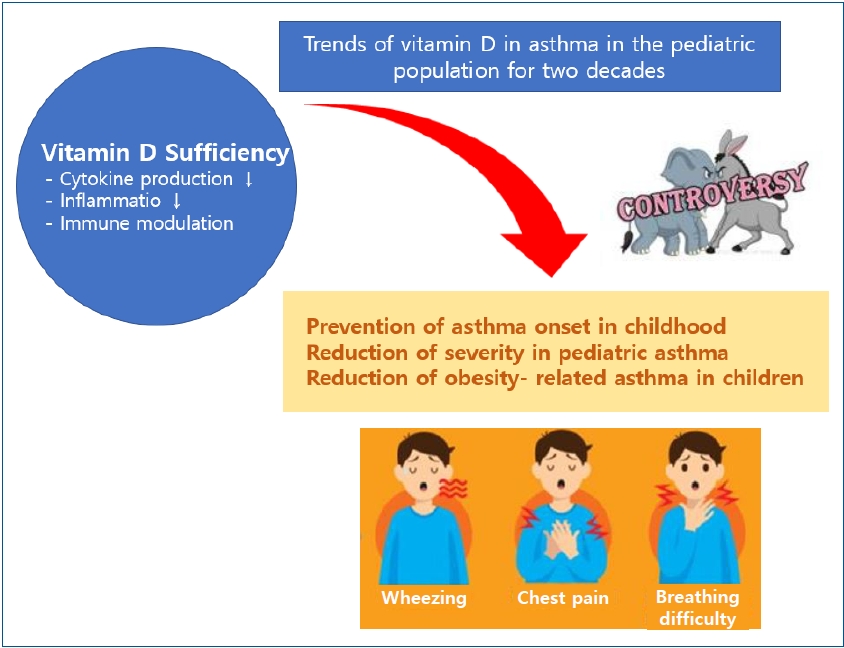
· Vitamin D may affect asthma via multiple mechanisms, including lung and optimal immune system functions.
· Many clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin D on asthma onset and aggravation. However, definitive clinical trials are lacking, and reports have detailed contradictory effects of vitamin D in children with asthma.
· Some exciting reports stated that obesity and vitamin D deficiency are associated with increased asthma symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Breastfeeding and vitamin D
- Ju Sun Heo, Young Min Ahn, Ai-Rhan Ellen Kim, Son Moon Shin; for the Korean Society of Breastfeeding Medicine
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):418-429. Published online December 14, 2021
-
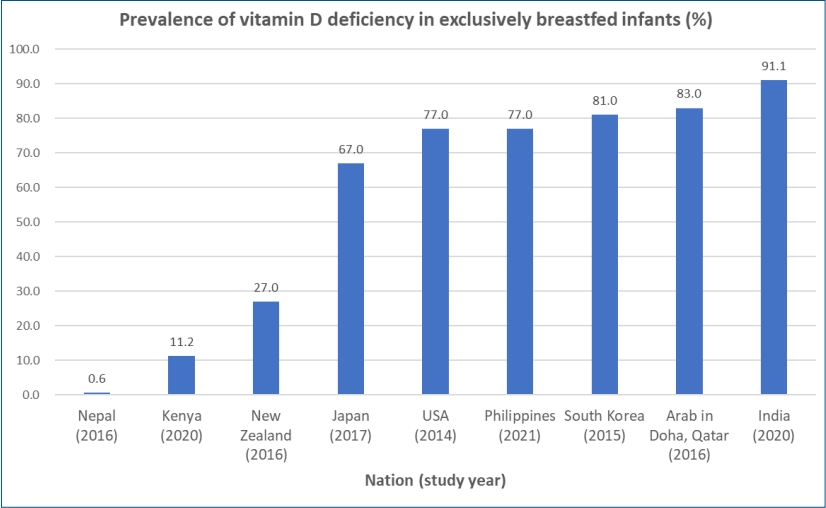
∙ Exclusively breastfed infants are at risk of developing vitamin D deficiency associated with hypocalcemia, rickets, and various health outcomes.
∙ The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in breastfed infants differs vastly between studies and nations at 0.6%–91.1%.
∙ The vitamin D content of breast milk does not meet the requirements of exclusively breastfed infants.
∙ Most international guidelines recommend that breastfed infants be supplemented with 400 IU/day of vitamin D during the first year of life.
∙ Vitamin D intake (milk+supplements) of 800 IU/day can be considered in preterm infants along with biochemical monitoring.
- General Pediatrics
- A new perspective on cholesterol in pediatric health: association of vitamin D metabolism, respiratory diseases, and mental health problems
- Jeana Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):65-72. Published online December 9, 2021
-
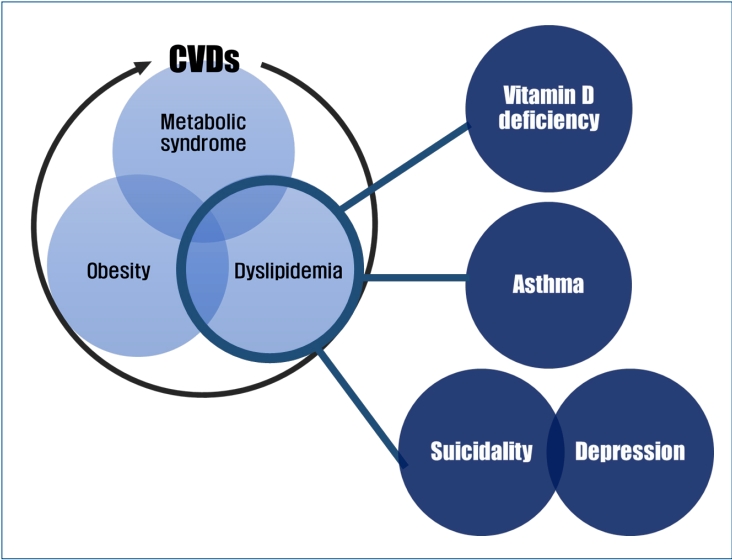
∙ Pediatric dyslipidemia is associated with several health problems besides cardiovascular diseases.
∙ There is a direct association between pediatric dyslipidemia and low serum vitamin D levels, asthma, and mental health problems regardless of body mass index.
∙ More large-scale nationally representative studies are needed to establish the appropriate cutoff points for the definition of dyslipidemia that is a prerequisite for further epidemiological studies in the Korean pediatric population.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Association between vitamin D level at birth and respiratory morbidities in very-low-birth-weight infants
- Ian Kim, Sung Shin Kim, Jee In Song, Seock Hwa Yoon, Ga Young Park, Yong-Wha Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):166-172. Published online October 24, 2018
-
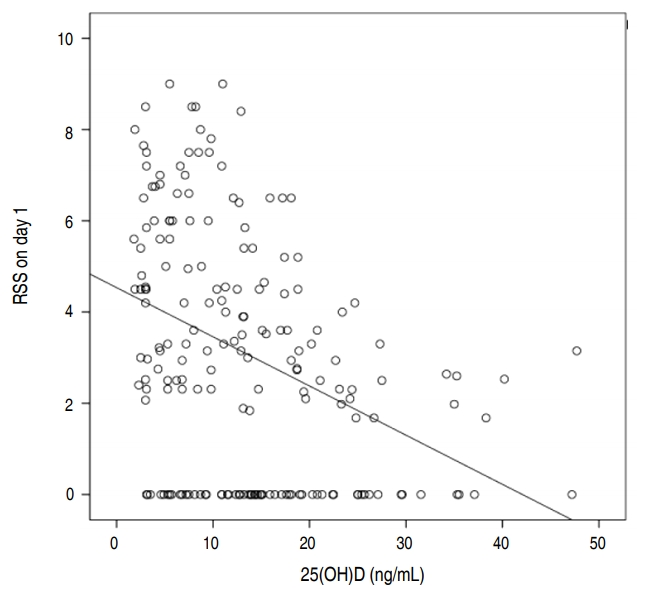
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate vitamin D status at birth in very-low-birth-weight infants (VLBWIs: <1,500 g) and to determine the association between vitamin D level and respiratory morbidity. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted at Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital between November 2013 and November 2017. We collected blood samples and data on respiratory morbidity from 230 VLBWIs on the first...
- Infection
- Association between vitamin D and urinary tract infection in children
- Abolfazl Mahyar, Parviz Ayazi, Sara Safari, Reza Dalirani, Amir Javadi, Shiva Esmaeily
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(3):90-94. Published online March 19, 2018
-
Purpose The present study aimed to determine the relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) level and Urinary tract infections (UTIs) in children.
Methods In this case-control study, 70 children with UTI (case group) were compared with 70 healthy children (control group) in terms of serum 25(OH)D levels. The children were between 1 month and 12 years of age. Serum 25(OH)D levels were measured...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effects of cord blood vitamin D levels on the risk of neonatal sepsis in premature infants
- Birgul Say, Nurdan Uras, Suzan Sahin, Halil Degirmencioglu, Serife Suna Oguz, Fuat Emre Canpolat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(8):248-253. Published online August 14, 2017
-
Purpose Vitamin D plays a key role in immune function. Vitamin D deficiency may play a role in the pathogenesis of infections, and low levels of circulating vitamin D are strongly associated with infectious diseases. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the effects of low vitamin D levels in cord blood on neonatal sepsis in preterm infants.
Methods One hundred seventeen premature...
- Cardiology
- Relationship between vitamin D levels and intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in Kawasaki disease
- Jae Sung Jun, Young Kwon Jung, Dong Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(7):216-220. Published online July 31, 2017
-
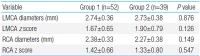
Purpose Vitamin D is associated with various pathological conditions such as cardiovascular diseases and cancer. We investigated the relationship between vitamin D and Kawasaki disease (KD).
Methods We performed a retrospective review of the medical records of patients with KD between February 2013 and March 2016 in Daegu Fatima Hospital. Study participants were grouped according to vitamin D serum concentration. Group 1 included...
- Endocrinology
- The serum level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D for maximal suppression of parathyroid hormone in children: the relationship between 25-hydroxyvitamin D and parathyroid hormone
- Jung In Kang, Yoon Suk Lee, Ye Jin Han, Kyoung Ae Kong, Hae Soon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(2):45-49. Published online February 27, 2017
-
Purpose Serum level of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-OHD) is considered as the most appropriate marker of vitamin D status. However, only a few studies have investigated the relationship between 25-OHD and parathyroid hormone (PTH) in children. To this end, this study was aimed at evaluating the lowest 25-OHD level that suppresses the production of parathyroid hormone in children.
Methods A retrospective record review was...
- Nutrition
- Increment in vitamin D level and bone mineral accrual in children with vitamin D deficiency
- Yashwant Kumar Rao, Tanu Midha, Satyajeet Singh, Anurag Bajpai, Amita Tilak
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(7):292-297. Published online July 31, 2016
-
Purpose To compare different regimens of vitamin D with respect to its serum increment levels and bone mineral accrual in vitamin D-deficient children.
Methods Children identified as being vitamin D deficient (serum levels<20 ng/mL) were divided into 3 treatment groups by stratified block randomization (group 1, 4,000 IU/day of vitamin D3 plus 50 mg/kg/day calcium for 12 weeks; group 2, 30,000 IU/wk of...
- Severe vitamin D deficiency in preterm infants: maternal and neonatal clinical features
- Sook-Hyun Park, Gi-Min Lee, Jung-Eun Moon, Heng-Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(11):427-433. Published online November 22, 2015
-
Purpose We investigated the vitamin D status of preterm infants to determine the incidence of vitamin D deficiency.
Methods A total of 278 preterm infants delivered at Kyungpook National University Hospital between January 2013 and May 2015 were enrolled. The serum concentrations of calcium, phosphorous, alkaline phosphatase, and 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-OHD) were measured at birth. We collected maternal and neonatal data such as...
- Vitamin D serum levels in children with allergic and vasomotor rhinitis
- Seung Jin Lee, Bong Hwa Kang, Bong Seok Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(9):325-329. Published online September 21, 2015
-
Purpose In addition to regulating calcium and phosphorus homeostasis and bone metabolism, vitamin D is known as an immune modulator. Recently, there has been increased worldwide interest in the association between low levels of vitamin D and allergic diseases. The purpose of this study was to assess the relationship between serum vitamin D levels and allergic/vasomotor rhinitis (AR/VR) in children.
Methods This study...
- Iron and vitamin D status in breastfed infants and their mothers
- Yu Sun Kang, Joon Hwan Kim, Eun Hee Ahn, Eun-Gyong Yoo, Moon Kyu Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(8):283-287. Published online August 21, 2015
-
Purpose We assessed the relationships between iron and vitamin D statuses in breastfed infants and their mothers and evaluated the determinants of iron and vitamin D deficiencies in breastfed infants.
Methods Seventy breastfed infants aged 4-24 months and their mothers participated in this study from February 2012 to May 2013. Complete blood counts, total iron binding capacity, and levels of C-reactive protein, iron,...
- Relationship between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and interleukin-31 levels, and the severity of atopic dermatitis in children
- Bo Ram Cheon, Jeong Eun Shin, Yun Ji Kim, Jae Won Shim, Deok Soo Kim, Hye Lim Jung, Moon Soo Park, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(3):96-101. Published online March 20, 2015
-
Purpose Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic inflammatory relapsing skin disorder. Vitamin D plays a pivotal role in the development of AD, and interleukin (IL) 31 is known to be related to pruritus in AD. The aim of our study was to determine whether 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) levels are related to IL-31 levels or to the severity of AD.
Methods We enrolled 91...
- Association between cord blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and respiratory tract infections in the first 6 months of age in a Korean population: a birth cohort study (COCOA)
- Youn Ho Shin, Jinho Yu, Kyung Won Kim, Kangmo Ahn, Seo-Ah Hong, Eun Lee, Song-I Yang, Young-Ho Jung, Hyung Young Kim, Ju-Hee Seo, Ji-Won Kwon, Byoung-Ju Kim, Hyo-Bin Kim, Jung Yeon Shim, Woo Kyung Kim, Dae Jin Song, So-Yeon Lee, Soo Young Lee, Gwang Cheon Jang, Dong In Suh, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Bong Sung Kim, Suk-Joo Choi, Soo-Young Oh, Ja-Young Kwon, Kyung-Ju Lee, Hee Jin Park, Pil Ryang Lee, Hye-Sung Won, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(10):439-445. Published online October 31, 2013
-
Purpose Previous studies suggest that the concentration of 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] in cord blood may show an inverse association with respiratory tract infections (RTI) during childhood. The aim of the present study was to examine the influence of 25(OH)D concentrations in cord blood on infant RTI in a Korean birth cohort.
Methods The levels of 25(OH)D in cord blood obtained from 525 Korean...
- Review Article
- Vitamin D status and childhood health
- Youn Ho Shin, Hye Jung Shin, Yong-Jae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(10):417-423. Published online October 31, 2013
-
Vitamin D is an essential component of bone and mineral metabolism; its deficiency causes growth retardation and skeletal deformities in children and osteomalacia and osteoporosis in adults. Hypovitaminosis D (vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency) is observed not only in adults but also in infants, children, and adolescents. Previous studies suggest that sufficient serum vitamin D levels should be maintained in...
- Original Article
- Vitamin D deficiency in infants aged 1 to 6 months
- You Jin Choi, Moon Kyu Kim, Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(5):205-210. Published online May 28, 2013
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to recognize the state of vitamin D among healthy infants aged 1 to 6 months in South Korea, and also to identify the risk factors affecting the level of vitamin D.
Methods A total of 117 infants were enrolled in this study for 12 months, from March 1, 2011 to February 29, 2012. Serum levels of...
- Prevalence and risk factors for vitamin D deficiency in children with iron deficiency anemia
- Jung Won Yoon, Sung Woo Kim, Eun Gyong Yoo, Moon Kyu Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(6):206-211. Published online June 21, 2012
-
Purpose The increasing prevalence of breast feeding has led to concerns about vitamin D deficiency (VDD) and iron deficiency anemia (IDA) in children. We evaluated the prevalence of VDD in a population of Korean children with IDA and assessed the risk factors for VDD in these children.
Methods A total of 79 children who were diagnosed with IDA were prospectively surveyed from April...
- Clinical characteristics and prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in children less than two years of age
- Ji Hyun Yoon, Cheong Soo Park, Ji Young Seo, Yun Sun Choi, Young Min Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(7):298-303. Published online July 31, 2011
-
Purpose To evaluate the clinical characteristics of vitamin D deficiency and its association with iron deficiency anemia (IDA).
Methods A total of 171 children aged less than two years underwent 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 tests between January 2007 and July 2009. The study was classified into two groups: normal and vitamin D insufficiency, by their vitamin 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels.
Results In total, 120 children were in the...
- Review Article
- Nutritional management of breastfeeding infants for the prevention of common nutrient deficiencies and excesses
- Jin Soo Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(7):282-286. Published online July 31, 2011
-
Breastfeeding is the best source of nutrition for every infant, and exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months is usually optimal in the common clinical situation. However, inappropriate complementary feeding could lead to a nutrient-deficient status, such as iron deficiency anemia, vitamin D deficiency, and growth faltering. The recent epidemic outbreak of obesity in Korean children emphasizes the need for us to...
- Vitamin D dependent rickets type I
- Chan Jong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(2):51-54. Published online February 28, 2011
-
Vitamin D is present in two forms, ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) produced by plants and cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) produced by animal tissues or by the action of ultraviolet light on 7-dehydrocholesterol in human skin. Both forms of vitamin D are biologically inactive pro-hormones that must undergo sequential hydroxylations in the liver and the kidney before they can bind to and activate...
- Original Article
- Clinical characteristics of vitamin D deficiency rickets in infants and preschool children
- Kyoung Huh, Mi Kyeong Woo, Jung Rim Yoon, Gyu Hong Shin, Myoung Jae Chey, Mi Jung Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(2):152-157. Published online February 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Vitamin D deficiency rickets is a significant public health problem that results from insufficient exposure to sunlight and inadequate vitamin D supplementation. The purpose of this study is to identify the clinical characteristics of vitamin D deficiency rickets in infants. Methods : Data of 35 infants diagnosed as vitamin D deficiency rickets at Sanggye-Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea, from March... -
- Review Article
- Recent concepts on vitamin D in children and adolescents
- Hye Ran Yang, Jeong Wan Seo, Yong Joo Kim, Jae Young Kim, Eell Ryoo, Jae Geon Sim, Hye Won Yom, Ju Young Chang, Ji A Jung, Kwang Hae Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(10):1082-1089. Published online October 15, 2009
-
Vitamin D is an important fat-soluble vitamin that functions as a prohormone and affects bone mineralization and calcium homeostasis. Vitamin D deficiency causesboth musculoskeletal manifestations, including rickets, and extra-musculoskeletal symptoms. Because vitamin D is naturally present in only some foods, intake of daily foods cannot meet the dietary reference intake for vitamin D. Sunlight is the main source of vitamin... -
- Original Article
- Eight cases of incidentally diagnosed as subclinical rickets
- Ji-Young Seo, Curie Kim, Hee-Woo Lee, Young-Min Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(8):812-819. Published online August 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Vitamin D plays a key role in bone mineralization of the skeleton and vitamin D deficiency can lead to rickets. It is well known that vitamin D deficiency is common in breast fed infants. Of these patients, clinically, some have no signs of rickets, but laboratory and radiographic findings are diagnostic for vitamin D deficiency rickets (subclinical vitamin... -
- Subclinical rickets in breastfed infants
- Sin Young Park, Sung Woo Park, Sung Kil Kang, Yong Hoon Jun, Soon Ki Kim, Byong Kwan Son, Jee Eun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(12):1188-1193. Published online December 15, 2007
-
Purpose : The prevalence of rickets in the world is on the rise not only in developing but also in developed countries. In Korea, breastfeeding has increased. There have been few studies on the possible association of rickets with breastfeeding. The purpose of this study was to identify the development and the clinical presentation of subclinical rickets in breastfed infants. Methods... -
- Review Article
- Calcium and phosphate metabolism and disorders in the newborn
- Hae Soon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(3):230-235. Published online March 15, 2007
-
In the early neonatal period, the neonate is challenged by the loss of the placental calcium transport and manifests a quick transition, from an environment in which PTHrP plays an important role to a PTH- and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D-controlled neonatal milieu. Disturbances in mineral homeostasis are common in the neonatal period, especially in premature infants and infants who are hospitalized in... -
- Original Article
- Effects of Insulin-like Growth Factor-I and 1,25-(OH)2 Vitamin D3 Concentration on Intrauterine Growth of Newborns from Mothers with Preeclampsia
- In Sook Yang, Jung Hyun Lee, Hyung Shin Lee, So Young Kim, Sung Dong Choi, In Kyung Sung, Chung Sik Chun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(5):527-531. Published online May 15, 2004
-
Purpose : This study was undertaken to observe the blood levels of IGF-I and 1,25-(OH)2 Vit. D3 in maternal and neonatal compartments and the effects of IGF-I concentration on intrauterine fetal growth and 1,25-(OH)2 Vit. D3 metabolism in the presence of preeclampsia. Methods : Thirty-four full-term pregnant women with preeclampsia and their newborns(preeclampsia group) and 10 normotensive full-term pregnant women and... -
- Case Report
- Three Cases of Hypercalcemia Due to Vitamin D Intoxication in Infancy
- Jin-Ho Choi, Mi-Sun Yum, Hyewon Hahn, Young Seo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(3):332-337. Published online March 15, 2004
-
Hypercalcemia in infancy is an uncommon disorder but has a potential of serious sequelae. Therefore, infants with hypercalcemia must be promptly investigated and need urgent management. We report three cases of infantile hypercalcemia caused by vitamin D intoxication, emphasizing diagnostic investigations and the course of treatment. The first and the second cases were thought to be vitamin D intoxication without... -
- A Case of Rickets Developed after Feeding on Sunsik for Seven Months
- Jeong-A Yang, Kyung-A Jang, Hye-Won Park, Wook Jang, Man-Yong Han, Young-A Cho, Eun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(11):1143-1146. Published online November 15, 2003
-
Rickets is a nutritional disorder which is caused either by deficiency of vitamin D or by a defective activation of vitamin D. In these days, even though the incidence of rickets has decreased through adequate nutritional support, we sometimes experience rickets in babies receiving a prolonged special diet as therapy for chronic diarrhea, or those subject to a in receiving... -
- Original Article
- Type I Vitamin D Dependent Rickets
- Soo Ja Hwang, Jung Soo Kim, Hae Il Cheong, Yong Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(7):877-882. Published online July 15, 1998
-
Purpose : Vitamin D dependent rickets(VDDR) is a rare, autosomal recessively transmitted disorder characterized by hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, increased alkaline phosphatase, secondary hyperparathyroidism and many other clinical features. Type Ⅰ VDDR arises from primary deficiency in the renal 1α-hydroxylase that produces 1,25(OH)2D3. So patients with type I VDDR require life long administration of vitamin D. Methods : There had been 6 children(4... -
- Hypophosphatemic Rickets.
- Kyung Mo Kim, Seong Hoon Ha, Dong Kyu Jin, Kwang Wook Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(4):437-447. Published online April 30, 1990
-
Seventeen patients who were diagnosed as primary hypophosphatemic rickets at Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children’s Hospital were analyzed to assess its clinical aspect and effect of treatment, especially on height and growth velosity. The average age of onset was 2 years, and their chief complaints were bowleg and short stature. Sex ratio was l.l:l(male: female). Familial hypophoshatemic rickets was known as X-linked... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







