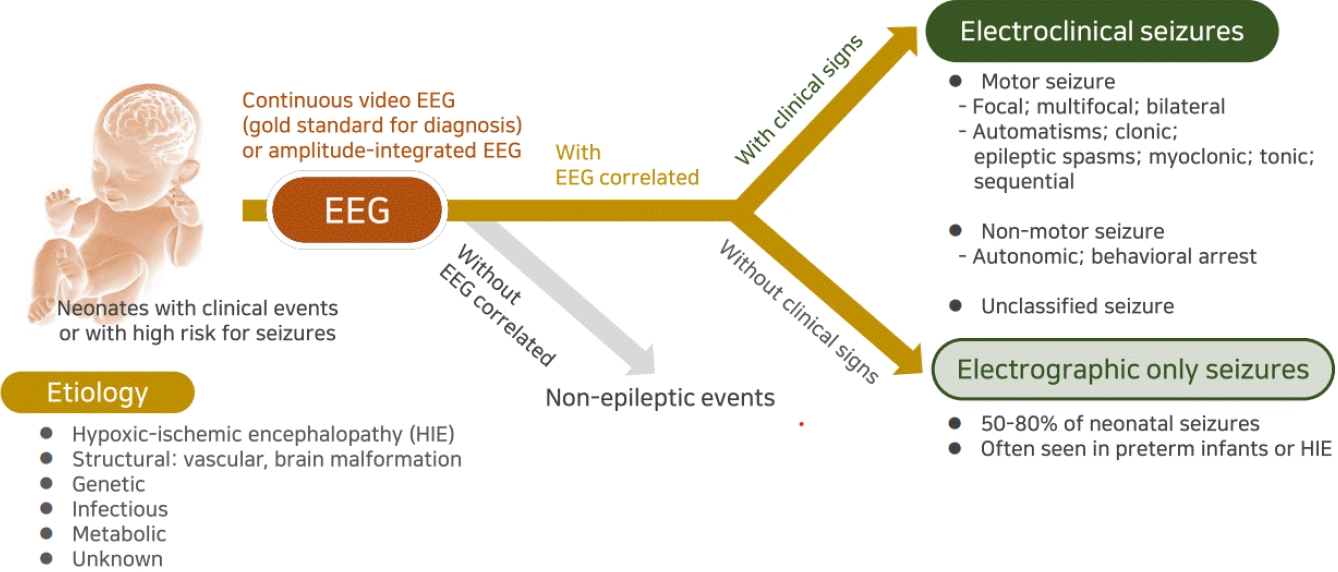
|
· Neonatal seizures are often electrographic-only seizures without clinical signs; therefore, the identification of electrical seizure activity on electroencephalography is the gold standard for diagnosis.
· Clinical signs of neonatal seizures are divided into motor or nonmotor seizures, and motor seizures are mostly focal or multifocal.
· Most neonatal seizures are caused by acute symptomatic etiologies, but in cases of intractable seizures, structural, genetic, or metabolic etiologies should be investigated. |




