|
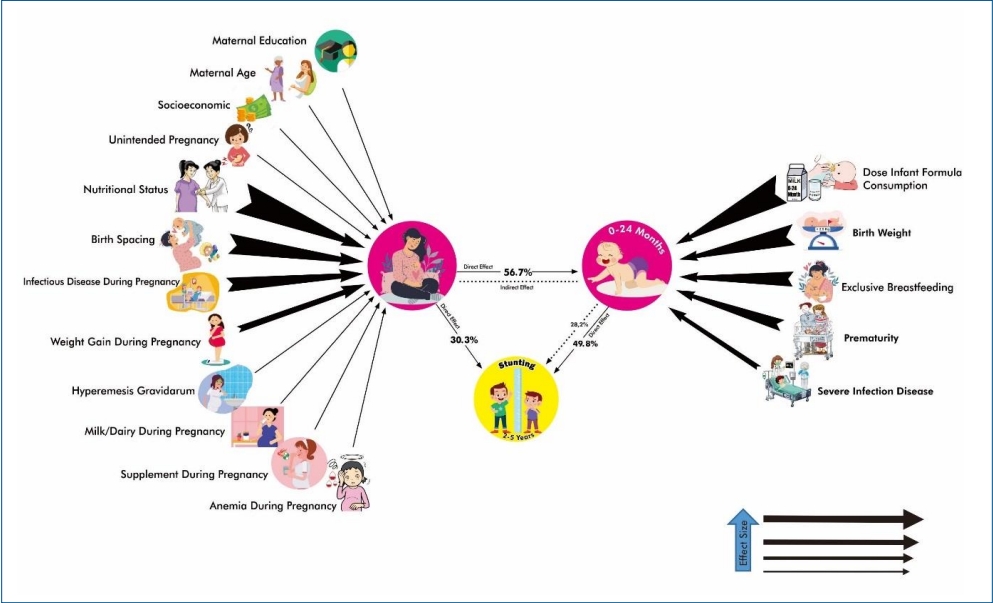
Question: What effects do maternal and child factors have on stunting? Are there significant indicators of stunting?
Finding: Child and maternal factors had 49.8% and 30.3% effects on stunting, respectively. The primary child factor was infant formula dose, while the primary maternal factor was nutritional status.
Meaning: More attention to nutritional status during pregnancy and ensuring the appropriate dose of infant formula at ages 6–24 months can prevent stunting. |


