Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Differential roles of interleukin-6 and adrenomedullin in early diagnosis and mortality predictions in late-onset neonatal sepsis
- Emilly Henrique dos Santos, Gabriel Acca Barreira, Mariana Okay Saippa, Maria Carolina Pires Cruz, Karen Alessandra Rodrigues, Ronaldo Arkader, Thelma Suely Okay
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):463-471. Published online December 23, 2024
-

Question: Can adrenomedullin (ADM) or interleukin-6 (IL-6) detect late-onset neonatal sepsis (LOS) at admission (area under the curve [AUC]>0.90) as an early diagnostic marker?
Finding: Only IL-6 consistently distinguished survivors from nonsurvivors (AUC>0.90) on admission and antibiotic treatment days 3 and 7. C-reactive protein level identified infections from day 3 but failed to predict outcomes (AUC<0.70).
Meaning: IL-6 level can improve LOS diagnosis and prognosis.
- Neonatal sepsis-causing bacterial pathogens and outcome of trends of their antimicrobial susceptibility a 20-year period at a neonatal intensive care unit
- Woo Sun Song, Hye Won Park, Moon Youn Oh, Jae Young Jo, Chae Young Kim, Jung Ju Lee, Euiseok Jung, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):350-357. Published online December 9, 2021
-
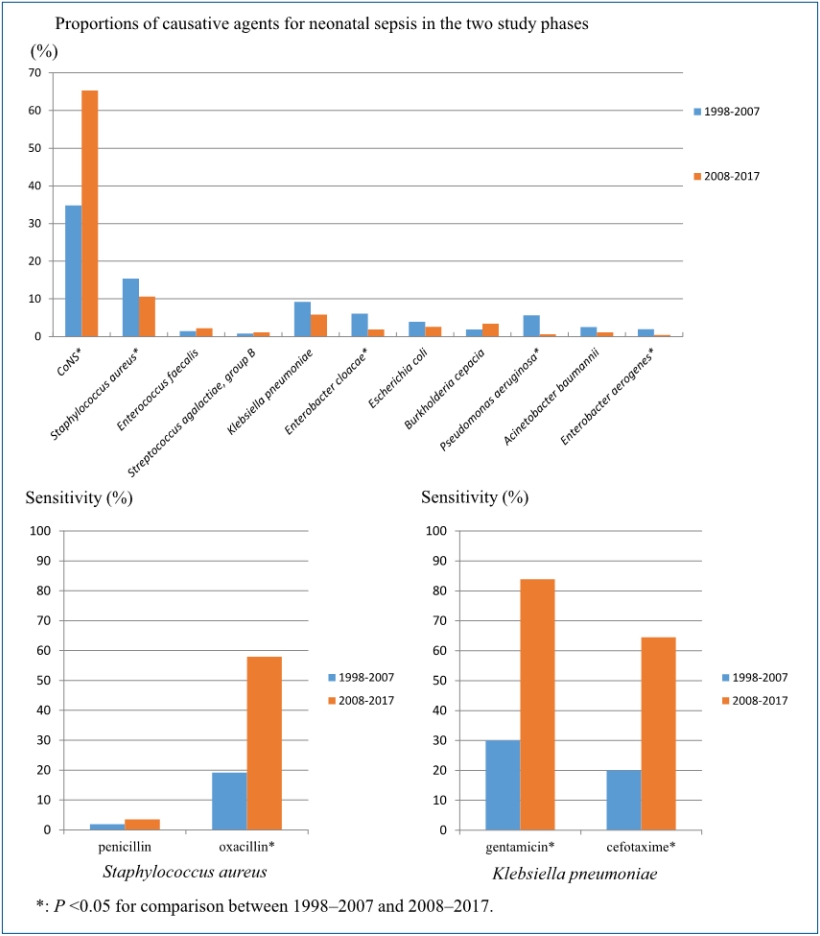
Question: What is prevalence of bacterial pathogens causing sepsis and their antimicrobial susceptibility over 20 years?
Finding: Coagulase-negative remains most common causative organism. The most common gram-negative organism was Klebsiella pneumonia. The susceptibility of staphylococcus aureus and K. pneumonia showed increased susceptability to oxacillin, cefotaxime and amikacin, gentamicin, respectively.
Meaning: Answers to the question asked is important in choosing antimicrobials and to monitor emergence of multidrug-resistant organisms.
- Diagnostic value of eosinopenia and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio on early onset neonatal sepsis
- Rocky Wilar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):217-223. Published online October 8, 2018
-
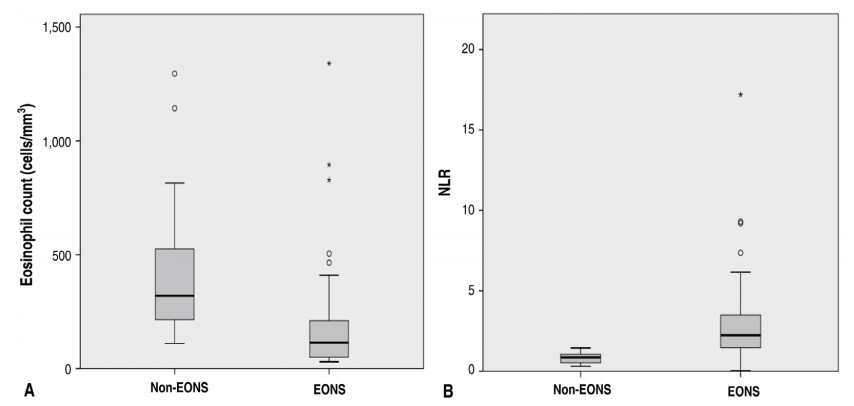
Purpose: To determine the diagnostic value of eosinopenia and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in the diagnosis of early onset neonatal sepsis (EONS). Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted in the Neonatology Ward of R.D. Kandou General Hospital Manado between July and October 2017. Samples were obtained from all neonates meeting the inclusion criteria for EONS. Data were encoded using logistic regression...
- Comparison of the accuracy of neutrophil CD64 and C-reactive protein as a single test for the early detection of neonatal sepsis
- Young Kwang Choo, Hyun-Seok Cho, In Bum Seo, Hyeon-Soo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(1):11-17. Published online January 31, 2012
-
Purpose Early identification of neonatal sepsis is a global issue because of limitations in diagnostic procedures. The objective of this study was to compare the diagnostic accuracy of neutrophil CD64 and C-reactive protein (CRP) as a single test for the early detection of neonatal sepsis.
Methods A prospective study enrolled newborns with documented sepsis (n=11), clinical sepsis (n=12) and control newborns (n=14). CRP,...
- Diagnostic value of various screening tests in neonatal sepsis
- Hyun Gon Je, Young Mi Jeoung, Soo Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(11):1167-1173. Published online November 15, 2006
-
Purpose : To evaluate various sepsis screening tests, individually and in combination, to formulate a guideline for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Methods : The study was a retrospective cohort study. It took place at the neonatal intensive care unit of the Paediatric Department, Il Sin Christian Hospital, Busan, Korea, over a period of 68 months from 1st, April, 2001 to... -
- Analysis of causative microorganisms and choice of antibiotics according to the onset of neonatal sepsis
- June Seung Sung, Dong Yeon Kim, Sun Hee Kim, Hyung Suk Byun, Tai Ju Hwang, Young Youn Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(6):623-629. Published online June 15, 2006
-
Purpose : The mortality rate of neonatal sepsis has been decreased, however, the incidence has not significantly decreased because of increased invasive procedures. This study was designed to make guidelines for choosing antibiotics by analyzing the causative microorganisms and their antibiotics sensitivity test according to the onset of neonatal sepsis. Methods : One hundred seven cases of culture proven sepsis... -
- The Effectiveness of Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Clinically Suspected Neonatal Sepsis
- Hyun Jung Na, Ji Young Kim, Gyeong Hoon Lee, Jun Hwa Lee, Eun Jin Choi, Jin Kyung Kim, Hai Lee Chung, Woo Taek Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(11):1187-1192. Published online November 15, 2005
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study is to determine the effectiveness of intravenous immunoglobuin (IVIG) administration in fullterm neonates having clinically suspected neonatal sepsis. Methods : Forty full-term neonates admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit with clinically suspected neonatal sepsis, who had at least two positive diagnostic criteria were enrolled. Twenty neonates were enrolled into the IVIG arm and... -
- Therapeutic Effect of Different Doses of Recombinant Human Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor(rhG-CSF) on Neonatal Sepsis Complicated by Neutropenia
- Moon Young Choi, Yeon Sook Jung, Dong Woo Son, Hyo Seop Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(4):439-448. Published online April 15, 2002
-
Purpose : The aim of this study is to determine and compare the effects of adjunctive therapy with different doses of recombinant human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor(rhG-CSF) on reversing sepsis-associated neonatal neutropenia, and their survival rate in a group I/II-type trial. Methods : RhG-CSF was injected subcutaneously to 10 septic-neutropenic neonates with doses of 10 μg/kg from Oct. 1995 to Sep. 1996,... -
- A Nationwide Survey on the Causative Organisms of Neonatal Sepsis in Korea
- Kyung Ah Kim, Son Moon Shin, Jung Hwan Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(1):55-63. Published online January 15, 2002
-
Purpose : A nationwide survey was conducted to investigate the most common causative organisms in neonatal sepsis in Korea. Methods : By reviewing medical records of newborn infants who were confirmed as neonatal sepsis by isolating organisms from blood culture during a one year study period from January to December in 1997, data for causative organisms, risk factors, accompanying focal infections and combinations of antibiotics... -
- Effect of Parenteral Nutrition Guideline Changes on Neonatal Sepsis in Premature Infants
- Chang-Ryul Kim, Jae-Won Oh, Myung-Kul Yum, Soo-Jee Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(6):620-626. Published online June 15, 2001
-
Purpose : We hypothesized that decreased parenteral nutrition would lower the incidence of neonatal sepsis in premature infants. Methods : The study involves 223 premature infants who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit of Hanyang University Kuri Hospital from July 1995 to January 1999. Infants were divided into two groups based on different parenteral nutrition guidelines : Old... -
- Effect of Granulocyte-macrophage Colony-stimulating Factor in Neonatal Infection
- Il-Young Jo, Sang-Hyun Byun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(12):1552-1557. Published online December 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Neutrophils are central to the defences against bacterial infection, and in neonates the number of neutrophils are decreased due to inhibited production and phagocytic function. This induces high mortality rates in infants suffering from neonatal sepsis. Exogenous GM-CSF can increase the number of neutrophils and improve the phagocytic function. To establish the most cost effective dose of exogenous... -
- Risk Factors for Neonatal Sepsis in Premature Infants Admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Chang-Ryul Kim, Jae-Won Oh, Myung-Kul Yum, Soo-Jee Moon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(9):1174-1179. Published online September 15, 2000
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study is to find out the risk factors of sepsis except the prematurity itself. Methods : Seventy-seven premature infants less than 37 weeks of gestation, who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit of Hanyang University Kuri Hospital between July 1995 and December 1996, were enrolled in this study. All 77 premature infants, 14... -
- Intralipid Infusions Effect on Nutrophil Elastase Level in Newborns
- Sue Jeen Min, Yong Woon Baek, Yong Woon Baek, Yong Woon Baek
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(5):666-671. Published online May 15, 1999
-
Purpose : Parenteral nutrition is given to infants who tempararily cannot take oral feeding adequately. A lipid emulsion is added to the parenteral to supply essential fatty acids. In neonatal sepsis, elastase from azuropilic granules of the neutrophils is released and rapidly bound to α1- Proteinase Inhibitor(α1-PI). The lipid emulsion has been noted to markedly inhibit chemotaxis of neutrophils, so... -
- Retrospective 3-year Clinical Study of Enterobacter Bacteremia in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Kwang Ok Chung, Chun Hyuk Chang, Sung Min Cho, Dong Seok Lee, Doo Kwun Kim, Sung Min Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(4):466-471. Published online April 15, 1998
-
Purpose : Enterobacter is one of the important organisms in neonatal intensive care unit. We reviewed the clinical characteristics, underlying diseases, invasive procedures during admission, mortality and antibiotic sensitivity of Enterobacter infection in NICU. Methods : We retrospectively reviewed 21 neonatal patients whose blood cultures yielded Enterobacter between June 1994 and June 1997 at Dongguk University Hospital. Results : Blood cultures were positive in 62... -
- The Significance of Increased Circulating Intercellular Adhesion Molecule 1(cICAM-1) in Neonatal Sepsis
- Hai Lee Chung, Eun Jung Park, Young Ho An, Jin Bok Hwang, Chang Ho Han, Young Dae Kwon, Sang Gyoung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(12):1651-1659. Published online December 15, 1997
-
Purpose : The early and efficient diagnosis of neonatal sepsis still remains a difficult task. Reliable laboratory test is not available yet and treatment is mainly based on the physical appearance of infants. And high number of negative blood cultures in cases of clinically diagnosed sepsis further emphasize the need for a more reliable index for early diagnosis. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1(ICAM-1) has been... -
- Genital Mycoplasmasin the Newborn Infants: Colonization, Prevalence and Clinical Significance
- Yun Sil Chang, Sung Gwon Kim, Beyong Il Kim, Won Soon Park, Bo Hyun Yoon, Eui Chong Kim, Jung-Hwan Choi, Chong Ku Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1996;39(8):1084-1094. Published online August 15, 1996
-
Purpose : The genital mycoplasmas: Ureaplasma urealyticum and Mycoplasma hominis have recently assumed an increasing importance as neonatal pathogens especially in preterm infants. The aim of the present study was to determine the prevalence of infections with these organisms in newborn infants who were admitted in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit(NICU) and who were suspected having infection in newborn nursery Methods : Sixty four inborns who... -
- Changes of Serum Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Interleukin-1β in the Sepsis of Neonates
- Mi Yeon Lee, Yeon Kyun Oh, Ji Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1995;38(10):1307-1314. Published online October 15, 1995
-
Purpose : Cytokines have recently been identified as important endogenous mediators of the host immune response to bacterial infection. But little is clarify about serum levels of cytokines in neonatal sepsis. The aim of this study was to know the changes of the level of cytokines during neonatal sepsis, to compare the level of cytokines in gram negative and gram... -
-
- Clinical Observation of Neonatal Sepsis according to Onset of Disease
- Young Chul Han, Soon Kyung Baik, Chang Sung Lim, Dong Jin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(12):1676-1686. Published online December 15, 1994
-
-
- Comparison between Preterm and Fullterm infants in Neonatal Sepsis
- Sung Hee Kim, Kum Hee Hur, Hee Sup Kim, Myoung Jae Chey, Kil Hyoun Kim, Hak Soo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(11):1542-1554. Published online November 15, 1993
-
We retrospectively evaluated datas on 61 cases of neonatal sepsis confirmed by clinical symptoms and blood cultures at the NICU of Gil General Hospital From Mar. 1989, to Reb. 1992. The result obtained were as follows : 1) The mean gestational age was 32.7±2.6 weeks in preterm infants, and 39±1.5weeks on term infants. The mean birth weight was 1,701.4±422.4g in preterm infants,... -
- A Clinical Study of Neonatal Sepsis
- Hyoung Shim Chang, Jung Sook Park, Young Ho Lee, Ahn Hong Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(6):771-777. Published online June 15, 1993
-
The 35 newborns with neonatal sepsis admitted to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit of Dong-A Univesity Hospital during 2 years and 6months from April 1990 to October 1992, and were reivewed on the bases of incidence, clinical manifestations, underlying conditions, etiologic organisms, results of antibiotics sensitivity test and mortality rate. The result were summarized as follows; 1) The incidence of neonatal sepsis... -
- A Clinical Study on Early Diagnosis in Neonatal Sepsis
- Jong Kwang Lee, Hae Won Cheon, Jee Hee Park, Jung Hwa Lee, Joo Won Lee, Soon Kyum Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(1):49-56. Published online January 15, 1993
-
Neonatal sepsis is a major contributing factor for increased mortality and morbidity in the newborn and its successful outcome depends on early detection and prompt institution of an effective antimicrobial therapy. Accurate diagnosis of the neonatal septicemia, however, is quite difficult because its early signs and symptoms are rather subtle. This study was conducted in an attempt to search for useful... -
- Case Report
- Four Case of Neonatal Group B Streptococcal Sepsis/Meningitis
- Jae Geon Sim, Soon Wha Kim, Young Jin Hong, Don Hee Ahn, Keun Chan Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(2):275-281. Published online February 15, 1992
-
Authors have experienced four cases of neonatal sepsis and meningitis whose organisms were group B streptococci which are thought to be rare causative agent for neonatal sepsis in Korea. Two of four cases were early onset type. Three of them were recovered with antibiotic therapy. One of three alives was found to have mild neurologic sequelae when we examined him... -
- Original Article
- Predictive factors and initial selection of antibiotics in neonatal sepsis.
- Dong Chul Park, Chul Lee, Kook In Park, Ran Namgung, Dong Gwan Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(6):755-762. Published online June 30, 1991
-
For simplifying and standardizing the interpretation of usual findings for neonatal sepsis, prenatal and perinatal factors, clinical symptoms and signs, method of management and hematologic findings were evaluated as a screening test. From the data obtained, a scoring system was formulated that assigns a score of 3 for diarrhea, 1. 5 for tachypnea, 1.5 for cyanosis, 1 for umbilical vessel catheterization, 1 for intravenous... -
- A Study of Clinical Observations in Neonatal Sepsis.
- E S Kim, K H Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(9):1180-1187. Published online September 30, 1990
-
We have experienced 67 cases of neonatal sepsis confirmed by clinical symptoms and blood culture between July 1983 and June 1988 at Ewha university hospital. The results obtained were as follows: 1) The incidence of septicemia was 0.6%. The sex ratio of patients was 0.97:1 with 33 males and 34 females. 2) The incidence was higher in preterm babies than in full term babies and higher in... -
- Sepsis Associated with Total Parenteral Nutrition in the Neonates.
- Jae Won Huh, Jo Sam Koo, Yun Joo Cheung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1989;32(4):495-499. Published online April 30, 1989
-
The retrospective study was performed on the 33 neonates with TPN admitted to the nursery of Gospel Hospital of Kosin medical college between January 1985 and Jun 1987. 1) The incidence of sepsis during TPN was 27% and it was related only to the duration of TPN received for more than 7 days. 2) Major organisms were S. epidermids (30%), Enterobacter cloacae (20%). 3) Major... -
- Analysis for Causative Agents in Neonatal Sepsis.
- Jung Sook Hong, Ki Ji Lee, Shul Hoe Koo, Yun Joo Cheung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1988;31(1):22-28. Published online January 31, 1988
-
To determine causative organisms and their antibitotics sensitivities in neonatal sepsis, we made a review on the 26 cases of neonatal sepsis. Patients were admitted to the special care nursery of Gospel hospital of Kosin Medical College during the period of 2 years from January 1985 to December 1986 and the results were: 1) The most frequently growing organism was Staphylococcus epidermidis (34.6%) and drugs... -
- Clinical Observations on Neonatal Sepsis.
- Beyong Il Kim, Hae Lim Chung, Yoon Deok Kim, Weon Soon Park, Son Moon Shin, Hoan Jong Lee, Jung Hwan Choi, Chong Ku Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1987;30(2):130-138. Published online February 28, 1987
-
We studied the 73 cases of proven neonatal sepsis among 11,102 newborn infant under 1 month of age, admitted to the pediatric ward, the nursery and the NICU of Seoul National University Hospital from Jan. 1, 1980, to Dec. 31, 1985. The results were as follows: 1) The incidence was 6.6/1000 live births. Incidence of male babies was 8.3/1000 live births. The morbidity rate of... -
- Clinical observation in 72 Cases with Neonatal Sepsis.
- Jae Seung Yang, Ran Namgung, Chul Lee, Dong Gwan Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1986;29(12):1309-1313. Published online December 31, 1986
-
Since the clinical features of neonatal sepsis were first reported by Dunham in 1933, there have been many studies. But because of the uncertain early symptoms and it’s rapid progression, the mortality rate of neonatal sepsis runs still high. We are reporting 72 cases of neonatal sepsis confirmed by clinical symptoms and blood culture studies over 3 years and 5 months between... -
- Premature Rupture of Membranes and Its Effect on Neonatal Sepsis.
- Weon Soon Park, Chong Ku Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(12):1162-1167. Published online December 31, 1984
-
A clinical study was carried out to evaluate the effect of PROM on neonatal sepsis on 626 newborns with PROM, who had been born at SNUH during the two-year period from January 1982 to December 1983. The results were as follows; 1) The incidence of PROM was 16.5% and the frequency of prematurity and neonatal sepsis was increased in newborns with PROM. 2) The... -
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











