Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Promising candidate cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of seizure disorder, infection, inflammation, tumor, and traumatic brain injury in pediatric patients
- Seh Hyun Kim, Soo Ahn Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):56-64. Published online August 23, 2021
-
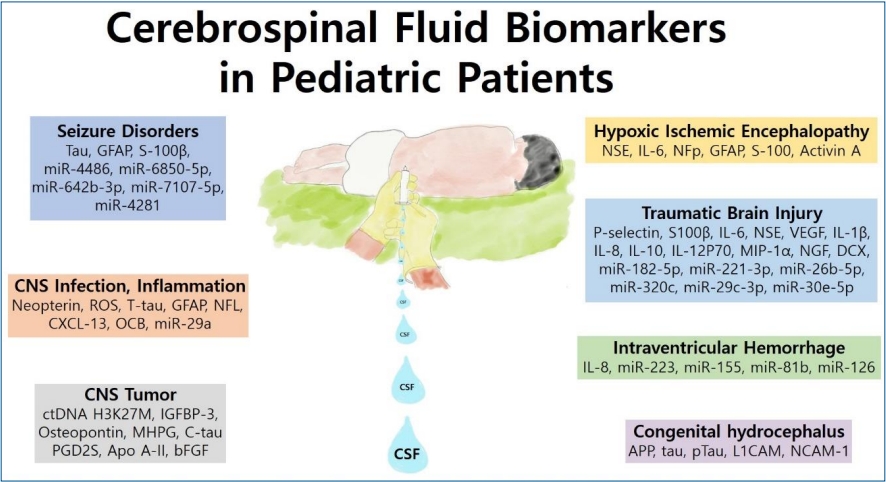
· Pediatric cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) components have been extensively evaluated as biomarkers of various neurologic diseases.
· Several promising candidate CSF biomarkers, including Tau, glial fibrillary acidic protein, neuron-specific enolase, S100β, and interleukins, have been studied in pediatric patients with seizure disorders, central nervous system infections, inflammation, tumors, hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, traumatic brain injuries, intraventricular hemorrhage, and congenital hydrocephalus.
· Circulating microRNAs in the CSF are a promising class of biomarkers for various neurological diseases.
- Original Article
- Gastroenterology
- Influence of proton pump inhibitor therapy on intestinal inflammation assessed by fecal calprotectin in pediatric patients
- Su Yeong Kim, Na Mi Lee, Sin Weon Yun, Soo Ahn Chae, In Seok Lim, Eung Sang Choi, Dae Yong Yi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):400-404. Published online July 3, 2019
-
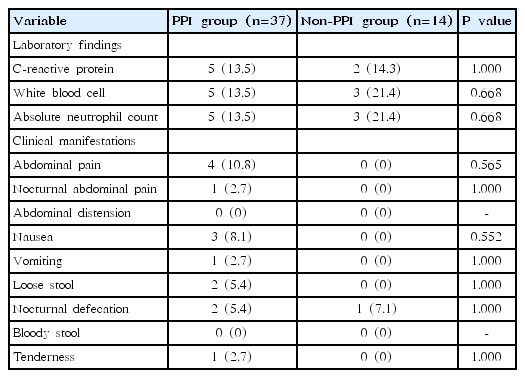
Background: An increase in the numbers of patients with gastrointestinal symptoms has recently been observed.
Purpose: To investigate the effects of proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy on intestinal inflammation in children and adolescents as confirmed by clinical manifestations and objectively assessed by fecal calprotectin (FC) level measurement. Methods: Consecutive children (aged 3–18 years) who presented with gastrointestinal symptoms and were treated with...
- Neuroprotective effects of mild hypoxia in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures
- Seh Hyun Kim, Woo Soon Lee, Na Mi Lee, Soo Ahn Chae, Sin Weon Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(4):142-147. Published online April 22, 2015
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to investigate the potential effects of mild hypoxia in the mature and immature brain.
Methods We prepared organotypic slice cultures of the hippocampus and used hippocampal tissue cultures at 7 and 14 days
in vitro (DIV) to represent the immature and mature brain, respectively. Tissue cultures were exposed to 10% oxygen for 60 minutes. Twenty-four hours...
- Susceptibility of rat hippocampal neurons to hypothermia during development
- Kyung Ah Seo, Sehhyun Kim, Na Mi Lee, Soo Ahn Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(10):446-450. Published online October 31, 2013
-
Purpose This study evaluated the extent of damage due to hypothermia in the mature and immature brain.
Methods Hippocampal tissue cultures at 7 and 14 days
in vitro (DIV) were used to represent the immature and mature brain, respectively. The cultures were exposed at 25℃ for 0, 10, 30, and 60 minutes (n=30 in each subgroup). Propidium iodide fluorescent images were captured 24...
- Clinical significance of matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 and 2 in Kawasaki disease
- Ki Wook Yun, Sin Weon Sin, Jung Ju Lee, Soo Ahn Chae, In Seok Lim, Eung Sang Choi, Byoung Hoon Yoo, Mi-Kyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(4):510-518. Published online April 15, 2010
-
Purpose : Kawasaki disease (KD) is a systemic vasculitis, a leading cause of pediatric acquired heart disease. Histopathological findings of coronary artery lesion (CAL) in KD indicate destruction of the coronary artery wall with diffuse vasculitis. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their endogenous tissue inhibitors (TIMPs) might play central roles in this process. Special attention to MMP-9 has recently been emerging.... -
- Epidemiologic and clinical features in children with acute lower respiratory tract infection caused by human metapneumovirus in 2006-2007
- Gwi Ok Park, Ji Hyun Kim, Jae Hee Lee, Jung Ju Lee, Sin Weon Yun, In Seok Lim, Dong Keun Lee, Eung Sang Choi, Byoung Hoon Yoo,, Mi Kyung Lee, Soo Ahn Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):330-338. Published online March 15, 2009
-
Purpose : The causes of acute lower respiratory tract infection (ALRTI) are mostly attributable to viral infection, including respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), parainfluenza virus (PIV), influenza virus A/B (IFV A/B), or adenovirus (ADV). Several Korean studies reported human metapneumovirus (hMPV) as a common pathogen of ALRTI. However, studies on seasonal distribution and clinical differences relative to other viruses are insufficient,... -
- Case Report
- A case of herpes zoster in a 4-month-old infant
- Ji Hyun Kim, Jung Ju Lee, Sin Weon Yun, Soo Ahn Chae, In Seok Lim, Dong Keun Lee, Eung Sang Choi, Byoung Hoon Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(12):1368-1371. Published online December 15, 2008
-
Herpes zoster in infancy is very rare but can be developed following intrauterine or postnatal exposure to varicella zoster virus. We report a case of herpes zoster in a 4-month-old male infant. He had no prior history of primary varicella or varicella vaccination. His mother had no history of varicella infection and no contact history with varicella during pregnancy. He... -
- Original Article
- Clinical significance of serum vascular endothelial growth factor in Kawasaki disease
- Ho Seok Lee, Sin Weon Yun, Young Soo Jung, Soo Ahn Chae, In Seok Lim, Dong Keun Lee, Eung Sang Choi, Byung Hoon Yoo, Mi Kyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(10):995-1004. Published online October 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Kawasaki disease is a systemic vasculitis, leading cause of pediatric acquired heart disease. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) has functions as vascular permeability factor, plays an important role in coronary artery lesion (CAL). We studied the clinical significance of serum VEGF in Kawasaki disease. Methods : Kawasaki group was 49 patients, and control group was 15 patients. Diagnosis followed... -
- Effects of electromagnetic stimulation on neurogenesis and neuronal proliferation in rat hippocampal slice culture
- Deok-Soo Kim, Eung Sang Choi, Soo Ahn Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(5):558-564. Published online May 15, 2006
-
Purpose : Transcranial electromagnetic stimulation(TMS) is a noninvasive method which stimulates the central nervous system through pulsed magnetic fields without direct effect on the neurons. Although the neurobiologic mechanisms of magnetic stimulation are unknown, the effects on the brain are variable according to the diverse stimulation protocols. This study aims to observe the effect of the magnetic stimulation with two... -
- Clinical Findings of Mycoplasma Pneumonia in Children, from 1998 to 2003
- Ji-Hyun Kim, Soo Ahn Chae, Dong-Keun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(9):969-975. Published online September 15, 2005
-
Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Chung Ang University, Seoul, Korea Purpose : We performed a study of clinical findings of Mycoplasma Pneumonia in children, to know differences between recent clinical manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumonia and previous studies. Methods : The subjects of this study were 393 children who were diagnosed as Mycoplasma pneumonia with high titers of Mycoplasma antibody(≥1 : 160)... -
- Clinical Lecture
- Clinical Approach to Headache in Childhood
- Soo Ahn Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(4):349-354. Published online April 15, 2005
-
Headache is a common complaint in pediatric office practices as well as in children presenting to emergency departments. Children who complain of headache usually are brought to medical attention by their parents, who seek reassurance that the headaches are not a sign of a serious illness. The etiologies of headache range from school problems to brain tumors. A history taking,... -
- Original Article
- The Significance of Serologic Allergy Tests in Children with Recurrent Pneumonia
- Yoon Hee Sim, Sin Weon Yun, Soo Ahn Chae, Dong Keun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(6):634-640. Published online June 15, 2004
-
Purpose : Pneumonia is one of the most common respiratory diseases in hospitalized children, and often recurs. It has been reported that asthma is one of the significant contributing factors to recurrent pneumonia. On the basis of similarities between asthma and recurrent pneumonia, we intended to evaluate the influence of allergy on recurrent pneumonia. Methods : Seventy one children with... -
- Apoptosis, P53, bax and Bcl-2 Protein Expressions in Neonatal rat Hippocampus by Kainic Acid-induced Seizure
- Shin Weon Yun, Soo Ahn Chae, Eung sang Choi, Byoung Hoon Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(1):85-96. Published online January 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Apoptosis is a process of active cell death which has been suggested to be part of hippocampal cell loss caused by kainic acid(KA). Immature rats showed higher susceptibility and mortality to KA but did not develop recurrent seizure, long term behavioral or neuropathologic changes. We investigated whether this was due to age-dependent resistance, and elucidated the molecular mechanics which mediate P53-induced apoptosis,... -
- Clinical Significance of Serum ECP in Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia
- Young Ghil Rah, Dong Keun Lee, In Seok Lim, Eung Sang Choi, Soo Ahn Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(5):672-678. Published online May 15, 1999
-
Purpose : Allergic inflammation of the lower respiratory tract is a characteristic clinical feature in asthma patients, in which eosinophils play an important role. The activity of eosinophil may be determined by measuring the level of eosinophil cationic protein(ECP) in sputum or serum as a potential marker of the inflammatory severity. Methods : We measured the serum concentrations of ECP... -
- Immunohistochemical Expression of c-fos Protein and Histologic Findings after Instillation of Kainic Acid in Hippocampus of Neonatal Rat Brain
- Soo Ahn Chae, Yong Soo Kim, Byoung Hoon Yoo, Won Bok Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(4):553-560. Published online April 15, 1999
-
Purpose : c-fos is rapidly and transiently induced in the intact CNS by a wide variety of exogenous stimuli that include seizures, glutamate receptor activation, sensory stimulation and stress. In adult animals, systemic KA administration produces limbic seizures that results in c-fos protein expression, irreversible morphological changes and localized neuronal death. So we studied the pattern of c-fos protein expression... -
- MELAS Syndrome Confirmed by Mitochondrial DNA Analysis in Siblings
- Young Ghil Rah, Soo Ahn Chae, In Suk Lim, Dong Keun Lee, Byoung Hun Yoo, Tae Sung Ko, Han Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(3):412-418. Published online March 15, 1999
-
MELAS(mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes) syndrome is a major subgroup of mitochondrial myopathy. Recent advances in molecular genetics revealed specific mutations in mitochondrial DNA which cause MELAS. We described here clinical and molecular genetic findings of sister and brother with MELAS syndrome. For molecular genetic studies, DNAs from peripheral blood nucleated cells were used. And the substitution... -
- Clinical Study of Post-Traumatic Seizure in Childhood and Adolescence
- Jang Weon Moon, Soo Ahn Chae, Dong Keun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(2):227-232. Published online February 15, 1999
-
Purpose : As morbidity and mortality resulting from physical trauma have significantly increased, the importance of trauma concerning medical, legal, and socioeconomic issues has been widely documented. Studies of post-traumatic seizure after head trauma have been reported, but mostly in adults. So this study was performed to analyse clinical findings on head trauma patients under 20 years of age. Methods :... -
- Nonspecific Bronlchial Reactivity Determined by Tidal Breathing Method and Chest Auscultation - A Comparison with Dosimeter Method -
- Soo Ahn Chae, Young Yull Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(7):946-952. Published online July 15, 1994
-
As a preliminary step to determine if we can perform methacholine challenge test in young children, we investigated the feasibility of modified technique of methacholine challenge test in which tidal breathing and chest auscultation were used instead of dosimeter and measurement of lung function in older children. The results are as follows 1) Values of PC20 measured by the tidal breathing... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Aicardi Syndrome with Cleft Lip and Palate
- In Seok Yang, Gyung Og Yu, Soo Ahn Chae, Dug Ha Kim, Chong Young Park, Ik Won Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(9):1325-1330. Published online September 15, 1993
-
A case of Aicardi syndrome with cleft lip and palate was experienced at the Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Hallym University, and the patient's infantile spasm was treated with ACTH. In previous studies, four cases of Aicardi syndrome accompanied by cleft lip and palate were reported. We present the fifth case of Aicardi syndrome with cleft lip and palate... -
- Original Article
- The Effectf Zonisamide in Children with Refractory Epilepsies
- Ki Joong Kim, Soo Ahn Chae, Tae Sung Ko, Dong Wook Kim, Yong Seung Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(8):1139-1145. Published online August 15, 1993
-
Zonisamide was amministered to 20 patients with refractory epileptic seizures. The mean duration of the administration was 6 months, and the mean dosage was 7.2mg/kg/day. The efficacy of zonisamide was rated remarkable in 15% of the cases, improvement in 40%, and no change in 45%. The response rates of zonisamide were 62.5% for myoclonic seizures, 50% for tonic-clonic seizures, 80% for... -
- Clinical Study on Spinal Muscular Atrophies
- Soo Ahn Chae, Yong Seung Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(12):1728-1736. Published online December 15, 1992
-
Spinal muscular atrophies (SMA) are degenerative diseases of motor neurons that begin in fetal life and continue to be progressive in infancy and childhood. Since Werdnig's description of Type 1 SMA in 1891, numerous clinical and experimental studies have been carried out in America and Europe. Few cases were reported about these diseases in Korea but there was no systemic... -
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94nd percentilePowered by







