Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Comparing ethyl chloride and 10% lignocaine spray for pediatric intravenous cannulation pain relief
- Susmitha Vellanki, Malavika Kulkarni, Arun Kumar H D, Deepali Shetty, Nikhil B Karthik, Mathew Tom
-
Background: Intravenous cannulation (IVC) is a routine yet distressing procedure in pediatric patients, often provoking significant anxiety and procedural pain. Although eutectic mixtures such as eutectic mixture of local anesthetic cream are widely used, their delayed onset limits their applicability in time-sensitive settings. Ethyl chloride vapocoolant spray and 10% lignocaine spray have been proposed as rapid-onset alternatives, yet direct comparative... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.00010 [Accepted]
- Review Article
- Infection
- Central line-associated bloodstream infections in neonates
- Hye Jung Cho, Hye-Kyung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(3):79-84. Published online December 19, 2018
-
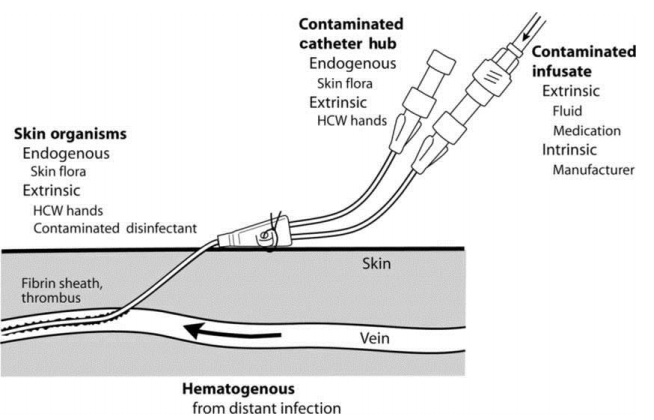
Newborn infants, including premature infants, are high-risk patients susceptible to various microorganisms. Catheter-related bloodstream infections are the most common type of nosocomial infections in this population. Regular education and training of medical staffs are most important as a preventive strategy for central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs). Bundle approaches and the use of checklists during the insertion and maintenance of central...
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Outcomes of transcatheter closure of ductus arteriosus in infants less than 6 months of age: a single-center experience
- Gwang-Jun Choi, Jinyoung Song, Yi-Seul Kim, Heirim Lee, June Huh, I-Seok Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(12):397-402. Published online September 19, 2018
-
Purpose: Transcatheter device closure of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is challenging in early infancy. We evaluated PDA closure in infants less than 6 months old. Methods: We performed a retrospective review of infants less than 6 months of age who underwent attempted transcatheter device closure in our institution since 2004. To compare clinical outcomes between age groups, infants aged 6–12 months...
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Recent advances in pediatric interventional cardiology
- Seong-Ho Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(8):237-244. Published online August 14, 2017
-
During the last 10 years, there have been major technological achievements in pediatric interventional cardiology. In addition, there have been several advances in cardiac imaging, especially in 3-dimensional imaging of echocardiography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and cineangiography. Therefore, more types of congenital heart diseases can be treated in the cardiac catheter laboratory today than ever before. Furthermore, lesions previously...
- Case Report
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Successfully treated infective endocarditis caused by methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus Aureus in extremely low birth weight infant - Sehwa Jung, Kyung Uk Jeong, Jang Hoon Lee, Jo Won Jung, Moon Sung Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(2):96-99. Published online February 29, 2016
-
Survival rates of preterm infants have improved in the past few decades, and central venous catheters play an important role in the intensive medical treatment of these neonates. Unfortunately, these indwelling catheters increase the risk of intracardiac thrombosis, and they provide a nidus for microorganisms during the course of septicemia. Herein, we report a case of persistent bacteremia due to...
- Original Article
- Validity of bag urine culture for predicting urinary tract infections in febrile infants: a paired comparison of urine collection methods
- Geun-A Kim, Ja-Wook Koo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(5):183-189. Published online May 22, 2015
-
Purpose Catheter urine (CATH-U) and suprapubic aspiration (SPA) are reliable urine collection methods for confirming urinary tract infections (UTI) in infants. However, noninvasive and easily accessible collecting bag urine (CBU) is widely used, despite its high contamination rate. This study investigated the validity of CBU cultures for diagnosing UTIs, using CATH-U culture results as the gold standard.
Methods We retrospectively analyzed 210 infants,...
- Ultrasound-guided internal jugular vein catheterization in critically ill pediatric patients
- Eu Jeen Yang, Hyeong Seok Ha, Young Hwa Kong, Sun Jun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(4):136-141. Published online April 22, 2015
-
Purpose Continuous intravenous access is imperative in emergency situations. Ultrasound-guided internal jugular vein (IJV) catheterization was investigated in critically ill pediatric patients to assess the feasibility of the procedure.
Methods Patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit between February 2011 and September 2012 were enrolled in this study. All patients received a central venous catheter from attending house staff under ultrasound guidance....
- Transcatheter closure of small ductus arteriosus with amplatzer vascular plug
- Eun Hyun Cho, Jinyoung Song, I-Seok Kang, June Huh, Sang Yoon Lee, Eun Young Choi, Soo Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(9):396-400. Published online September 30, 2013
-
Purpose The purpose of this study was to share our experience of transcatheter closure of small patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) by using an Amplatzer vascular plug (AVP).
Methods We reviewed the medical records of 20 patients who underwent transcatheter closure at Samsung Medical Center and Sejong General Hospital from January 2008 to August 2012. The size and shape of the PDAs were evaluated...
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome in young people, from childhood to young adulthood: relationships between age and clinical and electrophysiological findings
- Hae Jung Jung, Hwang Young Ju, Myung Chul Hyun, Sang Bum Lee, Yeo Hyang Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(12):507-511. Published online December 31, 2011
-
Purpose The aim of the present study was to evaluate the characteristics of electrophysiologic studies (EPS) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) performed in subjects aged less than 30 years with Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome, particularly pediatric patients under 18 years of age, based on our experience.
Methods Two hundred and one consecutive patients with WPW syndrome were recruited and divided to 3 groups according to...
- Review Article
- Catheter-related bloodstream infections in neonatal intensive care units
- Jung Hyun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(9):363-367. Published online September 30, 2011
-
Central venous catheters (CVCs) are regularly used in intensive care units, and catheter-related bloodstream infection (CRBSI) remains a leading cause of healthcare-associated infections, particularly in preterm infants. Increased survival rate of extremely-low-birth-weight infants can be partly attributed to routine practice of CVC placement. The most common types of CVCs used in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) include umbilical venous catheters,...
- Original Article
- Clinical outcome of transcatheter closure of patent ductus arteriosus in small children weighing 10 kg or less
- Young A Park, Nam Kyun Kim, Su-Jin Park, Bong Sic Yun, Jae Young Choi, Jun Hee Sul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(12):1012-1017. Published online December 31, 2010
-
Purpose Transcatheter closure has become an effective therapy in most patients with patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). However, there are difficulties in transcatheter closure of PDA in small children. We reviewed clinical outcomes of transcatheter closure of PDA in children weighing less than 10 kg in a single center.
Methods Between January 2003 and December 2009, 314 patients with PDA underwent transcatheter closure in...
- Case Report
- Use of an Amplatzer Vascular Plug to occlude a tubular type of patent ductus arteriosus
- Eun-Young Choi, So-Ick Jang, Soo-Jin Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(9):1035-1037. Published online September 15, 2009
-
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a common congenital heart defect. All PDAs, regardless of size or degree of symptoms, require occlusion. Transcatheter PDA occlusion features fewer complications than trans-thoracic closure. It is also more cost-effective and has an excellent occlusion rate. Therefore, transcatheter PDA occlusion is accepted as the standard treatment option for PDA. However, tubular-type PDAs are difficult to... -
- Original Article
- The efficacy and safety of transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect with Amplatzer septal occluder in young children less than 3 years of age
- Soo Hyun Lee, Deok Young Choi, Nam Kyun Kim, Jae Young Choi, Jun Hee Sul
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(4):494-498. Published online April 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Applicability of transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect (ASD) has been expanded by accumulation of clinical experiences and evolutions of the device. This study was performed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of transcatheter closure of ASD with Amplatzer septal occluder (ASO) in young children less than 3 years of age. Methods : From May 2003 to December... -
- Case Report
- Availability of peripheral inserted central catheters in severe hemophilia patients with inhibitors
- Youngshil Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(12):1359-1362. Published online December 15, 2008
-
The most effective treatment strategy for patients with hemophilia is replacement therapy with FVIII or FIX concentrates, which usually requires long-term, uncomplicated venous access. However, central venous access device (CVADs, ports) insertion requires inpatient admission and general anesthesia, and presents some problems regarding health insurance coverage. Peripherally inserted central catheters (PICCs) were inserted in two severe hemophilia patients aged 7... -
- Original Article
- Complications of transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects using the amplatzer septal occluder
- Seo Jin Jea, Hyo Jin Kwon, Gi Young Jang, Jae Young Lee, Soo Jin Kim, Chang Sung Son, Joo Won Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(4):401-408. Published online April 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects (ASD) is currently established therapy as an alternative to surgery. But rarely, complications are reported in some studies. We report early and intermediate term complications associated with transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects using the Amplatzer septal occluder (ASO). Methods : From June 2003 to May 2006, 64 patients underwent transcatheter closure of... -
- Review Article
- Characteristics of allergic pollens and the recent increase of sensitization rate to weed pollen in childhood in Korea
- Jae-Won Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(4):355-361. Published online April 15, 2008
-
Pollen is very important causing factor for allergy such as allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, and asthma, and pollen allergy has a remarkable clinical impact all over Korea. The main pollination period covers about half the year, from spring to autumn, and the distribution of airborne pollen taxa of allergological interest is related to pollen season dynamics. Korean academy of pediatric... -
- Original Article
- Results of radiofrequency catheter ablation in children and adolescent with tachyarrhythmia
- Young Beom Chang, Seung Hyun Lee, Eun Young Kang, Kyoung-Suk Rhee, Chan Uhng Joo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(11):1085-1090. Published online November 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFCA) has become an effective therapeutic modality for treating pediatric tachyarrhythmias. Using conventional RFCA catheters, ablation of parahisian accessory pathways may be difficult and have high risk for heart block. We reviewed the efficacy and complications of the RFCA in children and adolescent with arrhythmias including parahisian accessory pathways. Methods : We studied 48 patients... -
- Case Report
- Perforation of azygos vein and right-sided hydrothorax caused by peripherally inserted central catheter in extremely low birth weight infant
- Kee Soo Ha, Jung Yeon Shin, Mi Jung Hwang, Young Ok Choi, Dong Han Shin, Gi Young Jang, Byung Min Choi, Kee Hwan Yoo, Young Sook Hong, Chang Sung Son
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(8):902-905. Published online August 15, 2006
-
We report a case in which routine chest roentgenograms of an 840 g infant led to the belief that the peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) was appropriately positioned within the superior vena cava when, in actuality, it was within the azygous arch. Although many cases of pleural effusions have been reported to be caused by a central venous catheter, a... -
- Original Article
- Umbilical venous line-related pleural and pericardial effusion causing cardiac tamponade in a premature neonate : A case report
- Eun Jeong Hong, Kyung A Lee, Il-Heon Bae, Mi-Jung Kim, Heon-Seok Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(6):686-690. Published online June 15, 2006
-
Cardiac tamponade with pleural and pericardial effusion is a rare but life-threatening complication of umbilical venous catheterization in the newborn. It requires a timely diagnosis and urgent treatment, such as pericardiocentesis, to save lives of affected patients. Recently, we experienced a 7 day-old, very low birth weight infant, who developed a cardiac tamponade with pleural and pericardial effusions complicated by... -
- Epidemiology of central venous catheter related blood stream infections in pediatric patients
- Jung Hyun Kim, Ho Sun Eun, Kyung Min Choi, Dong Soo Kim, Dong Eun Young
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(2):157-161. Published online February 15, 2006
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study is to investigate the pathogens of central venous catheter-related blood stream infections and search for the association among the insertion site, the duration and the underlying conditions with the prevalence of central venous catheter-related blood stream infections under 15 years old. Methods : A retrospective study was performed from Jan, 2003 to Dec, 2003... -
- Case Report
- Transcatheter Closure of a Residual Shunt after Surgical Repair of Traumatic Ventricular Septal Defect
- Hee Jeong Jeong, Han Hyuk Lim, Jae Hyun Yu, Jae Hwan Lee, Hong Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(10):1143-1147. Published online October 15, 2005
-
The traumatic ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a rare but potentially life threatening complication of chest wall injury. The traumatic VSD occurs in up to 4.5% of penetrating cardiac trauma. Most of the patients are usually operated on because of heart failure and/or significant left-to-right shunt. The feasibility of surgical repair under cardiopulmonary bypass may be affected by coexisting pulmonary,... -
- Original Article
- Clinical Use and Complications of Percutaneous Central Venous Catheterization in Very Low Birth Weight Infants
- Hyang Kim, Sun Hui Kim, Hyung Suck Byun, Young Youn Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(9):953-959. Published online September 15, 2005
-
Purpose : The administration of total parenteral nutrition(TPN) has become a standard procedure in the management of nutritionally deprived and critically low birth weight neonates. Sepsis remains the most frequent serious complication during TPN, resulting in increased morbidity, mortality and health care costs. This study was performed to evaluate the clinical efficacy and complications of percutaneous central venous catheterization(PCVC) in... -
- Impact of Device Evolution in Transcatheter Closure of Patent Ductus Arteriosus Using Duct-Occlud Coils : Comparison of Mid-term Results
- Myung Kwan Kim, Dong Ki Han, Jae Young Choi, Yuria Kim, Byung Won Yoo, Deok Young Choi, Jun Hee Sul, Sung Kue Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(2):158-164. Published online February 15, 2005
-
Purpose : We reviewed the therapeutic results of various Duct-Occlud coils(pfm AG, K ln, Germany) to evaluate the efficacy of the most-recently modified Duct-Occlud coil(Nit-Occlud) in the transcatheter closure of patent ductus arteriosus(PDA), including large defects more than 4 mm in diameter. Methods : Two hundred and five patients who underwent percutaneous PDA occlusion using Duct- Occlud devices from March... -
- Mid-term Result of the Transcatheter Occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with Duct-Occlud Device and Procedure-Related Problems
- Yuria Kim, Jae Young Choi, Jong Kyun Lee, Jun Hee Sul, Sung Kyu Lee, Young Hwan Park, Bum Koo Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(1):36-43. Published online January 15, 2004
-
Purpose : We will present our mid-term result of transcatheter closure of PDA with Duct-Occlud device(pfm. AG. Germany) after 12 months follow up and report the problems during the procedure. Methods : In total 154 patients, the Duct-Occlud devices were inserted in our institute from March, 1996 to August, 2002. Three types of Duct-Occlud device, i.e standard, reinforced, reinforced reverse cone... -
- Postoperative Progress and Influencing Factors in Patients after Rastelli Procedure
- Se Heui Kim, Kyeong Sik Kim, Jong Kyun Lee, Jae Young Choi, Jun Hee Sul, Sung Kyu Lee, Young Whan Park, Bum Koo Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(3):259-264. Published online March 15, 2003
-
Purpose : We have performed an analysis on patients who received Rastelli operation in our institute and reviewed their progress postoperatively. Various factors with suspected relationship to the outcome have been considered to help in future treatment and follow-up. Methods : We analyzed retrospectively 43 patients who either received Rastelli operation in Yonsei University Cardiovascular Center from March 1995 to April... -
- Intraarterial Catheter-directed Urokinase Infusion for Femoral Artery Thrombosis after Cardiac Catheterization in Infants and Children
- Hyoung Doo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(11):1397-1402. Published online November 15, 2002
-
Purpose : One of the major complication of arterial catheterization is the thrombosis of the iliac or femoral arteries. Tissue loss following femoral artery catheterization is rare. However long- term sequelae such as impaired limb growth and future impairment of vascular access, are also important in pediatric cardiac patients. But standard methods to treat thrombotic complication of arterial catheterization in... -
- Study of Neonatal Cardiac Catheterization for Over the Last 10 Years
- Jinyoung Song, Sungkyu Lee, Jaeyoung Lee, Sujin Kim, Wooseup Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(5):615-621. Published online May 15, 2002
-
Purpose : The neonatal cardiac catheterization and angiogram for transcatheter therapy are still essential methods in congenital heart disease, so we reviewed our experience with neonatal cardiac catheterization over 10 years at a single institution. Methods : A retrospective review of all 139 neonatal catheterizations from January 1991 to December 2000 at Sejong Heart Institution was performed. The purpose of the... -
- The Effectiveness of Propofol on Pediatric Cardiac Catheterization and Electrophysiologic Study
- Woo Saeng Park, Myung Chul Hyun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(7):773-777. Published online July 15, 2001
-
Purpose : Our purpose was to evaluate the effectiveness of propofol on pediatric cardiac catheterization or radiofrequency catheter ablation. Methods : We measured the serial changes of arterial oxygen saturation, heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure at 4 stages, a baseline(during normal sleep), stage 1(just after loading of propofol 2 mg/kg over 10 minutes), stage 2(10-15 minutes after propofol continuous... -
- Case Report
- Three Cases of Hemolysis After Transcatheter Closure of A Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Sang-Bum Lee, Myung Chul Hyun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(10):1399-1403. Published online October 15, 2000
-
Severe hemolysis occurred after transcatheter occlusion of a patent ductus arteriosus in 3 patients among 41 patients who underwent transcatheter occlusion of a patent ductus arteriosus. The problems were managed by a standard surgical ligation of the duct, leaving the occlusion device(the Rashkind umbrella and a detachable coil) in situ in one patient, surgical removal of the detachable coil and... -
- A Case of Transcatheter Occlusion of Aortopulmonary Window(APW) after APW Banding
- Young Seok Lee, In Seung Park, Jae Young Lee, Soo Jin Kim, Mi Young Han, Do Jun Cho, Eun Jung Bae, Seong Ho Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(9):1290-1293. Published online September 15, 2000
-
Aortopulmonary window is an uncommon cardiac anomaly accounting for approximately 0.2-0.6% of all congenital cardiac anomalies in which there is a connection between the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk. Since the first report of successful surgical repair, many investigators have advocated surgical closure of all types of aortopulmonary windows using different technique. The majority of aortopulmonary windows require surgical therapy... -
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











