Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Balancing therapeutic benefits and hidden risks of proton pump inhibitors in pediatric practice: a narrative review and update
- Maria Rogalidou, Alexandra Papadopoulou
-
Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) effectively treat acid-related disorders, including gastroesophageal reflux disease, eosinophilic esophagitis, peptic ulcers, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Long-term use, particularly in children, may lead to microbiome alterations, nutrient deficiencies, infections, renal injury, osteoporosis, fractures, and other gastrointestinal changes. PPI therapy should be guided by clear clinical indications, prescribed at the lowest effective dose for the shortest necessary duration, and regularly reassessed to minimize risks in young children. -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.02761 [Epub ahead of print]
- Multiomics approaches in Kawasaki disease: insights into pathogenesis and emerging directions for diagnosis and treatment
- Jong Gyun Ahn, Insoo Kang
-
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute febrile vasculitis and the leading cause of acquired heart disease in children. Despite decades of research, the etiology remains unknown and key mechanisms linking systemic inflammation to coronary artery lesions are incompletely defined. High-throughput technologies—including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, epigenomics, and immunomics—have enabled systems-level profiling of KD and highlighted reproducible inflammatory and vascular pathways.... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.02901 [Epub ahead of print]
- Editorial
- Early prediction of bronchopulmonary dysplasia using new classification in high-risk preterm infants
- Ga Won Jeon
-
The definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) has continued to evolve. Recently, newer definitions based on respiratory support at 36 weeks’ postmenstrual age better predict long-term outcomes but diagnose BPD relatively late. To address this limitation, the New Japanese Classification uses early postnatal factors, including small for gestational age and bubbly or cystic chest radiographic findings, to predict severe BPD and enable early targeted interventions. -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2026.00143 [Epub ahead of print]
- Original Article
- Long-term outcome in children with infantile epileptic spasms syndrome: a multicenter retrospective study in Korea
- Sun Ah Choi, Minhye Kim, Hye Jin Kim, Woo Joong Kim, Byung Chan Lim, Ji Yeon Han, Hunmin Kim, Min-Jee Kim, Mi-Sun Yum, Jiwon Lee, Jeehun Lee, Hyewon Woo, Jon Soo Kim
-
Background: Infantile epileptic spasms syndrome (IESS) is a severe form of infantile epilepsy with a high lifetime morbidity burden.
Purpose: We aimed to assess the long-term epilepsy and neurodevelopmental outcomes based on how children with IESS have been managed over the past few decades. Methods: This retrospective multicenter study included children diagnosed with IESS between 1994 and 2021 with a minimum follow-up... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.02089 [Accepted]
- Context-dependent features of transcriptomic landscapes in pregnant mother-neonate dyads of preeclampsia
- Yu-Chun Cheng, Yun-Ju Lai, Wei-Shiung Lian, Ching-Chang Tsai, Hsin-Hsin Cheng, Hong-Ren Yu, Mao-Meng Tiao, Jiunn-Ming Sheen, Ying-Lun Hsu, Feng-Sheng Wang, I-Chun Lin
-
Background: Preeclampsia (PE) is a serious complication of pregnancy that affects the offspring and mothers. Those with a history of PE are at higher risk of future cardiometabolic diseases, the etiology of which remains uncertain.
Purpose: To investigate the transcriptomic profiles of mothers and neonates to determine whether certain genes are commonly affected after shared exposure to PE. Methods: In this observational... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.02565 [Accepted]
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Tocilizumab as a key therapeutic option in high-risk pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy
- Jon Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):114-116. Published online January 26, 2026
-
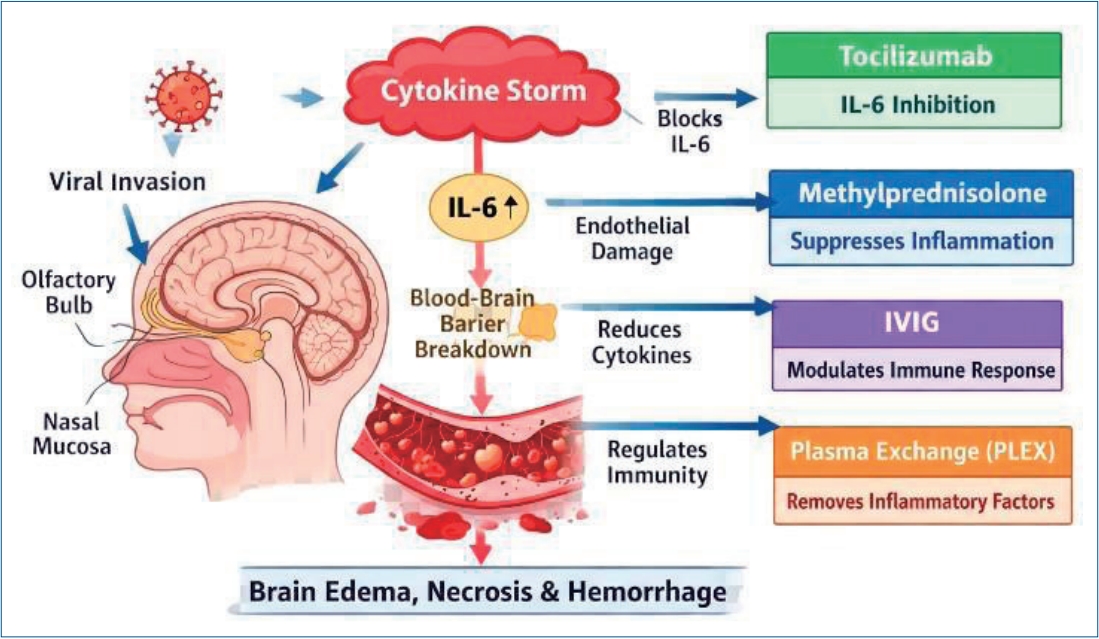
· Acute necrotizing encephalopathy (ANE) is a severe, infection- triggered encephalitis driven primarily by cytokine- mediated immune dysregulation rather than direct viral cytotoxicity.
· Tocilizumab, through targeted inhibition of interleukin-6 signaling, is an important therapeutic option for ANE that may improve survival and neurological outcomes of high-risk pediatric patients.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- Systematic review of influence of ethnicity on efficacy and safety of pharmacotherapy for childhood and adolescent obesity
- Surendra Gupta, Purushottam Lal, Abhishek Gupta, Brajesh Raj Chaudhary
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):84-102. Published online January 26, 2026
-
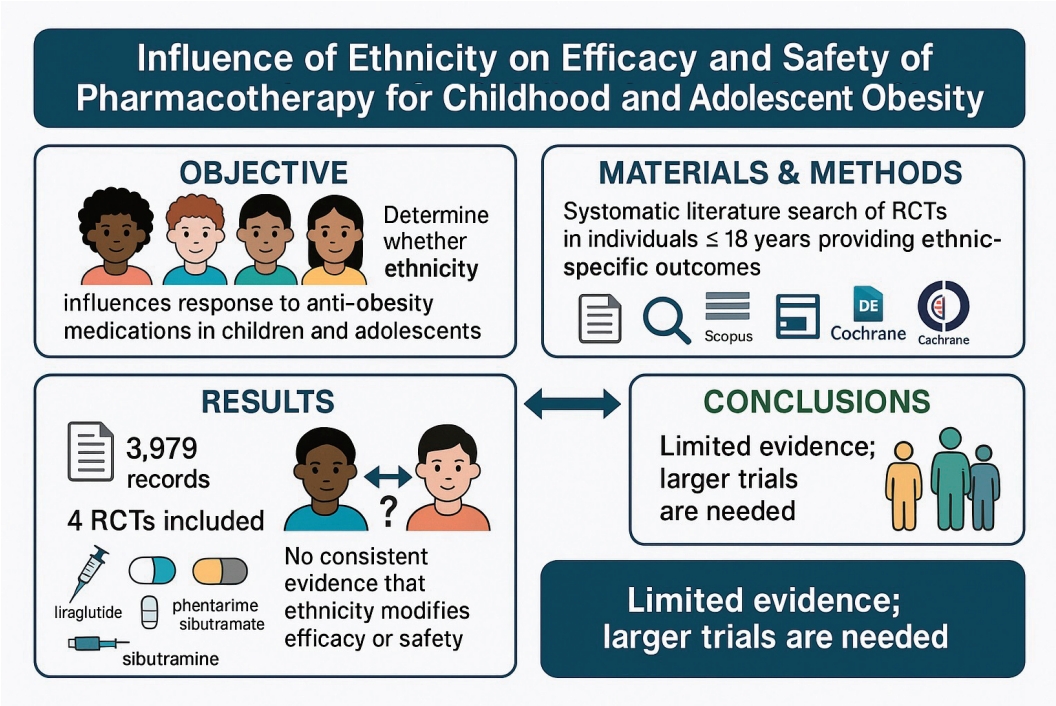
Ethnic variations may influence the response of children and adolescents to obesity pharmacotherapy. Current evidence does not show consistent differences in efficacy or safety among ethnic groups; however, available data are limited. Larger, ethnically diverse trials are needed to develop personalized obesity treatment strategies.
- Clinical Note
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Happle-Tinschert syndrome in an infant: clinical, radiologic and genetic correlation
- Belén Rodríguez-Sanchez, Francisco Javier Narbona-Cárceles, Jorge Martín-Nieto-González, Marina de la Puente-Alonso, Luis Zamarro-Díaz, Luis Jiménez-Briones, Julia Suárez-González, Francisco Arias-Lotto, Minia Campos-Domínguez
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):182-185. Published online January 20, 2026
-
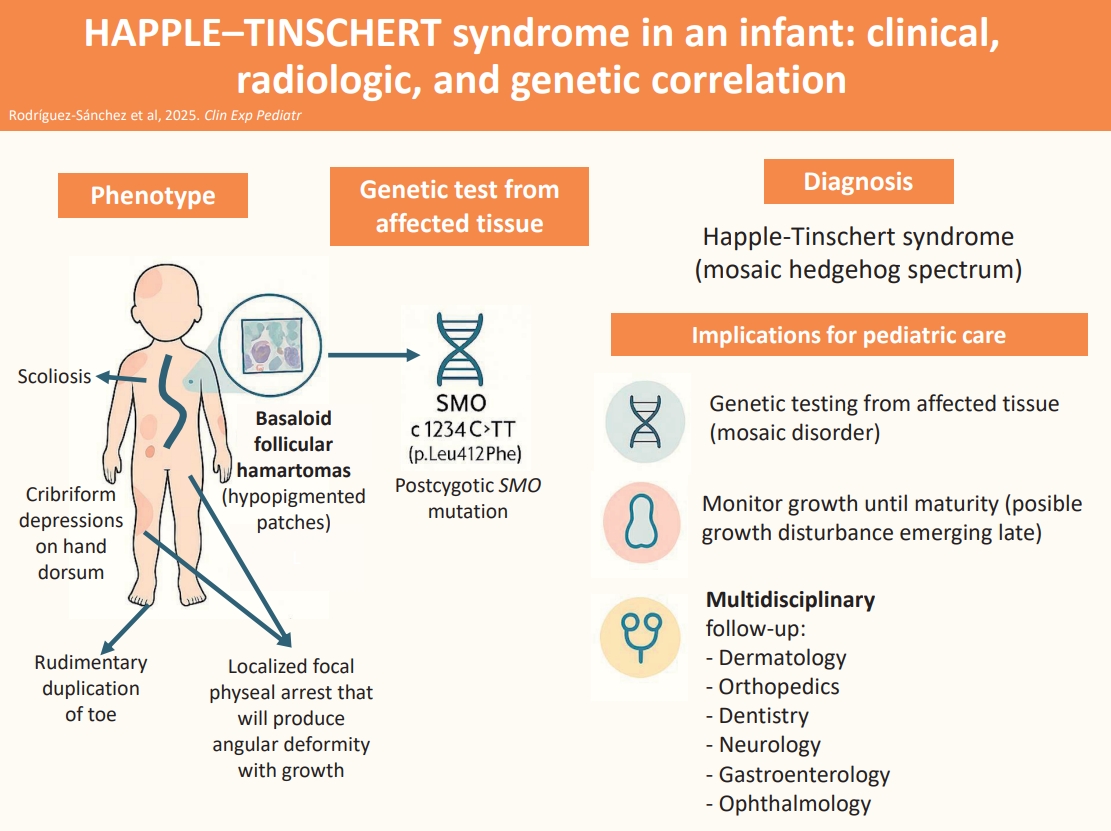
- Original Article
- Validation of a new Japanese classification for predicting severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm infants
- Masato Ito, Shinya Hirano, Fumihiko Namba
-
Background: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is the most prevalent chronic lung disease in very preterm infants; however, conventional classifications have limited ability to predict severity before 36 weeks' postmenstrual age (PMA). A new Japanese classification, based on small for gestational age (SGA), bubbly/cystic chest radiographic findings, and chorioamnionitis (CAM), was proposed to enable earlier risk stratification. However, its validation in homogeneous cohorts is warranted.
Purpose: This study aimed to examine... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.02642 [Accepted]
- Can a basophil activation test of cord blood predict a cow's milk allergy?
- Dilara Fatma Kocacik Uygun, Durmuş Burgucu, Vedat Uygun, Gül Alkan Bulbul, Fulden Duyar, Cem Yasar Sahnal, Aysen Bingöl
-
Question: Can a basophil activation test (BAT) of cord blood predict a cow's milk allergy?
Finding: Infants with a high casein-BAT value were more likely to develop food allergy symptoms in the first year, whereas cow’s milk BAT showed no predictive association.
Meaning: Cord blood casein BAT may help identify newborns at increased risk for early-life food allergies, enabling closer monitoring and preventive strategies, although larger studies are needed for validation. -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.01697 [Epub ahead of print]
- Influence of atrial septal defect on mitral valve growth after repair of coarctation of the aorta or an interrupted aortic arch in infants
- Yi-Chia Wang, Hen-Wen Chou, Chi-Hsiang Huang, Hsing-Hao Huang, Yih-Sharng Chen, En-Ting Wu, Shyh-Jye Chen, Ming-Tai Lin, Shuenn-Nan Chiu, Shu-Chien Huang
-
Background: Patients with coarctation of the aorta (CoA) and an interrupted aortic arch (IAA) may present with small mitral valves (MVs) and a reduced left ventricular (LV) volume. Biventricular repair (BVR) in these patients is dependent on adequate size of the left cardiac structures.
Purpose: This study evaluated the impact of the hemodynamic characteristics of atrial septal defects (ASDs) on MV... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.02110 [Accepted]
- Hemodynamics and cerebral oxygenation in the neonatal transition: a prospective pilot study
- Daniel Pfurtscheller, Christoph Schlatzer, Nina Höller, Bernhard Schwaberger, Lukas Mileder, Nariae Baik-Schneditz, Magdalena Holter, Gerhard Pichler
-
Background: The impact of arterial blood pressure on cerebral oxygenation during immediate postnatal transition is poorly understood.
Purpose: Here we investigated the association between arterial blood pressure (BP), cerebral tissue oxygenation index (cTOI), and cerebral fractional tissue oxygen extraction (cFTOE) during the immediate postnatal transition in preterm and full-term neonates. Methods: This prospective observational study included preterm and term neonates who did... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.02572 [Accepted]
- Granulocyte transfusion improves survival in pediatric febrile neutropenia: a 15-year cohort study
- Witsanu Phetsai, Kleebsabai Sanpakit, Jassada Buaboonnam, Kamon Phuakpet, Nassawee Vathana, Nattee Narkbunnam, Fon Kladed, Chayamon Takpradit
-
Question: Does granulocyte transfusion improve survival and clinical recovery in pediatric febrile neutropenia?
Finding: In this 15-year real-world cohort, granulocyte transfusion significantly increased 30-day survival (92.3 % vs. 65.4%; adjusted odds ratio, 0.105; P=0.020) and accelerated fever and neutrophil recovery without serious adverse events.
Meaning: Granulocyte transfusion may be an effective adjunctive therapy for severe neutropenic infections in children, particularly in low- and middle-income settings. -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.01186 [Epub ahead of print]
- Guideline
- Infection
- Recommendation for use of 15- and 20-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines in Korean infants and children
- Ki Wook Yun, Dong Hyun Kim, Jong Gyun Ahn, Byung-Wook Eun, Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Taek-Jin Lee, Hyunju Lee, Dae Sun Jo, Eun Young Cho, Hye-Kyung Cho, Soo-Han Choi, Young June Choe, Ui Yoon Choi, Yun-Kyung Kim; The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):76-83. Published online December 30, 2025
-
Compared to PCV13, PCV15 includes 2 (22F and 33F), and PCV20 includes 7 (8, 10A, 11A, 12F, 15B, 22F, and 33F) additional serotypes. The vaccination schedule remains the same: primary doses at 2, 4, and 6 months, and a booster at 12–15 months. If PCV13 was administered in the primary series, PCV15 and PCV20 may be used to complete it or as a booster.
- Original Article
- Improvements in obesity-related measures among Asian patients with severe obesity following a structured lifestyle intervention
- Pei-Shan Chen, Shu-Mei Tsai, Chih-Hsuan Chang, Hui-Ru Yang, Yen-Ju Huang, Hsiang-Yin Liu, Kai-Chi Chang, Huey-Ling Chen
-
Question: How does obesity severity affect baseline fitness and improvements in key obesity-related measures following participation in a structured lifestyle modification program?
Finding: Severely obese youth showed poorer baseline physical fitness but greater improvements in key obesity-related measures following lifestyle interventions.
Meaning: Early targeted intervention may help prevent progression to more severe obesity and declines in physical fitness in patients with obesity. -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.01774 [Epub ahead of print]
- Prolonged cerebral oxygenation surveillance with algorithm-based management: a neurocritical care bundle for extremely preterm infants
- Kai-Hsiang Hsu, Wei-Hung Wu, Shu-Yu Lin, Chih-Chen Chang, Mei-Yin Lai, I-Hsyuan Wu, Shih-Ming Chu, Ming-Chou Chiang, Reyin Lien
-
Background: Cerebral hypoxia-ischemia impairs brain development in extremely preterm infants and is associated with poor neurological outcomes. Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a noninvasive continuous monitoring method for regional cerebral oxygen saturation (rcSO2).
Purpose: This study evaluated the clinical feasibility and neurological impact of a neurocritical care bundle that incorporates prolonged multidisciplinary hemodynamic monitoring and a stepwise management algorithm. Methods: Preterm infants with... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.02117 [Accepted]
- Perinatal risk factors for hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus in very low birth weight infants
- Jie Hee Jue, So Young Shin, Jae Hyun Park, Chun Soo Kim, Hee Joung Choi
-
Background: Multiple perinatal factors influence hemodynamically significant patent ductus arteriosus (HS PDA) in preterm infants.
Purpose: This study aimed to identify the risk factors associated with HS PDA in very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs) and determine the predictors of surgical ligation. Methods: This retrospective study included VLBWIs born at 23–32 weeks’ gestation whose HS PDA properties could be identified using... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.01893 [Accepted]
- Thrombocytopenia in preterm infants born to mothers with systemic lupus erythematosus: a retrospective cohort study
- Ru Xue, Guoqing Zhang, Xiafang Chen, Jun Bu, Lanlan Mi, Fei Bei
-
Question: What are the characteristics and clinical implications of thrombocytopenia in preterm neonates born to mothers with systemic lupus erythematosus?
Finding: Nearly one-third of preterm infants developed thrombocytopenia. Key modulators of this risk included gestational age, maternal hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, and hydroxychloroquine use. Thrombocytopenia may be associated with neonatal morbidity.
Meaning: Platelet count should be monitored during the first week of life, and infants should be assessed for potential complications. -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.01942 [Epub ahead of print]
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Prioritizing maternal sleep: a public health strategy for preventing childhood allergic diseases
- Eunchae Lee, Seohyun Hong, Dong Keon Yon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):22-25. Published online December 18, 2025
-

Sleep disorders affect more than half of pregnancies worldwide and can harm maternal health and offspring outcomes. Prioritizing maternal sleep as a public health strategy may help prevent prenatal and pediatric allergic diseases and reduce their burden. Other maternal health strategies may also reduce the burden of offspring allergic diseases, while adequate maternal sleep is associated with other offspring outcomes, underscoring its importance as a key public health strategy.
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Pubertal induction in prepubertal males with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: testosterone or gonadotropins?
- Paolo Cavarzere, Riccardo Battiston, Valentina Lupieri, Valentina Mancioppi, Claudio Maffeis
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):1-10. Published online December 18, 2025
-

The pubertal induction process in males still poses a challenge for pediatric endocrinologists. The existing literature is limited, and it is not yet possible to make definitive recommendations. We described the various treatment for this condition and tried to analyze the unresolved questions to address the question posed in the title of our manuscript.
- Gastroenterology
- Ingestion of foreign bodies and caustic substances in children: a narrative review on clinical evaluation and management update
- Maria Rogalidou
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):11-21. Published online December 10, 2025
-

Foreign body and caustic substance ingestion in children aged 1–5 years can feature to severe and, sometimes life-threatening complications. High-risk items include batteries, magnets, and corrosive chemicals. Severity depends on object type, location, and ingestion timing. Prompt diagnosis and early endoscopic intervention are crucial. Individualized management, high clinical suspicion, and parental education are essential to improving outcomes and preventing immediate and long-term complications affecting a child’s quality of life.
- Original Article
- Longitudinal analysis of gut microbiota dysbiosis and bacterial signatures predictive of postoperative enterocolitis in children with Hirschsprung disease
- Sireekarn Chantakhow, Chanon Kunasol, Jiraporn Khorana, Kanokkan Tepmalai, Nipon Chattipakorn, Siriporn C. Chattipakorn
-
Question: Do gut microbiota differ between patients with Hirschsprung disease (HSCR) and healthy children, and can specific bacterial taxa predict postoperative HSCRassociated enterocolitis (HAEC)?
Finding: Patients with HSCR showed gut dysbiosis with reduced diversity. Postoperative microbial changes included increased alpha diversity. Certain taxa, such as Eubacterium and Collinsella, were associated with recovery or HAEC.
Meaning: Distinct microbial signatures may help identify HAEC risk and guide microbiota-based strategies to improve outcomes. -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.01886 [Epub ahead of print]
- Gastroenterology
- Progression from acute to chronic pancreatitis in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Endre Botond Gagyi, Mahmoud Obeidat, Edina Tari, Szilárd Váncsa, Dániel Sándor Veres, Peter Banovcin, Péter Jenő Hegyi, Péter Hegyi, Bálint Erőss
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):117-129. Published online December 4, 2025
-
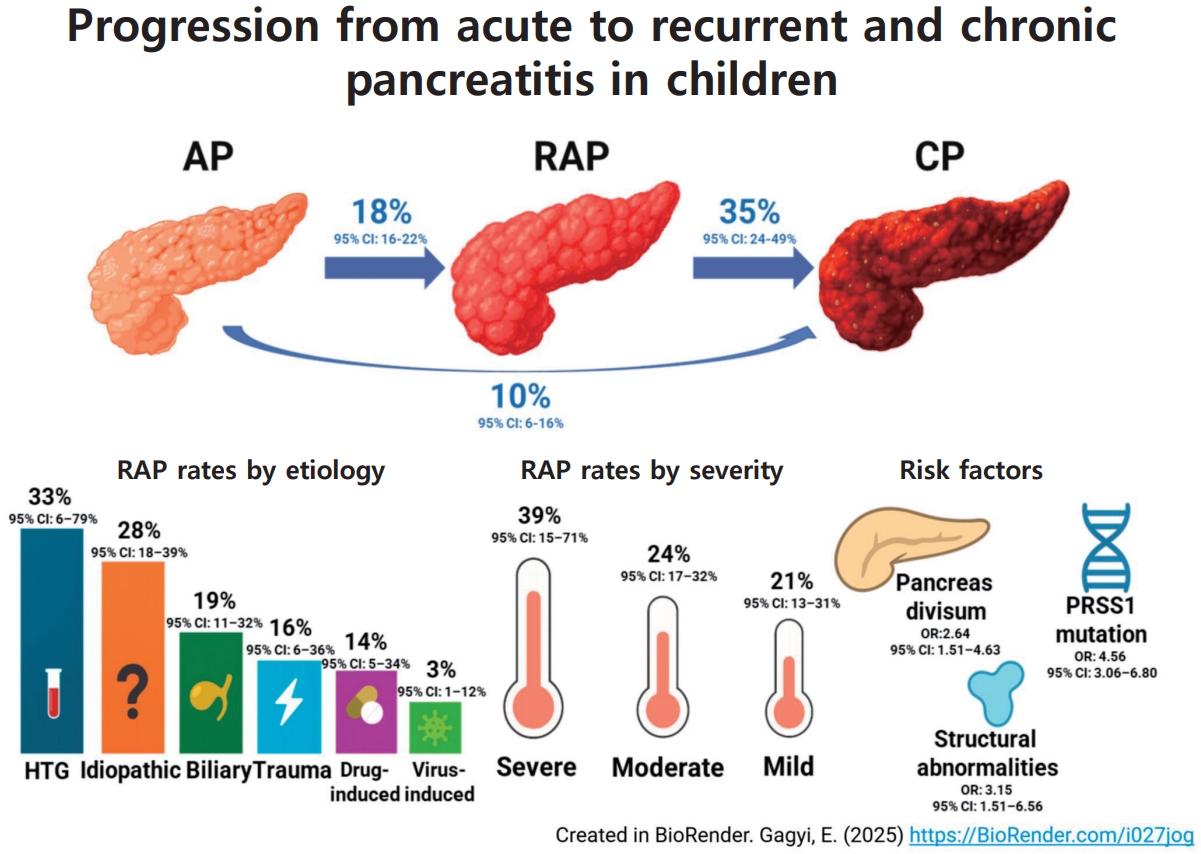
Approximately 1 in 5 children with acute pancreatitis develops recurrent attacks, and over one-third of such cases progress to chronic pancreatitis. Progression is closely linked to genetic mutations, particularly PRSS1, and anatomical abnormalities, whereas demographic and routine clinical factors lack predictive value. These results support early genetic and anatomical assessments, enabling targeted follow-ups and timely interventions in highrisk pediatric patients.
- Clinical Note
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- External tracheal compression and mucosal injury in a neonate with cervical teratoma: a rare airway challenge
- Rhodora Guillen, Arijit Lodha, Prashanth Murthy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):73-75. Published online December 4, 2025
-

- Review Article
- Neurology
- Sacral dimple: clinical perspectives of lesions hidden beneath the skin
- Jin Eun, Kwan Sung Lee, Seung Ho Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(2):103-113. Published online November 26, 2025
-
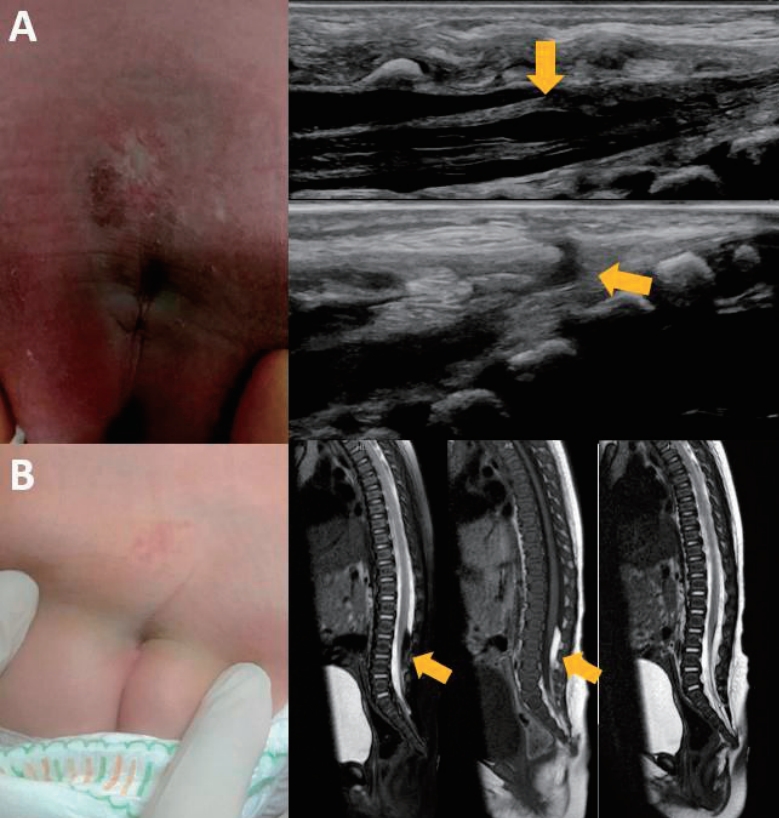
· Most sacral dimples are benign, but atypical features may indicate occult spinal dysraphism.
· Simple dimples meeting strict criteria require no imaging, whereas atypical dimples require targeted ultrasonography or magnetic resonance imaging.
· The early diagnosis and surgical management of highrisk cases prevents irreversible neurological, orthopedic, and urological deficits.
- Editorial
- Infection
- Beyond COVID-19: meeting the challenge of evolving pediatric invasive group A streptococcal disease
- Han Wool Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):971-973. Published online November 26, 2025
-
Pediatric for invasive group A Streptococcus has resurged globally with increasing severity and toxin-mediated presentations. Beta-lactams remain the first-line treatment, but linezolid has emerged as a safe alternative in cases refractory to β-lactams. Early intravenous immunoglobulin use may improve outcomes in severe streptococcal toxic shock syndrome cases, while C-reactive protein and procalcitonin aid early risk stratification. Integrating global surveillance and individualized therapy is crucial in the postpandemic era.
- Original Article
- Discordance between antibiotic therapy and recurrent urinary tract infections in young children with third-generation cephalosporin-resistant infections
- Yusin Kim, Hyun A Lee, Gil Lee, Kyungseok Park, Ye Kyung Kim, Peong Gang Park
-
Question: Does completing a third-generation cephalosporin course, despite in vitro resistance, increase the early urinary tract infection recurrence rate in children?
Finding: Among 989 Korean children, discordant therapy increased the 2-month recurrence risk by 40% compared with concordant or susceptible therapy.
Meaning: Checking isolate susceptibility and switching to an active oral drug may curb recurrence and limit the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.01417 [Epub ahead of print]
- General Pediatrics
- Lipoprotein(a) prevalence trends in Portuguese children and adolescents: a real-world perspective
- Isabel Morais Ribeiro, Susete Vieira, Miguel Saraiva, Mónica Tavares, José Carlos Oliveira, Isabel Mangas Palma, Helena Ferreira Mansilha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):1031-1040. Published online November 24, 2025
-

Early lipid screening, including lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)), in children/adolescents is key to identifying and managing dyslipidemia and reducing the risk of early-onset cardiovascular disease. This study shows that prevalence of elevated Lp(a) in high-risk Portuguese children is alarming, with over 30% at intermediate/high risk and nearly 1% at very high-risk (>430 nmol/L). Since Lp(a) is mostly genetically determined, one-time early screening in atrisk children is crucial for timely monitoring and prevention.
- Review Article
- Oncology
- Breaking the barrier: a guidelines-based review of antiangiogenesis drug resistance in pediatric cancer therapy
- Nader Shakibazad, Mahdi Shahriari, Mani Ramzi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):952-962. Published online November 24, 2025
-
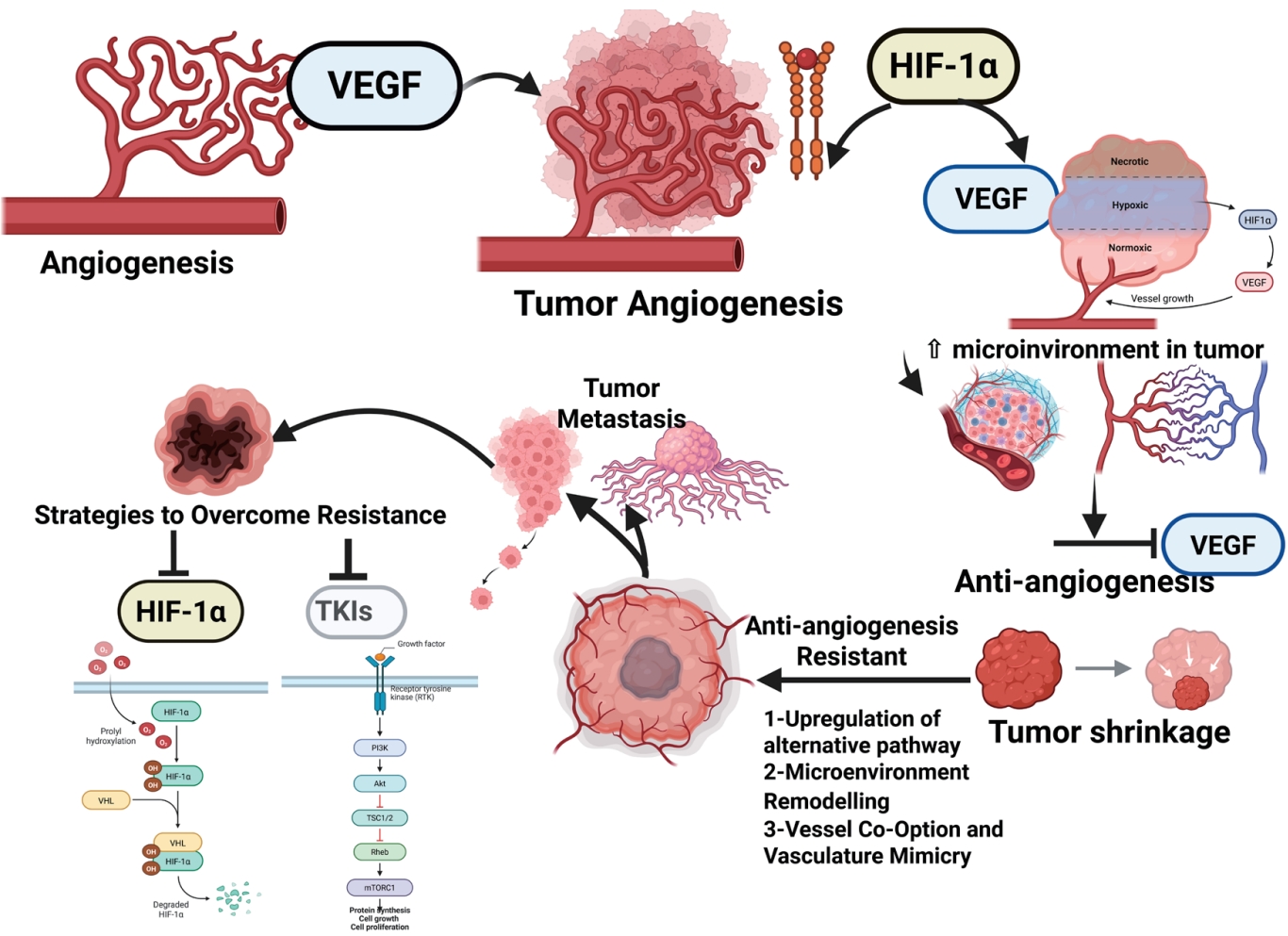
Antiangiogenic therapy resistance in pediatric cancers involves alternative angiogenic pathways, microenvironmental support, hypoxia-driven signaling, metabolic reprogramming, and structural adaptations such as vascular co-option. Metabolic adaptation highlights tumor plasticity. Effective treatments combine immunotherapy with biomarkers. To address vascular endothelial growth factor limitations, emerging targets include hypoxia-inducible factor-2α, endoglin, CXCR4, angiopoietin/Tie2, and bispecific antibodies. In resource-constrained settings, the guidelines recommend low-dose chemotherapy plus oral multiantiangiogenic agents to ensure improved accessibility and treatment outcomes.
- Original Article
- Other
- Comparing ethyl chloride and 10% lignocaine spray for pediatric intravenous cannulation pain relief
- Susmitha Vellanki, Malavika Kulkarni, H.D. Arun Kumar, Deepali Shetty, Nikhil Karthik B, Mathew Tom
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2026;69(1):65-72. Published online November 21, 2025
-

Background: Intravenous cannulation (IVC) is a routine yet distressing procedure in pediatric patients, often provoking significant anxiety and procedural pain. Although eutectic mixtures such as eutectic mixture of local anesthetic cream are widely used, their delayed onset limits their applicability in time-sensitive settings. Ethyl chloride vapocoolant spray and 10% lignocaine spray have been proposed as rapid-onset alternatives, yet direct comparative...
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











