Most downloaded
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Most downloaded
"Most downloaded" Articles are from the articles published in 2024 during the last six months.
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Effect of metabolic syndrome on pulmonary dysfunction in children with asthma
(14 times)
-
Hyo-Bin Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):136-137. Published online November 13, 2024
-
|
|
· The prevalence of metabolic syndrome increased in Korean children during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic owing to reduced physical activity resulting from social distancing.
· Metabolic syndrome impacts pulmonary dysfunction in childhood asthma.
· Further studies are needed to understand the mechanism linking asthma and metabolic syndrome and develop interventions. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Exploring the role of laryngeal masks in neonatal resuscitation
(11 times)
-
Euiseok Jung
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):247-248. Published online December 28, 2023
-
|
|
· Laryngeal masks (LMs) offer stable airway access and skill retention advantages, making them promising alternatives to positive-pressure ventilation in neonatal care.
· The ease of teaching LM insertion techniques to less experienced providers addresses the need for swift intervention and skill retention.
· Careful consideration of the benefits and challenges of LMs is essential in determining their effective integration into enhanced neonatal resuscitation protocols. |
-
-
- Immunology
- Utility of eosinophil granule proteins in management of pediatric chronic cough
(11 times)
-
Chang-Keun Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):519-520. Published online April 17, 2024
-

|
· Pediatric chronic cough often involves eosinophilic inflammation; however, objective measurements are not routinely used in treatment decisions.
· Accurate biomarkers of eosinophil activity, such as eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) and cationic proteins (ECP), should be used. EDN, which overcomes the shortcomings of ECP, recently received approval for use in Korean healthcare settings.
· EDN and ECP can play a role in treatment period and drug selection decisions. |
-
-
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Comparative analysis of adolescent hypertension definitions for predicting early adulthood carotid artery intima-media thickness: Tehran lipid and glucose study
(11 times)
-
Maryam Barzin, Shirin Yaghoobpoor, Maryam Mahdavi, Behnaz Abiri, Majid Valizadeh, Fereidoun Azizi, Pooneh Dehghan, Farhad Hosseinpanah
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):694-703. Published online September 12, 2024
-
|
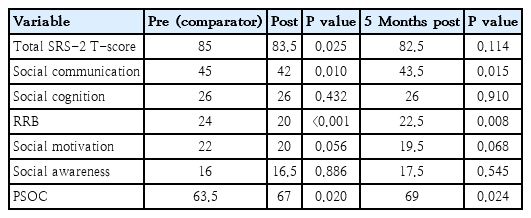
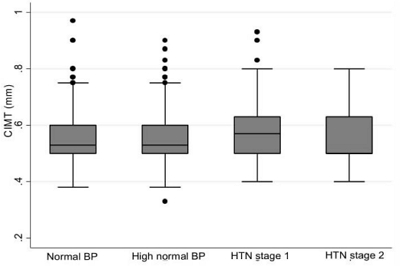
Question: What is the prevalence of HTN among adolescents enrolled in the TLGS according to 3 different accepted definitions (4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG). Also, what is the ability of each of these definitions in predicting early adulthood CIMT, as a surrogate for cardiovascular disease events?
Finding: The highest and lowest prevalence of stage 1 HTN was observed with the AAP-CPG (17.7%) and ESH (8.8%), respectively. Similarly, the highest and lowest prevalence of stage 2 HTN was noted with the AAP-CPG (1.5%) and ESH (0.8%), respectively. The highest to lowest predictive abilities belonged to the 4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG, respectively.
Meaning: Among the various definitions of pediatric HTN, the 4th report offered the best ability to predict a high CIMT during early adulthood, followed by the ESH and AAP-CPG. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Trends in food allergen immunotherapy in Korea after changed national regulations
(10 times)
-
Tae Won Song
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):201-202. Published online November 21, 2023
-
|
|
National regulations, academic guidelines, and clinical trends in food allergen immunotherapies (FA-AIT) differ among countries and have changed rapidly. Current officially approved FA-AIT are oral immunotherapy (OIT) using heated milk/egg in Korea and peanut OIT using standardized products in the United States and Europe. FA-AIT should be administered by specialist physicians with experience administering oral food challenge tests and managing severe allergic reactions inside and outside research settings. |
-
-
- Infection
- Preventing bloodstream infections in children after liver transplantation
(10 times)
-
Young June Choe
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):599-600. Published online April 18, 2024
-
|
|
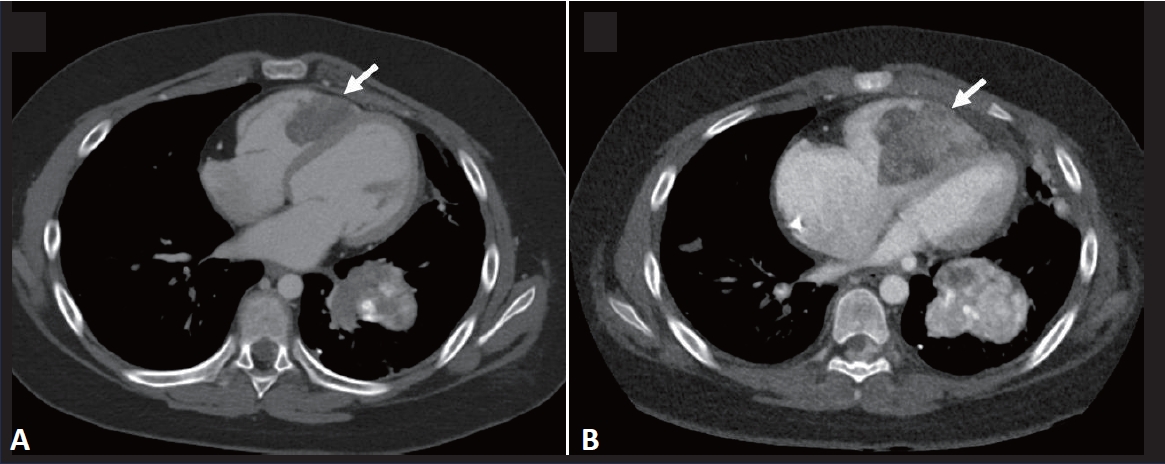
Liver transplantation (LT) is crucial for children with end-stage liver diseases, yet bloodstream infections (BSI) pose significant risks, despite medical advancements. Immunosuppressants, essential for preventing organ rejection, heighten infection susceptibility. Understanding BSI organisms is vital due to antimicrobial resistance. Pediatric LT recipients have unique risk factors, demanding tailored preventive measures. This systematic review on bacterial BSI emphasizes the urgency of effective prevention strategies, considering the high incidence and distinct organism profile. Further research is vital for optimizing antibiotic management and improving outcomes for this vulnerable population. |
-
-
- Review Article
- Other
- Children’s health affected by parent’s behavioral characteristics: a review
(9 times)
-
Sung Eun Kim, Jongin Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(5):232-239. Published online August 21, 2023
-

|
· Parents’ occupational hazards, long working hours, and smoking behaviors should be modified adequately to minimize adverse health effects on their children.
· As of 2023, several diseases from fetal exposure to occupational hazards can be compensated with Industrial Accident Compensation Insurance in South Korea.
· A directed acyclic graph is recommended for medical research to control the effects of parents’ behaviors on children’s health. |
-
-
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Quantifying myelin in neonates using magnetic resonance imaging: a systematic literature review
(9 times)
-
Nabila Hanem Arshad, Hasyma Abu Hassan, Nur Farhayu Omar, Zurina Zainudin
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):371-385. Published online December 6, 2023
-

|
Question: This systematic review attempts to discover the best magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technique for myelin quantification in neonates by evaluating various MRI parameters and their reproducibility.
Finding: Since the benefits of using synthetic MRI for quantifying myelin in neonates outweigh the very minor draw- backs, it is recommended.
Meaning: The findings suggest the importance of identifying noninvasive MRI techniques available to assess myelin tissue in neonates, which aid in diagnosing neurodevelopmental disorders.
|
-
-
- Clinical Note
- Neurology
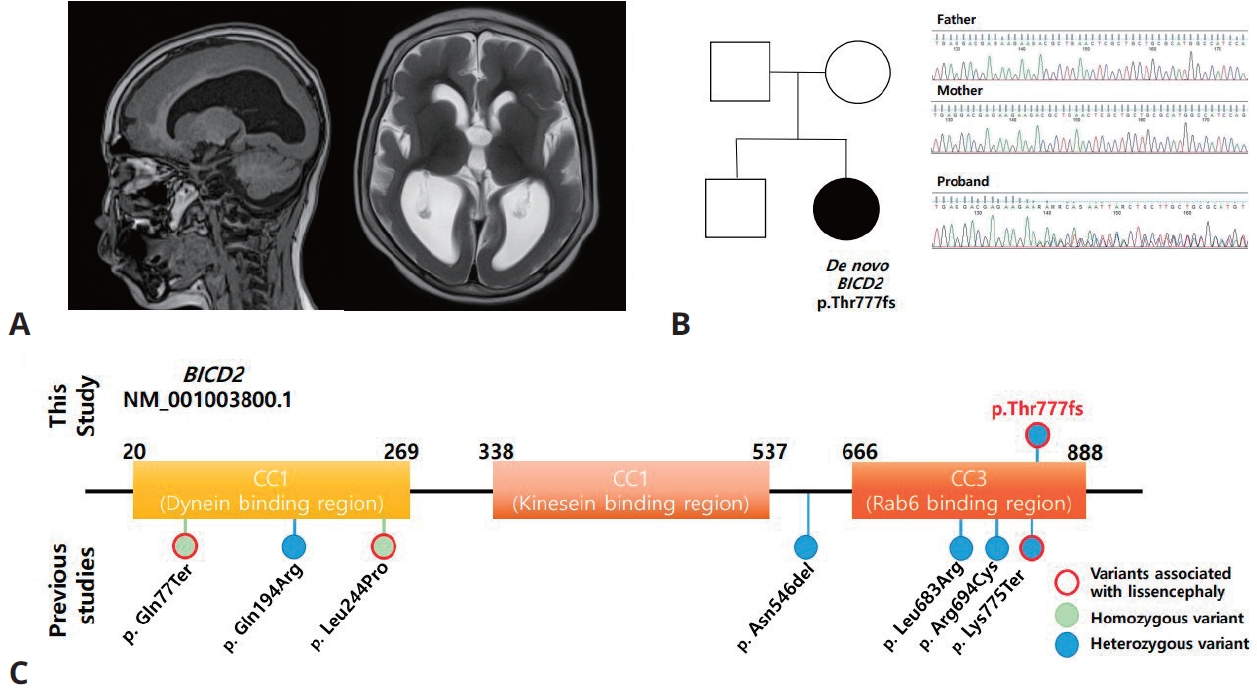
- Expanding association between BICD2 variants and brain malformations and associated lissencephaly
(9 times)
-
Jaeso Cho, Haeryung Kim, Seoungbok Lee, Jihoon G Yoon, HyeJin Kim, Minhye Kim, Seoyun Jang, Woojoong Kim, Soo Yeon Kim, Jong Hee Chae
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(1):54-56. Published online December 21, 2023
-
-
-
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Protective effect of recombinant interleukin-10 on newborn rat lungs exposed to short-term sublethal hyperoxia
(9 times)
-
Hyeon-Soo Lee, Young-Joon Ryu, Min-Jae Lee
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(10):540-549. Published online September 27, 2024
-

|
Lung injury is generated from the early stage of hyperoxia through the biologic effects of cell death and inflammatory response, which eventually leads to evolution of bronchopul-monary dysplasia. Therefore, a protective measure against hyperoxia-induced lung injury is needed. The present study observed that anti-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-10 had protective effects on newborn rat lungs from injury induced at the early stage of hyperoxia, by preventing cell death and down-regulating inflammatory response. |
-
-
- Neurology
- Changes in frequency of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis and their viral causes before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a single-center study
(8 times)
-
Hyejin Na, Sanghoon Lee, Seo Hee Kim, Young Ok Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):213-220. Published online March 19, 2024
-
|
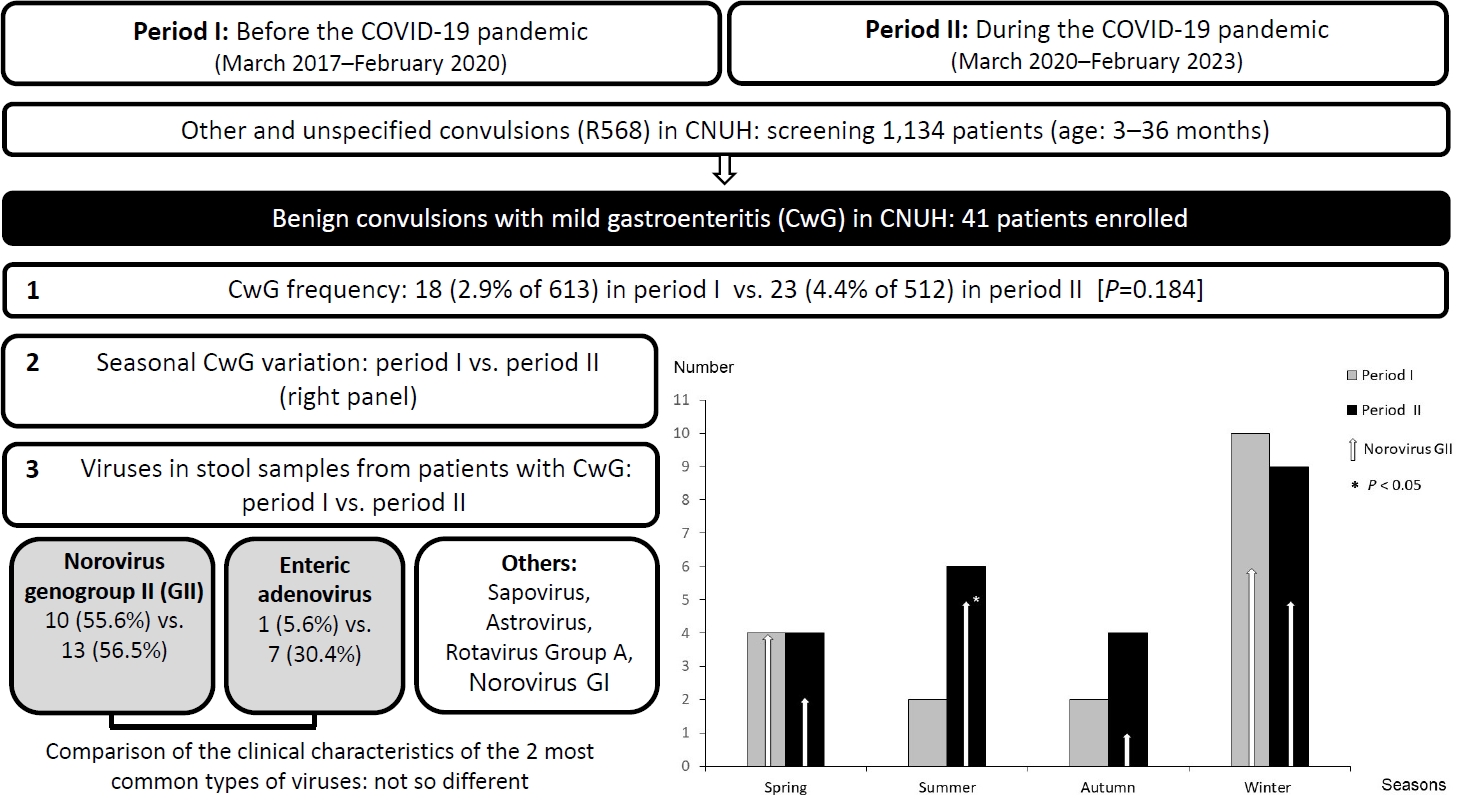
Question: Did coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) affect the frequency, seasonal variation, or virus type of benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis (CwG)?
Findings: We compared 41 cases of CwG before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. After March 2020, frequency did not change significantly (18 patients vs. 23 patients), seasonal variation was lost, and number of cases of enteric adenovirus-associated CwG increased (1 cases vs. 7 cases).
Meaning: The COVID-19 pandemic affected CwG. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Neurobehavior
- Importance of pediatrician’s role in preventing positional plagiocephaly
(8 times)
-
Hee-Jeong Kang
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(6):294-295. Published online May 21, 2024
-

|
· Plagiocephaly is characterized by the asymmetrical shape of a baby’s head.
· Since positional plagiocephaly is associated with developmental delay and further musculoskeletal problems, early detection allows for timely intervention and prevents worsening of the condition.
· Pediatricians can educate parents about proper head positioning and encourage supervised tummy time during awake hours. |
-
-
- Critical Care Medicine
- Is it possible to provide palliative care to pediatric patients with neurological diseases?
(7 times)
-
Young-Hoon Kim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(8):403-404. Published online February 15, 2024
-
|
|
· Patients with neurological diseases often require external mechanical support to maintain mechanical ventilation or supply.
· Little has been done to help the families of affected children make difficult decisions that carry significant physical and psychological consequences.
· The establishment of a department that provides pediatric palliative care for neurological patients should be considered. |
-
-
- Editorial
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Impacts of maternal COVID-19 during pregnancy on neonatal health and epidemiology
(6 times)
-
Jae Woo Lim
-
Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(3):149-151. Published online December 28, 2023
-

|
Newborns born to mothers infected with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) should be closely monitored for respiratory disorders, such as transient tachypnea of the newborn, regardless of their COVID-19 test results. Further research is required of the development of infants born to mothers with COVID-19. The trends in Korea's birth rate and infant mortality rates have not been significantly affected by COVID-19. |
-
-