Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Establishing an induced pluripotent stem cell bank using urine cells from pediatric patients with neurogenetic diseases
- Hien Bao Dieu Thai, WonWoo Jung, Sol Choi, Woo Joong Kim, JangSup Moon, ByungChan Lim
-
Background: Inadequate knowledge of the fundamental mechanisms underlying pediatric neurological disorders impedes their effective treatment. Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are essential for exploring the course of neurological diseases because they enable disease modeling at the cellular level.
Purpose: This study aimed to generate an iPSC bank using urine cells (UCs) for clinical applications, particularly the study of pediatric neurogenetic diseases.... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2024.01830 [Accepted]
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Reconsideration of urine culture for the diagnosis of acute pyelonephritis in children: a new challenging method for diagnosing acute pyelonephritis
- Jun Ho Lee, Seonkyeong Rhie
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(12):433-437. Published online October 18, 2019
-
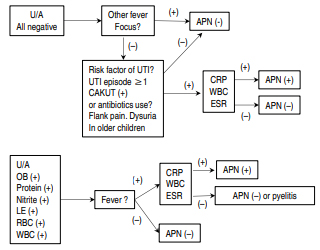
Acute pyelonephritis (APN) should be detected and treated as soon as possible to reduce the risk of the development of acquired renal scarring. However, in the medical field, urine culture results are not available or considered when the prompt discrimination of APN is necessary and empirical treatment is started. Furthermore, urine culture cannot discriminate APN among children with febrile urinary...
- Original Article
- Validity of bag urine culture for predicting urinary tract infections in febrile infants: a paired comparison of urine collection methods
- Geun-A Kim, Ja-Wook Koo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(5):183-189. Published online May 22, 2015
-
Purpose Catheter urine (CATH-U) and suprapubic aspiration (SPA) are reliable urine collection methods for confirming urinary tract infections (UTI) in infants. However, noninvasive and easily accessible collecting bag urine (CBU) is widely used, despite its high contamination rate. This study investigated the validity of CBU cultures for diagnosing UTIs, using CATH-U culture results as the gold standard.
Methods We retrospectively analyzed 210 infants,...
- Taurine exerts neuroprotective effects via anti-apoptosis in hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats
- Ji Eun Jeong, Tae Yeol Kim, Hye Jin Park, Kye Hyang Lee, Kyung Hoon Lee, Eun Jin Choi, Jin Kyung Kim, Hai Lee Chung, Eok Su Seo, Woo Taek Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(12):1337-1347. Published online December 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) is a simple sulfur-containing amino acid. It is abundantly present in tissues such as brain, retina, heart, and skeletal muscles. Current studies have demonstrated the neuroprotective effects of taurine, but limited data are available for such effects during neonatal period. The aim of this study was to determine whether taurine could reduce hypoxic-ischemic (HI) cerebral... -
- Effect of renin inhibition on an experimental glomerulonephritis - a preliminary report
- Ju Hyung Kang, Jae Kyung Huh, Young Sook Lee, Ji Young Han, Il Soo Ha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(8):938-943. Published online August 15, 2009
-
Purpose:We performed this study in order to investigate the effect of direct renin inhibition on an experimental animal model with nephrotoxic serum nephritis and tried to give useful information for clinical research and renin inhibitor treatment. Methods:Thirty BALB/c 6-week-old male mice were divided into 4 groups: control group (CO, n=5), control-treatment group with aliskiren (CT, n=5), disease group (DO, n=10), and disease treatment... -
- Factors affecting the contamination of bag urine culture in febrile children under two years
- Wook Hyun Choi, In Seok Lim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):346-350. Published online March 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Since children under two years with suspected urinary tract infections (UTIs) cannot control urination, urine cultures in such children are usually performed via urine bags. This method is noninvasive but has a high contamination rate. We studied the contamination rate of bag urine culture in diagnosing UTI in infants under two years and the factors responsible for contamination. Methods... -
- Inherited metabolic diseases in the urine organic acid analysis of complex febrile seizure patients
- Hee Jeong Cheong, Hye Rim Kim, Seong Soo Lee, Eun Joo Bae, Won Il Park, Hong Jin Lee, Hui Chul Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(2):199-204. Published online February 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Seizure associated with fever may indicate the presence of underlying inherited metabolic diseases. The present study was performed to investigate the presence of underlying metabolic diseases in patients with complex febrile seizures, using analyses of urine organic acids. Method : We retrospectively analyzed and compared the results of urine organic acid analysis with routine laboratory findings in 278... -
- Review Article
- Pathophysiology and management of disorders in water metabolism
- Dong Un Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(5):430-435. Published online May 15, 2007
-
Even though we drink and excrete water without recognition, the amount and the composition of body fluid remain constant everyday. Maintenance of a normal osmolality is under the control of water balance which is regulated by vasopressin despite sodium concentration is the dominant determinant of plasma osmolality. The increased plasma osmolality (hypernatremia) can be normalized by the concentration of urine,... -
- Original Article
- Factors which contribute to time of first stool and first urine passage in Newborns
- Hye Jin Lee, Hyun Gon Jae, Sang Hee Son
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(5):482-488. Published online May 15, 2006
-
Purpose : To evaluate the factors which contribute to the time of the first stool and the first urine passage. Methods : We retrospectively reviewed a chart of 1,221 infants ≥34 weeks of gestational age admitted to the normal newborn nursery of Il Sin Christian Hospital, Busan, from November 2004 to April 2005. We compared the time to first stool and... -
- Case Report
- A case of alkaptonuria : the first case in Korea
- Ji Hyung Nam, Jong Hyun Lee, Kyung Bae Park, Dong Hwan Le
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(3):329-331. Published online March 15, 2006
-
Alkaptonuria is a rare metabolic disease in which homogentisic acid cannot be metabolized due to a lack of the enzyme homogentisic acid oxidase. The disease often manifests itself in childhood by darkening of the urine upon standing. The disease leads to such serious consequences as ochronosis of cartilage and connective tissues with arthritis. It is expected that treatment with ascorbic... -
- Original Article
- Follow-up of children with isolated microscopic hematuria detected in a mass school urine screening test
- Mi-sun Yum, Hoe Soo Yoon, Joo Hoon Lee, Hyewon Hahn, Young Seo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(1):82-86. Published online January 15, 2006
-
Purpose : The isolated microscopic hematuria is the most common abnormality detected by school urinary screening, but there is no consensus about the range of investigations and long-term outcomes of isolated hematuria in children yet. This study aims to elucidate the prognosis of hematuria and the range of diagnostic studies by follow-up results. Methods : Students with isolated hematuria who were... -
- Antibiotic Sensitivity to the Major Causative Organisms of Acute Urinary Tract Infection in Children
- Yung Kwun Lee, Hee Chul Lee, Jung Mi Chun, So Young Yoon, Woo Gill Lee, Son Moon Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(7):760-765. Published online July 15, 2005
-
Purpose : We studied the changes in antibiotic sensitivity to the causative organisms of urinary tract infection(UTI), in order to provide useful information on the choice of adequate drugs in the treatment of UTI. Methods : We retrospectively analyzed the major causative organisms and their antibiotic sensitivities in 69 patients diagnosed with UTI in the Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Cheil Hospital... -
- Medical Lecture Course
- Renal Transport Proteins Involved in Urinary Concentrating Mechanism
- Dong Un Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(5):480-484. Published online May 15, 2004
-
Renal tubule and vasa recta are arranged in complex but specific anatomic relationships and the production of a concentrated urine is achieved by countercurrent multiplication mechanism in the renal medulla. This model requires that the ascending thin limb is highly permeable to NaCl but impermeable to water, while the descending thin limb is impermeable to NaCl but highly permeable to... -
- Original Article
- The Usefulness of Spot Urine Protein/Creatinine Ratio in Evaluating Proteinuria in Children and the Correlation between 24-hour Urinary Protein Amount and Spot Urine Protein/Creatinine Ratio
- Seon Young Hong, Ji Young Kim, Woo Yeong Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(2):173-177. Published online February 15, 2003
-
Purpose : Recently, different results about factors affecting accurate quantitation of 24-hr urinary protein(24UP) amount using spot urine protein/creatinine ratio(PCR) have been reported. The current study was designed to evaluate correlation between 24UP amounts and PCR in children, and the effect of 24UP amounts, age, sex, and glomerular filtration rate(GFR) on this correlation. Methods : Among 94 patients who visited the... -
- A Change of Adrenal Androgen and Cortisol in Kawasaki Disease
- Sun-Hee Lee, Jae-Hong Yu, Hong-Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(5):654-658. Published online May 15, 2002
-
Purpose : Endocrine and immune systems are connected and interdependent. Adrenal glands play an important role in this network and control the balance between serum levels of dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate(DHEAS) and cortisol. These steroids have an antagonistic effect on the T cell progression into Th1 and Th2 cells and on the induction of correlated interleukins. Therefore we evaluated the role of... -
- Case Report
- Three Cases of Urine Abnormalities Associated with Ketogenic Diet
- Hye Won Hahn, Ki Jung Kim, Il Soo Ha, Hae Il Jung, Yong Seung Hwang, Yong Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(6):709-713. Published online June 15, 2001
-
Ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low carbohydrate, low protein diet used in treatment of pediatric epilepsy since the 1920s. Currently it is used primarily to treat refractory childhood epilepsy. Few serious complications caused by ketogenic diet have been reported. Short-term complications include dehydration, hypoglycemia, vomiting, diarrhea, and refusal to eat. Long-term complications include kidney stones, recurrent infections, metabolic derangement, hypercholesterolemia,... -
- A Case of Maple Syrup Urine Disease Associated with Acrodermatitis Enteropathica-like Syndrome Due to Iisoleucine Deficinecy During Diet Therapy
- Ki Hyang Moon, Oh Sook Gwon, Jung Im Lee, Seong Woo Rho, Seong Sook Jeon, Son Sang Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(4):469-474. Published online April 15, 2001
-
Maple syrup urine disease(MSUD) is an autosomal recessive disorder involving the metabolism of the branched-chain amino acids(BCAA) such as leucine, isoleucine and valine. The disorder is due to a defect in branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase(BCKAD) and the classic form causes rapid progressive and overwhelming illness beginning in the first weeks of life, present with poor feeding, lethargy, change in muscle tone,... -
- A Case of Maple Syrup Urine Disease Controlled by Peritoneal Dialysis and Diet
- Ju Wan Kim, June Huh, Won Il Park, Kyung Ja Lee, Hong Jin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2001;44(1):94-98. Published online January 15, 2001
-
Maple syrup urine disease is an autosomal recessive disease caused by a deficiency of the branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex. The disease is often suspected because of the peculiar odor of maple syrup in urine. Maple syrup urine disease is usually confirmed by amino acid analysis and urine organic acid analysis showing marked elevations of leucine, isoleucine, valine, and respective ketoacids in... -
- Original Article
- Organic Acid Analysis on Urine Samples Obtaine3d from Dried Filter Paper in Newborns : Development of Screening Method for Organic Aciduria in Newborns
- Eun Ha Lee, Si Houn Hahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(10):1311-1317. Published online October 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Neonatal screening for inherited metabolic disease is aimed at identifying affected infants early, thus permitting medical intervention to prevent or minimize the effect of the disease. However, organic aciduria, most of which causes severe disease and mental retardation, is not yet screened routinely because of the difficulty of tests, sample collection, and expenditure of time and financial resources.... -
- Random Urine Ca/Cr Ratio in Healthy Neonates
- Hea Young Lee, So Young Park, Eun Sun Yoo, Eun Ae Park, Seung Joo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(3):378-382. Published online March 15, 1998
-
Purpose : Recently, in high risk preterm infants, we experienced high incidence of hypercalciuria, nephrolithiasis & nephrocalcinosis. To screen hypercalciuria, we need the normal value of random urine Ca/Cr ratio in healthy neonates according to gestational age, postnatal age, milk and calcium intake. Methods : Random urine Ca/Cr ratio was checked in 260 healthy full-term infants at the 2-7th day, and... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Maple Syrup Urine Disease
- Dong Hyun Cho, Hyun Mi Lee, Soon Young Kim, Chang Soo Ra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1997;40(9):1297-1302. Published online September 15, 1997
-
-
- Original Article
- Urinary Vitamin C Loading Test and Therapeutic Effect of Vitamin C in Children with Idiopathic Recurrent Epistaxis
- In Soon Park, Woo Yeong Chung, Soon Yong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(2):266-272. Published online February 15, 1993
-
Recurrent epistaxis is not one of rare symptoms in children, the well-known causes of which are anatomical abnormalities of nasal cavity and systemic bleeding tendency. But, in the majority of cases of recurrent epistasix, it is usually very difficult to find out their underlying causes, so that the treatment is only symptomatic control of nasal bleeding whenever epistaxis occurs, but... -
- A study for mass screening of galactosemia using galactitol level by spot urine method among Korean infants.
- Jin Tae Kim, Chong Won Bae, Sa Jun Chung, Chang Il Ahn, Suyama I , Isshiki G
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(7):949-958. Published online July 31, 1991
-
For mass screening of the galactosemia, we used spot urine method using filter paper which was newly developed by Department of Pediatrics, Kyung Hee University Hospital and Department of Pediatrics, Osaka City University in Japan. We used control groups as followed, 7 of normal adults,- one patient of I, II, III types of galactosemia, respectively. The experimental groups were 62 infants of 0 to... -
- Diagnosis of Meconium Aspiration by Spectrophotometric Analysis of Urine.
- Chang Yul Kim, Hye Kyung Bae, Mee Kyung Namgoong, Baek Keun Lim, Joong Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1988;31(10):1275-1280. Published online October 31, 1988
-
We measured optical density of aqueous extracts of meconium and meconium stained amniotic fluid at 390 nm, 405 nm, 420 nm, 435 nm, 450 nm by spectrophotometry. We also applied the spectrophotometric method to the urine from 25 infants with clinical sign of meconium aspiration and from normal infants. The absorption band at 450 nm observed on the spectra of urine was estimated as... -
- The Relationship of Specific Gravity by Refractometer and Osmolality in the Urine of Neonates.
- Hae Young Lee, In Soon Ahn, Jae Seung Yang, Beak Keun Lim, Jong Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1988;31(5):555-558. Published online May 31, 1988
-
Comparison of urinary specific gravity by refractometer and osmolality in 238 neonates demonstrated as followings; 1) The regression line is represented by the equation: Y = 107+14.2 (X-1000) while Y = osmolality in mosm/kg X = Specific gravity by refractometer r=0.8545 2) Osmolality is the only accurate measure of urine concentration in newborn infants. If the specific gravity by refractometer is used to screen for urine concentration, an elevated level... -
- A Study on Changes of Serum Prootein, Immunoglobulins, and Electrolyte Metabolism in Childhood Nephrotic Syndrome after Steroid Therapy.
- Kyung Rae Moon, Chang Soo Ra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1986;29(1):32-44. Published online January 31, 1986
-
The author determined serum and 24hr urine protein(total protein and albumin), immunoglobulins(lgG, IgA, and IgM) and serum electrolytes(Na, K, Ca, P, Mg, and Cl) in 5 cases of childhood nephrotic syndrome before and after steroid therapy, until urinary excretion of protein was negative (remission).The results observed are summarized as follows; 1) Serum protein; Before treatment, the mean serum total protein... -
- Change of Renal Excretion of Ascorbic Acid in Children.
- Chang Yeal Jeon, Jong Duck Kim, Heon Sook Lee, Jung Soo Kim, Kyung Woo Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(6):548-553. Published online June 30, 1984
-
In order to investigate the development of renal function, especially of the capacity of reabsorption of ascorbic acid in proximal tubule, in function of aging, experiments have been done. 1)Urinary flow, creatinine and electrolytes excretion in children (age :1~13yrs, weight: 10~39 kg) increased by aging and reached near the adult value at 11~13 years old. 2) Urinary concentration ability was matured... -
- Serum and Urine Zinc Values in Infectious Diseases.
- Yong Tai Suh, Hwa Young Kim, Jai Sook Mah, Tai Ju Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(3):237-245. Published online March 31, 1984
-
Using atomic absorption spectrophotometer, serum-and urine zinc levels of healthy children aging 4.7 to 6.9 years, and of various infectious diseases, including acute viral hepatitis, tuberculosis, salmonellosis, and shigellosis were determined. The mean zinc levels in healthy children were 76±15.2^g/100 ml in serum and 275土 142.4/ug/L in urine respectively. There was no statistical difference attributable to sex. No remarkable changes... -
- Urine Sediments and Protein in Healthy Newborn Infants.
- Jeh Hoon Shin, Eui Soo Park, Woo Gill Lee, Chong Moo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(12):1159-1167. Published online December 31, 1983
-
h7Routine urine examination in neonatal period is one of the most basic laboratory examination for early diagnosis of various diseases such, as urinary tract infection, congenital anomalies, and renovascular disorders etc. There are many methods to collect urine, but each of these methods has a problem, that is, catheterization causes urethral injury and ascending infection; suprapublic puncture is the most... -
- Urinary Excretion of Iron Renal Diseases.
- Kyung Ja Bang, Jaeh Hoon Shin, Woo Gil Lee, Chong Moo Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(11):1095-1101. Published online November 30, 1983
-
Iron is an essential element which participates in a variety of vital processes as well as hemoglobin synthesis of human body. Its hemeostasis is unique in that it is regulated primarily by absorption and not by excretion. Since the capacity of excreted iron is very limited, its absorption from the intestine must be controlled so that tissue accumulations do not reach. In adult males,... -
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











