Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics and associated factors of pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy: a retrospective study
- Huiling Zhang, Yilong Wang, Qianyun Ding, Xuekun Li, Sheng Ye
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):153-162. Published online November 11, 2024
-
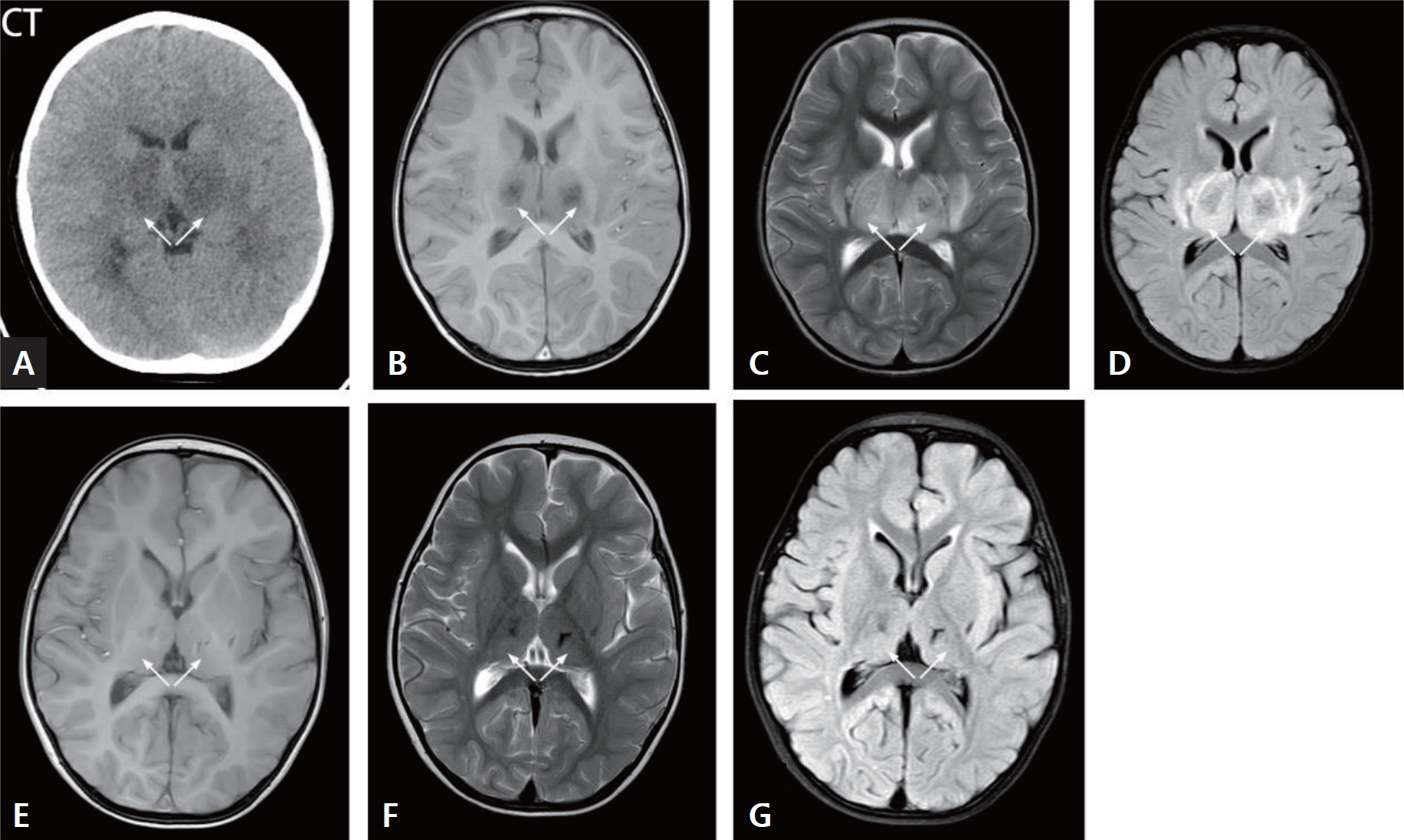
· The mortality rate of acute necrotizing encephalopathy was high.
· Laboratory tests revealed that the fatal group had higher creatinine, lactate, activated partial thromboplastin time, thrombin time, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, creatine kinase, and D-dimer than survivors.
· The fatal group displayed lower Glasgow Coma Scale scores and arterial pH.
- Review Article
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Development of orphan drugs for rare diseases
- Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(7):315-327. Published online June 28, 2023
-
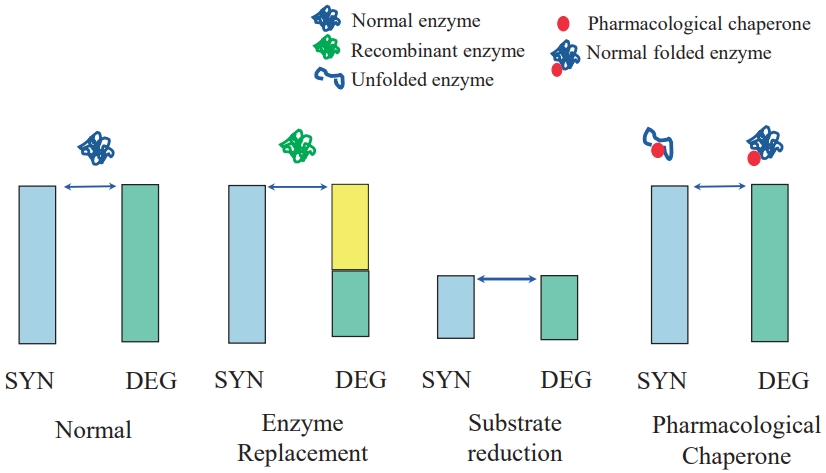
· Orphan disease is a rare disease, primarily affecting newborn and children. Vast majority of orphan diseases has genetic background.
· Orphan disease is individually rare. But as a whole, it is not rare, becoming a great socioeconomic burden.
· The diagnosis of rare genetic disease has been problematic, but recent progress of genome analysis technologies makes it faster and more precise.
· There are many unmet needs as to the curative treatment. However, the number of treatable rare diseases is growingly increasing owing to the development of biotechnology.
· Most orphan drugs are extremely expensive because of numer ous hurdles during the process of drug development as well as small number of patients.
- Allergy
- Trends of vitamin D in asthma in the pediatric population for two decades: a systematic review
- Myongsoon Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(8):339-347. Published online June 14, 2023
-
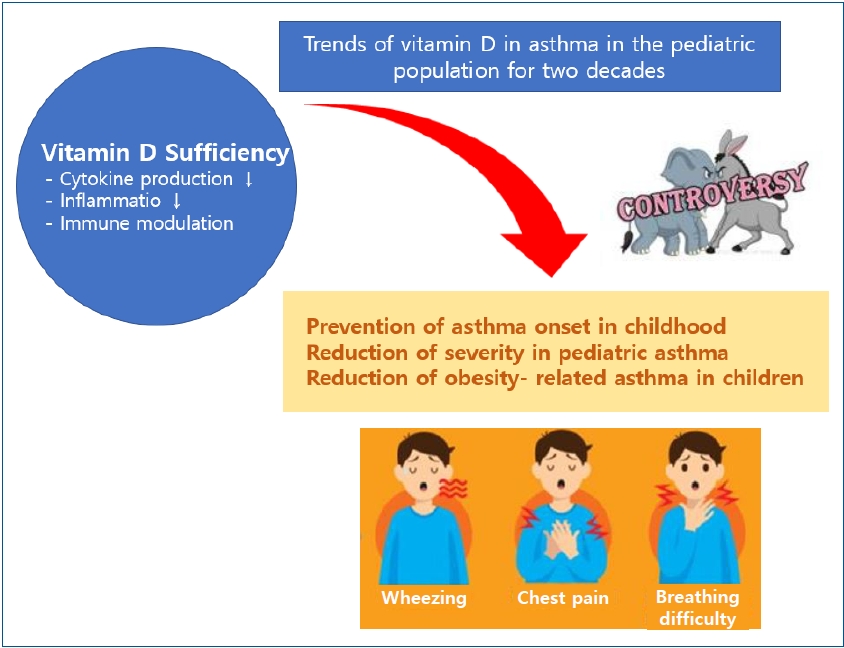
· Vitamin D may affect asthma via multiple mechanisms, including lung and optimal immune system functions.
· Many clinical trials have demonstrated the beneficial effects of vitamin D on asthma onset and aggravation. However, definitive clinical trials are lacking, and reports have detailed contradictory effects of vitamin D in children with asthma.
· Some exciting reports stated that obesity and vitamin D deficiency are associated with increased asthma symptoms in the pediatric population.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Ferritin in pediatric critical illness: a scoping review
- Ivy Cerelia Valerie, Anak Agung Sagung Mirah Prabandari, Dyah Kanya Wati
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):98-109. Published online September 16, 2022
-
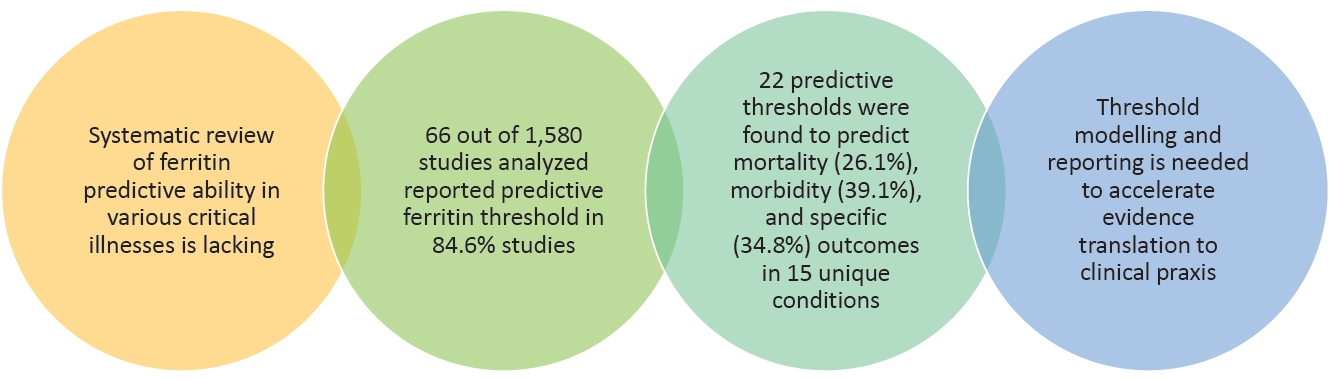
The number of studies on ferritin predictive ability in pediatric critical illness has grown exponentially over the past 2 decades. However, among the 66 of 1,580 studies analyzed here, summary statistics for overall and condition-specific studies were only reported in 45.4% and 71.2%, respectively. In contrast, ferritin as a categorical variable with a preset threshold was a significant predictor in 84.6% of studies.
- Original Article
- Other
- Clinical spectrum and short-term outcomes of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in a south Indian hospital
- Muruganantham Balagurunathan, Thrilok Natarajan, Jothilakshmi Karthikeyan, Venkateshwaran Palanisamy
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(10):531-537. Published online August 4, 2021
-

Question: What are the clinical spectrum, course, and short-term outcomes of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C)?
Finding: MIS-C can have variable clinical manifestations. Fever is most common, followed by gastrointestinal and cardiovascular symptoms. Early identification and appropriate management lead to favorable outcomes.
Meaning: MIS-C can present in a myriad of ways and severities. High suspicion is necessary to ensure its early identification and appropriate management and favorable patient outcomes.
- Gastroenterology
- Celiac disease in children: Increasing prevalence and changing clinical presentations
- Hasan M. Isa, Eman Farid, Jaafar J. Makhlooq, Afaf M. Mohamed, Jumana G. Al-Arayedh, Fawzeya A. Alahmed, Shima Medani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):301-309. Published online October 17, 2020
-
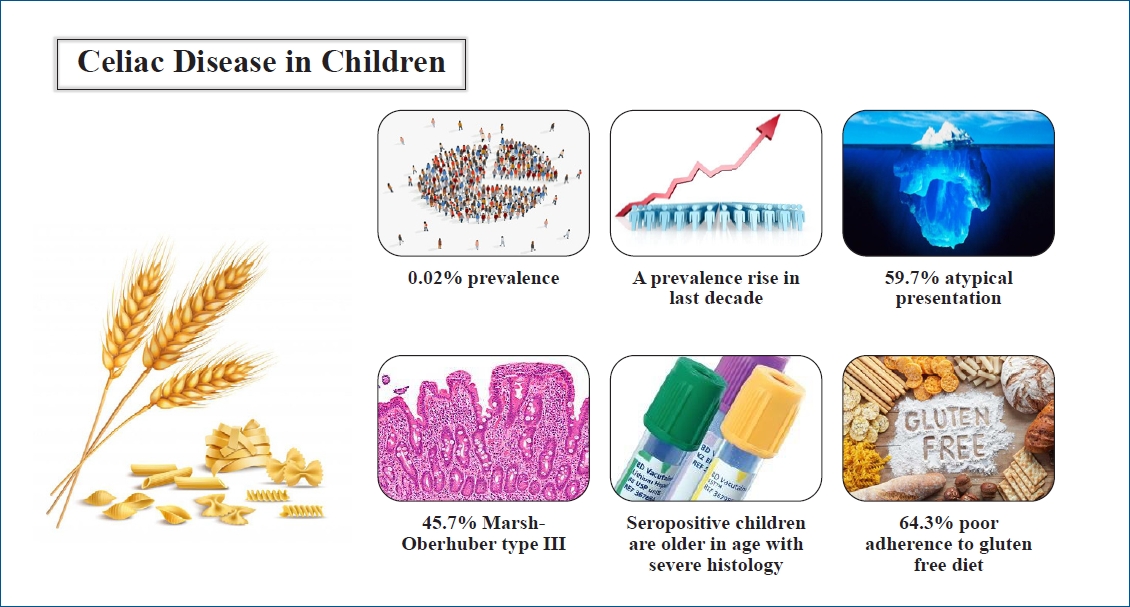
Question: What are the prevalence and clinical characteristics of celiac disease (CD) in children in Bahrain?
Finding: We found a significant increase in CD prevalence over the last decade (P=0.0001). A male predominance was noted. Atypical presentations were common. Most patients had poor adherence to a gluten-free diet.
Meaning: CD is an underdiagnosed condition. Atypical symptoms should be considered to prevent missing patients with CD.
- Endocrinology
- Influence of subclinical hypothyroidism on metabolic parameters in obese children and adolescents
- Ozlem Kara
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(3):110-114. Published online March 6, 2020
-

Question: Does subclinical hypothyroidism in obese children and adolescents affect metabolic parameters?
Finding: Insulin, HOMA-IR, and TG levels were higher and the HDL-C level was lower in patients with SH.
Meaning: A clear association is observed between SH, and insulin resistance and dyslipidemia in obese children. It can be said that the TSH may be evaluated as a metabolic risk factor in obese patients.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Clinical features and prognostic factors of early-onset sepsis: a 7.5-year experience in one neonatal intensive care unit
- Se Jin Kim, Ga Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Park, Sang Lak Lee, Chun Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(1):36-41. Published online September 27, 2018
-
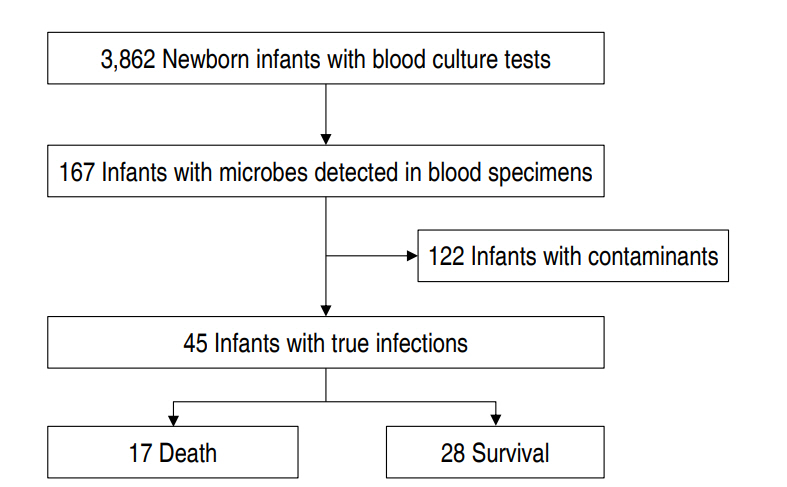
Purpose: In this study, we investigated the clinical features and prognostic factors of early-onset sepsis (EOS) in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) patients. Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on medical records from January 2010 to June 2017 (7.5 years) of a university hospital NICU. Results: There were 45 cases of EOS (1.2%) in 3,862 infants. The most common pathogen responsible for...
- Infection
- Clinical and laboratory profiles of hospitalized children with acute respiratory virus infection
- Eunjin Choi, Kee-Soo Ha, Dae Jin Song, Jung Hwa Lee, Kwang Chul Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(6):180-186. Published online June 25, 2018
-

Purpose Despite the availability of molecular methods, identification of the causative virus in children with acute respiratory infections (ARIs) has proven difficult as the same viruses are often detected in asymptomatic children.
Methods Multiplex reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assays were performed to detect 15 common respiratory viruses in children under 15 years of age who were hospitalized with ARI between January 2013...
- Applying the bacterial meningitis score in children with cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis: a single center's experience
- Jungpyo Lee, Hyeeun Kwon, Joon Soo Lee, Heung Dong Kim, Hoon-Chul Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(7):251-255. Published online July 22, 2015
-
Purpose The widespread introduction of bacterial conjugate vaccines has decreased the risk of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pleocytosis due to bacterial meningitis (BM) in children. However, most patients with CSF pleocytosis are hospitalized and treated with parenteral antibiotics for several days. The bacterial meningitis score (BMS) is a validated multivariate model derived from a pediatric population in the postconjugate vaccine era and...
- Neurofibromatosis type 1: a single center's experience in Korea
- Min Jeong Kim, Chong Kun Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(9):410-415. Published online September 30, 2014
-
Purpose Neurofibromatosis 1 (NF1) is an autosomal dominant condition caused by an
NF1 gene mutation. NF1 is also a multisystem disorder that primarily affects the skin and nervous system. The goal of this study was to delineate the phenotypic characterization and assess theNF1 mutational spectrum in patients with NF1.Methods A total of 42 patients, 14 females and 28 males, were enrolled...
- Prader-Willi syndrome: a single center's experience in Korea
- Yea Ji Kim, Chong Kun Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(7):310-316. Published online July 23, 2014
-
Purpose Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) is a complex genetic disorder that results from the lack of paternally expressed genes in the chromosome 15q11-q13 region. This study was performed to delineate the clinical features of PWS infants and toddlers and the effects of two-year growth hormone (GH) treatment according to gender and age at the start of treatment.
Methods The clinical characteristics and the results...
- Case Report
- Chronic intermittent form of isovaleric aciduria in a 2-year-old boy
- Jin Min Cho, Beom Hee Lee, Gu-Hwan Kim, Yoo-Mi Kim, Jin-Ho Choi, Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(8):351-354. Published online August 27, 2013
-
Isovaleric aciduria (IVA) is caused by an autosomal recessive deficiency of isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase (IVD). IVA presents either in the neonatal period as an acute episode of fulminant metabolic acidosis, which may lead to coma or death, or later as a "chronic intermittent form" that is associated with developmental delays, with or without recurrent acidotic episodes during periods of stress, such...
- Review Article
- Understanding noninferiority trials
- Seokyung Hahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(11):403-407. Published online November 23, 2012
-
Noninferiority trials test whether a new experimental treatment is not unacceptably less efficacious than an active control treatment already in use. With continuous improvements in health technologies, standard care, and clinical outcomes, the incremental benefits of newly developed treatments may be only marginal over existing treatments. Sometimes assigning patients to a placebo is unethical. In such circumstances, there has been...
- Systematic review of the clinical and genetic aspects of Prader-Willi syndrome
- Dong Kyu Jin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(2):55-63. Published online February 28, 2011
-
Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) is a complex multisystem genetic disorder that is caused by the lack of expression of paternally inherited imprinted genes on chromosome 15q11-q13. This syndrome has a characteristic phenotype including severe neonatal hypotonia, early-onset hyperphagia, development of morbid obesity, short stature, hypogonadism, learning disabilities, behavioral problems, and psychiatric problems. PWS is an example of a genetic condition caused...
- Genetic testing in clinical pediatric practice
- Han Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(3):273-285. Published online March 15, 2010
-
Completion of the human genome project has allowed a deeper understanding of molecular pathophysiology and has provided invaluable genomic information for the diagnosis of genetic disorders. Advent of new technologies has lead to an explosion in genetic testing. However, this overwhelming stream of genetic information often misleads physicians and patients into a misguided faith in the power of genetic testing.... -
- Diagnosis of neonatal seizures
- Hee Jung Chung, Yun Jung Hur
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(9):964-970. Published online September 15, 2009
-
Neonatal seizures are generally not only brief and subtle but also not easily recognized and are usually untreated. In sick neonates, seizures are frequently not manifested clinically but are detected only by electroencephalography (subclinical EEG seizures). This phenomenon of electroclinical dissociation is fairly common in neonates. On the other hand, neonates frequently show clinical behaviors such as stiffening, apnea, or... -
- Original Article
- A study of the frequency and characteristics of minor clinical manifestations in children with atopic dermatitis
- Ji Eun Cho, You Hoon Jeon, Hyeon Jong Yang, Bok Yang Pyun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(7):818-823. Published online July 15, 2009
-
Purpose : We aimed to evaluate the frequency and characteristics of minor clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis (AD) in Korean children to aid the diagnosis and treatment of AD. Methods : From April 2007 to December 2007, we enrolled 106 children (aged 1 month [infants] to 15 years) diagnosed with AD at the Pediatric Allergy Respiratory Center in Soonchunhyang University Hospital.... -
- Short-term clinical outcomes of late preterm infants
- Ji Youn Na, Narimi Park, Eun Sun Kim, Jin-A Lee, Gyu Hong Shim, Jin-A Lee, Chang Won Choi, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim, Beyong Il Kim, Jung-Hwan Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):303-309. Published online March 15, 2009
-
Purpose : To identify the short-term clinical outcomes of late preterm infants and to test the hypothesis that late preterm infants have more clinical problems during the early postnatal period than term infants. Methods : One hundred late preterm infants [gestational age (GA) 34+0-36+6 weeks] and the same number of term infants (GA 37+0-41+6 weeks) were randomly selected from 289 late... -
- Complex febrile convulsions: A clinical study
- Jeong Sic Kang, Sa-Ra Kim, Dong Wook Kim, Tae Won Song, Nam Hee Kim, Jong Hee Hwang, Jin Soo Moon, Chong Guk Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(1):81-86. Published online January 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Febrile convulsions are classified into simple or complex types, the latter being characterized by increased risk of recurrence and progression to epilepsy. This study aimed to delineate the clinical characteristics of complex febrile convulsions. Methods : Between January 2003 and December 2006, 550 children were diagnosed with febrile convulsions at the Department of Pediatrics, Ilsan Paik Hospital. Their... -
- A clinical study of congenital chylothorax and octreotide therapy
- Ung Geon Oh, Kyoung Eun Choi, Kyung Ah Kim, Sun Young Ko, Yeon Kyung Lee, Son Moon Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(11):1172-1178. Published online November 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Congenital chylothorax is an accumulation of lymphatic fluid within the pleural space. It is a common cause of unidentified hydrops fetalis. We examined the perinatal history, clinical manifestation, diagnosis, treatment, and outcome in 6 newborns diagnosed to have congenital chylothorax with hydrops fetalis. We also studied the effect of octreotide therapy for congenital chylothorax in relation to conservative... -
- Case Report
- Cytogenetic evaluation of a patient with ring chromosome 9 presenting failure to thrive and developmental delay
- Yun Mi Park, Han Nae Nho, Sook Za Kim, Young Min Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(4):426-430. Published online April 15, 2008
-
We report clinical, cytogenetic, and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) studies of a patient with ring chromosome 9. She presented with failure to thrive, facial dysmorphysm and mild psychomotor development delay in the absence of major malformations. Peripheral blood karyotype of the patient was 46,XX,r(9)(p24q34). G-band analysis suggested no loss of material in the ring chromosomes. FISH analysis using the... -
- Original Article
- Serum levels of free insulin-like growth factor-I and clinical value in healthy children
- Young Hee Chung, Woo Yeong Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(1):47-53. Published online January 15, 2008
-
Purpose : The serum levels of total insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding protein (IGFBP)- 3 reflect endogenous growth hormone (GH) secretion in healthy children. Free form of IGF-I which is suggested to have more potent biological action than complex form of IGF-I. The aim of this study is to investigate the serum levels of free IGF-I and its... -
- Review Article
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children: past, present and future
- Hyoung Jin Kang, Hee Young Shin, Hyo Seop Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(7):601-605. Published online July 15, 2007
-
The cure rate of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in children dramatically improved over past 5 decades from zero to about 80%. The main cause of improvement is owing to the development of chemotherapy by multicenter clinical trial of large study groups with the understanding of leukemia biology. Recently, pediatric ALL protocols were applied to the treatment of adolescent and even... -
- Original Article
- Analysis of the association between bronchial hyperresponsiveness and genetic polymorphism of β2-adrenoceptor in adolescents with long-term asthma remission
- Hee Kang, Young Yull Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(6):556-564. Published online June 15, 2007
-
Purpose : We hypothesized that the persisting bronchial hyperresponsiveness (BHR) of adolescents with asthma remission may be controlled mainly by genetic factors, and the BHR of symptomatic asthma by airway inflammation. β2-adrenoceptor gene is considered to be a candidate gene in the development of BHR. Thus, β2-adrenoceptor gene polymorphism may be associated with the BHR of adolescents with asthma remission,... -
- Review Article
- Regionalization of neonatal care and neonatal transport system
- Jong Beom Sin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(1):1-6. Published online January 15, 2007
-
In the United States, The concept of designation for hospital facilities that care for newborn infants according to the level of complexity of care provided was first proposed in 1976. The extent of perinatal health care regionalization varies widely from one area to the other. facilities that provide hospital care for newborn are classified into three categories on the basis... -
- Original Article
- Clinical characteristics and risk factors for staphylococcal infections in neonatal intensive care unit
- Min Kook Chung, Jeong Ho Choi, Jin Keun Chang, Sung Hoon Chung, Chong Woo Bae, Sung Ho Cha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(12):1287-1295. Published online December 15, 2006
-
Purpose : The importance of staphylococcal infections in NICU has been emphasized in terms of increased resistant strains and increased incidence of morbidity and mortality. In this study, we inrestignted the clinical characteristics and risk factors for staphylococcal infections, and looked into sensitivity trends of antibiotics in the era of a high rate of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in our... -
- Review Article
- Diagnosis of inherited metabolic disorders based on their diverse clinical features and laboratory tests
- Han-Wook Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(11):1140-1151. Published online November 15, 2006
-
Inherited metabolic disorders are individually rare but as a whole, they are nor rare. Since Archibald Garrod introduced a concept of “inborn error of metabolism” or “chemical individuality”, more than 500 diseases are currently known, affecting approximately one in 500 newborns cumulatively. They frequently manifest with acute, life-threatening crisis that require immediate specific intervention or they present with insidious diverse... -
- Original Article
- Clinical characteristics and outcomes of status epilepticus as an initial seizure in children
- Mi Jeong Kim, Young Ok Kim, Sun Hee Kim, Woo Yeon Choi, Hyung Suk Byun, Chan Jong Kim, Young Jong Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(6):659-664. Published online June 15, 2006
-
Purpose : To evaluate the morbidity and mortality of children with status epilepticus(SE) as an initial seizure and to compare these according to age groups. Methods : The 78 cases(38 cases <2 years and 38 cases ≥2 years) with SE as an initial seizure admitted to the Chonnam national university hospital from Jan. 2000 to Jan. 2004 were reviewed. Developmental profiles,... -
- Review Article
- Early recognition of high risk factors of acute abdominal pain in children
- Jin-Bok Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(2):117-128. Published online February 15, 2006
-
Non-traumatic acute abdominal pain in children presents a diagnostic dilemma. Numerous disorders can cause abdominal pain. Although many etiologies are benign, some require a rapid diagnosis and treatment in order to minimize morbidity. This review concentrates on the clinical office evaluation of acute abdominal pain in infants and children and details the clinical guideline for the diagnostic approach to imaging... -
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











