|
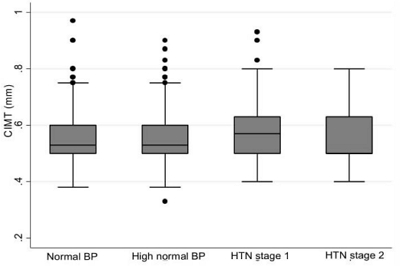
Question: What is the prevalence of HTN among adolescents enrolled in the TLGS according to 3 different accepted definitions (4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG). Also, what is the ability of each of these definitions in predicting early adulthood CIMT, as a surrogate for cardiovascular disease events?
Finding: The highest and lowest prevalence of stage 1 HTN was observed with the AAP-CPG (17.7%) and ESH (8.8%), respectively. Similarly, the highest and lowest prevalence of stage 2 HTN was noted with the AAP-CPG (1.5%) and ESH (0.8%), respectively. The highest to lowest predictive abilities belonged to the 4th report, ESH, and AAP-CPG, respectively.
Meaning: Among the various definitions of pediatric HTN, the 4th report offered the best ability to predict a high CIMT during early adulthood, followed by the ESH and AAP-CPG. |


