Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Less invasive surfactant administration versus intubation-surfactant-extubation: a single-center retrospective study
- C.S. Jithin, A. Nalina, A. Shashidhar, P.N. Suman Rao
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(12):991-997. Published online October 2, 2025
-
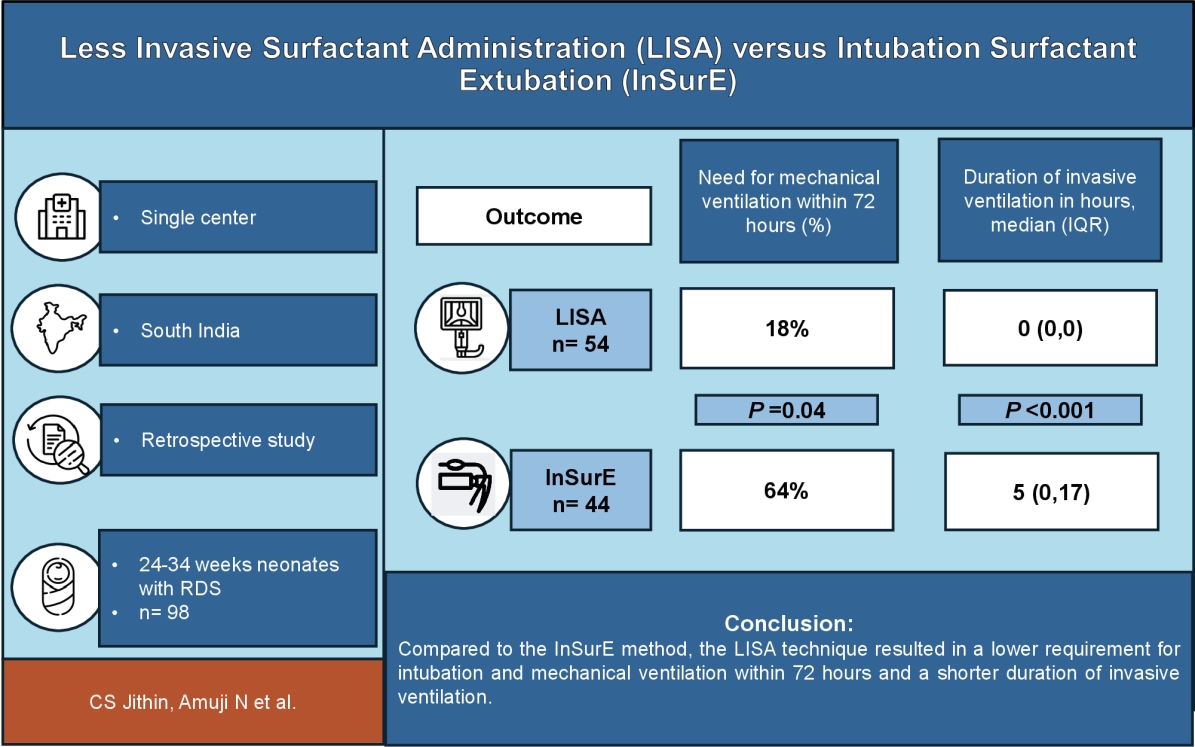
Question: Does less invasive surfactant administration (LISA) (vs. intubation-surfactant-extubation) improve clinical outcomes in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome?
Finding: LISA significantly reduced intubation and invasive mechanical ventilation needs within the first 72 hours and shortened the overall invasive respiratory support duration without increasing other morbidities.
Meaning: LISA is a less invasive and safer surfactant delivery alternative. Larger multicenter trials are needed to confirm its long-term safety and efficacy, especially in low- and middle-income countries.
- Hematology
- Hyperhomocysteinemia in pediatric β-thalassemia: links to vitamin cofactor deficiencies and oxidative stress
- Arzu Dadashova, Gunay Aliyeva, Rana Rahimova, Gulnara Azizova, Khayala Mammadova
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(10):819-830. Published online July 8, 2025
-
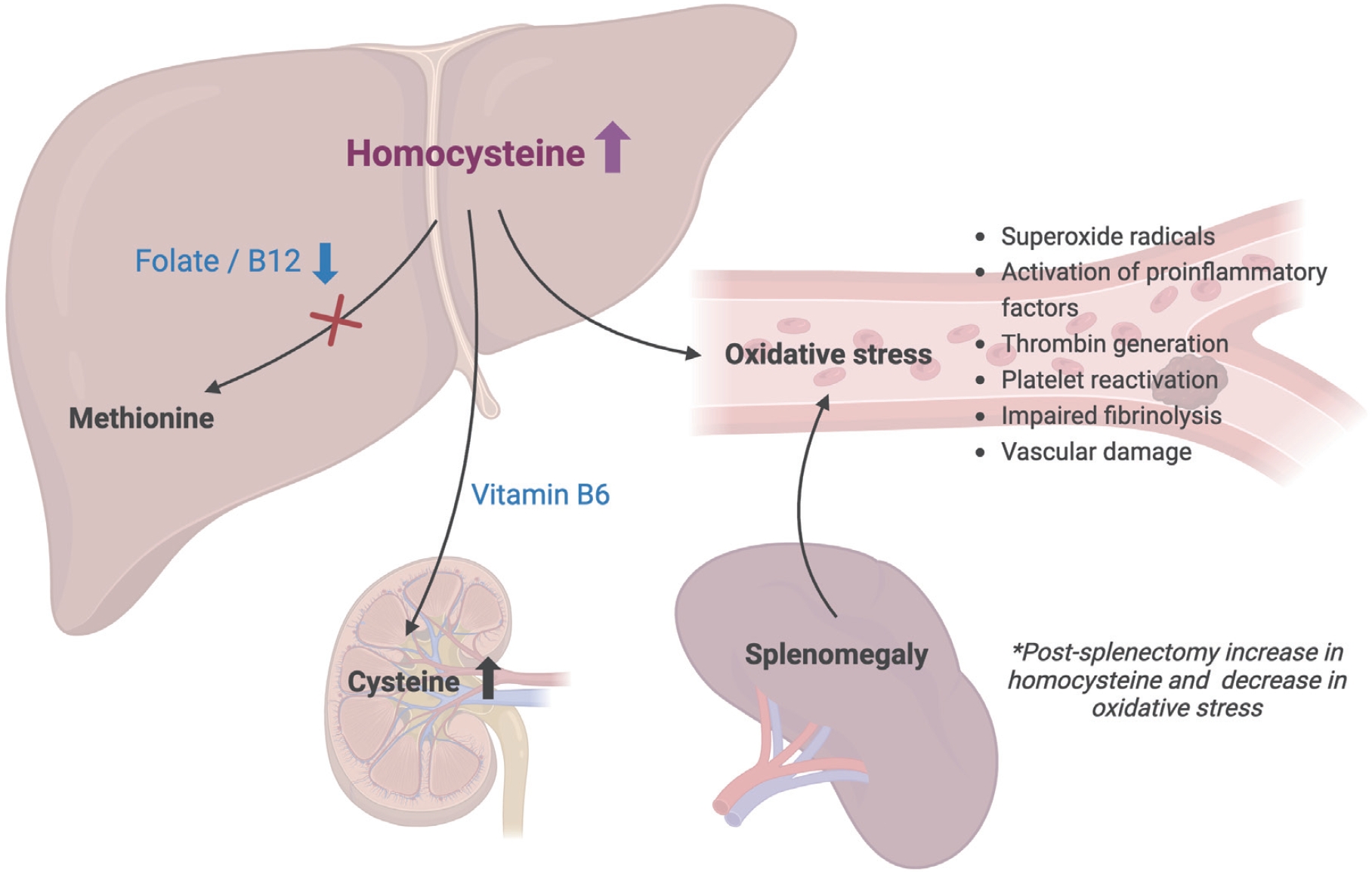
Question: What are the biochemical and clinical correlates of hyperhomocysteinemia in pediatric β-thalassemia, and how does it relate to vitamin status, oxidative stress, and splenectomy?
Finding: Most pediatric β-thalassemia patients exhibited severe hyperhomocysteinemia, which was strongly associated with folate and B12 deficiencies and influenced oxidative stress patterns, particularly in splenectomized individuals.
Meaning: These findings suggest that routine monitoring and correction of B-vitamin deficiencies may mitigate hyperhomocysteinemia-related risks in pediatric thalassemia.
- Pulmonology
- Association of macrophage migration-inhibitory factor gene and growth differentiation factor 15 gene polymorphisms and their circulating levels with respiratory distress syndrome among preterm neonates
- Ali Helmi Bakri, Mohammed H. Hassan, Khaled Abdalla Abd-Elbaseer, Mahmoud Abo-Alhassan Sayed, Ahmed Alamir Mahmoud Abdallah, Eman Ahmed Abd-Elmawgood
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(9):680-689. Published online April 1, 2025
-

Question: Do macrophage migration-inhibitory factor (MIF) and growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15) levels and their gene polymorphisms affect RDS among preterm babies?
Finding: Significantly higher serum MIF and GDF-15 levels were observed in patients with severe respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). The mutant G- and C-alleles of GDF-15 rs4808793 C>G single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and MIF rs755622 G>C SNP were present at significantly higher frequencies in preterm neonates with RDS.
Meaning: MIF and GDF-15 play a significant role in neonatal RDS and its severity.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and stress among parents of neonates admitted to neonatal intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Asha P. Shetty, Kurvatteppa Halemani, Alwin Issac, Latha Thimmappa, Sanjay Dhiraaj, Radha K, Prabhaker Mishra, Vijai Datta Upadhyaya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):104-115. Published online November 14, 2023
-
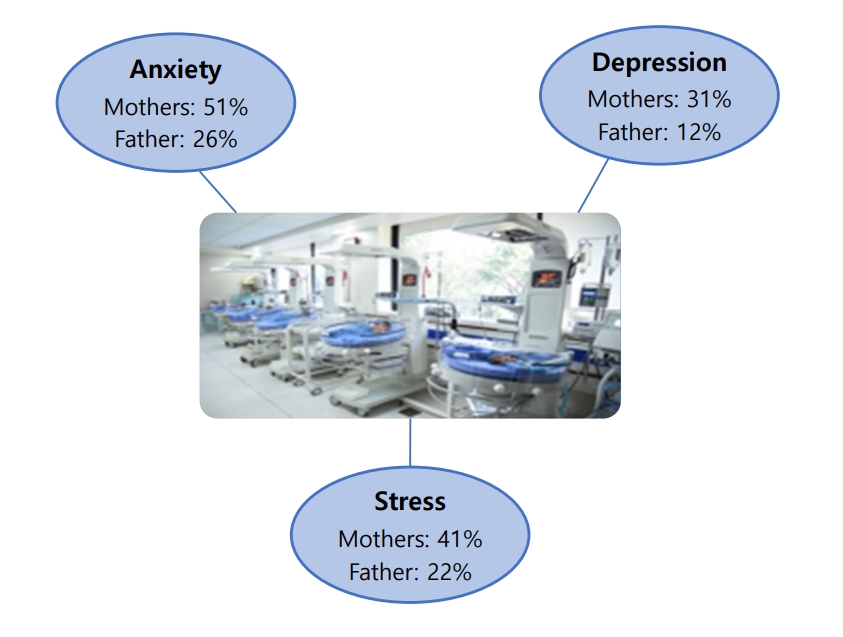
Question: What emotions do parents experience when their newborns are admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)?
Finding: Mothers experienced more anxiety (51%), depression (31%), and stress (41%) symptoms than fathers (26%, 12%, and 22%, respectively).
Meaning: Parents often experience anxiety, stress, and depression following NICU admission. Healthcare workers are responsible for providing regular parental counseling.
- Pulmonology
- Predictors of high-flow nasal cannula failure in pediatric patients with acute respiratory distress
- Kantara Saelim, Busawan Thirapaleka, Kanokpan Ruangnapa, Pharsai Prasertsan, Wanaporn Anuntaseree
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):595-601. Published online November 1, 2022
-

SpO2/FiO2 ratio ≤166, pediatric respiratory rate-oxygenation index <132, and clinical respiratory score ≥6 at 12 hours after high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) initiation were useful bedside predictors for HFNC failure in pediatric patients.
- Review Article
- Neurobehavior
- Jeopardized mental health of children and adolescents in coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic
- Bohyun Jin, Sohee Lee, Un Sun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):322-329. Published online June 3, 2022
-
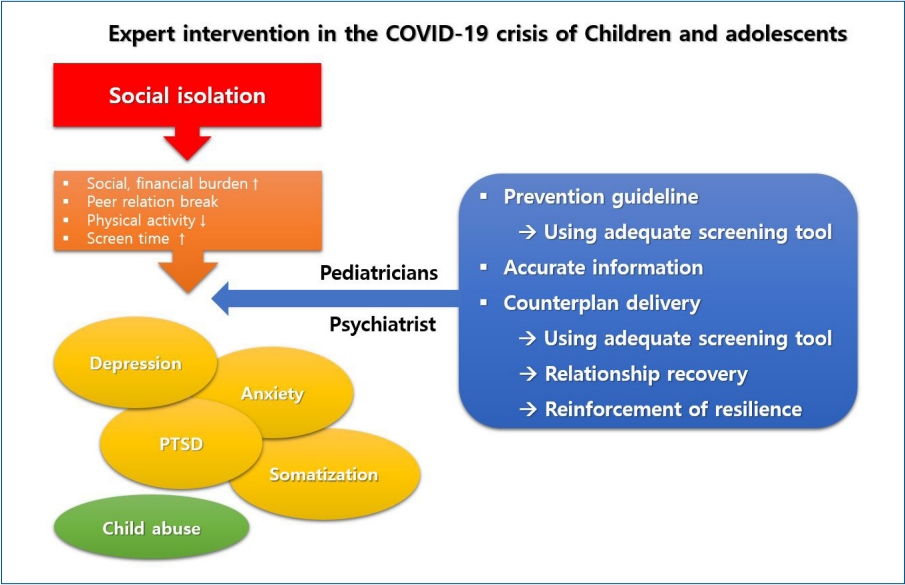
∙ The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has required preventive measures like self-quarantine, school closures, and lockdown, which ultimately make youth directly and indirectly vulnerable to depression, anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, and somatization.
∙ Child abuse is more common in the COVID-19 era than previously.
∙ Pediatricians should carefully examine parental and child mental health to directly and indirectly aid their physical and mental health.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Comparison of minimally invasive surfactant therapy with intubation surfactant administration and extubation for treating preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized clinical trial
- Mohammad Kazem Sabzehei, Behnaz Basiri, Maryam Shokouhi, Sajad Ghahremani, Ali Moradi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):188-193. Published online July 28, 2021
-
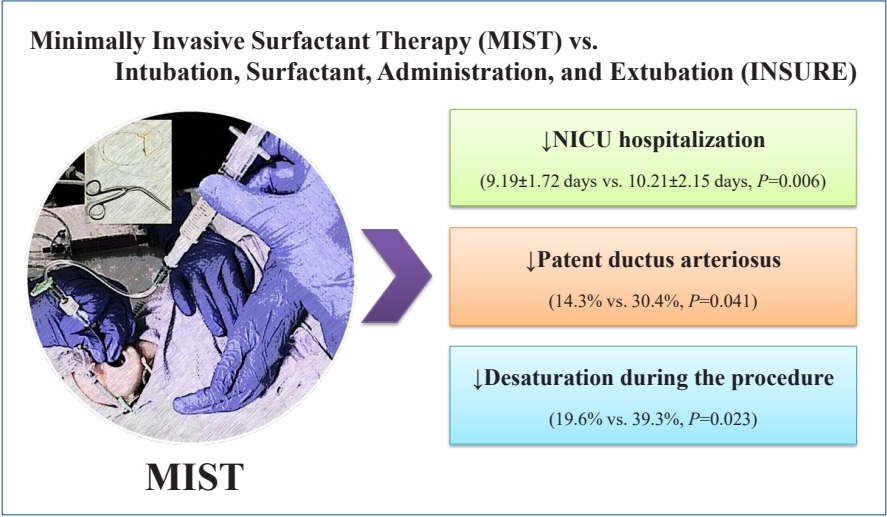
Question: Are the short-term outcomes of minimally invasive surfactant therapy (MIST) relatively superior to those of INtubation, SURfactant administration, and Extubation (INSURE) in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)?
Finding: MIST could be an appropriate substitution for INSURE in preterm infants with RDS since it reduced hospitalization time and number of side effects.
Meaning: MIST is recommended for surfactant administration for its proven advantages over the INSURE technique.
- Pulmonology
- Modified high-flow nasal cannula for children with respiratory distress
- Sarocha Itdhiamornkulchai, Aroonwan Preutthipan, Jarin Vaewpanich, Nattachai Anantasit
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):136-141. Published online May 24, 2021
-
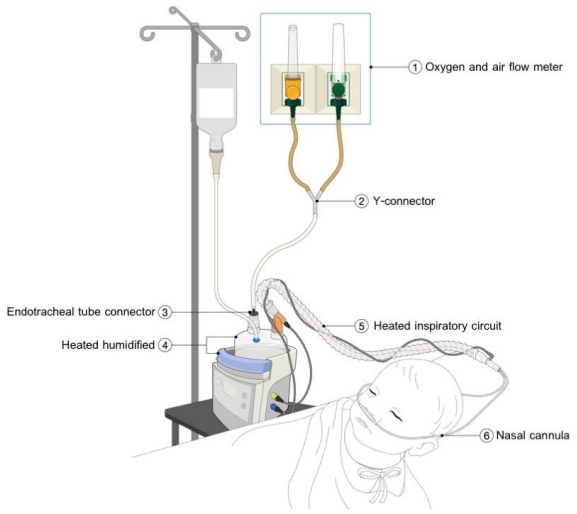
Question: Can the modified high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) provide alternative respiratory support for children with acute respiratory distress?
Finding: A total of 74 patients were assigned to the modified or commercial HFNC groups. The intubation rate, length of hospital stay, and adverse events did not differ between the 2 groups.
Meaning: The modified HFNC can provide alternative respiratory support for pediatric respiratory distress.
- Review Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Pediatric postintensive care syndrome: high burden and a gap in evaluation tools for limited-resource settings
- Chanapai Chaiyakulsil, Rapee Opasatian, Paweethida Tippayawong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(9):436-442. Published online December 18, 2020
-
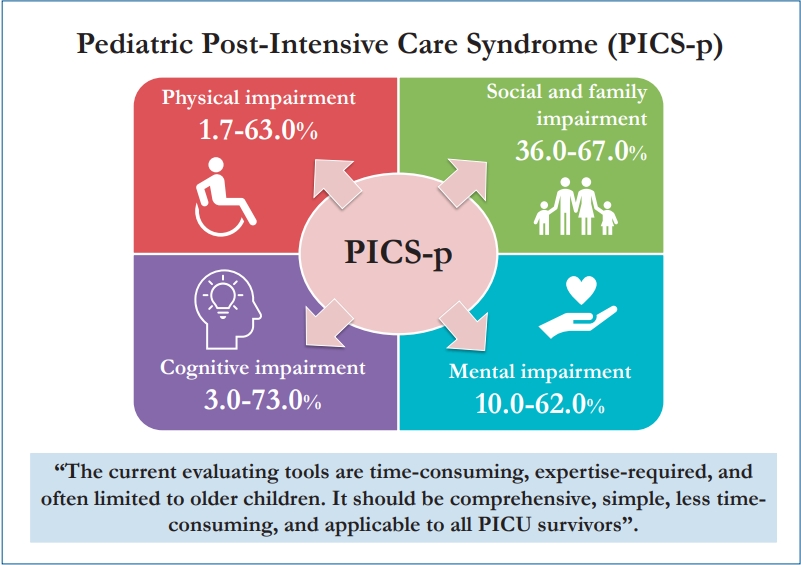
Pediatric postintensive care syndrome has high impact and burden and can affect a child’s life for decades. The early evaluation and detection of such problems require a simple and less time-consuming surveillance tool. Current evaluation tools can be difficult and strenuous for areas with limited resources. Thus, a new simple tool is required for the early detection and intervention of postintensive care syndrome in critically ill children
- Original Article - Clinical trial
- WITHDRAWN:Randomized controlled trial of effect of N-acetylcysteine as an antioxidant on iron overload in children with thalassemia major
- Yasmen A Mohamed, Mohamed H Meabed, Amany Ashraf, Dalia S Morgan, Mostafa G Abdul Latif, Rehab M Abd-Elkareem, Heba M Ahmed
-
Background: β-Thalassemias are characterized by the presence of mutations in the globin gene that result in the absence or reduced synthesis of β-globin chains of the hemoglobin tetramer. Several studies have reported increased oxidative stress in β-thalassemia major (β-TM) patients. N-acetylcysteine (NAC), a derivative of L-cysteine amino acid, is commonly used as a mucolytic drug. Numerous studies have reported efficient... -
- Review Article
- Neurology
- Myths and truths about pediatric psychogenic nonepileptic seizures
- Jung Sook Yeom, Heather Bernard, Sookyong Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):251-259. Published online October 17, 2020
-
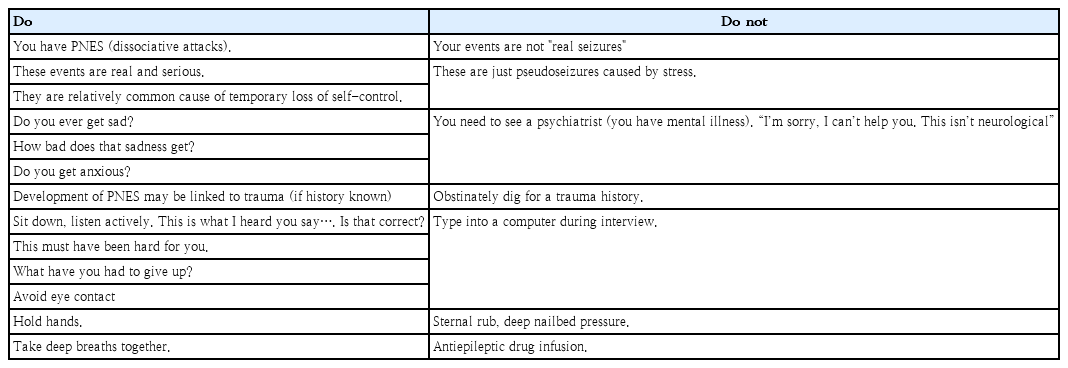
• Psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (PNES) are events that look like epileptic seizures but are not caused by abnormal electrical discharges.
• PNES are a manifestation of psychological and emotional distress.
• Treatment for PNES does not begin with the psychological intervention but starts with the diagnosis and how the diagnosis is delivered.
• A multifactorial biopsychosocial process and a neurobiological review are both essential components when treating PNES
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Effects of α-tocopherol on hemolysis and oxidative stress markers on red blood cells in β-thalassemia major
- Nora Sovira, Munar Lubis, Pustika Amalia Wahidiyat, Franciscus D. Suyatna, Djajadiman Gatot, Saptawati Bardosono, Mohammad Sadikin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):314-320. Published online August 15, 2020
-

Question: Is the α-tocopherol as an exogenous antioxidant supplementation effective in improving hemolysis and oxidative stress on β-thalassemia major?
Finding: We found significant enhancements in plasma haptoglobin were noted in the α-tocopherol group (3.01 mg/dL; range, 0.60–42.42 mg/dL; P=0.021).
Meaning: The α-tocopherol can improve hemolysis by increasing the haptoglobin level as hemolysis marker.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Surfactant preparations for preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome: past, present, and future
- Ga Won Jeon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):155-161. Published online February 8, 2019
-

Following the first successful trial of surfactant replacement therapy for preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) by Fujiwara in 1980, several animal-derived natural surfactants and synthetic surfactants have been developed. Synthetic surfactants were designed to overcome limitations of natural surfactants such as cost, immune reactions, and infections elicited by animal proteins contained in natural surfactants. However, first-generation synthetic surfactants...
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Association between vitamin D level at birth and respiratory morbidities in very-low-birth-weight infants
- Ian Kim, Sung Shin Kim, Jee In Song, Seock Hwa Yoon, Ga Young Park, Yong-Wha Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(5):166-172. Published online October 24, 2018
-
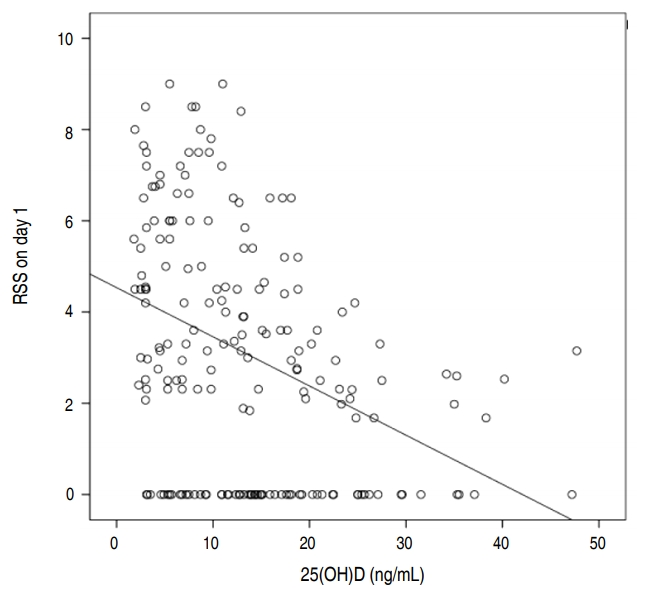
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate vitamin D status at birth in very-low-birth-weight infants (VLBWIs: <1,500 g) and to determine the association between vitamin D level and respiratory morbidity. Methods: A retrospective study was conducted at Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital between November 2013 and November 2017. We collected blood samples and data on respiratory morbidity from 230 VLBWIs on the first...
- Transient intubation for surfactant administration in the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in extremely premature infants
- Ji Won Koh, Jong-Wan Kim, Young Pyo Chang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):315-321. Published online September 16, 2018
-
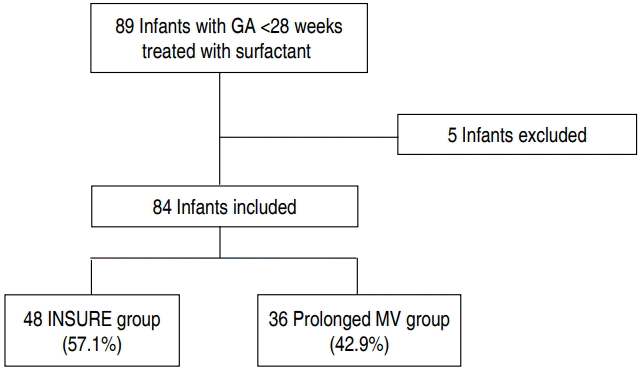
Purpose: To investigate the effectiveness of transient intubation for surfactant administration and extubated to nasal continuous positive pressure (INSURE) for treatment of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and to identify the factors associated with INSURE failure in extremely premature infants. Methods: Eighty-four infants with gestational age less than 28 weeks treated with surfactant administration for RDS for 8 years were included. Perinatal...
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Update of minimally invasive surfactant therapy
- Gyu-Hong Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(9):273-281. Published online September 21, 2017
-

To date, preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) after birth have been managed with a combination of endotracheal intubation, surfactant instillation, and mechanical ventilation. It is now recognized that noninvasive ventilation (NIV) such as nasal continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) in preterm infants is a reasonable alternative to elective intubation after birth. Recently, a meta-analysis of large controlled trials...
- Genetic risk factors associated with respiratory distress syndrome
- Heui Seung Jo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(4):157-163. Published online April 30, 2014
-
Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) among preterm infants is typically due to a quantitative deficiency of pulmonary surfactant. Aside from the degree of prematurity, diverse environmental and genetic factors can affect the development of RDS. The variance of the risk of RDS in various races/ethnicities or monozygotic/dizygotic twins has suggested genetic influences on this disorder. So far, several specific mutations in...
- Case Report
- Idiopathic acute eosinophilic pneumonia in a 14-month-old girl
- Ha Neul Park, Bo Hyun Chung, Jung Eun Pyun, Kwang Chul Lee, Ji Tae Choung, Choon Hak Lim, Young Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(1):37-41. Published online January 29, 2013
-
Idiopathic acute eosinophilic pneumonia (IAEP), characterized by acute febrile respiratory failure associated with diffuse radiographic infiltrates and pulmonary eosinophilia, is rarely reported in children. Diagnosis is based on an association of characteristic features including acute respiratory failure with fever, bilateral infiltrates on the chest X-ray, severe hypoxemia and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid >25% eosinophils or a predominant eosinophilic infiltrate in lung...
- Review Article
- Ambient air pollution and allergic diseases in children
- Byoung-Ju Kim, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(6):185-192. Published online June 21, 2012
-
The prevalence of allergic diseases has increased worldwide, a phenomenon that can be largely attributed to environmental effects. Among environmental factors, air pollution due to traffic is thought to be a major threat to childhood health. Residing near busy roadways is associated with increased asthma hospitalization, decreased lung function, and increased prevalence and severity of wheezing and allergic rhinitis. Recently,...
- Original Article
- Comparative study on effects of volume-controlled ventilation and pressure-limited ventilation for neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
- Jae Jin Kim, Mun Jung Hwang, Sang Geel Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(1):21-27. Published online January 15, 2010
-
Purpose:In contrast with traditional time-cycled, pressure-limited ventilation, during volume-controlled ventilation, a nearly constant tidal volume is delivered with reducing volutrauma and the episodes of hypoxemia. The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of pressure-regulated, volume controlled ventilation (PRVC) to Synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV) in VLBW infants with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS). Methods : 34 very low birth... -
- Review Article
- Neonatal respiratory distress: recent progress in understanding pathogenesis and treatment outcomes
- So Young Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(1):1-6. Published online January 15, 2010
-
Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN), respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), and persistent pulmonary hypertension (PPHN) are the three most common disorders that cause respiratory distress after birth. An understanding of the pathophysiology of these disorders and the development of effective therapeutic strategies is required to control these conditions. Here, we review recent papers on the pathogenesis and treatment of neonatal... -
- Original Article
- Clinical feature of neonatal pneumothorax induced by respiratory distress syndrome and pneumonia
- Ji-Sun Jung, Sang-Woo Park, Chun-Soo Kim, Sang-Lak Lee, Tae-Chan Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):310-314. Published online March 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Pneumothorax is an important factor responsible for increased mortality and morbidity in neonates. Here, we compared the clinical findings and prognosis for neonatal pneumothorax induced by respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and pneumonia. Methods : Between January 2001 and December 2005, 80 patients with neonatal pneumothorax induced by RDS and pneumonia and admitted to the NICU of Dongsan Medical... -
- Study of the risk factors for pulmonary interstitial emphysema related to mechanical ventilator care
- Sang Yeob Kim, Pil Sang Lee, Sang Geel Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(11):1179-1184. Published online November 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Pulmonary interstitial emphysema (PIE) primarily occurs in preterm infants suffering from respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and kept under mechanical ventilator care. Therefore, this study aimed to examine various risk factors for PIE, to identify conditions that can decrease the possibility of PIE development. Methods : PIE classification was conducted for 183 patients diagnosed to have RDS and receiving mechanical... -
- The pharmacological treatment of patent ductus arteriosus in premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome: oral ibuprofen vs. indomethacin
- Soo Jin Lee, Ji Young Kim, Eun Ae Park, Sejung Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(9):956-963. Published online September 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Indomethacin is widely used for the prophylaxis and treatment of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA); however, it is associated with side effects such as renal failure, intraventricular hemorrhage, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Intravenous ibuprofen has been shown to be as effective as indomethacin in prompting PDA closure. If treatment with oral ibuprofen is as effective as indomethacin, it would have... -
- Case Report
- A case of acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with congenital H-type tracheoesophageal fistula and gastroesophageal reflux
- Heewon Chueh, Myo Jing Kim, Jin-A Jung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(8):892-895. Published online August 15, 2008
-
H-type tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is extremely rare in infants and children, and clinical manifestations of this condition are diverse based on its severity. Some cases of congenital TEF diagnosed in adulthood have been reported, which indicate the difficulty of early diagnosis of this disease. Gastroesophageal reflux (GER) may induce chronic aspiration, pulmonary aspiration, apparent life-threatening events, and failure to thrive.... -
- Original Article
- Oxygenation index as a respiratory parameter of respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants
- Ji Hyun Jeon, Ran Namgung, Min Soo Park, Kook In Park, Chul Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(2):145-149. Published online February 15, 2008
-
Purpose : To examine whether changes of oxygenation index (OI) by postnatal age were different by the number of surfactant administration, and different between subgroups of survival and death. Methods : From January 2005 to June 2006, preterm infants (n=84) diagnosed as respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and treated with surfactant and ventilator were included. They were divided into two groups: Group... -
- Effects of puromycin aminonucleoside on the cytoskeletal changes of glomerular epithelial cells
- Jun Ho Lee, Tae Sun Ha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(1):54-61. Published online January 15, 2008
-
of microvilli, but also separated the intercellular gaps and linear ZO-1. PAN induced oxidative stresses in time and dose dependent manners and increases of intercellular permeability in anti-oxidants inhibitable manners. High concentration of PAN induced not only actin polymerization and disorganization, but also the conglomerulation and internal dislocation of α-actinin protein. The intensities of fluorescences of ZO-1 protein were diminished... -
- Cord blood IL-10, IL-12 in preterm newborns as predictors of respiratory distress syndrome and bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Jee Yoon Park,, Ji Young Kim, Soo Jin Cho, Young Ju Kim, Hye sook Park, Eun Hee Ha, Eun Ae Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(3):248-254. Published online March 15, 2007
-
Purpose : Inflammation plays a major role in the pathogenesis of RDS and BPD in the immature lung. We investigated the possible role of IL-10 and IL-12 in the cord blood of preterm newborns with RDS or BPD. Methods : Forty preterm newborns whose mothers received antenatal care at Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital between January 2003 to June 2005, and... -
- Case Report
- A case of acute respiratory distress syndrome treated with surfactant and low dose methylprednisolone
- Bo Yeon Choi, Kyong Mo Kim, Jong Seo Yoon, Joon Sung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(4):455-459. Published online April 15, 2006
-
The major pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is an inflammatory process that results from a diversity of injuries to the body. Due to the various cytokines and vasoactive peptides released from the endothelium, the vascular permeability is increased; the migration of inflammatory cells and the leakage of plasma proteins then occur and edema develops in the alveolus. There... -
- Original Article
- A Study on the Effects of Early Surfactant Replacement and Gentle Ventilation in the Treatment of Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Yong Suk Lee, Ji Hye Lee, Sang Geel Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(10):1096-1101. Published online October 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Recently, early surfactant replacement and tidal volume based gentle ventilation has been a fundamental treatment of respiratory distress syndrome(RDS). The aims of this study were to survey the changes in ventilator care duration and rate of complication in RDS groups. Methods : We performed a retrospective study of 255 newborn infants less than 1,500 g admitted to the... -
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











