Topics
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Topics
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (3)
- Allergy (52)
- Cardiology (76)
- Critical Care Medicine (8)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (17)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (51)
- Gastroenterology (57)
- General Pediatrics (37)
- Genetics and Metabolism (20)
- Hematology (11)
- Immunology (12)
- Infection (66)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (103)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (49)
- Neurology (88)
- Nutrition (25)
- Oncology (15)
- Neurobehavior (11)
- Pulmonology (25)
- Rheumatology (2)
- Other (28)
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: how can we improve its outcomes?
- Tae-Jung Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):367-373. Published online May 17, 2019
-
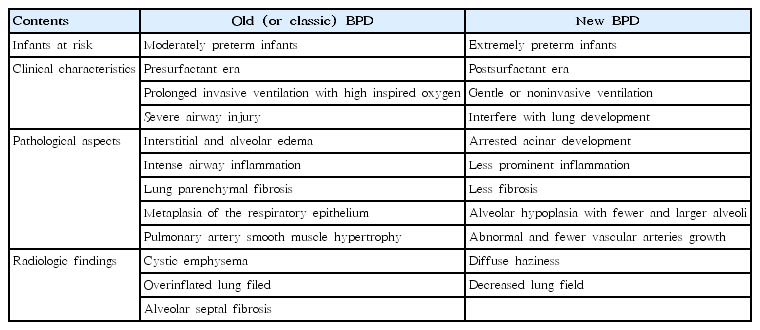
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is a chronic lung disease of preterm infants with multiple factors affected from prenatal to postnatal periods. Despite significant advances in neonatal care over almost 50 years, BPD rates have not decreased; in fact, they may have even increased. Since more preterm infants, even at periviable gestational age, survive today, different stages of lung development affect the...
- Original Article
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Effect of omega-3 plus methylphenidate as an alternative therapy to reduce attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder in children
- Soleiman Mohammadzadeh, Narmin Baghi, Fayegh Yousefi, Bahar Yousefzamani
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(9):360-366. Published online May 20, 2019
-

Background: Attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is one of the most common chronic behavioral disorders in school-aged children.
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the effect of omega-3 supplementation as an alternative therapy for ADHD, which can be caused by vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Methods: This was a double-blinded clinical trial study. Sixty-six children with ADHD (aged 6–12 years) referred to our child...
- Allergy
- Nasal eosinophilia and eosinophil peroxidase in children and adolescents with rhinitis
- Yeonu Choi, Haeun Jeon, Eun Ae Yang, Jong-Seo Yoon, Hyun Hee Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(9):353-359. Published online April 24, 2019
-

Background: Researchers have shown that eosinophil peroxidase (EPO) is a relatively accurate marker of eosinophilia and eosinophil activity. However, its use as a marker of eosinophilic inflammation in nasal secretions is limited because the diagnostic cutoff values of EPO for use as a one-time test for allergic diseases such as allergic rhinitis have not been established.
Purpose: To identify the correlation...
- Nutrition
- The effect of high fat dietary modification and nutritional status on the outcome of critically ill ventilated children: single-center study
- Nehal Mohamed El Koofy, Hanaa Ibrahim Rady, Shrouk Moataz Abdallah, Hafez Mahmoud Bazaraa, Walaa Ahmed Rabie, Ahmed Ali El-Ayadi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(9):344-352. Published online April 2, 2019
-
Background: Ventilator dependency constitutes a major problem in the intensive care setting. Malnutrition is considered a major determinant of extubation failure, however, attention has been attracted to modulating carbon dioxide production through decreasing carbohydrate loading and increasing the percent of fat in enteral feeds. The detected interrelation between substrate oxidation and ventilation outcome became the base of several research to...
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Is determining nasal eosinophil count and nasal eosinophil peroxidase concentration clinically useful in children with rhinits?
- Bong Seok Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(9):342-343. Published online July 9, 2019
-
- Should partially hydrolyzed infant formula be given to the general infant population for the primary prevention of allergic disease?
- Tae Won Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(9):340-341. Published online May 17, 2019
-
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Understanding the importance of cerebrovascular involvement in Kawasaki disease
- Jung Sook Yeom, Jae Young Cho, Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(9):334-339. Published online May 16, 2019
-
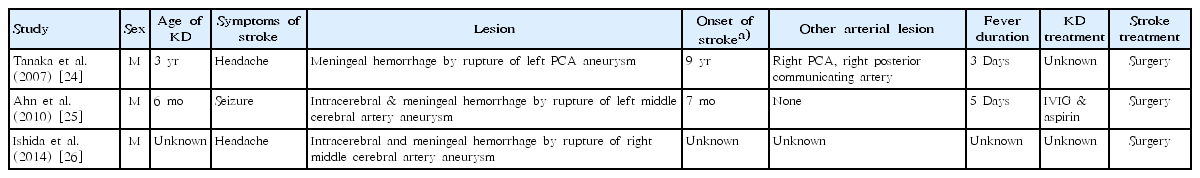
Kawasaki disease (KD) is a systemic vasculitis in infants and young children. However, its natural history has not been fully elucidated because the first case was reported in the late 1960s and patients who have recovered are just now entering middle age. Nevertheless, much evidence has raised concerns regarding the subclinical vascular changes that occur in post-KD patients. KD research...
- Allergy
- Phenotypes of allergic diseases in children and their application in clinical situations
- Eun Lee, Soo-Jong Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(9):325-333. Published online April 23, 2019
-
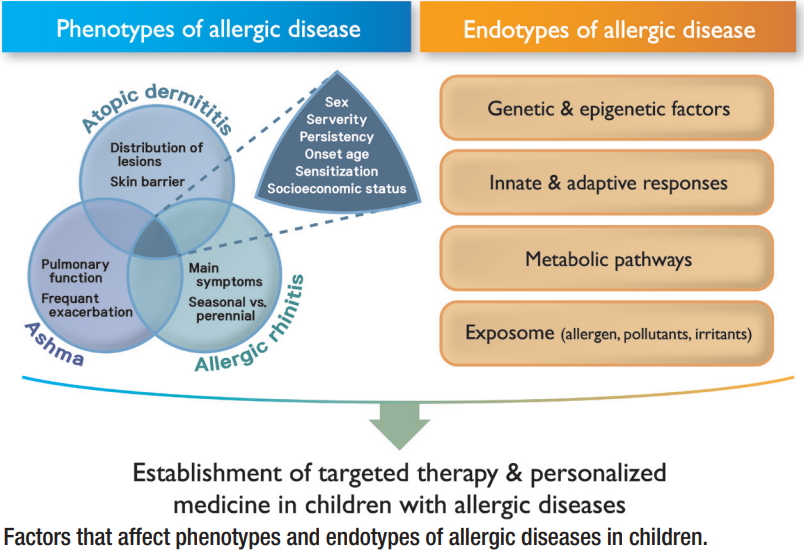
Allergic diseases, including allergic rhinitis, asthma, and atopic dermatitis, are common heterogeneous diseases that encompass diverse phenotypes and different pathogeneses. Phenotype studies of allergic diseases can facilitate the identification of risk factors and their underlying pathophysiology, resulting in the application of more effective treatment, selection of better treatment responses, and prediction of prognosis for each phenotype. In the early phase...
- Original Article
- General Pediatrics
- Prevalence of hyperuricemia and its association with metabolic syndrome and cardiometabolic risk factors in Korean children and adolescents: analysis based on the 2016–2017 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Jung Hyun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):317-323. Published online June 24, 2019
-
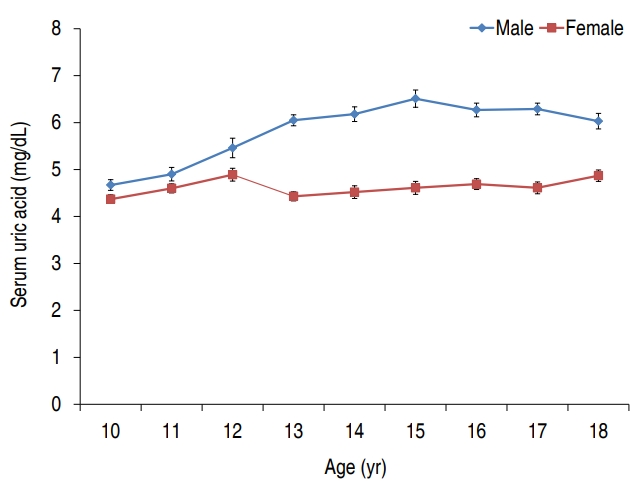
Purpose: Investigating the prevalence of hyperuricemia and its association with metabolic syndrome (MetS) and cardiometabolic risk factors (CMRFs) in Korean children and adolescents. Methods: This cross-sectional survey used data from the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2016–2017); 1,256 males and females aged 10–18 years were included. Hyperuricemia was defined as serum uric acid levels were >6.6 mg/dL at...
- Neurology
- Evaluation of hematologic profile may be needed for patients treated with oxcarbazepine
- Gu Hyun Jung, Su Jeong You
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):312-316. Published online April 11, 2019
-
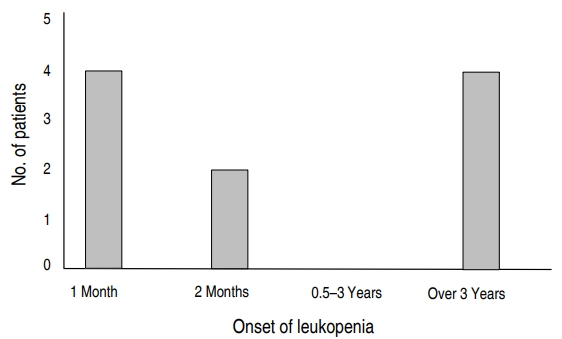
Purpose: The major side effects of treatment with oxcarbazepine (OXC) are skin rash and hyponatremia. Hematologic side effects are reported rarely. The aim of this study was to investigate the rate and types of the hematologic side effects of OXC. Methods: The medical records of 184 patients diagnosed with epilepsy or movement disorder and on OXC monotherapy, at the Department of...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- The relation between serum levels of epidermal growth factor and necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm neonates
- Heba Mostafa Ahmed, Nsreen Mostafa Kamel
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):307-311. Published online March 15, 2019
-

Purpose: Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is one of the most serious complications of prematurity. Many risk factors can contribute to the development of NEC. The epidermal growth factor (EGF) plays a major role in intestinal barrier function, increases intestinal enzyme activity, and improves nutrient transport. The aim of this study was to assess the role of epidermal growth factor in the...
- Cardiology
- Iron deficiency anemia as a predictor of coronary artery abnormalities in Kawasaki disease
- Sohyun Kim, Lucy Youngmin Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):301-306. Published online February 8, 2019
-
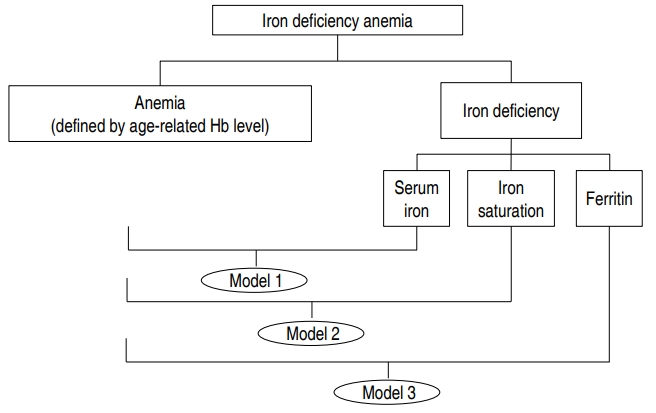
Purpose: Coronary artery abnormalities (CAA) are the most important complications of Kawasaki disease (KD). Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) is a prevalent micronutrient deficiency and its association with KD remains unknown. We hypothesized that presence of IDA could be a predictor of CAA. Methods: This retrospective study included 173 KD patients, divided into 2 groups according to absence (group 1) and presence...
- Editorial
- Allergy
- Why should we monitor for hematologic adverse drug reactions to oxcarbazepine?
- Gwang Cheon Jang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):299-300. Published online June 24, 2019
-
- Cardiology
- Can iron be a risk factor for coronary lesions in Kawasaki disease?
- Kyung Lim Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):297-298. Published online June 7, 2019
-
- Review Article
- Cardiology
- Reality of Kawasaki disease epidemiology
- Gi Beom Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):292-296. Published online July 9, 2019
-
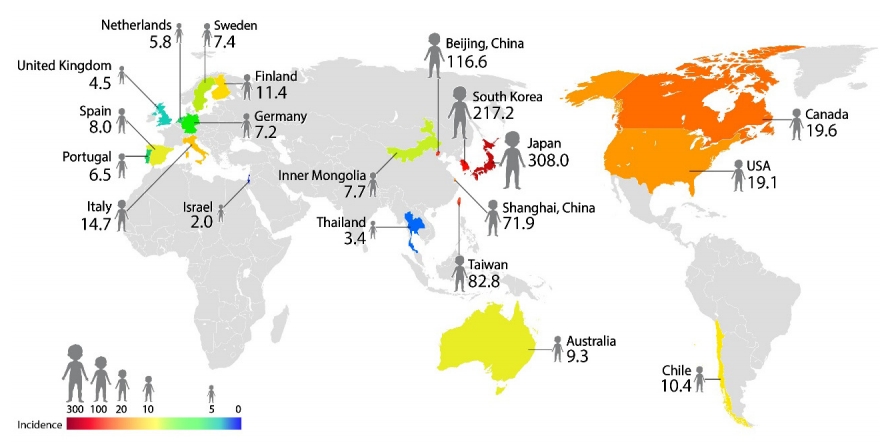
Epidemiologic studies of Kawasaki disease (KD) have shown a new pattern or change of its occurrence suggestive of its pathophysiology or risk factors from the first patient with KD reported in 1961. The incidence of KD in Northeast Asian countries including Japan, South Korea, China, and Taiwan is 10–30 times higher than that in the United States and Europe. Knowing...
- Gastroenterology
- The role of fecal calprotectin in pediatric disease
- Su Jin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(8):287-291. Published online March 28, 2019
-
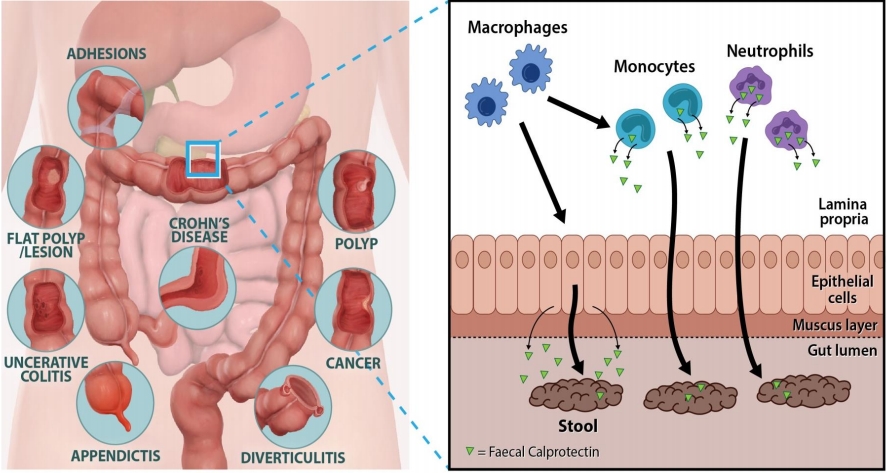
Fecal calprotectin (FC) is a calcium- and zinc-binding protein of the S100 family, mainly expressed by neutrophils and released during inflammation. FC became an increasingly useful tool both for gastroenterologists and for general practitioners for distinguishing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) from irritable bowel syndrome. Increasing evidences support the use of this biomarker for diagnosis, follow-up and evaluation of response to...
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Correlation of serum S100B levels with brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in children with status epilepticus
- Prastiya Indra Gunawan, Darto Saharso, Dian Purnama Sari
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(7):281-285. Published online May 8, 2019
-
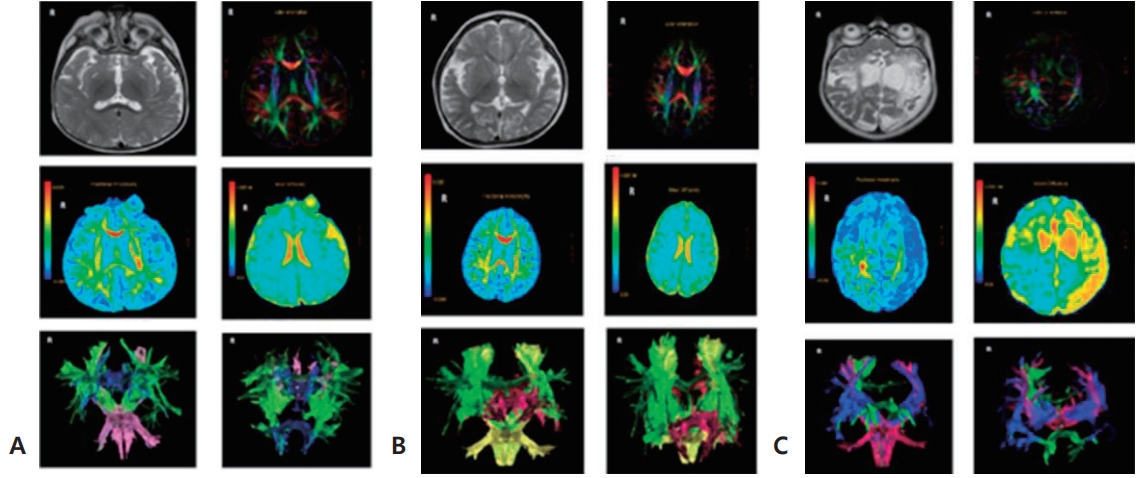
Purpose: To evaluate the association between elevated S100B levels with brain tissue damage seen in abnormalities of head magnetic resonance imaging (MRI; diffusion tensor imaging [DTI] sequence) in patients with status epilepticus (SE). Methods: An analytical observational study was conducted in children hospitalized at Dr Soetomo Hospital, Surabaya, from July to December 2016. The patients were divided into 2 groups: SE...
- Endocrinology
- Comparison of effectiveness of growth hormone therapy according to disease-causing genes in children with Noonan syndrome
- Kyo Jin Jo, Yoo Mi Kim, Ju Young Yoon, Yeoun Joo Lee, Young Mi Han, Han-Wook Yoo, Hyang-Sook Kim, Chong Kun Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(7):274-280. Published online December 3, 2018
-
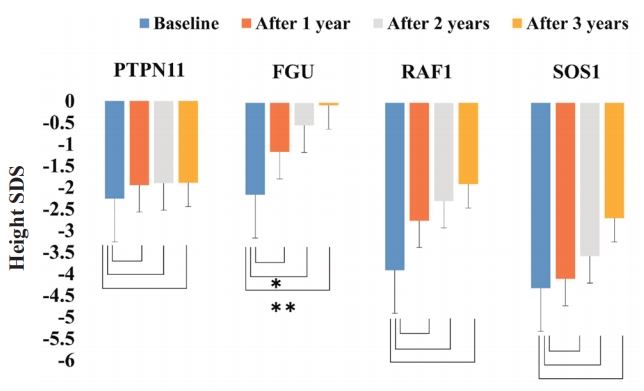
Purpose: To analyze the growth response to growth hormone (GH) therapy in prepubertal patients with Noonan syndrome (NS) harboring different genetic mutations. Methods: Twenty-three patients with prepubertal NS treated at Pusan National University Children’s Hospital between March 2009 and July 2017 were enrolled. According to the disease-causing genes identified, the patients with NS were divided into 4 groups. Three groups were...
- Neurology
- Efficacy and tolerability of adjunctive perampanel treatment in children under 12 years of age with refractory epilepsy
- Yuni Yun, Dongsub Kim, Yun-Jeong Lee, Soonhak Kwon, Su-Kyeong Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(7):269-273. Published online December 26, 2018
-

Purpose: There is limited data on the use of perampanel in children under 12 years of age. We evaluated the efficacy and tolerability of adjunctive perampanel treatment in children under 12 years of age with refractory epilepsy. Methods: This retrospective observational study was performed in Kyungpook National University Hospital from July 2016 to March 2018. A responder was defined as a...
- Endocrinology
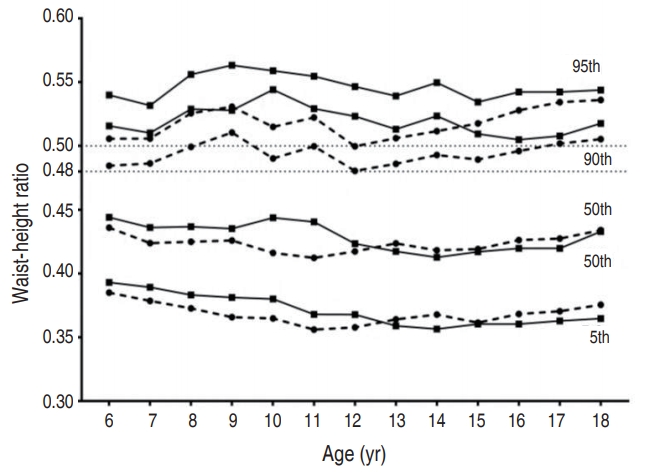
- Secular change in waist circumference and waist-height ratio and optimal cutoff of waist-height ratio for abdominal obesity among Korean children and adolescents over 10 years
- Min Sub Kim, Se Young Kim, Jae Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(7):261-268. Published online December 3, 2018
-
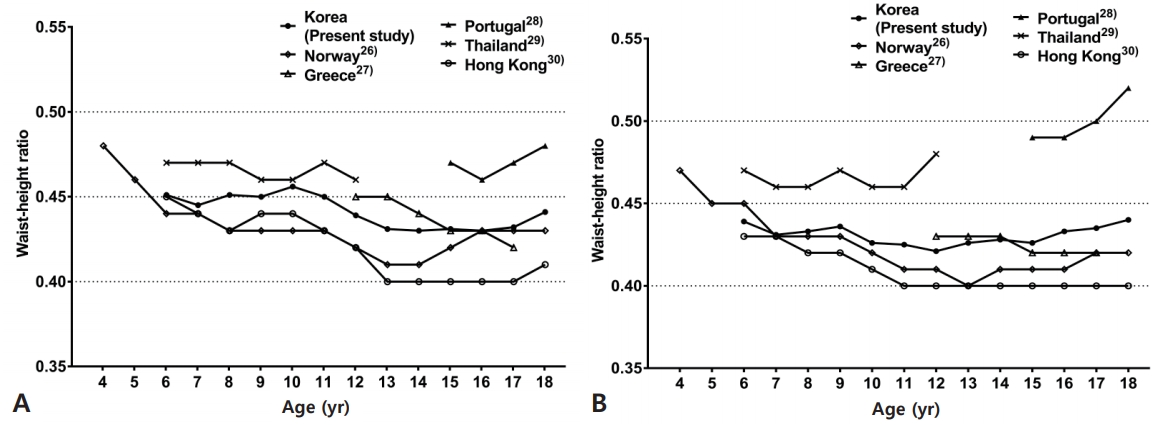
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the time trends of waist circumference (WC) and waist-height ratio (WHR), and to present WC and WHR distributions with optimal WHR cutoff for abdominal obesity in Korean children and adolescents. Methods: We performed a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of data from 13,257 children and adolescents (6,987 boys and 6,270 girls) aged 6–18 years who were included...
- Editorial
- Neurology
- Perampanel is also a useful adjunctive treatment option in refractory epilepsy in children
- Jon Soo Kim, Won Seop Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(7):259-260. Published online March 5, 2019
-
- Endocrinology
- Simple universal cutoff point of waist-height ratio for metabolic risk in Korean children and adolescents
- Hae Soon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(7):257-258. Published online March 28, 2019
-
- Review Article
- Recommended immunization schedule for children and adolescents: Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society, 2018
- Eun Hwa Choi, Su Eun Park, Yae-Jean Kim, Dae Sun Jo, Yun-Kyung Kim, Byung-Wook Eun, Taek-Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Hyunju Lee, Ki Hwan Kim, Hye-Kyung Cho, Eun Young Cho, Jong-Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(7):252-256. Published online July 15, 2019
-

The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society recommended immunization schedule for children and adolescents aged 18 years or younger in the 9th (2018) edition of Immunization guideline. This report provides the revised recommendations made by the committee and summarizes several changes from the 2015 guideline. National immunization program (NIP) launched a human papillomavirus (HPV) immunization for girls...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Practice for preterm patent ductus arteriosus; focusing on the hemodynamic significance and the impact on the neonatal outcomes
- Jin A Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(7):245-251. Published online April 8, 2019
-
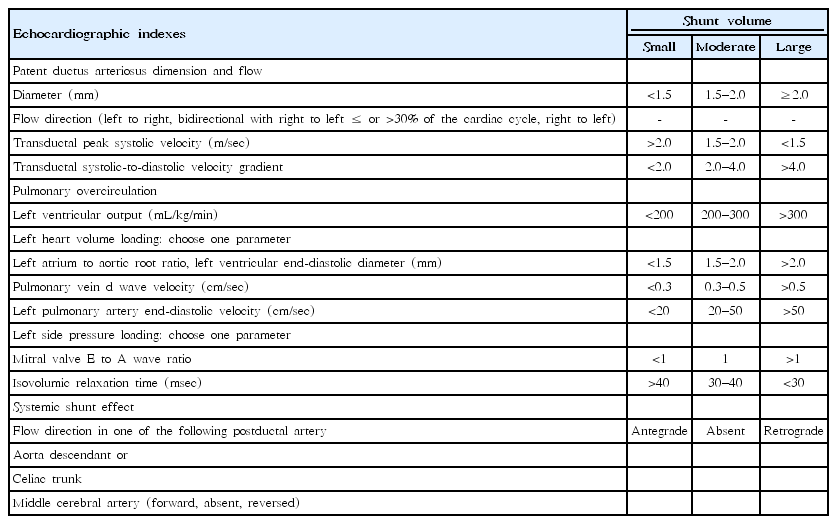
Hemodynamically significant preterm patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) affects mortality; comorbidities such as necrotizing enterocolitis, intraventricular hemorrhage, and bronchopulmonary dysplasia; and adverse long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes in preterm infants, particularly in very low birth weight infants. However, recent studies have indicated that there is no consensus on the causal relationship between PDA and neonatal outcomes, the benefit of PDA treatment, the factors...
- Corrigendum: Correction of the fourth author’s name and institution
- Corrigendum: Cardiac function associated with home ventilator care in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Sangheun Lee, Heeyoung Lee, Lucy Youngmin Eun, Seung-Woong Gang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):244-244. Published online June 14, 2019
-
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Change of coronary artery indices according to coronary dominance pattern in early childhood
- Yoon jin Lee, Kyoung Soo Park, Hong Ryang Kil
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):240-243. Published online November 22, 2018
-

Purpose: Coronary arterial lesion assessment in children can be difficult, depending on the coronary dominance pattern. Although it is easier to determine coronary dominance with echocardiography in children than in adults, it is still difficult. This study aimed to examine the coronary dominance pattern according to the objective coronary artery (CA) indices. Methods: The CA diameter, aortic valve annulus, and abdominal...
- High antistreptolysin O titer is associated with coronary artery lesions in patients with Kawasaki disease
- Dong Eun Min, Do Hee Kim, Mi Young Han, Sung Ho Cha, Kyung Lim Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):235-239. Published online November 7, 2018
-
Purpose: In Kawasaki disease (KD) patients, coronary artery complications, incomplete and refractory types occur more frequently in patients with streptococcal or other bacterial/viral infections. Recently, we observed a higher incidence of coronary lesions in KD patients with high anti-streptolysin O (ASO) titer. Therefore, we hypothesized that KD patients diagnosed with concurrent streptococcal infection have poor prognosis, with respect to treatment...
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Clinical and molecular characterization of Korean children with infantile and late-onset Pompe disease: 10 years of experience with enzyme replacement therapy at a single center
- Min-Sun Kim, Ari Song, Minji Im, June Huh, I-Seok Kang, Jinyoung Song, Aram Yang, Jinsup Kim, Eun-Kyung Kwon, Eu-Jin Choi, Sun-Ju Han, Hyung-Doo Park, Sung Yoon Cho, Dong-Kyu Jin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):224-234. Published online October 4, 2018
-

Purpose: Pompe disease (PD) is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a deficiency of acid alphaglucosidase resulting from pathogenic GAA variants. This study describes the clinical features, genotypes, changes before and after enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), and long-term outcomes in patients with infantile-onset PD (IOPD) and late-onset PD (LOPD) at a tertiary medical center. Methods: The medical records of 5 Korean...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Diagnostic value of eosinopenia and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio on early onset neonatal sepsis
- Rocky Wilar
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):217-223. Published online October 8, 2018
-
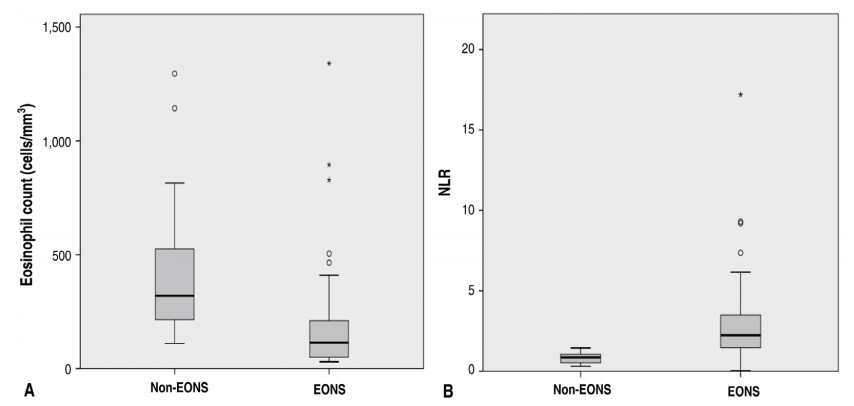
Purpose: To determine the diagnostic value of eosinopenia and the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in the diagnosis of early onset neonatal sepsis (EONS). Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted in the Neonatology Ward of R.D. Kandou General Hospital Manado between July and October 2017. Samples were obtained from all neonates meeting the inclusion criteria for EONS. Data were encoded using logistic regression...
- Editorial
- Cardiology
- Importance of coronary artery dominance in children to determine coronary artery dilatation
- Hee Joung Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):215-216. Published online May 3, 2019
-
-

-
-

-

-
Impact Factor4.2
-
6.52022CiteScore92nd percentilePowered by







