Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Infection
- Changes in age-specific seroprevalence of Japanese encephalitis virus and impact of Japanese encephalitis vaccine in Korea
- Byung Ok Kwak, Young Jin Hong, Dong Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):108-114. Published online September 24, 2021
-

Since the introduction of a universal Japanese encephalitis (JE) vaccination program and urbanization, the incidence of JE has dramatically decreased in Korea. However, recent JE cases have occurred, predominantly among unvaccinated adults and with a shift in age distribution. Continuous surveillance of the seroprevalence of JE is required to establish a proper immunization policy in Korea.
- Neurology
- Autoimmune encephalitis and epilepsy: evolving definition and clinical spectrum
- Joo Hee Seo, Yun-Jin Lee, Ki Hyeong Lee, Elakkat Gireesh, Holly Skinner, Michael Westerveld
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):291-300. Published online August 16, 2019
-
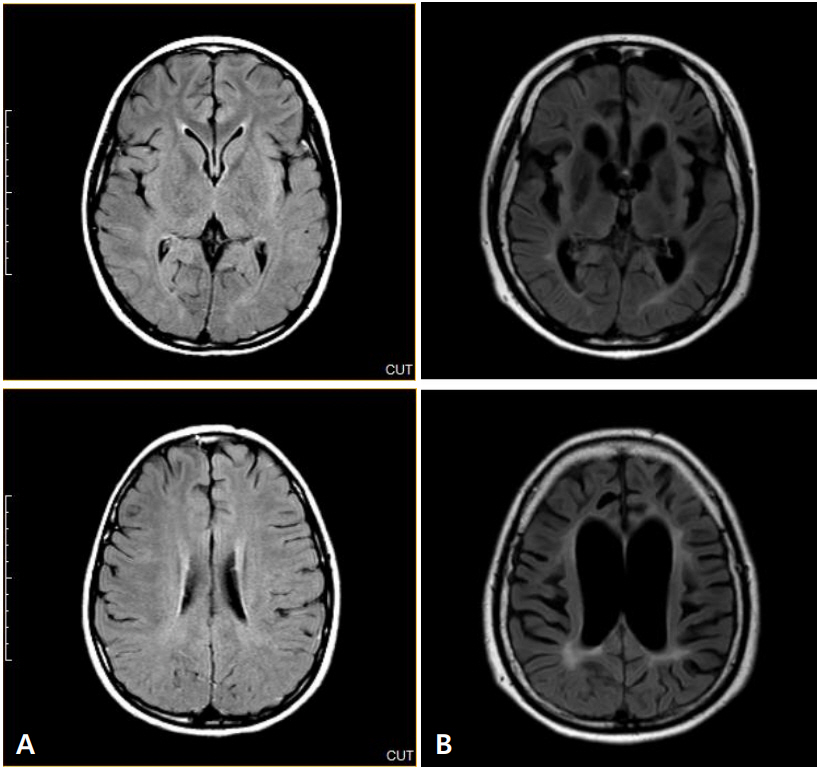
Advances in autoimmune encephalitis studies in the past 10 years have led to the identification of new syndromes and biomarkers that have transformed the diagnostic approach to the disorder. The disorder or syndrome has been linked to a wide variety of pathologic processes associated with the neuron-specific autoantibodies targeting intracellular and plasma membrane antigens. However, current criteria for autoimmune encephalitis...
- Case Report
- Neurology
- A long-term subacute sclerosing panencephalitis survivor treated with intraventricular interferon-alpha for 13 years
- Minsun Kwak, Hye-Ryun Yeh, Mi-Sun Yum, Hyun-Jin Kim, Su Jeong You, Tae-Sung Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(3):108-112. Published online September 18, 2018
-
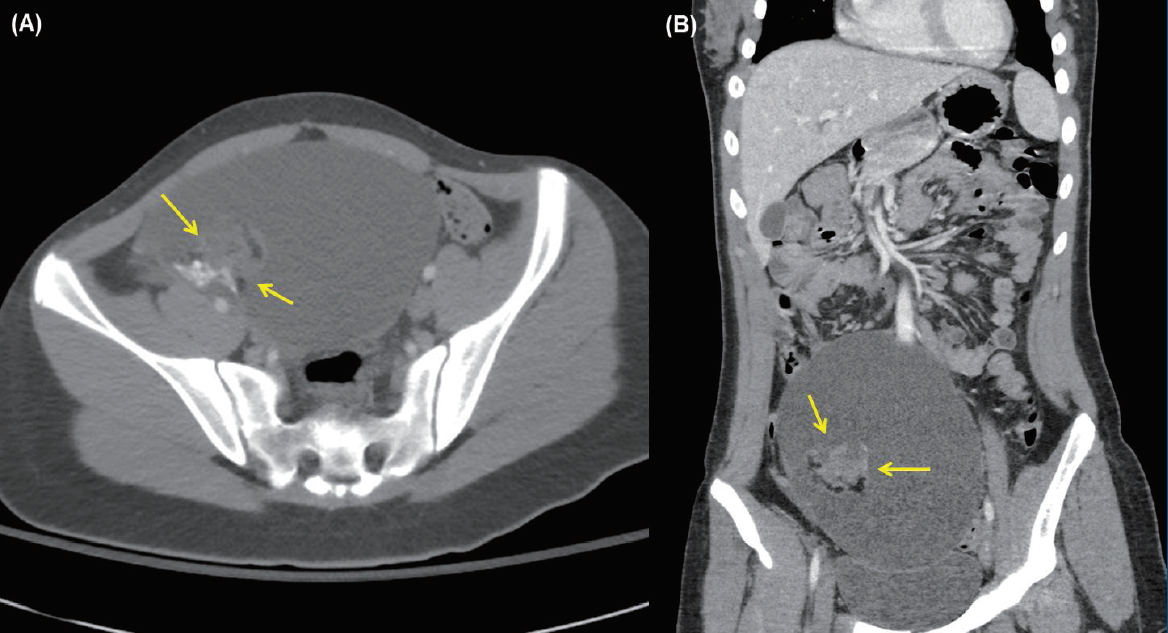
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) is a rare, progressive, and fatal central nervous system disorder resulting from persistent measles virus infection. Long-term data are scarce, with a maximum follow-up period of 10 years. Interferon-alpha (IFN-α) is a protein that exerts its antiviral activity via enhancement of cellular immune response and is reported to be an effective drug for the treatment of...
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Serum neuron specific enolase is increased in pediatric acute encephalitis syndrome
- Dian Pratamastuti, Prastiya Indra Gunawan, Darto Saharso
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(9):302-306. Published online September 21, 2017
-
Purpose This study aimed to investigate whether serum neuron-specific enolase (NSE) was expressed in acute encephalitis syndrome (AES) that causes neuronal damage in children.
Methods This prospective observational study was conducted in the pediatric neurology ward of Soetomo Hospital. Cases of AES with ages ranging from 1 month to 12 years were included. Cases that were categorized as simple and complex febrile seizures...
- Case Report
- Neurology
- A young child of anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis presenting with epilepsia partialis continua: the first pediatric case in Korea
- Eun-Hee Kim, Yeo Jin Kim, Tae-Sung Ko, Mi-Sun Yum, Jun Hwa Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(Suppl 1):S133-S138. Published online November 30, 2016
-
Anti-
N -methyl D-aspartate receptor (anti-NMDAR) encephalitis, recently recognized as a form of paraneoplastic encephalitis, is characterized by a prodromal phase of unspecific illness with fever that resembles a viral disease. The prodromal phase is followed by seizures, disturbed consciousness, psychiatric features, prominent abnormal movements, and autonomic imbalance. Here, we report a case of anti-NMDAR encephalitis with initial symptoms of epilepsia partialis...
- Massive pulmonary hemorrhage in enterovirus 71-infected hand, foot, and mouth disease
- Dong Seong Lee, Young Il Lee, Jeong Bae Ahn, Mi Jin Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Nam Hee Kim, Jong Hee Hwang, Dong Wook Kim, Chong Guk Lee, Tae Won Song
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(3):112-115. Published online March 20, 2015
-
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is an acute, mostly self-limiting infection. Patients usually recover without any sequelae. However, a few cases are life threatening, especially those caused by enterovirus 71 (EV71). A 12-month-old boy was admitted to a primary hospital with high fever and vesicular lesions of the mouth, hands, and feet. After 3 days, he experienced 3 seizure...
- A pediatric case of Bickerstaff's brainstem encephalitis
- Ju Yi Park, Kyong Og Ko, Jae Woo Lim, Eun Jung Cheon, Jung Min Yoon, Hyo Jeong Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(12):542-545. Published online December 31, 2014
-
Bickerstaff's brainstem encephalitis is characterized by ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, and disturbance of consciousness. It is similar to Miller Fisher syndrome, a variant of Guillain-Barre syndrome, in that they share features such as ophthalmoplegia and ataxia. The difference is that patients with Bickerstaff's brainstem encephalitis have impaired consciousness, whereas patients with Miller Fisher syndrome have alert consciousness and areflexia. Here, we report...
- Overlapping Guillain-Barré syndrome and Bickerstaff's brainstem encephalitis associated with Epstein Barr virus
- Young Il Rho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(10):457-460. Published online October 31, 2014
-
A flaccid tetraparesis in Bickerstaff's brainstem encephalitis (BBE) is presumed to be a sign of overlapping Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). In addition, BBE and Fisher syndrome, which are clinically similar and are both associated with the presence of the immunoglobulin G anti-GQ1b antibody, represent a specific autoimmune disease with a wide spectrum of symptoms that include ophthalmoplegia and ataxia. A 2-year-old...
- Transient asymptomatic white matter lesions following Epstein-Barr virus encephalitis
- Yoon Young Jang, Kye Hyang Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(9):389-393. Published online September 30, 2011
-
We present the case of a patient with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) encephalitis who developed abnormal white matter lesions during the chronic phases of the infection. A 2-year-old-boy was admitted for a 2 day history of decreased activity with ataxic gait. The results of the physical examination were unremarkable except for generalized lethargy and enlarged tonsils with exudates. Brain magnetic resonance...
- Original Article
- A case of meningoencephalitis caused by
Listeria monocytogenes in a healthy child - Ji Eun Lee, Won Kyoung Cho, Chan Hee Nam, Min Ho Jung, Jin Han Kang, Byung Kyu Suh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(5):653-656. Published online May 31, 2010
-
Listeria monocytogenes is a facultative anaerobic, gram-positive bacillus that is isolated from the soil, vegetables, and wild or domestic animals. Listeria occurs predominantly in the elderly, immunocompromised patients, pregnant women and newborns. Infections by this microorganism are rare in healthy infants and children.L. monocytogenes may cause meningitis, meningoencephalitis, brain abscess, pyogenic arthritis, osteomyelitis, and liver abscesses in children. The...
- Case Report
- A case of Bickerstaff's brainstem encephalitis in childhood
- Ji Youn Kim, Young Ok Kim, Young Jun Son, Young Jong Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(4):607-611. Published online April 15, 2010
-
Bickerstaff's brainstem encephalitis (BBE) is a rare disease diagnosed by specific clinical features such as 'progressive, relatively symmetric external ophthalmoplegia and ataxia by 4 weeks' and 'disturbance of consciousness or hyperreflexia' after the exclusion of other diseases involving the brain stem. Anti-ganglioside antibodies (GM, GD and GQ) in the serum or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are sometimes informative for the diagnosis... -
- A case of paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis due to ovarian mature teratoma
- Seong Heon Kim, hye Young Kim, Young Tak Im, Sang Ook Nam, Young Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(4):603-606. Published online April 15, 2010
-
Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis, a remote effect of cancer without nervous system metastasis, is rare, especially in childhood. Here, we report a case of paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis associated with an ovarian mature teratoma in an adolescent girl. The 15-year-old girl developed neuropsychiatric symptoms, memory loss, seizures, and unconsciousness. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis and brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings were normal, while... -
- A case of postoperative nasopharyngeal reflux associated with retropharyngeal lymphangioma in newborn infant
- Ah Reum Kwon, Eun Jung Park, Ki Hwan Kim, Dong Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(2):262-266. Published online February 15, 2010
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) is a major proinflammatory cytokine involved in the pathophysiology of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Etanercept is an effective inhibitor of TNF-α and has shown a beneficial effect in patients with JRA. However, the most important cause of concern related to etanercept administration is infection. We report a case of encephalitis in a JRA patient receiving long-term treatment... -
- A case of fatal pneumococcal 19A meningoencephalitis despite administration of seven-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccines
- Ah Rum Heo, Jun Hwa Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(4):508-511. Published online April 15, 2009
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a major cause of serious invasive diseases in children, especially in young infants, but seven- valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV7) is believed to prevent invasive pneumococcal pneumonia and meningitis in young children. However, recently, the incidence of non-PCV7 serotype has increased after PCV7 vaccination. A 14-month- old female patient presented at our emergency room with mental change... -
- Two cases of central nervous system complications caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
- Shin Mi Kim, Ji Seung Heo, Eun Jung Shim, Dae Hyoung Lee, Do Jun Cho, Dug Ha Kim, Ki Sik Min, Ki Yang Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(5):533-537. Published online May 15, 2008
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. pneumoniae) infection causes a wide variety of clinical manifestations in children and young adults, the main one being pneumonia. M. pneumoniae is transmitted from person to person by infected respiratory droplets. Symptoms caused by M. pneumoniae infection can be divided into those involving the respiratory tract, and those caused by extrapulmonary disease. M. pneumoniae infections may cause... -
- A Case of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia Complicated with Guillain-Barr Syndrome and Encephalitis
- Soon Bum Lee, Hee Jung, Yong Seok Lee, Bum Sun Kwon, Jeesuk Yu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(12):1338-1348. Published online December 15, 2004
-
The most common pathogen of respiratory tract infection among school-age children and adolescents is Mycoplasma pneumoniae, which causes clinical manifestations of pneumonia, acute asthmatic attack, pharygitis, and tonsilitis. It can also cause extrapulmonary infections that involves skin, the nervous system, the digestive system, the cardiovascular system, and the hematopoietic system. It is reported that the central nervous system symptoms may... -
- Original Article
- The Findings and Significances of Brain SPECT in Acute Mealses Encephalitis
- Jung Chul Kim, Ju Mi Choung, So Hee Eun, Dae-Yeol Lee, Jung Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(11):1373-1380. Published online November 15, 2002
-
Purpose : Acute measles encephalitis(ME) is characterized by an abrupt onset of fever and obtundation, frequently accompanied by seizures and multifocal neurological signs. The aim of this study was to clarify the clinical manifestation, progression and the brain SPECT patterns in patients with acute ME. Methods : This study included 11 children with acute ME admitted to Chonbuk National University Hospital. Ten patients received a... -
- Immune Response to SA14-14-2 Live Attenuated Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine
- Min Soo Park, Hye Ok Rho, Young Mo Sohn, Laura Chandler, Robert Shope, Theodore F. Tsai
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(3):351-359. Published online March 15, 2000
-
Purpose : SA14-14-2 live attenuated Japanese encephalitis(JE) vaccine has been administered safely and effectively to more than 100 million children in China since 1988, and recently licensure of the vaccine in Korea has been sought. Immune response to the vaccine was investigated. Methods : In the first clinical evaluation of the vaccine outside of China, we monitored side effects in 93... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Brainstem Encephalitis
- Tae Hoon Kang, Ki Ook Kim, Gyu Geun Hywang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1996;39(7):1010-1014. Published online July 15, 1996
-
We experienced a case of brainstem encephalitis that is possibly caused by herpes simplex virus infection in a 3 year-old girl. The diagnosis was made by clinical symptoms, neurologic exam, serologic test, brain CT, brain MRI and brainstem biopsy. Herpes simplex virus specific antibody was detected from cerebrospinal fluid and the titer was 11.78 by enzyme immunoassay. Stereotaxic brainstem biopsy was done for differenciate... -
- Original Article
- The Study of Distribution of HI Antibody Titers Aganist Japanese Encephalitis Virus Among Children in Seoul
- Jin A Kim, Tae Sung Ko, Young Seo Park, Hyung Nam Moon, Chang Yee Hong, Hae Wol Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1996;39(2):230-237. Published online February 15, 1996
-
Purpose : Incidence of Japanese encephalitis has been markedly decreased, but this disease is known to be high and lethal in the young age group. This study was designed to find out the HI antibody titers and associated factors of Japanese encephalitis of children in Seoul, and to establish the plan of vaccination. Methods : The survey was conducted from the... -
- Report of Nationwide Epidemiology of Aseptic Meningitis Outbreak in 1993 in Korea
- Sung Hee Oh, Moo-Song Lee, Jin Han Kang, Chang Hwi Kim, Chong Young Park, Young Mo Sohn, Hoan Jong Lee, Chung Sik Chun, Sang Mann Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1996;39(1):42-52. Published online January 15, 1996
-
Purpose : There has been no nationwide report pertaining to the epidemiology of aseptic meningitis, although a great numer of patients have been diagnosed of the illness. Therefore, we report an explosive outbreak of aseptic meningitis occured in a nationwide scale in 1993. Methods : Aseptic meningitis epidemiology surveillence was performed retrospectively on the patients diagnosed of aseptic meinigitis from January... -
- A case of neonatal herpes simplex virus encephalitis.
- Kook In Park, Young Mo Sohn, Dong Soo Kim, Ran Namgung, Chul Lee, Dong Gwan Han, Won Young Lee, Ki Keun Oh, Myung Joon Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1991;34(9):1276-1285. Published online September 30, 1991
-
Neonatal herpes simplex virus infection still remains a life-threatening infection for the newborn. With an increasing incidence of genital herpes and an increase in the incidence of neonatal herpes simplex virus infections, it is important that pediatricians and neonatologists continue to maintain a high index of suspicion in infants whose symptoms may be compatible with herpes simplex virus infections so that early identification leads... -
- Clinical Observation of Encephalitis Empasizing the Clinically Suspected Herpes Encephalitis Cases.
- Young Sook Lee, Young Don Lee, Yong Seung Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1990;33(5):615-622. Published online May 31, 1990
-
The prognosis in all encephalitis is guarded with respect to both immediate outcome and sequelae. But, in fact, there is no specific treatment agent for encephatitis except herpes encephalitis which is almost fatal without adequate treatment. Acyclovir(9- [2-hydroxyethoxymetry] -guanine) has proved to be a safe and effective agent for therapy of early stage of herpes simplex virus infections. So, in herpes encephalitis, early diagnosis... -
- Clinical Study of Encephalitis and Encephalopathy in Children.
- Dong Hunb Lee, Soo Chun Kim, Sa Jun Chung, Chang Il Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1989;32(4):500-510. Published online April 30, 1989
-
This study was undertaken to evaluate the electronencephalographic and clinical findings in 132 cases of encephalitis and encephalopathy in the Department of Pediatrics, Kyung Hee University Hospital for 9 years from Jan. 1979 to Dec. 1987. The results were summerized as follows; 1) The incidence of ecephalitis was 0.46%{86 cases) and the incidence of encephalopathy was 0.25 % (46 cases) among total in-patient (18,671). 2) Male... -
- Evaluation of Epidemic Encephalitis Vaccine.
- Kap Seoung Kim, Yeo Joong Kim, Tai Ju Kwang, Chull Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1985;28(1):40-44. Published online January 31, 1985
-
To evaluate the effect of Epidemic Encephalitis vaccine, the authors compared vaccinated group with non-vaccinated group at the point of morbidity, sequelae and mortality in Cho- nnam area, 1982. 551,660 children(43.4%) out of the total 1,270,669 children who aged 3 to 15 year old were vaccinated, and vaccinated history was confirmed 179 only out of the total 647 Epide- mic Encephalitis patients. The results were summaried... -
- A Study on Factors Influencing the Prognosis of Epidemic Encephalitis.
- Jong bum Kim, San Ho Kim, Bock Keun Kee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1985;28(1):33-39. Published online January 31, 1985
-
58 cases of epidemic encephalitis admitted to the Pediatric Department of Won Kwang University Hospital during the period of August to October 1982 were studied. The results were as follows; 1)Much sequelae occured in 0~5 age group and the mortality rate was highest in 6~10 age:group. The ratio of male to female patientwas 1.76 : 1. 2) The comparison of living... -
- Decrease Serum Amylase Activity in Acutely Starvated Children with Epidemic Enephalitis.
- Kyung Yong Huh, Chull Shon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(12):1185-1191. Published online December 31, 1984
-
To evaluate the effects of acute starvation on blood constituents, serum amylase activity and levels of serum urea nitrogen (BUN) and protein fractions were measured in 336 normal children and 60 children acutely starved as a result of encsphalitis. The mean starvation period was 4 days. Hypoalbuminemic children were also examined. The tests revealed that starvation resulted in a significant reduction in serum amylase... -
- Early Reduction of Serum Amylase Activity in Children with Epidemic Encephalitis.
- Suk Jung Chang, Eui Hyung Kim, Tai Ju Hwang, Chull Sohn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(4):350-357. Published online April 30, 1984
-
In 52 children aged form 5 to 13 years who were acutely starving from epidemic encephalitis, authors measured the level of amylase activity, BUN, GOT, GPT, alkaline phosphatase, total protein, albumin, globulin, creatinine in serum and GOT, GPT, amylase activity in CSF. And in another group of 7 children with acute viral hepatitis, GOT, GPT in serum and CSF were... -
- A Study on Factor Influencing the Prognosis of Epidermic Encephalitis.
- Sang Hyun Byun, Koe Jong Park, Jeong Soon Hwang, Young Hun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(10):978-985. Published online October 31, 1983
-
The purpose Qf this study is to presume the severity of epidemic encephalitis. 36 cases were selected among 81 cases of epidemic encephalitis admitted to Chungnam National University Hospital during Jan. 1981 to Dec. 1982, and divided into clinically mild and severe group. Two groups were compared the differences of their demographic, clinical and laboratory findings. The parameters significantly more encountered in the severe... -
- Clinical Features and Hemagglutination Inhibition(H-I) Test Results in 140 Cases of Japanes B Encephalitis Encountered in 1982.
- Young Kyung Park, In Sung Lee, Ki Bok Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1983;26(7):655-662. Published online July 31, 1983
-
In 104 cases of Japanese B encephalitis admitted to the Department during the epidemic in the Summer of 1982, the clinical features and the results of the H-I test were analysed. The results are summarized as follows: 1) All 104 cases occurred between August 1 and October 31, with 76 cases or 73.1% coming in September. 2) The incidence was greatest in children between 4... -
-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











