Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Effect of postoperative enteral protein supplementation on nitrogen balance in critically ill children
- Irene Yuniar, Kadek Apik Lestari, Antonius Hocky Pudjiadi, Fatima Safira Alatas, Yoga Devaera
-
Background: Critically ill children are at risk of postoperative malnutrition. Thus, optimal nutritional therapy is essential for preventing morbidity development and reducing mortality rates among this population. An adequate protein intake increases anabolism. However, data on the effect of enteral protein supplementation on nitrogen balance and intestinal fatty acid–binding protein (I-FABP) levels in postoperative critically ill children remain limited.
Purpose: This... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.00227 [Accepted]
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Characterization of gut microbiota in very low birth weight infants with versus without bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate, Kamonnut Singkhamanan, Komwit Surachat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(7):503-511. Published online February 26, 2025
-

Question: Does the gut microbiota differ between very low birth weight (VLBW) infants with versus without bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)?
Finding: Common respiratory pathogens were notably elevated in the BPD group, whereas anaerobic and butyrate-producing taxa, key components of postbiotics, were dominant in the non-BPD group.
Meaning: In gut-lung communication, the interplay between the intestinal and respiratory systems may implicate pro- and postbiotics in VLBW infants with BPD.
- Review Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Protocolized sedation may reduce ventilation and sedation requirements in the pediatric intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Ambrus Szemere, Alíz Fazekas, Anna Réka Sebestyén, Rani Ezzeddine, Veronika Upor, Marie Anne Engh, Péter Hegyi, Zsolt Molnár, Klára Horváth
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(6):406-416. Published online February 19, 2025
-
Protocolized sedation may reduce ventilation requirements, pediatric intensive care unit length of stay, and sedative exposure. However, it may increase the likelihood of unplanned extubation, highlighting the importance of incorporating preventive measures to mitigate this risk.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Effect of high-frequency oscillatory ventilation with intermittent sigh breaths on carbon dioxide levels in neonates
- Kulthida Baingam, Anucha Thatrimontrichai, Manapat Praditaukrit, Gunlawadee Maneenil, Supaporn Dissaneevate
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):178-184. Published online November 13, 2024
-
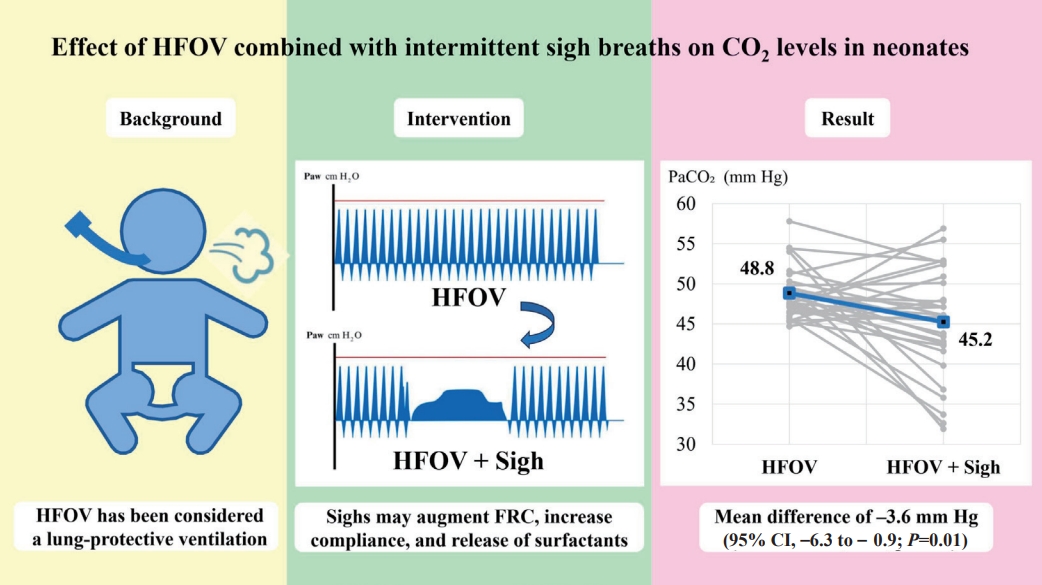
Question: Can sigh breaths (Sighs) application during high-frequency oscillatory ventilation (HFOV) decrease partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) levels?
Finding: The mean PaCO2 level after Sighs during HFOV was significantly decreased compared to that after HFOV alone (mean difference, -3.6 mmHg).
Meaning: HFOV plus Sighs functionality can reduce PaCO2 levels. However, further studies are required to conclusively determine the effects of Sighs.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Strategies to support language development in neonatal intensive care unit: a narrative review
- Ju Sun Heo, Ee-Kyung Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(12):651-663. Published online November 6, 2024
-
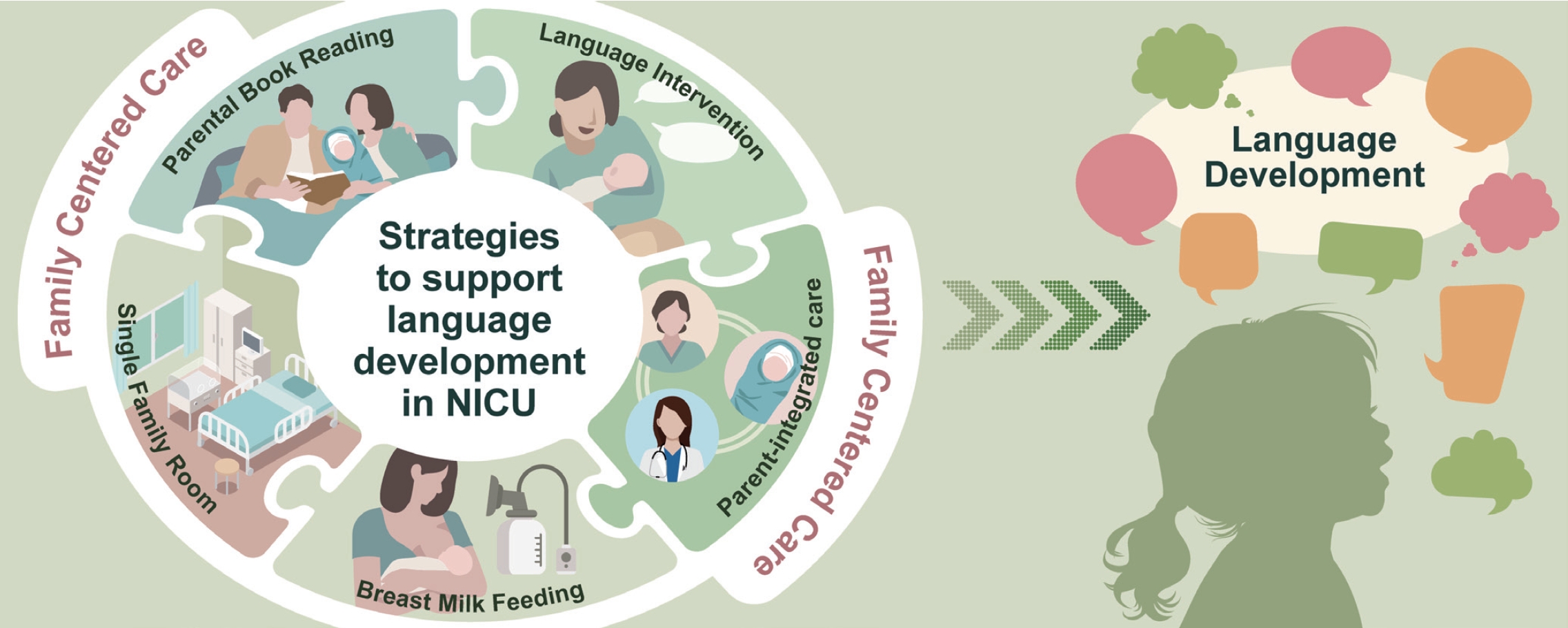
· Preterm infants often experience speech and language development delays during early childhood, impacting children's ultimate outcomes.
· Promoting breastfeeding, increasing parent-infant interactions in a single-family room, promoting a nurturing language environment by parental book reading and language interventions, and parent-integrated interventions in the neonatal intensive care unit could potentially enhance children's language development.
· Integrating these strategies through family-centered care is essential.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Mortality of very low birth weight infants by neonatal intensive care unit workload and regional group status
- Sung-Hoon Chung, Chae Young Kim, Yong-Sung Choi, Myung Hee Lee, Jae Woo Lim, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim; the Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):619-627. Published online September 12, 2024
-

Question: How do structural and staffing characteristics of neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) influence the mortality rates of very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs)?
Findings: NICUs with higher staffing levels, particularly with more neonatologists, and those offering advanced care levels were associated with lower mortality rates. Additionally, regional disparities were observed, with some areas demon-strating significantly higher survival rates.
Meaning: Adequate staffing and equitable regional distribution of medical resources are crucial for improving survival outcomes in VLBWIs. Efforts to enhance NICU staffing and address regional healthcare disparities are essential for optimizing care quality and reducing mortality in this vulnerable population.
- Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and stress among parents of neonates admitted to neonatal intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Asha P. Shetty, Kurvatteppa Halemani, Alwin Issac, Latha Thimmappa, Sanjay Dhiraaj, Radha K, Prabhaker Mishra, Vijai Datta Upadhyaya
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(2):104-115. Published online November 14, 2023
-
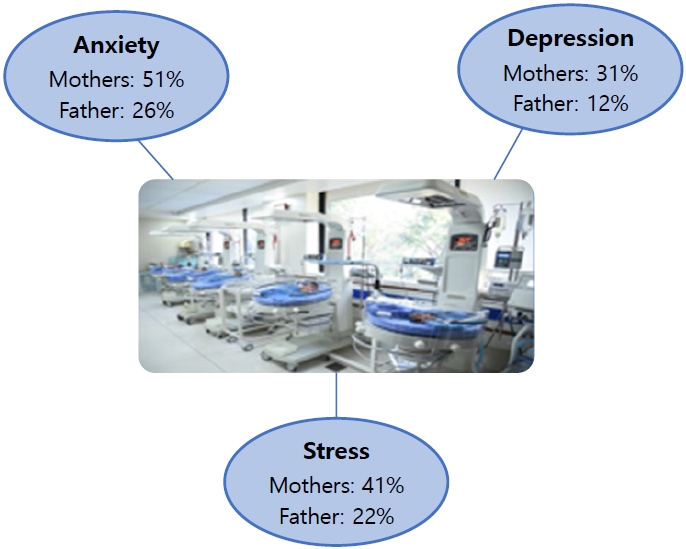
Question: What emotions do parents experience when their newborns are admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)?
Finding: Mothers experienced more anxiety (51%), depression (31%), and stress (41%) symptoms than fathers (26%, 12%, and 22%, respectively).
Meaning: Parents often experience anxiety, stress, and depression following NICU admission. Healthcare workers are responsible for providing regular parental counseling.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal family-centered care: evidence and practice models
- Juyoung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(4):171-177. Published online June 14, 2023
-
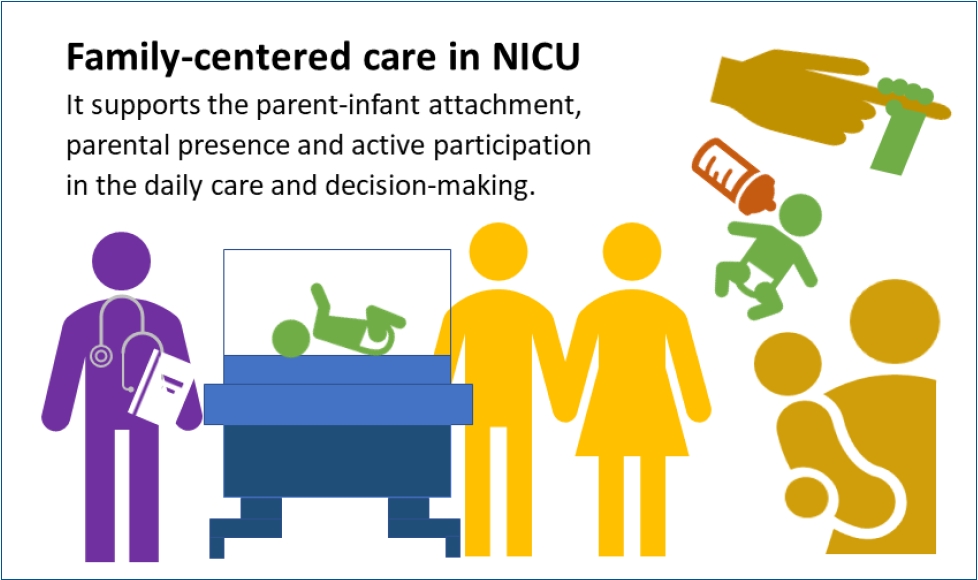
· Concrete evidence exists of early parent-infant attachment supported by family-centered care (FCC) in the neonatal intensive care unit.
· FCC involves the parents’ presence and participation in the infant’s care and decision-making.
· A private and comfortable space should be provided. A single-family room is ideal; however, a quiet space with a recliner can be a good alternative.
· Care culture changes and staff training are required.
- Critical Care Medicine
- Ferritin in pediatric critical illness: a scoping review
- Ivy Cerelia Valerie, Anak Agung Sagung Mirah Prabandari, Dyah Kanya Wati
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(3):98-109. Published online September 16, 2022
-
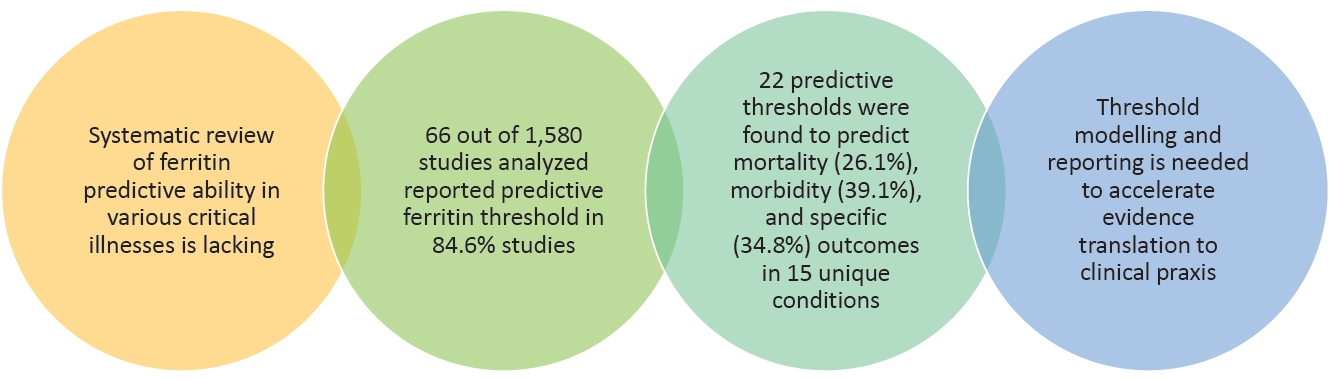
The number of studies on ferritin predictive ability in pediatric critical illness has grown exponentially over the past 2 decades. However, among the 66 of 1,580 studies analyzed here, summary statistics for overall and condition-specific studies were only reported in 45.4% and 71.2%, respectively. In contrast, ferritin as a categorical variable with a preset threshold was a significant predictor in 84.6% of studies.
- Original Article
- Other
- Evaluation of goodness of fit of semiparametric and parametric models in analysis of factors associated with length of stay in neonatal intensive care unit
- Fatemeh Kheiry, Sadegh Kargarian-Marvasti, Sima Afrashteh, Abolfazl Mohammadbeigi, Nima Daneshi, Salma Naderi, Seyed Hossein Saadat
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):361-367. Published online June 10, 2020
-

Question: Hospitalization in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is associated with life-threatening hazards. What factors associated with neonatal length of stay (LOS) in the NICU?
Finding: Breastfeeding, phototherapy, acute renal failure (ARF), mechanical ventilation, and central venous catheter (CVC) access were identified as factors associated with NICU length of stay.
Meaning: Protective effects of breastfeeding and CVC access, whereas increase effects of phototherapy, ARF, and mechanical ventilation in LOS can be supporting evidence to establish effective interventions to reduce length of NICU stay.
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Short- and long-term outcomes of very low birth weight infants in Korea: Korean Neonatal Network update in 2019
- Jang Hoon Lee, YoungAh Youn, Yun Sil Chang; Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(8):284-290. Published online February 5, 2020
-

The Korean Neonatal Network (KNN) has collected population-based data for very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs) born in Korea since 2013. The survival rate of all VLBWIs was 86% in Korea. The overall prevalence of cerebral palsy was 6.2%–6.6%. Bilateral blindness and hearing loss were reported in 0.2%–0.3%, 0.8%–1.9%, respectively. The KNN has published annual reports and papers for facilitating the improvement of VLBWIs outcome in Korea.
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Comparative validity of microalbuminuria versus clinical mortality scores to predict pediatric intensive care unit outcomes
- Shifa Nismath, Suchetha S. Rao, B.S. Baliga, Vaman Kulkarni, Gayatri M. Rao
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):20-24. Published online August 12, 2019
-

Question: Does microalbuminuria predict mortality in pediatric intensive care unit?
Finding: Positive correlation was found between albumin-creatinine ratio and pediatric intensive care unit stay, organ dysfunction and need of inotropes. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for albumin-creatinine ratio was comparable to mortality scores.
Meaning: Microalbuminuria is a good predictor of outcome in pediatric intensive care unit and is comparable with mortality scores.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Clinical impact of admission hypothermia in very low birth weight infants: results from Korean Neonatal Network
- Na Hyun Lee, Soo Kyung Nam, Juyoung Lee, Yong Hoon Jun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(10):386-394. Published online May 22, 2019
-
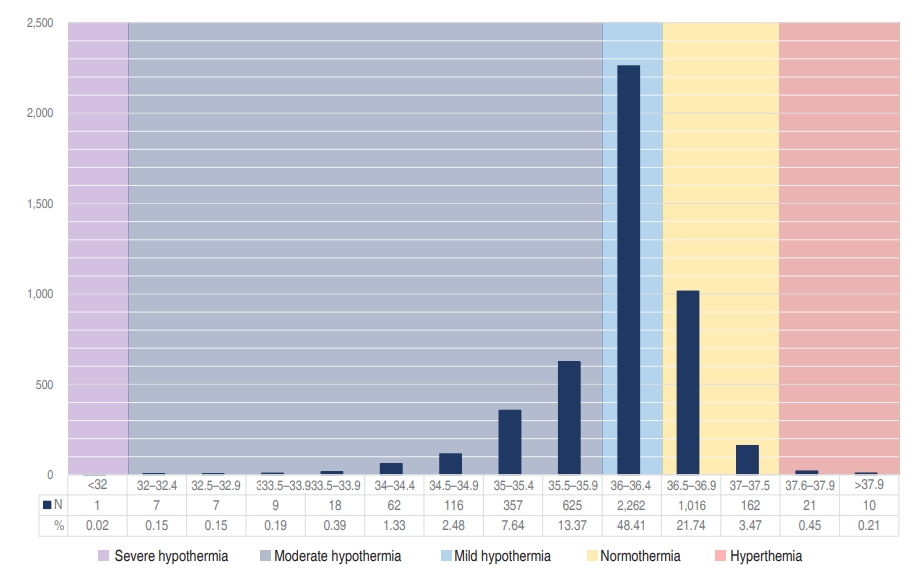
Background: Preterm infants have difficulty maintaining body temperature after birth. However, clinical guidelines advocate that neonatal body temperature should be maintained at 36.5°C–37.5°C.
Purpose: We aimed to investigate the incidence of admission hypothermia in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants and to determine the association of admission temperature with in-hospital mortality and morbidities. Methods: A cohort study using prospectively collected data involving...
- Review Article
- Infection
- Central line-associated bloodstream infections in neonates
- Hye Jung Cho, Hye-Kyung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(3):79-84. Published online December 19, 2018
-
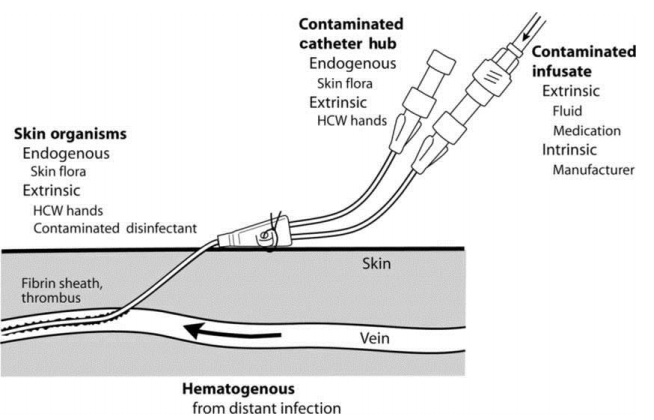
Newborn infants, including premature infants, are high-risk patients susceptible to various microorganisms. Catheter-related bloodstream infections are the most common type of nosocomial infections in this population. Regular education and training of medical staffs are most important as a preventive strategy for central line-associated bloodstream infections (CLABSIs). Bundle approaches and the use of checklists during the insertion and maintenance of central...
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Clinical features and prognostic factors of early-onset sepsis: a 7.5-year experience in one neonatal intensive care unit
- Se Jin Kim, Ga Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Park, Sang Lak Lee, Chun Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(1):36-41. Published online September 27, 2018
-
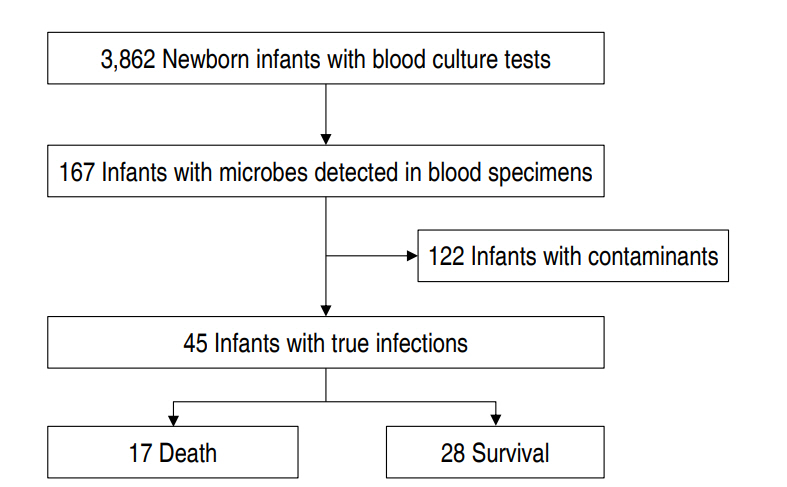
Purpose: In this study, we investigated the clinical features and prognostic factors of early-onset sepsis (EOS) in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) patients. Methods: A retrospective analysis was conducted on medical records from January 2010 to June 2017 (7.5 years) of a university hospital NICU. Results: There were 45 cases of EOS (1.2%) in 3,862 infants. The most common pathogen responsible for...
- Parental concerns about their premature infants' health after discharge from the neonatal intensive care unit: a questionnaire survey for anticipated guidance in a neonatal follow-up clinic
- Ji-Yun Cho, Juyoung Lee, Young Ah Youn, Soon Ju Kim, So Young Kim, In Kyung Sung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(8):272-279. Published online August 23, 2012
-
Purpose The aim of this study was to develop an appropriate nursing information guideline according to corrected age, after investigating parents' concerns about the growth, development, and diseases of their premature infants after discharge from the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).
Methods The parents of premature infants (birth weight, <2,500 g; gestational age, <37 weeks) who went to a neonatal follow-up clinic after...
- Review Article
- Catheter-related bloodstream infections in neonatal intensive care units
- Jung Hyun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(9):363-367. Published online September 30, 2011
-
Central venous catheters (CVCs) are regularly used in intensive care units, and catheter-related bloodstream infection (CRBSI) remains a leading cause of healthcare-associated infections, particularly in preterm infants. Increased survival rate of extremely-low-birth-weight infants can be partly attributed to routine practice of CVC placement. The most common types of CVCs used in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) include umbilical venous catheters,...
- Original Article
- Outcome and risk factors of pediatric hemato-oncology patients admitted in pediatric intensive care unit
- Bo Eun Kim, Eun Ju Ha, Keun Wook Bae, Seongguk Kim, Ho Joon Im, Jong Jin Seo, Seong Jong Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(10):1153-1160. Published online October 15, 2009
-
Purpose : To evaluate the risk factors for mortality and prognostic factors in pediatric hemato-oncology patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU). Methods : We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of pediatric hemato-oncology patients admitted at the PICU of the Asan Medical Center between September 2005 and July 2008. Patients admitted at the PICU for perioperative or terminal... -
- Review Article
- What can we do for dying neonate in NICU?
- Chung-Sik Chun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(8):851-855. Published online August 15, 2009
-
Death is not only a medical problem; it is also an ethical problem. When doctors face a dying neonate, their knowledge of bioethics and the opinions of ethical specialists and religious leaders are helpful for them and the family of the dying baby. In recent years, due to the increase of surviving babies who have suffered from severe illness, those born too... -
- Original Article
- Performance effectiveness of pediatric index of mortality 2 (PIM2) and pediatricrisk of mortality III (PRISM III) in pediatric patients with intensive care in single institution: Retrospective study
- Hui Seung Hwang, Na Young Lee, Seung Beom Han, Ga Young Kwak, Soo Young Lee, Seung Yun Chung, Jin Han Kang, Dae Chul Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(11):1158-1164. Published online November 15, 2008
-
Purpose : To investigate the discriminative ability of pediatric index of mortality 2 (PIM2) and pediatric risk of mortality III (PRISM III) in predicting mortality in children admitted into the intensive care unit (ICU). Methods : We retrospectively analyzed variables of PIM2 and PRISM III based on medical records with children cared for in a single hospital ICU from January 2003... -
- Case Report
- Two cases of Chryseobacterium meningosepticum infection in a neonatal intensive care unit
- Hye Sun Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(7):698-701. Published online July 15, 2007
-
We report on two premature infants who developed nosocomial infection caused by Chryseobacterium meningosepticum in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). One premature infant developed sepsis, meningitis, and hydrocephalus, and was treated successfully with ciprofloxacin plus trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole combination therapy for 4 weeks and with a ventriculoperitoneal shunt. The other premature infant, who was in a chronically debilitated state, had infection... -
- Original Article
- Diagnostic classification and clinical aspects of floppy infants in the neonatal and pediatric intensive care units
- Eun Sun Kim, Kyung Eun Jung, Sang Duk Kim, Eo Kyung Kim, Jong Hee Chae, Han Suk Kim, June Dong Park, Ki Joong Kim, Beyong Il Kim, Yong Seung Hwang, Jung-Hwan Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(11):1158-1166. Published online November 15, 2006
-
Purpose : The purpose of this study is to make a diagnostic classification and discuss a diagnostic strategy of floppy infants by investigating clinical, neurological, electrophysiological, and genetic analysis of infants admitted to intensive care units with the complaint of hypotonia. Methods : A retrospective study was performed from Jan. 1993 to Dec. 2005 in neonatal and pediatric intensive care units... -
- Outbreak of Acinetobacter septicemia in a neonatal intensive care unit
- Myo Jing Kim, Hye Jin Lee, Sang Hee Son, Jae Won Huh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(5):494-499. Published online May 15, 2006
-
Purpose : Acinetobacter baumannii is increasingly recognized as an important cause of nosocomial infection, especially in neonatal intensive care units. But little is known about the clinical significance and hospital epidemiology of Acinetobacter species other than A. baumannii. The objective of this study is to describe the clinical characteristics and epidemiology of septicemia due to Acinetobacter species other than A.... -
- Analysis of Etiology and Prognosis of Pulmonary Complications in Children with Hematological or Oncological Disorders in Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
- Jin Young Jung, Soo-Jong Hong, Young Jun An, Ja Hyung Kim, Jong Jin Seo, Hyung Nam Moon, Thad Ghim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(8):1000-1006. Published online August 15, 2002
-
Purpose : In the course of treatment, patients with hematological or oncological disorders often develop pulmonary complication. The patients who develop a severe pulmonary complication have a poor outlook. The causes of pulmonary complication are either infectious or non-infectious in origin. We have analyzed the etiology and outcome of these patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit of Asan... -
- Neonatal Systemic Candidiasis : Comparison of Albicans and Parapsilosis Infection
- Jung Mie Han, Ho Young Lee, Mi Jeong Kang, Sun Young Ko, Yun Sil Chang, Won Soon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(8):1052-1058. Published online August 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Systemic Candidiasis has become an increasingly important cause of morbidity and mortality in NICU infants. Severe infections caused by non-albicans Candida species have been increasingly reported in NICU infants. The purpose of the present study was to compare relative severity, mortality rates for C. albicans(CA) and C. parapsilosis(CP) infections in our NICU. Methods : This study included 16 infants... -
- Clinical and Molecular-epidemiologic Analysis of A Nosocomial Outbreak of Acinetobacter baumannii in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Hye Kyung Lee, Han Jin Kim, Young Chang Kim, Sung Ran Cho, Hwi Jun Kim, Wee Gyo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(1):43-48. Published online January 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Acinetobacter species are aerobic gram-negative rods that can be widely found in nature and are a part of the normal flora of humans. The most clinical isolates of A. baumannii reflect infection rather than colonization. Recent reports suggest that the organisms cause serious and often fetal nosocomial infection such as ventilator-associated pneumonia. Methods : From March to September 1998, we experienced thirty... -
- Compatibility of Neonatal Parenteral Nutrient Solutions with Commonly Used Drugs during Y-site Delivery in NICU
- Ju Hun Choi, Kyong Ju Jeong, Ha Ryung Cho, Dong Soo Yim, Seung Ki Choi, Kyu Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(7):893-900. Published online July 15, 1998
-
Purpose : Because vascular access sites in neonates are limited, intravenous(IV) medications must often be mixed with maintenance fluids, including parenteral nutrient(PN) solutions. This study was done to determine whether IV medications commonly prescribed in the neonatal in- tensive care unit(NICU) are compatible with the two neonatal PN solutions. Methods : The compatibility of neonatal PN solutions and selected other drugs... -
- Clinical Characteristics of Inborn and Outborn Infants Admitted to the NICU
- Hyun Cheol Lee, Jin Young Choi, Hwang Min Kim, Baek Keun Lim, Jong Soo Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(12):1647-1655. Published online December 15, 1993
-
Regionalization of high-risk perinatal care has been advocated because intensive care of small and ill newborn infants lowers mortality and morbidity. This report is based on analysis of admissions to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) at the Wonju Christian Hospital during the 4-year period from January, 1988 to December, 1991. There were 786 inborn infants and 1155 outborn... -
- Continuous Arteriovenous Hemofiltration in Children.
- Hae Il Cheong, Dong Kyu Jin, Young Seo park, Yong Choi, Kwang Wook Ko
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1989;32(2):230-238. Published online February 28, 1989
-
Among those who were admitted to the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU), Seoul National University Children’s Hospital and developed acute renal failure (ARF) during the disease course, 11 children received continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration (CAVH) by pediatricians during a 3-year- period from Nov. 85 to Oct. 88. Their clinical findings were analyzed retrospectively, and the results were as follows; 1) They were 5 boys and 6... -
- Clinical and Statistical Study of High Risk Infants.
- B K Chung, S K Kim, S O Byun, M H Shin, J S Oh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1984;27(1):9-18. Published online January 31, 1984
-
Clinical study was done on 6,588 liveborn infants and 2,644 high risk infants who were born in WMBH during the period of 2 years from June 1980 to May 1982. The following results were obtained: 1)Of 6,588 liveborn infants 2,644, 40,1%, were born associated with high risk factors. The mortality rate was 1.47% in normal newborn infant. 2)High risk factors... -
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











