Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Review Article
- Infection
- Consideration in treatment decisions for refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Hye-Kyung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(9):459-467. Published online February 10, 2021
-
• To avoid unnecessary exposure to secondary antibiotics, it is needed to diagnose Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) pneumonia carefully, especially when unresponsiveness to macrolide is suspected.
• Serologic and molecular tests for MP infection and excluding respiratory infection caused by other pathogens might be considered.
• It is necessary to continuously monitor antibiotic susceptibility of MP, and efforts to lower antibiotic pressure are required.
- Pulmonology
- Current perspectives on atypical pneumonia in children
- Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):469-476. Published online June 10, 2020
-
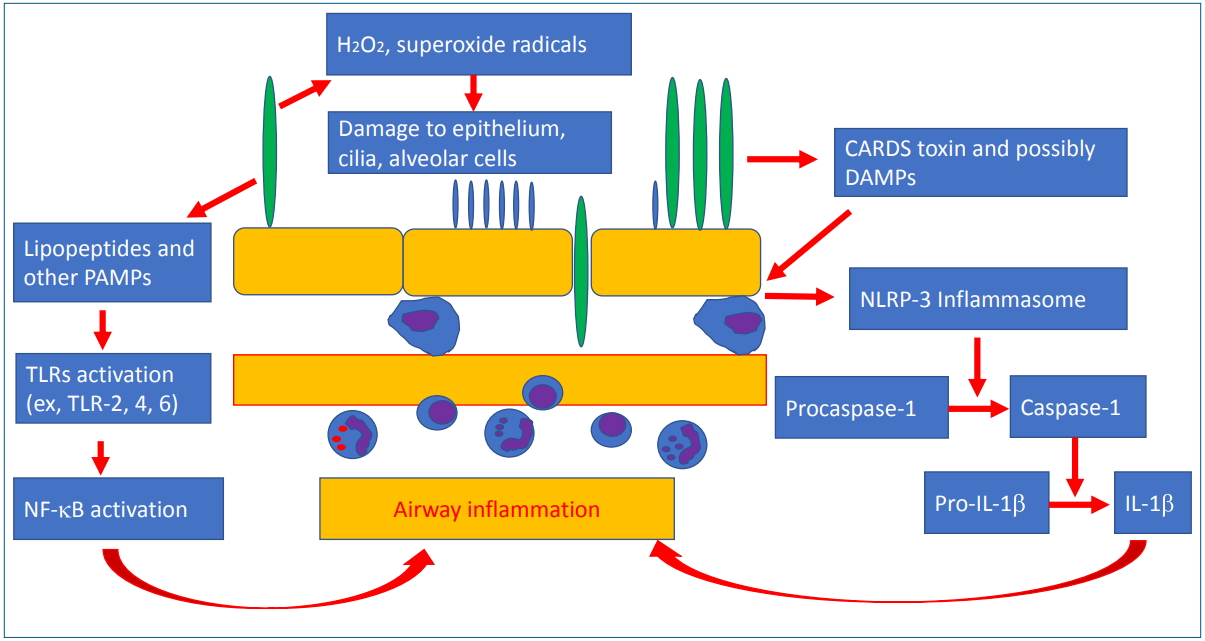
Macrolides are the first line treatment in atypical pneumonia caused by M. pneumoniae, C. pneumoniae, and L. pneumophila. Macrolide-resistant mycoplasma pneumonia (MRMP) is emerging worldwide, especially in East Asia. Immune modulators such as corticosteroids or second line antibiotics are treatment options for MRMP. Pediatricians should be careful with empirical therapy of macrolides in children with mild to moderate community-acquired pneumonia not to increase the risk of MRMP.
- Benefits and risks of therapeutic alternatives for macrolide resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children
- Hyeon-Jong Yang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2019;62(6):199-205. Published online March 15, 2019
-
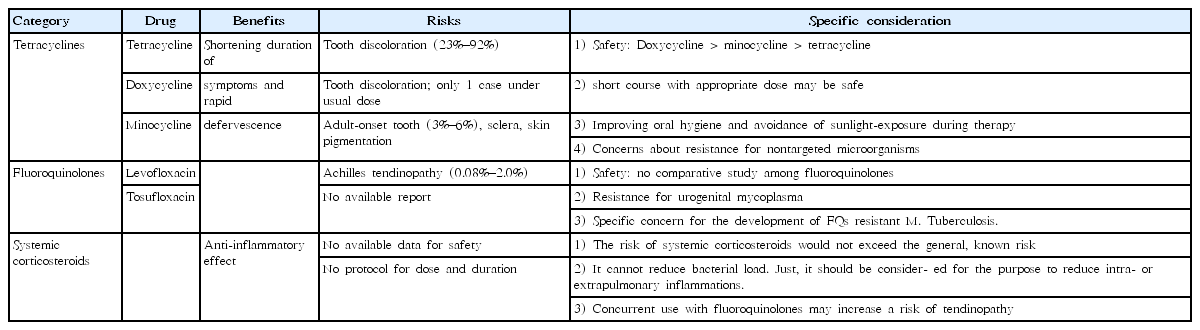
Although Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) has been generally susceptible to macrolides, the emergence of macrolide-resistant MPP (MRMP) has made its treatment challenging. MRMP rapidly spread after the 2000s, especially in East Asia. MRMP is more common in children and adolescents than in adults, which is likely related to the frequent use of macrolides for treating M. pneumoniae infections in children....
- Mechanism of resistance acquisition and treatment of macrolide-resistant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children - Hyeon-Jong Yang, Dae Jin Song, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(6):167-174. Published online June 22, 2017
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) is one of the most common forms of community-acquired pneumonia in children and adolescents. Outbreaks of MPP occur in 3- to 7-year cycles worldwide; recent epidemics in Korea occurred in 2006–2007, 2011, and 2015–2016. Although MPP is known to be a mild, self-limiting disease with a good response to macrolides, it can also progress into a...
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Prevalence and clinical manifestations of macrolide resistant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children - Eun Lee, Hyun-Ju Cho, Soo-Jong Hong, Jina Lee, Heungsup Sung, Jinho Yu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2017;60(5):151-157. Published online May 31, 2017
-
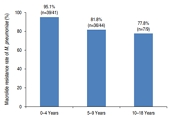
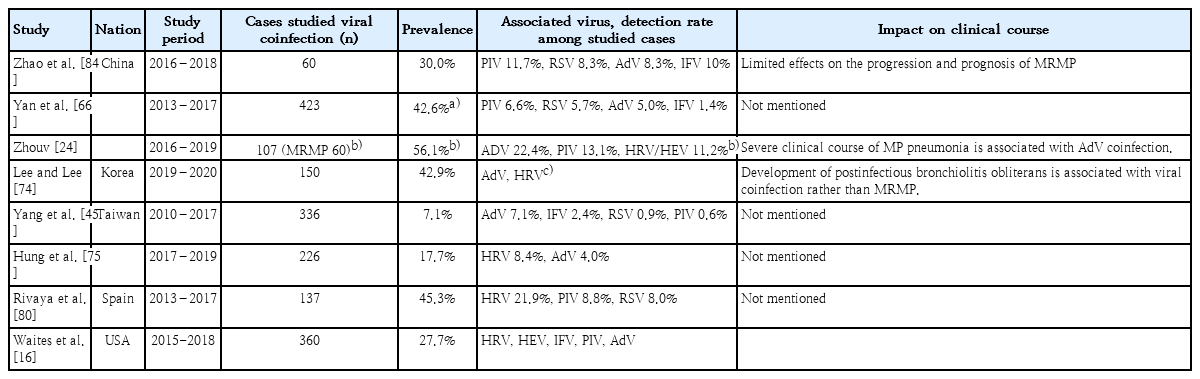
Purpose Macrolide resistance rate of
Mycoplasma pneumoniae has rapidly increased in children. Studies on the clinical features between macrolide susceptible-M. pneumoniae (MSMP) and macrolide resistant-M. pneumoniae (MRMP) are lacking. The aim of this study was to identify the macrolide resistance rate ofM. pneumoniae in Korean children withM. pneumoniae penupmonia in 2015 and compare manifestations between MSMP and MRMP.Methods Among 122...
- Case Report
- Neurology
- Complete occlusion of the right middle cerebral artery associated with
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia - Ben Kang, Dong Hyun Kim, Young Jin Hong, Byong Kwan Son, Myung Kwan Lim, Yon Ho Choe, Young Se Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2016;59(3):149-152. Published online March 31, 2016
-
We report a case of a 5-year-old girl who developed left hemiparesis and left facial palsy, 6 days after the initiation of fever and respiratory symptoms due to pneumonia. Chest radiography, conducted upon admission, showed pneumonic infiltration and pleural effusion in the left lung field. Brain magnetic resonance imaging showed acute ischemic infarction in the right middle cerebral artery territory....
- Original Article
- Hepatitis associated with
Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in Korean children: a prospective study - Kyu Won Kim, Jae Jin Sung, Hann Tchah, Eell Ryoo, Hye Kyung Cho, Yong Han Sun, Kang Ho Cho, Dong Woo Son, In Sang Jeon, Yun Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(6):211-217. Published online June 22, 2015
-
Purpose Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) infection is a major cause of respiratory infection in school-aged children. Extrapulmonary manifestations of MP infection are common, but liver involvement has been rarely reported. The aim of this study was to determine the clinical characteristics of MP-associated hepatitis.Methods This prospective study included 1,044 pediatric patients with MP infection diagnosed serologically with MP IgM at one medical center...
- Epidemiological comparison of three
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia epidemics in a single hospital over 10 years - Eun-Kyung Kim, You-Sook Youn, Jung-Woo Rhim, Myung-Seok Shin, Jin-Han Kang, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2015;58(5):172-177. Published online May 22, 2015
-
Purpose Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) pneumonia epidemics have occurred in 3- to 4-year cycles in Korea. We evaluated the epidemiologic characteristics of MP pneumonia in Daejeon, Korea, from 2003 to 2012.Methods We retrospectively analyzed 779 medical records of children (0-15 years of old) with MP pneumonia admitted to our institution and compared the data from 3 recent epidemics.
Results In 779 patients, the mean age...
- Increased risk of refractory
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children with atopic sensitization and asthma - Jeong Eun Shin, Bo Ram Cheon, Jae Won Shim, Deok Soo Kim, Hae Lim Jung, Moon Soo Park, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(6):271-277. Published online June 30, 2014
-
Purpose A nationwide outbreak of
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MP) refractory to macrolide antibiotics occurred in Korea during 2011. Steroid therapy has been reported to be both efficacious and well tolerated in pediatric patients with refractory MP. We compared clinical features and laboratory characteristics between children with refractory MP requiring steroid treatment and those with macrolide-responsive MP and evaluated the risk factors...
- Predictive value of C-reactive protein in response to macrolides in children with macrolide-resistant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia - Young Ho Seo, Jang Su Kim, Sung Chul Seo, Won Hee Seo, Young Yoo, Dae Jin Song, Ji Tae Choung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2014;57(4):186-192. Published online April 30, 2014
-
Purpose The prevalence of macrolide-resistant
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MRMP) has increased worldwide. The aim of this study was to estimate the proportion of MRMP in a tertiary hospital in Korea, and to find potential laboratory markers that could be used to predict the efficacy of macrolides in children with MRMP pneumonia.Methods A total of 95 patients with
M. pneumoniae pneumonia were enrolled in...
- Case Report
Mycoplasma pneumoniae associated stroke in a 3-year-old girl- Gun-Ha Kim, Won Hee Seo, Bo-Kyung Je, So-Hee Eun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2013;56(9):411-415. Published online September 30, 2013
-
Infectious diseases precede a significant proportion of acute ischemic strokes in children. Here, we report a case of acute ischemic stroke in a 3-year-old girl with a
Mycoplasma pneumonia -associated respiratory tract infection. She developed an acquired prothrombotic state of protein S deficiency and had increased fibrinogen and fibrinogen degradation product levels and increased titer of antinuclear antibodies. However, these conditions...
- Original Article
- Detection of genetic mutations associated with macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Chi Eun Oh, Eun Hwa Choi, Hoan Jong Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(2):178-183. Published online February 15, 2010
-
Purpose : The aim of this study was to identify mutations associated with macrolide resistance in Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) and to establish a cultural method to determine antimicrobial susceptibility. Methods : Nasopharyngeal aspirates (NPAs) were collected from 62 children diagnosed with MP pneumonia by a serologic method or polymerase chain reaction. The 23S rRNA and L4 ribosomal protein genes of MP... -
- Clinical significance of codetection of the causative agents for acute respiratory tract infection in hospitalized children
- Eui Jung Roh, Young Pyo Chang, Jae Kyung Kim, In Soo Rheem, Kwi Sung Park, Eun Hee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(6):661-666. Published online June 15, 2009
-
Purpose : To determine the prevalence and clinical features of codetected respiratory etiological agents for acute respiratory infection in hospitalized children. Methods : Nasopharyngeal aspirates were obtained from hospitalized children with acute respiratory infection at Dankook University Hospital from September 2003 through June 2005. Immunofluorescent staining and culture were used for the detection of respiratory viruses (influenza virus [IFV] types... -
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Korean children, from 1979 to 2006-a meta-analysis
- Jin Woo Kim, Hyun Kyong Seo, Eun Gyong Yoo, Sung Jin Park, So Hwa Yoon, Hye Young Jung, Manyong Han
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):315-323. Published online March 15, 2009
-
Purpose : This study aimed to perform a systematic review of the reports on Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in the last 30 years (1980-2006) to investigate the intervals between outbreaks, change in the peak incidence age, and diagnostic methods. We also aimed to validate the proper diagnostic criteria for M. pneumoniae pneumonia. Methods : We reviewed 62 original articles on M. pneumoniae... -
- Review Article
- Mycoplasma and chlamydia infection in Korea
- Kyung Won Kim, Kyu-Earn Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(3):277-282. Published online March 15, 2009
-
Pneumonia, which usually requires hospitalization for children, is caused by various pathogens. According to recent surveys, the prevalence of atypical pneumonia caused by Mycoplasma or Chlamydia has increased, especially in preschool children. Also, the evidence has been accumulated that Mycoplasma or Chlamydia infection is associated with asthma including both inception and exacerbation. Therefore, it is important to consider how the... -
- Case Report
- Atypical presentation of Kawasaki disease resembling a retropharyngeal abscess
- Sun-Hee Choi, Yu-Min Lee, Yeong-Ho Rha
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(2):247-250. Published online February 15, 2009
-
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) presents with widespread blisters, erythematous or purpuric macules, and one or more mucous membrane erosions. Various etiologic factors, including infection, vaccination, drug administration, systemic diseases, physical agents, and food have been implicated as causes of SJS. Mycoplasma pneumoniae is the most common infectious agent to cause SJS in children. In recent literature, M. pneumoniae-induced SJS with mucositis... -
- Two cases of central nervous system complications caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
- Shin Mi Kim, Ji Seung Heo, Eun Jung Shim, Dae Hyoung Lee, Do Jun Cho, Dug Ha Kim, Ki Sik Min, Ki Yang Yoo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(5):533-537. Published online May 15, 2008
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. pneumoniae) infection causes a wide variety of clinical manifestations in children and young adults, the main one being pneumonia. M. pneumoniae is transmitted from person to person by infected respiratory droplets. Symptoms caused by M. pneumoniae infection can be divided into those involving the respiratory tract, and those caused by extrapulmonary disease. M. pneumoniae infections may cause... -
- Original Article
- Increased vascular endothelial growth factor in children with acute Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia and wheezing
- Young Seo, Byung Keun Yu, Yeon Joung Oh, Yoon Lee, Young Yoo, Ji Tae Choung, Young Yull Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(5):487-491. Published online May 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Although Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M. pneumoniae) infection can cause wheezing in non-asthmatic children, the mechanisms of this symptom remain unclear. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a major mediator of angiogenesis and vascular permeability, and is also known to be elevated in cases of chronic pulmonary disease such as asthma. We hypothesized that VEGF may increase in children with... -
- Clinical Findings of Mycoplasma Pneumonia in Children, from 1998 to 2003
- Ji-Hyun Kim, Soo Ahn Chae, Dong-Keun Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(9):969-975. Published online September 15, 2005
-
Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Chung Ang University, Seoul, Korea Purpose : We performed a study of clinical findings of Mycoplasma Pneumonia in children, to know differences between recent clinical manifestations of Mycoplasma pneumonia and previous studies. Methods : The subjects of this study were 393 children who were diagnosed as Mycoplasma pneumonia with high titers of Mycoplasma antibody(≥1 : 160)... -
- Hepatitis Complicated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection in Children
- Seung Min Lee, Sung Moon Lee, Hann Tchah, In Sang Jeon, Eell Ryoo, Kang Ho Cho, Yong Han Seon, Dong Woo Son, Hee Joo Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(8):832-838. Published online August 15, 2005
-
Purpose : Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection is relatively common in childhood. Its extrapulmonary manifestations have been reported so much, but hepatitis associated with it has been reported rarely in Korea. Methods : A clinical study was performed on 556 patients of M. pneumoniae pneumonia diagnosed serologically at Gil hospital from January 2001 to December 2004. We reviewed 65 cases among these patients,... -
- A Study of Antibody Conversion Rate During a Mycoplasma pneumoniae Epidemic Period(the Second Half of 2003)
- Do Kyun Kim, Young Yoo, Jinho Yu, Young Yull Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(5):500-505. Published online May 15, 2005
-
Purpose : This study was designed to estimate the prevalence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection during an epidemic period by means of examining the antibody conversion rate and to investigate the association of the antibody conversion with age, initial antibody titer, and atopy. Methods : We chose 191 children whose antibody titer to M. pneumoniae was negative, 1 : 40, or... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Kawasaki Disease with Mycoplasma Pneumonia
- Se Min Lee, So Eun Park, Yeun Woo Kim, Jung Yeun Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(4):438-442. Published online April 15, 2005
-
Kawasaki disease is an acute febrile vasculitis that occurs predominantly in young children under 5- years-old. The patients present generally with a high spiking fever that is unresponsive to antibiotics and lasts for more than five days at least. Prolonged fever has been shown to be a risk factor in the development of coronary artery disease. It seems to be... -
- Original Article
- Clinico-epidemiologic Study of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia(1993 through 2003)
- Seung-Hyun Lee, Suk-Man Noh, Kyung-Yil Lee, Hyung-Shin Lee, Ja-Hyun Hong, Mi-Hee Lee, Joon-Sung Lee, Byung-Chul Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2005;48(2):154-157. Published online February 15, 2005
-
Purpose : We evaluated the epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of mycoplasma pneumonia. Methods : A total of 559 medical records of children with mycoplasma pneumonia admitted to The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, were retrospectively analyzed. Results : The mean annual number of cases was 51. There was a higher occurrence in autumn (September-November, 41.7%) and in winter(26.7%). Outbreaks... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia Complicated with Guillain-Barr Syndrome and Encephalitis
- Soon Bum Lee, Hee Jung, Yong Seok Lee, Bum Sun Kwon, Jeesuk Yu
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(12):1338-1348. Published online December 15, 2004
-
The most common pathogen of respiratory tract infection among school-age children and adolescents is Mycoplasma pneumoniae, which causes clinical manifestations of pneumonia, acute asthmatic attack, pharygitis, and tonsilitis. It can also cause extrapulmonary infections that involves skin, the nervous system, the digestive system, the cardiovascular system, and the hematopoietic system. It is reported that the central nervous system symptoms may... -
- Original Article
- Study of Exchange Phenomenon of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Children from 1997-2002
- Sung Seok Kim, Hoon Kang, Byung Moon Ahn, Won Wook Lee, Eun Ryoung Kim, Soo Yeon Kim, Hyun Pil Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2004;47(1):24-30. Published online January 15, 2004
-
Methods : We enrolled 504 patients out of 547 patients, who were admitted to the Department of Pediatrics, Sung-Ae and Kwangmyung Sung-Ae General Hospital from November 1996 to October 2002. They were diagnosed as M. pneumoniae pneumonia by clinical characteristics and indirect particle agglutination test of M. pneumoniae. To classify into two groups, the group specific polymerase chain reaction amplification... -
- Pattern of Occurrence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia in Admitted Children : Southern Central Korea, from 1989 to 2002
- Ki Su Kang, Hyang-Ok Woo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(5):474-479. Published online May 15, 2003
-
Purpose : The determination of exposure and prevalence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia of any region should be helpful for clinical diagnosis. We studied the pattern of occurrence of M. pneumoniae pneumonia among children living in southern central Korea during the last 13 years. This area has a relatively small population and less mobility compared with metropolitan areas. Methods : We performed... -
- Comparison of Eosinophil Markers between Acute and Recovery Stages in Children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia
- Kyu Min Nah, Eun Kyeong Kang, Hee Kang, Yang Park, Young Yull Koh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(10):1227-1233. Published online October 15, 2002
-
Purpose : Several studies have shown that increases of eosinophil markers are common findings of asthma and Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection, and eosinophil markers reflect the clinical stage of asthma. The purpose of this study was to investigate the change of eosinophil markers according to the clinical stage of Mycoplasma pneumonia. Methods : The patient group consisted of 33 outpatient children with Mycoplasma pneumonia. Peripheral blood... -
- Case Report
- A Case of Cerebral Infarction Complicated by Mycoplasma pneumoniae Pneumonia
- Kyoung Whoon Cheon, Won Sik Kang, Byeong Hee Son, Sung Won Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(5):673-678. Published online May 15, 2002
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is the most common pathogen of the respiratory tract among school- aged children and young adults. The incidence of CNS complication is reported as 0.1-7% of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. We experienced a case of cerebral infarction complicated by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and reviewed the literature about the CNS complication of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. -
- A Case of Bilateral Spontaneous Tension Pneumothorax Associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
- Jae Won Lee, Mi Young Heo, Hae Soon Kim, Seung Joo Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(3):401-405. Published online March 15, 2002
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae(M. pneumoniae) is the leading cause of pneumonia in school-age children and young adults. The clinical courses are usually mild but recently, severe cases were reported such as lung abscess, Swyer-James syndrome and adult respiratory distress syndrome. Spontaneous pneumothorax associated with M. pneumoniae infection is rare. Carlisle reported a 6-year-old patient with bilateral spontaneous pneumothorax associated with M. pneumoniae... -
- A Case of Guillain-Barré Syndrome Coinciding with Bronchial Asthma associated with Mycoplasma Pneumonia
- Kyung-Yil Lee, Dong-Joon Lee, Ji-Whan Han, Sang-Won Ch, John-Sung Lee, Kyung-Tai Whang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(8):1165-1169. Published online August 15, 1999
-
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is the most common etiologic agent of pneumonia in school-aged children and young adults. It involves not only the respiratory system but includes extrapulmonary complications such as exanthem, hemolysis, arthritis, hepatic dysfuction, cardiac disease, and central nervous system disease. The pathogenesis of extrapulmonary involvements may be an autoimmune phenomena. Recent studies suggest that bronchial asthma can be initiated... -
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









