Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Nutrition
- Survey of Korean pediatrician’s perceptions of barriers to and improvements in breastfeeding
- Seong Phil Bae, Woo Ryoung Lee, Won-Ho Hahn, Hye-Jung Shin, Young Min Ahn, Son Moon Shin, Yong Joo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim, Youn Jeong Shin, Dae Yong Yi, Soon Min Lee, Juyoung Lee, Jin A Lee, Sung-Hoon Chung, Euiseok Jung, Eui Kyung Choi, Ju Sun Heo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):540-546. Published online July 29, 2022
-
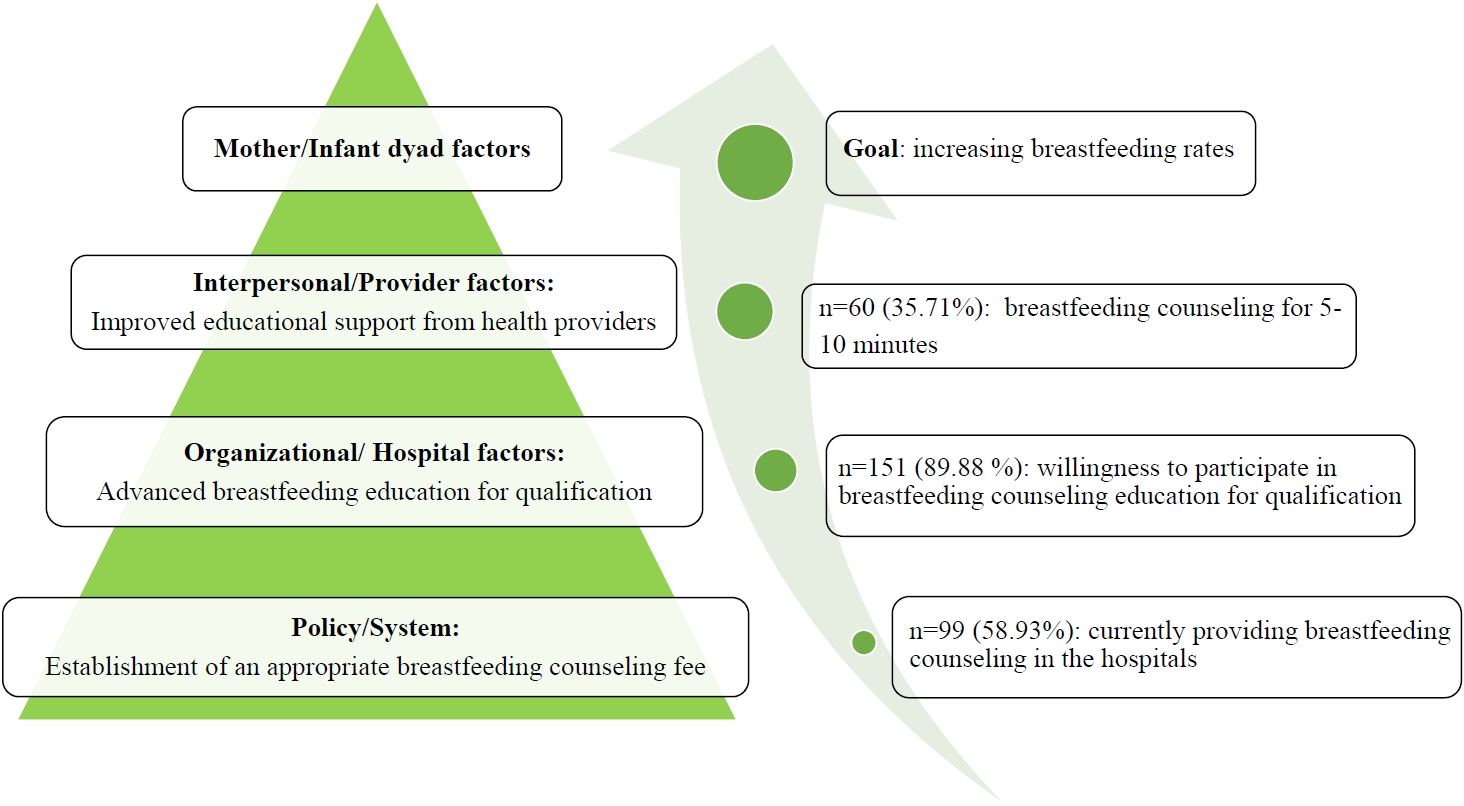
Question: What barriers to breastfeeding do Korean pediatricians perceive?
Finding: Regardless of medical institution, breastfeeding counseling for parents is currently limited, and breastfeeding is commonly discontinued due to various maternal and neonatal factors.
Meaning: To promote breastfeeding, increasing pediatrician participation in breastfeeding counseling with the establishment of appropriate breastfeeding counseling fees and the expansion of practical and high-quality breastfeeding education for medical staff should be considered.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Mediation effect of cord blood cortisol levels between maternal prepregnancy body mass index and birth weight: a hospital-based cross-sectional study
- Nisanth Selvam, Jayashree K, Prasanna Mithra
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):500-506. Published online July 29, 2022
-

Question: What is the association between cord blood cortisol and maternal weight, birth weight, and cord blood lipid profile?
Finding: Cord blood cortisol levels did not influence the relationship between maternal weight changes or birth weight. Maternal weight changes, birth weight, and cortisol levels altered the cord blood lipid profile.
Meaning: Our findings may aid United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 3 (Good Health and Well-Being) achievement by 2030.
- Nutrition
- Not breastfeeding and risk of autism spectrum disorders among children: a meta-analysis
- Ensiyeh Jenabi, Saeid Bashirian, Amir Mohammad Salehi, Salman Khazaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):28-31. Published online July 19, 2022
-
This study aimed to determine whether there is an association between not breastfeeding (versus breastfeeding) and the risk of autism spectrum disorders (ASD) among children. We found that the risk of ASD associated with not breastfeeding had an odds ratio of 1.81 (95% confidence interval, 1.35–2.27; I2=0 %). These findings suggest the importance of breastfeeding in decreasing the risk of ASD among children.
- Review Article
- Gastroenterology
- Current diagnosis and image-guided reduction for intussusception in children
- Jisun Hwang, Hee Mang Yoon, Pyeong Hwa Kim, Ah Young Jung, Jin Seong Lee, Young Ah Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2023;66(1):12-21. Published online July 4, 2022
-
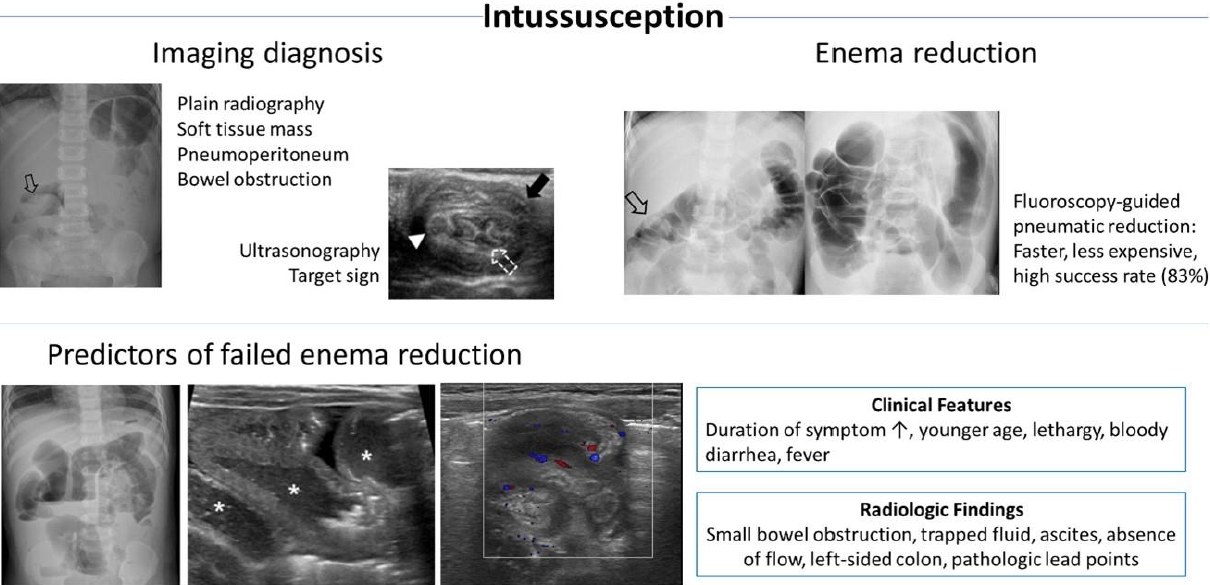
· Intussusception, the most common cause of small bowel obstruction in young children, has an overall incidence in Korea of 28.3 cases per 100,000 person-years.
· Its cause is idiopathic inmost cases, although viral or bacterial gastroenteritis has beenpostulated as a cause. Approximately 4% of children have pathological lead points for intussusception, and Meckel’s diverticulum is the most common cause.
· Intussusception in preterm infants is extremely rare. Older children (>5 years of age) are at increased risk of pathological lead points.
- Infection
- Therapeutics for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 in children and adolescents
- Soo-Han Choi, Jae Hong Choi, Ki Wook Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):377-386. Published online June 27, 2022
-
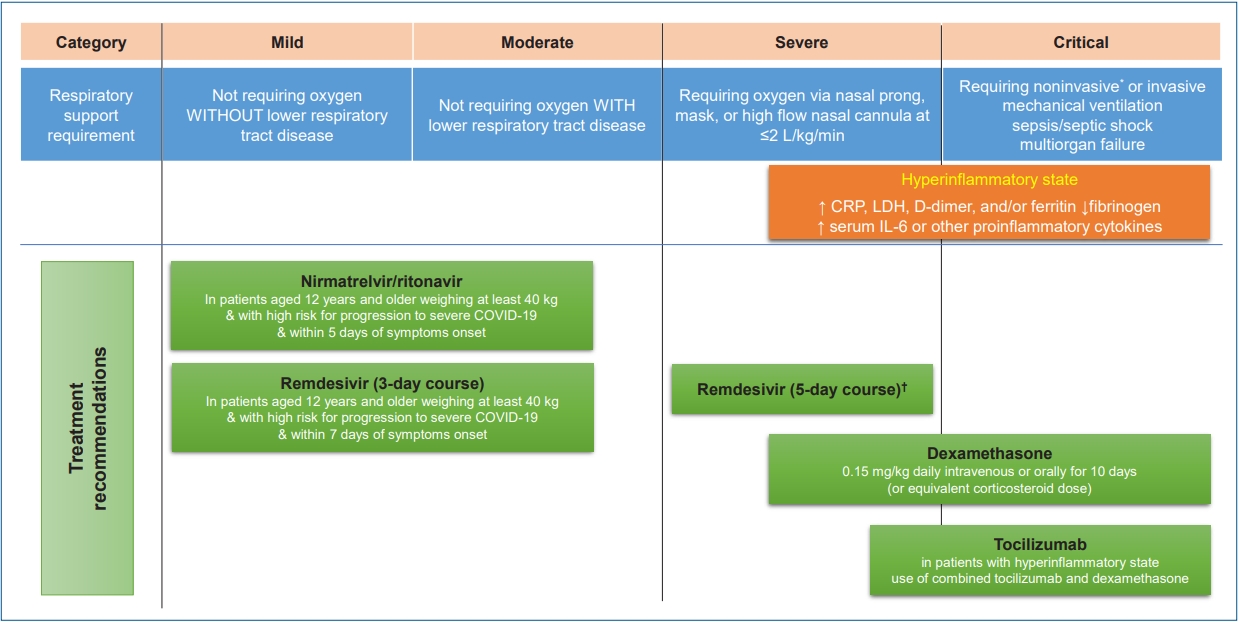
· Children and adolescents with high risks for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) should be identified and proper treatment should be provided promptly according to the patient’s condition.
· Remdesivir can be considered for pediatric patients of all ages with COVID-19 who have an emergent or increase in supplemental oxygen.
· The use of corticosteroids is not recommended for patients with nonsevere COVID-19. Corticosteroids are recommended in children and adolescents with severe and critical COVID-19.
- Original Article
- Hematology
- Effect of cyclic pamidronate administration on osteoporosis in children with β-thalassemia major: a single-center study
- Mahmoud A. El-Hawy, Nagwan Y. Saleh
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):405-409. Published online June 7, 2022
-
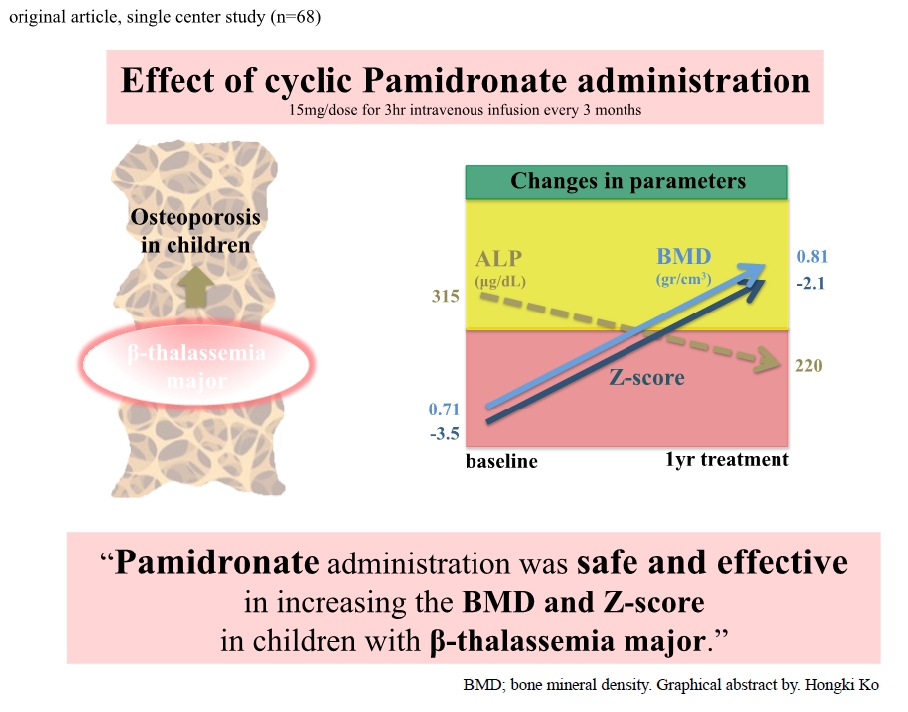
Question: What is the effect of cyclic pamidronate administration on osteoporosis in children with β-thalassemia major?
Finding: The dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry scan findings of children with β-thalassemia major and osteoporosis were improved after pamidronate administration.
Meaning: Cyclic pamidronate effectively treated osteoporosis in children with β-thalassemia major.
- Review Article
- Other
- Epidemiology of pediatric fractures before versus during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic
- Chi Hoon Oh, Siyeong Yoon, Kyung Rae Ko, Young Woo Kwon, Kyeong Mi Kim, Hyun Seo Park, Hogyeong Kang, Inseok Jang, Soonchul Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):330-336. Published online June 3, 2022
-

∙ The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was first reported in December 2019 as a cluster outbreak in Wuhan, since then, national lockdowns have included school closures, stay-at-home orders.
∙ The characteristics of adolescent fractures were often related to physical activity such as sports-related injury.
∙ During the COVID-19 pandemic, both in the East and the West, the incidence of fractures in children and adolescents is showing a decreasing trend worldwide.
∙ Fractures in children and adolescents were significantly reduced in the proportion of relatively low-energy damage, and the incidence of fractures in adolescents with greater activity compared to children was reduced.
∙ If COVID-19 pandemic ends, normal academic and sports activities increase due to the easing of lockdown policies, the number of trauma patients related to increased activity may increase rapidly, and clinics should prepare for this change.
- Neurobehavior
- Jeopardized mental health of children and adolescents in coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic
- Bohyun Jin, Sohee Lee, Un Sun Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):322-329. Published online June 3, 2022
-
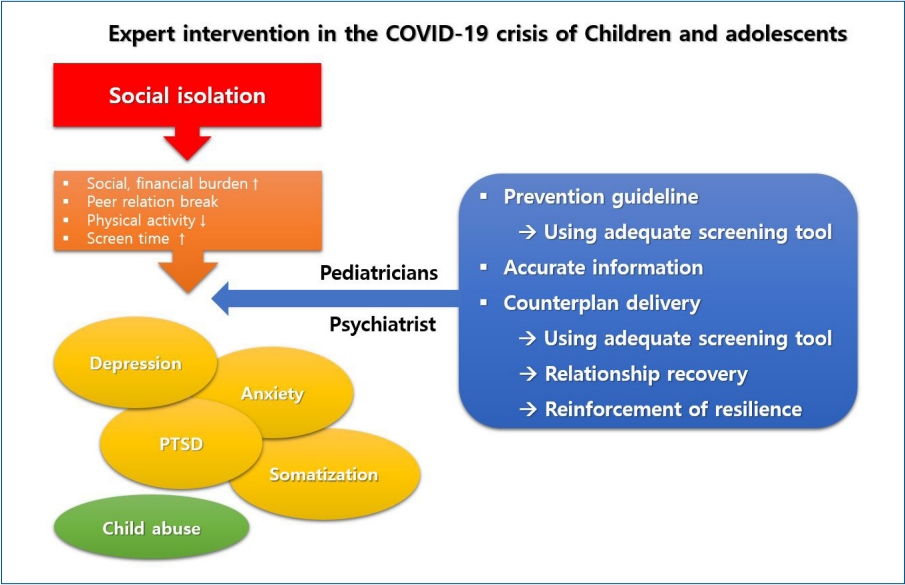
∙ The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has required preventive measures like self-quarantine, school closures, and lockdown, which ultimately make youth directly and indirectly vulnerable to depression, anxiety, posttraumatic stress disorder, and somatization.
∙ Child abuse is more common in the COVID-19 era than previously.
∙ Pediatricians should carefully examine parental and child mental health to directly and indirectly aid their physical and mental health.
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Neonatal hypertension: concerns within and beyond the neonatal intensive care unit
- Kathleen Altemose, Janis M. Dionne
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):367-376. Published online May 30, 2022
-
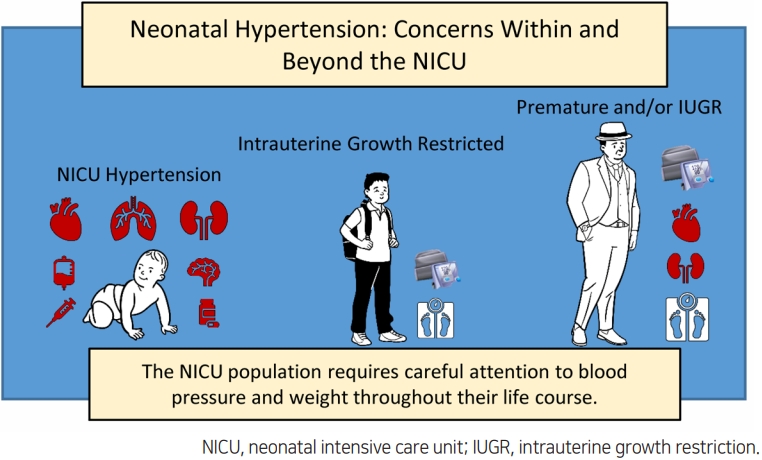
Some neonates, especially those who are premature, may experience hypertension while in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). The most common causes are prematurity-related and the hypertension usually resolves over the first 1–2 years of life. Unfortunately, the increasing population of NICU graduates is at risk for later cardiovascular and kidney disease in childhood and adulthood. This population requires careful attention to blood pressure and weight throughout their life course.
- Original Article
- Oncology
- Treatment outcomes of high-dose chemotherapy plus stem cell rescue in high-risk neuroblastoma patients in Thailand
- Kunanya Suwannaying, Piti Techavichit, Patcharee Komvilaisak, Napat Laoaroon, Nattee Narkbunnam, Kleebsabai Sanpakit, Kanhatai Chiengthong, Thirachit Chotsampancharoen, Lalita Sathitsamitphong, Chalongpon Santong, Panya Seksarn, Suradej Hongeng, Surapon Wiangnon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):453-458. Published online May 24, 2022
-

Question: This study aimed to elucidate the outcomes of high-risk neuroblastoma (HR-NB) patients treated with high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell rescue without immunotherapy.
Finding: The 5-year overall survival and event-free survival rates were 45.1% and 40.4%, respectively.
Meaning: High-dose chemotherapy plus stem cell rescue followed by cis-retinoic acid for 12 months is well tolerated and could improve survival in patients with HR-NB in limited resource settings.
- Other
- Plastic bottle feeding produces changes in biochemical parameters in human infants – A pilot study
- Mahendra K. Pant, Abul. H. Ahmad, Manisha Naithani, Jayanti Pant
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):459-465. Published online May 19, 2022
-

Question: Plastic feeding bottles are used commonly to feed infants who cannot be breastfeed. Does plastic bottle feeding produce biochemical changes in infants?
Finding: The plastic bottles leach out endocrine disruptors and affects bodily functions in terms of biochemical alterations like increased blood urea, raised creatine-kinase–MB levels, and altered lipid profile in infants exposed to bottle feeding.
Meaning: Plastic bottles feeding alters bodily functions in infants.
- Infection
- Role of lung ultrasound patterns in monitoring coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome in children
- Satyabrata Roychowdhoury, Subhajit Bhakta, Manas Kumar Mahapatra, Saptarshi Ghosh, Sayantika Saha, Mithun Chandra Konar, Mihir Sarkar, Mousumi Nandi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):358-366. Published online May 13, 2022
-

Question: Potential role of patterns of lung ultrasonography (US) in monitoring changes in mechanically ventilated patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia.
Finding: Interstitial syndrome, an irregular pleural line, and peripheral microconsolidation were the most prevalent findings. Changes in lung aeration after mechanical ventilation corelated with improved oxygenation. A fall in lung ultrasound reaeration score ≤ 5 may predict successful weaning.
Meaning: Lung US is gaining wider utility for monitoring COVID-19 pneumonia.
- Review Article
- Allergy
- Diagnosis and management of asthma in infants and preschoolers
- Hai Lee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(12):574-584. Published online April 19, 2022
-
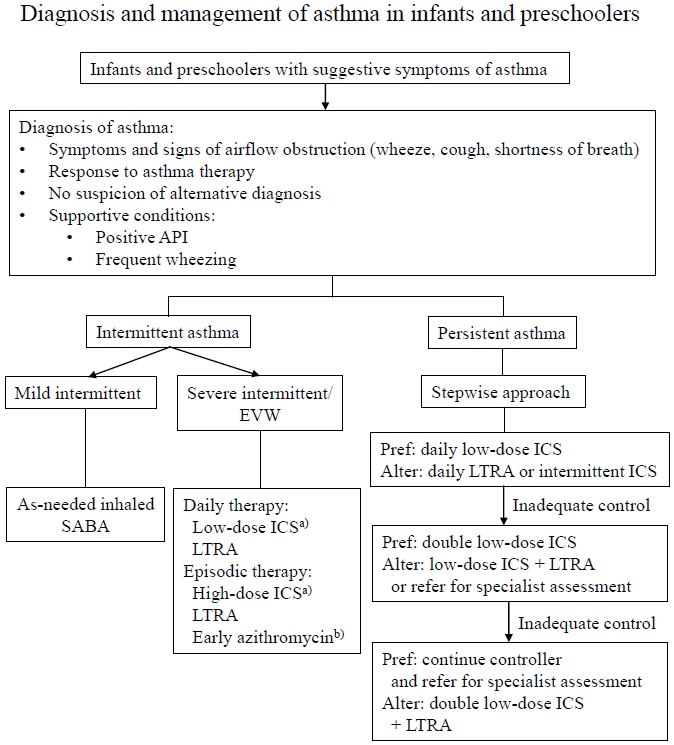
· Asthma in infants and preschoolers involves heterogeneous phenotypes.
· Asthma diagnosis is based on symptom patterns, therapeutic responses, and the presence of risk factors with careful consideration of differential diagnosis.
· Daily inhaled corticosteroid therapy remains the most effective strategy for managing persistent asthma symptoms irrespective of phenotype.
· Future research, including genetic and molecular studies, is needed to develop a clear definition of asthma and personalized therapeutic approaches.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal seizures: stepping outside the comfort zone
- Menna Hashish, Mohamed Reda Bassiouny
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):521-528. Published online April 4, 2022
-
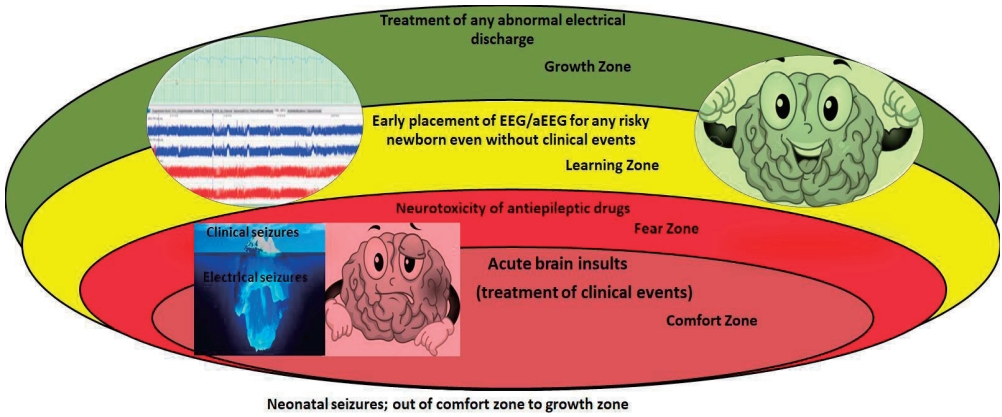
· Use conventional and amplitude-integrated electroencephalography to confirm clinical seizures and screen high-risk newborns.
· Select an explicit clear elective event to be treated with less toxic and more effective antiepileptics.
- Neurology
- Neonatal seizures: diagnostic updates based on new definition and classification
- Eun-Hee Kim, Jeongmin Shin, Byoung Kook Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):387-397. Published online April 4, 2022
-
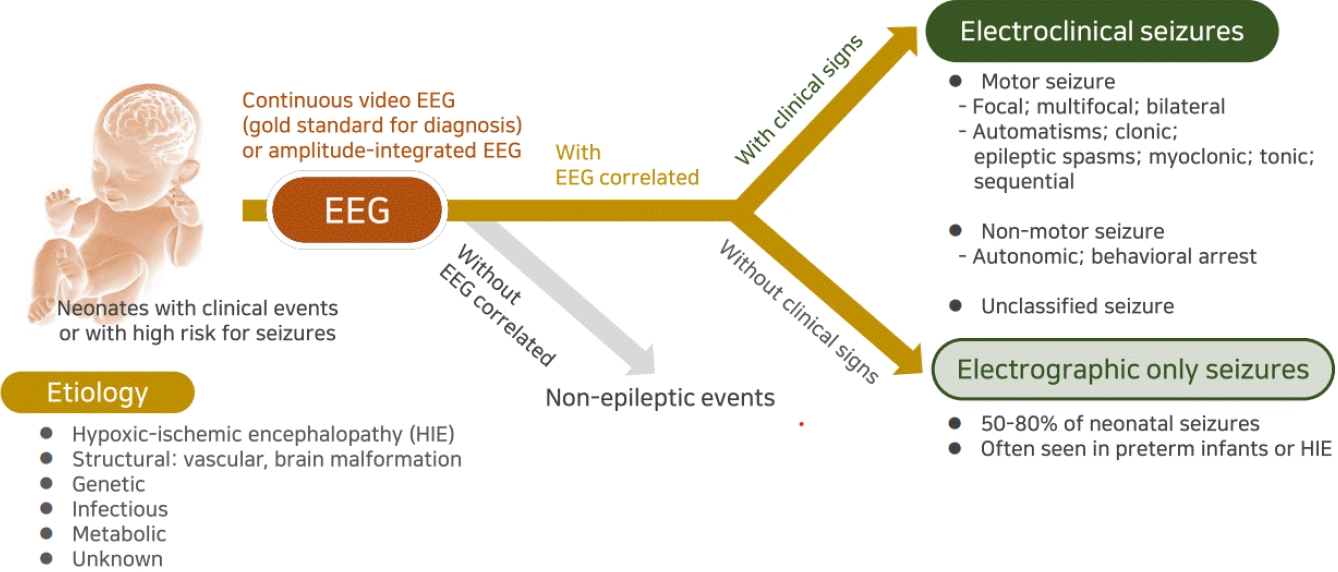
· Neonatal seizures are often electrographic-only seizures without clinical signs; therefore, the identification of electrical seizure activity on electroencephalography is the gold standard for diagnosis.
· Clinical signs of neonatal seizures are divided into motor or nonmotor seizures, and motor seizures are mostly focal or multifocal.
· Most neonatal seizures are caused by acute symptomatic etiologies, but in cases of intractable seizures, structural, genetic, or metabolic etiologies should be investigated.
- General Pediatrics
- Motor performance of children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: focus on the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency
- Khushboo Prashant Adhvaryu, Suruliraj Karthikbabu, Pratiksha Tilak Rao
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(11):512-520. Published online February 17, 2022
-
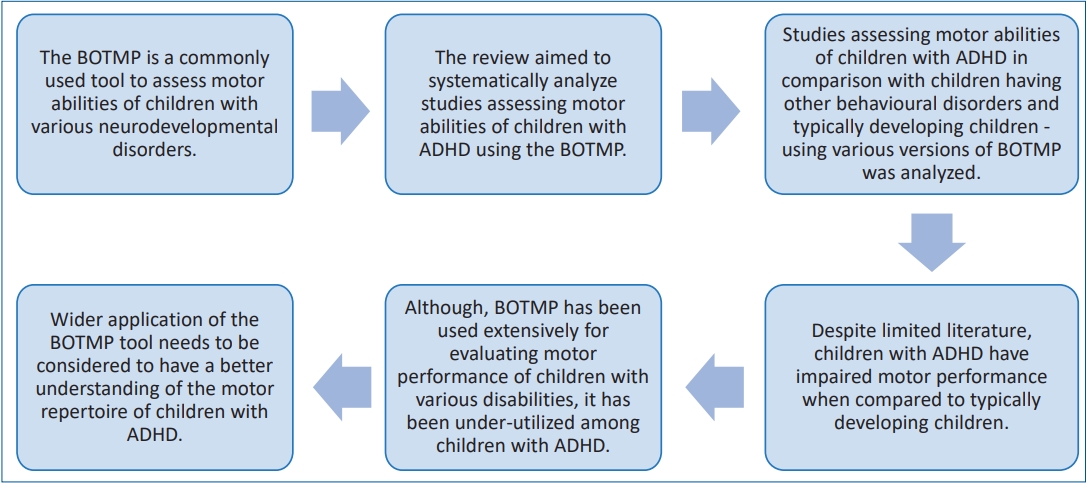
· Children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) tend to have impaired motor performance that may affect their growth and development.
· Although widely used among children with developmental disorders, the Bruininks-Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency (BOTMP) is used sparsely among children with ADHD.
· Assessment by the BOTMP increases our understanding of the motor repertoire of children with ADHD.
· Wider usage of the BOTMP will enable more comprehensive planning of rehabilitation goals to enhance the motor abilities of children with ADHD.
- Neurology
- Rotavirus infection-associated central nervous system complications: clinicoradiological features and potential mechanisms
- Kyung Yeon Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):483-493. Published online February 7, 2022
-

∙ Rotavirus infection-associated central nervous system (CNS) complications are fairly common in children.
∙ Common clinicoradiological features include benign convulsions with mild gastroenteritis, acute encephalopathies/encephalitis, cerebellitis, and neonatal rotavirus-associated leukoencephalopathy.
∙ Possible mechanisms for CNS complications include direct viral invasion into the brain via several potential routes such as the blood-brain barrier and vagus nerve, and entry of various brain-damaging mediators and activated immune cells into the brain.
- Oncology
- Application of 3-dimensional printing implants for bone tumors
- Jong Woong Park, Hyun Guy Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(10):476-482. Published online December 23, 2021
-

∙ The application of 3-dimensional (3D) printing in orthopedic oncology is summarized into bone and tumor modeling, patient-specific instruments (PSIs), custom-made implants, and tissue engineering.
∙ The 3D-printed customized implant is the most central application, while modeling and PSI often play adjunct roles.
∙ Short-term surgical outcomes of custom-made 3D-printed implants are promising.
- Gastroenterology
- Factors influencing development of the infant microbiota: from prenatal period to early infancy
- Sujin Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(9):439-447. Published online December 23, 2021
-
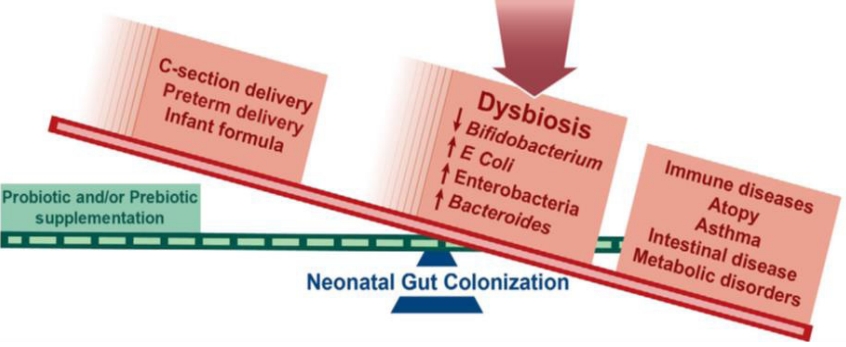
∙ Microbial colonization primarily occurs after birth but there may be some colonization in utero, although this remains highly controversial.
∙ Maternal factors during pregnancy affect the infant microbiota: diet, weight, gestational weight gain, and antibiotic usage.
∙ Microbes are passed from mother-to-infant during and after birth. Delivery mode, breastfeeding, early life antibiotic, and proton pump inhibitor treatment have the largest effects on microbial composition in early life.
∙ The early life gut microbiome plays an important role in the development of the immune system and metabolism.
- Original Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Neonatal sepsis-causing bacterial pathogens and outcome of trends of their antimicrobial susceptibility a 20-year period at a neonatal intensive care unit
- Woo Sun Song, Hye Won Park, Moon Youn Oh, Jae Young Jo, Chae Young Kim, Jung Ju Lee, Euiseok Jung, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim, Ellen Ai-Rhan Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):350-357. Published online December 9, 2021
-
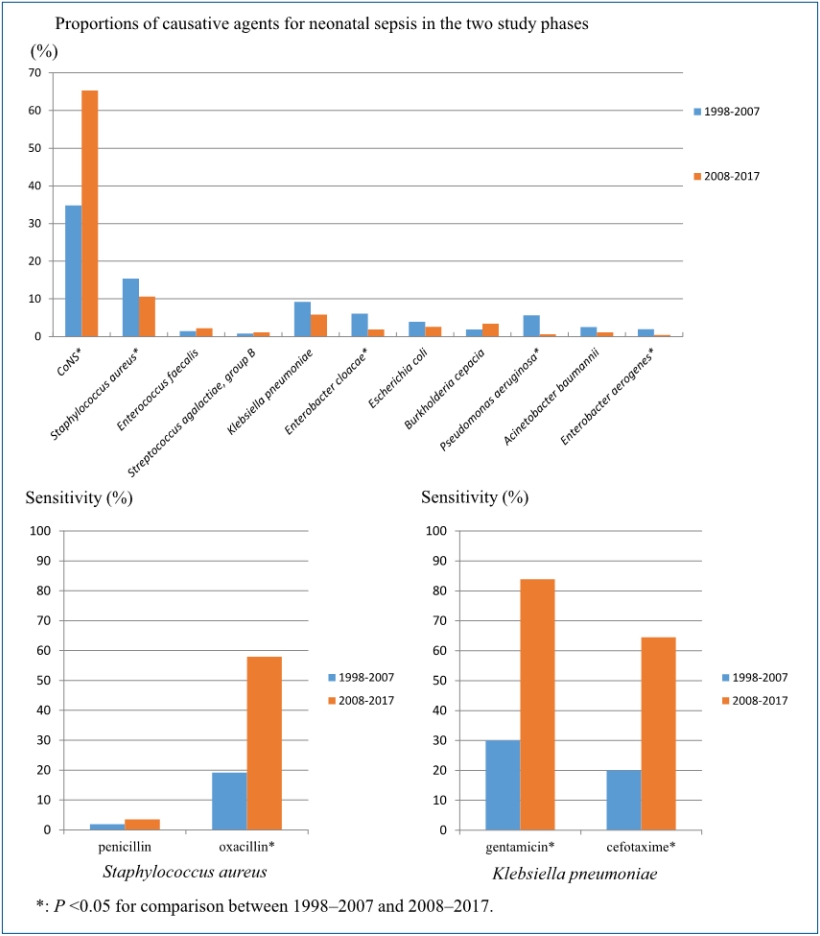
Question: What is prevalence of bacterial pathogens causing sepsis and their antimicrobial susceptibility over 20 years?
Finding: Coagulase-negative remains most common causative organism. The most common gram-negative organism was Klebsiella pneumonia. The susceptibility of staphylococcus aureus and K. pneumonia showed increased susceptability to oxacillin, cefotaxime and amikacin, gentamicin, respectively.
Meaning: Answers to the question asked is important in choosing antimicrobials and to monitor emergence of multidrug-resistant organisms.
- Neurology
- Neurodevelopmental outcomes and comorbidities of children with congenital muscular torticollis: evaluation using the National Health Screening Program for Infants and Children database
- Og Hyang Kim, Seung Won Lee, Eun Kyo Ha, Ju Hee Kim, Yun Hye Jo, Seongyeong Rhie, Man Yong Han, Kyu Young Chae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):312-319. Published online December 9, 2021
-

Question: What comorbidities are increased in children with congenital muscular torticollis (CMT)? Are there differences in the neurodevelopmental outcomes of children with CMT who received physical therapy versus those who did not?
Finding: The risk of congenital musculoskeletal deformities is increased in CMT. Children who did not receive physical therapy were at greater risk of neurodevelopmental delay.
Meaning: In CMT, musculoskeletal comorbidities should be identified and active early treatment provided.
- Review Article
- General Pediatrics
- A new perspective on cholesterol in pediatric health: association of vitamin D metabolism, respiratory diseases, and mental health problems
- Jeana Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(2):65-72. Published online December 9, 2021
-
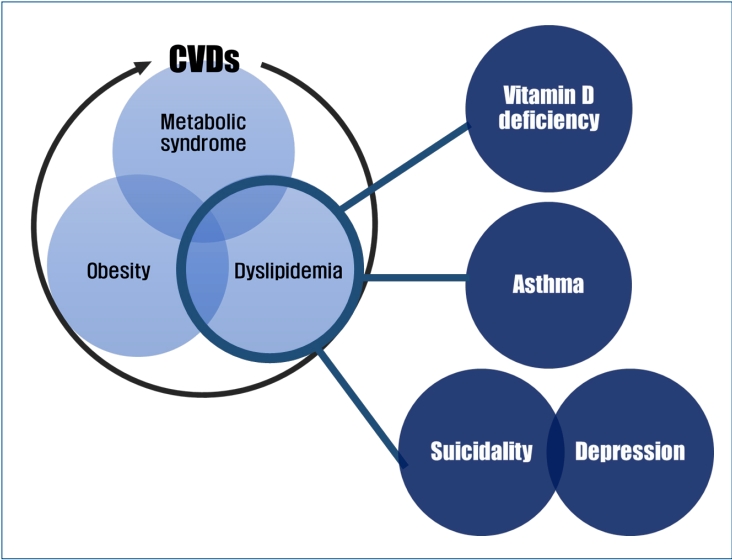
∙ Pediatric dyslipidemia is associated with several health problems besides cardiovascular diseases.
∙ There is a direct association between pediatric dyslipidemia and low serum vitamin D levels, asthma, and mental health problems regardless of body mass index.
∙ More large-scale nationally representative studies are needed to establish the appropriate cutoff points for the definition of dyslipidemia that is a prerequisite for further epidemiological studies in the Korean pediatric population.
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- Early myocardial functional abnormalities in primary dyslipidemia: clinical and echocardiographic observations in young children from a highly consanguineous population
- Nehal M. El-koofy, Aya M. Fattouh, Areef Ramadan, Mohamed A. Elmonem, Dina H. Hamed
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):410-416. Published online December 8, 2021
-
In children with primary dyslipidemia, functional myocardial abnormalities can occur at young age, including diastolic functional impairment of both ventricles and narrowing of the aortic valve and the sinus of Valsalva. Echocardiographic evaluations of high-risk children may be as important as biochemical evaluations.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Epidemiological changes in infectious diseases during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Korea: a systematic review
- Jong Gyun Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):167-171. Published online November 30, 2021
-
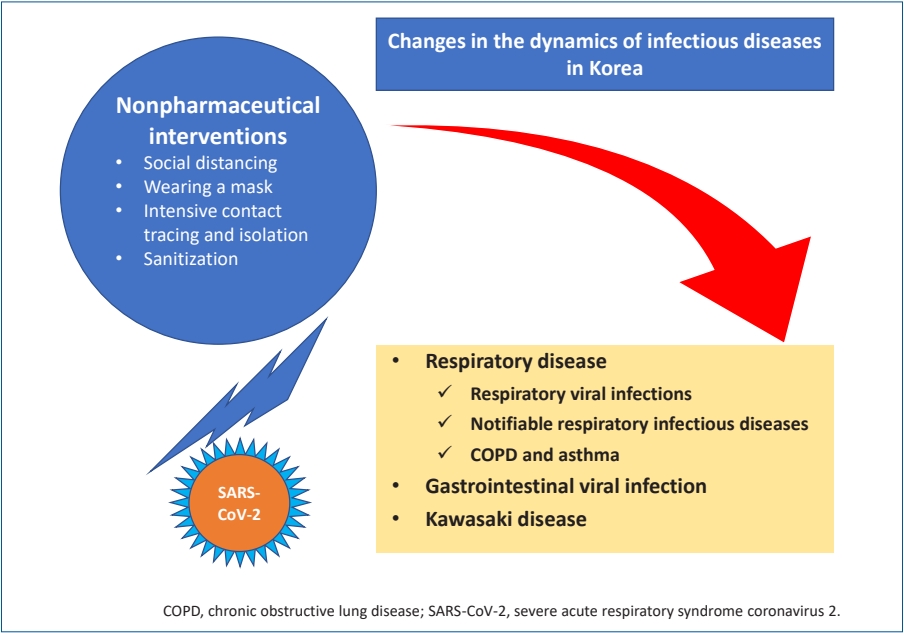
· Nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) have had a major impact on the epidemiology of various infectious diseases in Korea.
· Respiratory diseases and gastrointestinal viral diseases were significantly reduced during the NPI period.
· The decrease in Kawasaki disease after the introduction of NPI is an unintended result.
· Infectious diseases that decreased during NPI use may re-emerge.
· We must continuously monitor the epidemiology of various infectious diseases during the coronavirus era
- Endocrinology
- Pediatric hypertension based on Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines (JSH 2019) with actual school blood pressure screening data in Japan
- Toru Kikuchi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):283-290. Published online November 26, 2021
-
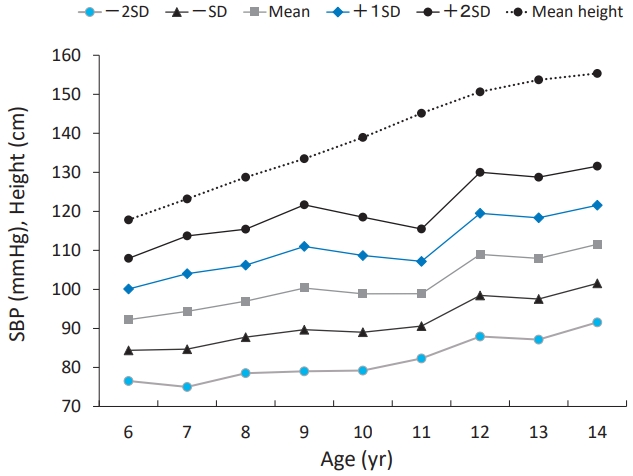
The prevalence of Japanese pediatric hypertension is 0.9% based on proper measurement protocols. Hypertensive children tend to be hypertensive adults. Pediatric essential hypertension is characterized by an absence of symptoms, obesity, a family history of hypertension, and a low birth weight. The most common causes of pediatric secondary hypertension are renal parenchymal and renovascular diseases. Important factors controlling pediatric hypertension include healthy lifestyle modifications and pharmacotherapy.
- Neurology
- Big data analysis and artificial intelligence in epilepsy – common data model analysis and machine learning-based seizure detection and forecasting
- Yoon Gi Chung, Yonghoon Jeon, Sooyoung Yoo, Hunmin Kim, Hee Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):272-282. Published online November 26, 2021
-
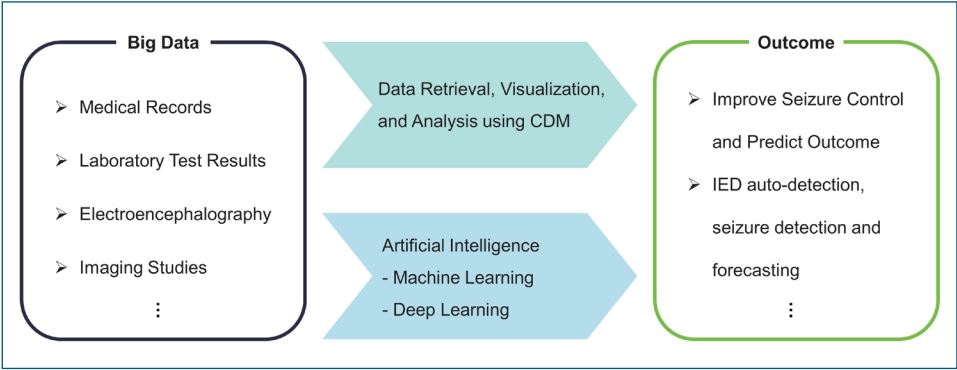
· Big data analysis, such as common data model and artificial intelligence, can solve relevant questions and improve clinical care.
· Recent deep learning studies achieved 0.887–0.996 areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve for automated interictal epileptiform discharge detection.
· Recent deep learning studies achieved 62.3%–99.0% accuracy for interictal-ictal classification in seizure detection and 75.0%– 87.8% sensitivity with a 0.06–0.21/hr false positive rate in seizure forecasting.
- Other
- Knowledge-guided artificial intelligence technologies for decoding complex multiomics interactions in cells
- Dohoon Lee, Sun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):239-249. Published online November 26, 2021
-
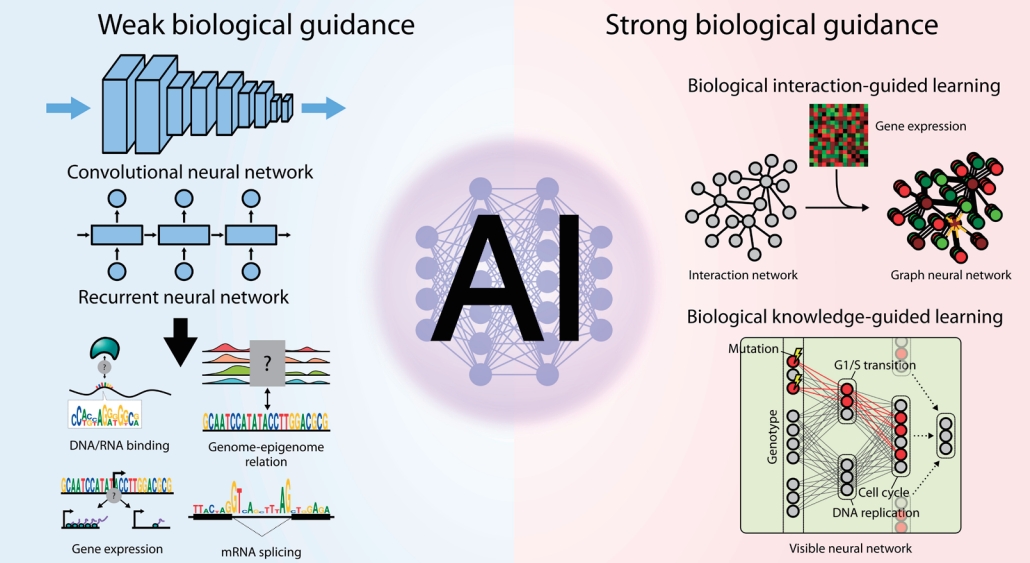
· The need for data-driven modeling of multiomics interactions was recently highlighted.
· Many artificial intelligence-driven models have been developed, but only a few have incorporated biological domain knowledge within model architectures or training procedures.
· Here we provide a comprehensive review of deep learning models to decipher complex multiomics interactions regarding the biological guidance imposed upon them to facilitate further development of biological knowledge-guided deep learning models.
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Effects of probiotics combined with dietary and lifestyle modification on clinical, biochemical, and radiological parameters in obese children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized clinical trial
- Thushara Rodrigo, Samaranayake Dulani, Sumudu Nimali Seneviratne, Arjuna P. De Silva, Jerad Fernando, H. Janaka De Silva, Jayasekera , V. Pujitha Wickramasinghe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):304-311. Published online November 11, 2021
-
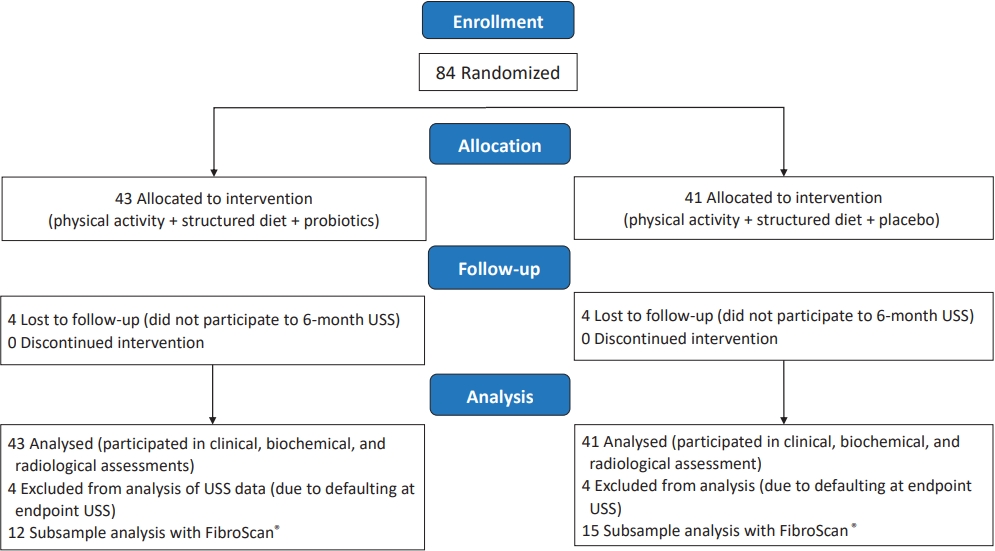
Question: Could probiotics be used as a therapeutic modality in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis?
Finding: There seem no added advantages over lifestyle modifications compared to Probiotics.
Meaning: There does not seem to be an advantage of probiotics over lifestyle modifications in improving obesity-associated metabolic derangement in children.
- Review Article
- Neurobehavior
- Psychological aspects in children and parents of children with chronic kidney disease and their families
- Alemsungla Aier, Priya Pais, Vijaya Raman
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):222-229. Published online November 10, 2021
-
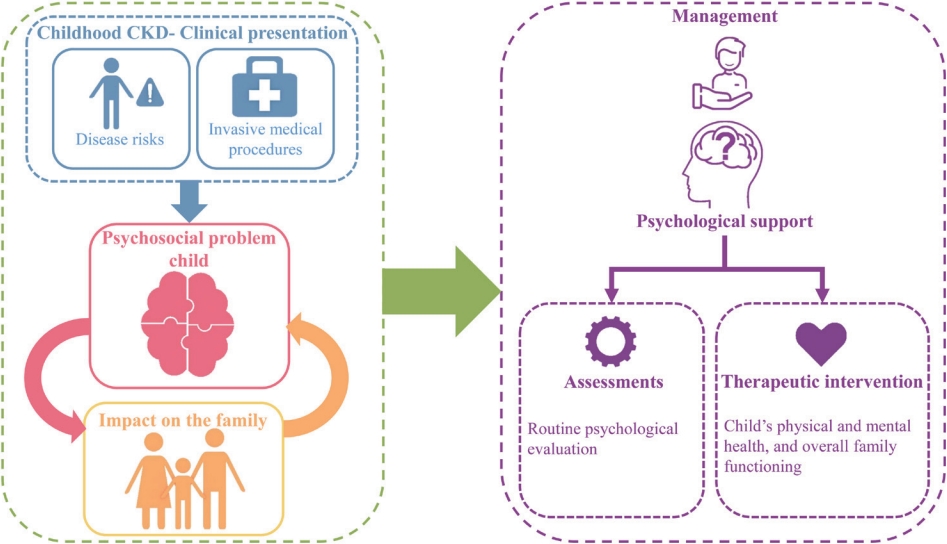
· Childhood chronic kidney disease (CKD) is complex and requires lifetime medical treatment.
· Children with CKD are at risk for emotional, behavioral, social, and academic difficulties that significantly affect their quality of life.
· Caring for children with CKD is stressful for families.
· These unique challenges are crucial and can negatively impact treatment outcomes.
· Awareness of and addressing these evolving psychosocial issues can foster their developing needs.
- Original Article
- Other
- Risk factors and screening timing for developmental dysplasia of the hip in preterm infants
- Ga Won Jeon, Hye Jung Choo, Yong Uk Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):262-268. Published online November 5, 2021
-

Question: When is the best screening timing and what is the risk factor for developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) in preterm infants?
Finding: Ultrasonography performed earlier than 38 weeks of postmenstrual age caused unnecessary subsequent ultrasonography. DDH did not occur predominantly on the left side or in breech infants.
Meaning: The screening timing, etiology, and risk factors for DDH in preterm infants are somewhat different from those in term infants.
-

-
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-









