Infection
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Infection
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (64)
- Cardiology (81)
- Critical Care Medicine (15)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (65)
- Gastroenterology (76)
- General Pediatrics (58)
- Genetics and Metabolism (26)
- Hematology (20)
- Immunology (16)
- Infection (82)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (127)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (54)
- Neurology (96)
- Nutrition (33)
- Oncology (19)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (35)
- Rheumatology (4)
- Other (44)
- Review Article
- Infection
- Therapeutics for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 in children and adolescents
- Soo-Han Choi, Jae Hong Choi, Ki Wook Yun
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(8):377-386. Published online June 27, 2022
-
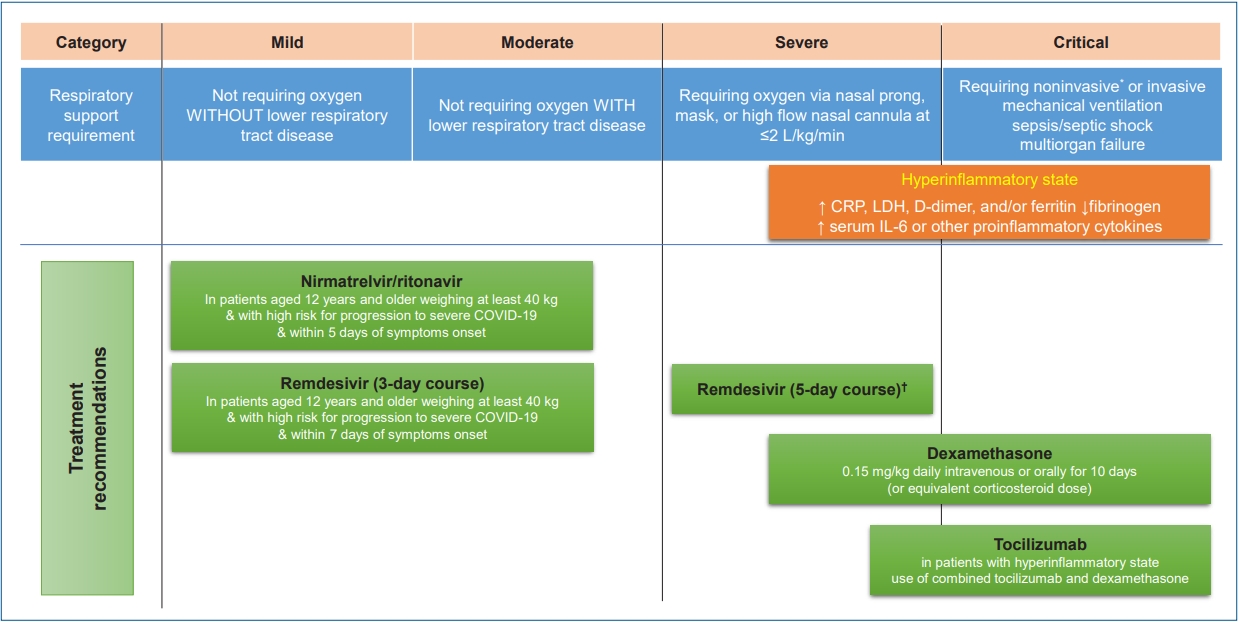
· Children and adolescents with high risks for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) should be identified and proper treatment should be provided promptly according to the patient’s condition.
· Remdesivir can be considered for pediatric patients of all ages with COVID-19 who have an emergent or increase in supplemental oxygen.
· The use of corticosteroids is not recommended for patients with nonsevere COVID-19. Corticosteroids are recommended in children and adolescents with severe and critical COVID-19.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Role of lung ultrasound patterns in monitoring coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome in children
- Satyabrata Roychowdhoury, Subhajit Bhakta, Manas Kumar Mahapatra, Saptarshi Ghosh, Sayantika Saha, Mithun Chandra Konar, Mihir Sarkar, Mousumi Nandi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(7):358-366. Published online May 13, 2022
-

Question: Potential role of patterns of lung ultrasonography (US) in monitoring changes in mechanically ventilated patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia.
Finding: Interstitial syndrome, an irregular pleural line, and peripheral microconsolidation were the most prevalent findings. Changes in lung aeration after mechanical ventilation corelated with improved oxygenation. A fall in lung ultrasound reaeration score ≤ 5 may predict successful weaning.
Meaning: Lung US is gaining wider utility for monitoring COVID-19 pneumonia.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
- Changes in epidemiology of parainfluenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus infection during coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Korea
- Kyung-Ran Kim, Hwanhee Park, Doo Ri Kim, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(6):320-321. Published online March 10, 2022
-
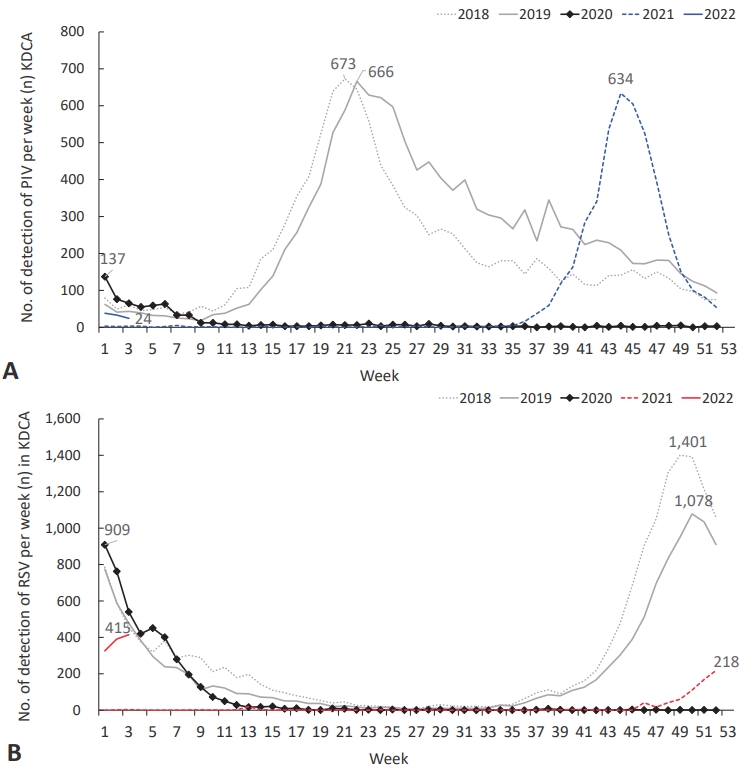
Question: How the epidemiology of other childhood respiratory viruses has changed during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea?
Finding: Parainfluenza virus (PIV) typically circulated in the spring, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) epidemic started in autumn in Korea before COVID-19 pandemic. PIV and RSV seasons disappeared in 2020 and came back in 2021 with atypical seasonality. PIV season was changed from spring to autumn, and the beginning of RSV season was slightly delayed from autumn to early winter in 2021.
Meaning: Circulation of PIV and RSV was changed to unusual seasons and patterns during COVID-19 pandemic period.
- Editorial
- Infection
- Effects of nonpharmaceutical interventions for coronavirus disease 2019
- Jae Hong Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):250-251. Published online March 22, 2022
-
∙ Nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) have decreased the incidence of various infectious diseases, including coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
∙ During the 2-year COVID-19 pandemic, NPIs changed patients’ daily lives, and the impact on mental health was notable.
∙ The effects of NPIs were evaluated in detail, considering both infections and mental health.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Four months of rifampicin monotherapy for latent tuberculosis infection in children
- Chi Eun Oh, Dick Menzies
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(5):214-221. Published online October 29, 2021
-
· Recently, the importance of a short-term treatment regimen including rifamycin has been highlighted in the treatment of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI).
· Four prospective or retrospective studies in children consistently reported that a 4-month daily rifampicin regimen (4R) had a higher completion rate than and comparable safety to a nine-month daily isoniazid regimen.
· We suggest rifampicin 20–30 mg/kg/day for children aged 0–2 years and 15–20 mg/kg/day for children aged 2–10 years in 4R to treat LTBI.
- Epidemiological changes in infectious diseases during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Korea: a systematic review
- Jong Gyun Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):167-171. Published online November 30, 2021
-
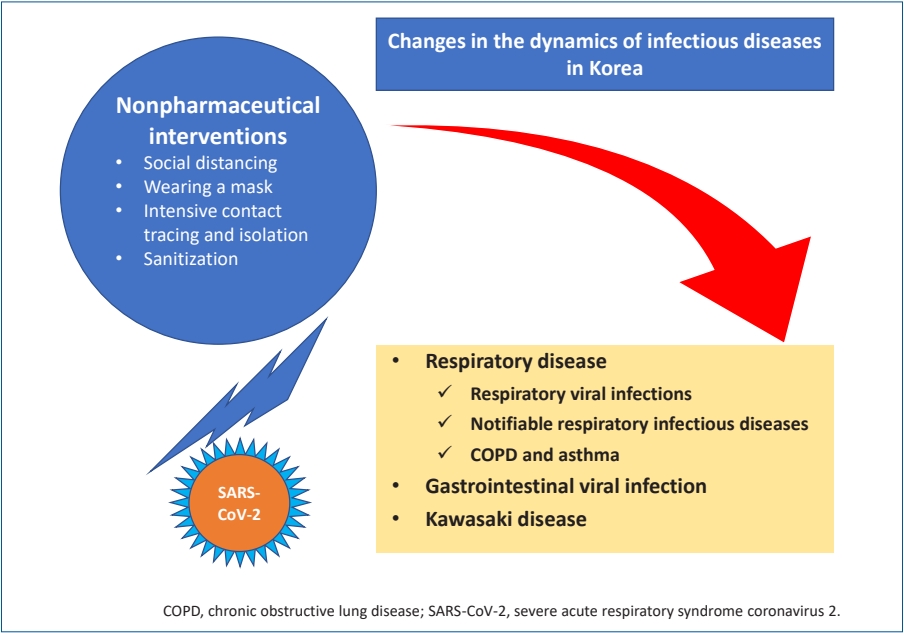
· Nonpharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) have had a major impact on the epidemiology of various infectious diseases in Korea.
· Respiratory diseases and gastrointestinal viral diseases were significantly reduced during the NPI period.
· The decrease in Kawasaki disease after the introduction of NPI is an unintended result.
· Infectious diseases that decreased during NPI use may re-emerge.
· We must continuously monitor the epidemiology of various infectious diseases during the coronavirus era
- Etiological and pathophysiological enigmas of severe coronavirus disease 2019, multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, and Kawasaki disease
- Jung-Woo Rhim, Jin-Han Kang, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(4):153-166. Published online November 23, 2021
-
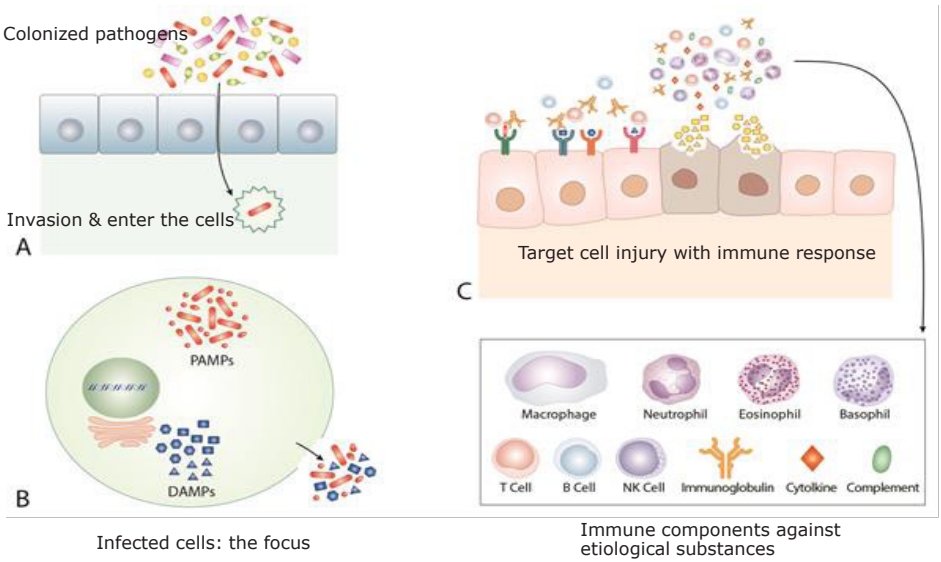
· Severe cases of coronavirus disease, Kawasaki disease (KD), and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) share similar findings: a protracted clinical course, multiorgan involvement, and similar activated biomarkers.
· Here we propose etiological agents in KD and MIS-C as species in the microbiota and introduce a common pathogenesis through the protein-homeostasis-system hypothesis.
· Early proper dose of corticosteroids and/or intravenous immunoglobulin may help to reduce morbidity and mortality in these diseases.
- Editorial
- Infection
- Importance of maintaining a high childhood vaccination rate and surveillance program against Japanese encephalitis in Korea
- Su Eun Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):127-128. Published online February 16, 2022
-

∙ Recent epidemiologic changes of Japanese encephalitis (JE) in Korea are area (rural to urban or suburban) and age shift (children to adult).
∙ Although the main factors contributing to recent epidemiologic changes of JE are not well identified, maintaining high vaccination rates of JE appear to be important in preventing of JE in all age groups.
∙ Continuous surveillance for epidemiology and seroprevalence should be carried out.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Changes in age-specific seroprevalence of Japanese encephalitis virus and impact of Japanese encephalitis vaccine in Korea
- Byung Ok Kwak, Young Jin Hong, Dong Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2022;65(3):108-114. Published online September 24, 2021
-

Since the introduction of a universal Japanese encephalitis (JE) vaccination program and urbanization, the incidence of JE has dramatically decreased in Korea. However, recent JE cases have occurred, predominantly among unvaccinated adults and with a shift in age distribution. Continuous surveillance of the seroprevalence of JE is required to establish a proper immunization policy in Korea.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Viral load and rebound in children with coronavirus disease 2019 during the first outbreak in Daegu city
- Mi Ae Chu, Yoon Young Jang, Dong Won Lee, Sung Hoon Kim, Namhee Ryoo, Sunggyun Park, Jae Hee Lee, Hai Lee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):652-660. Published online October 12, 2021
-
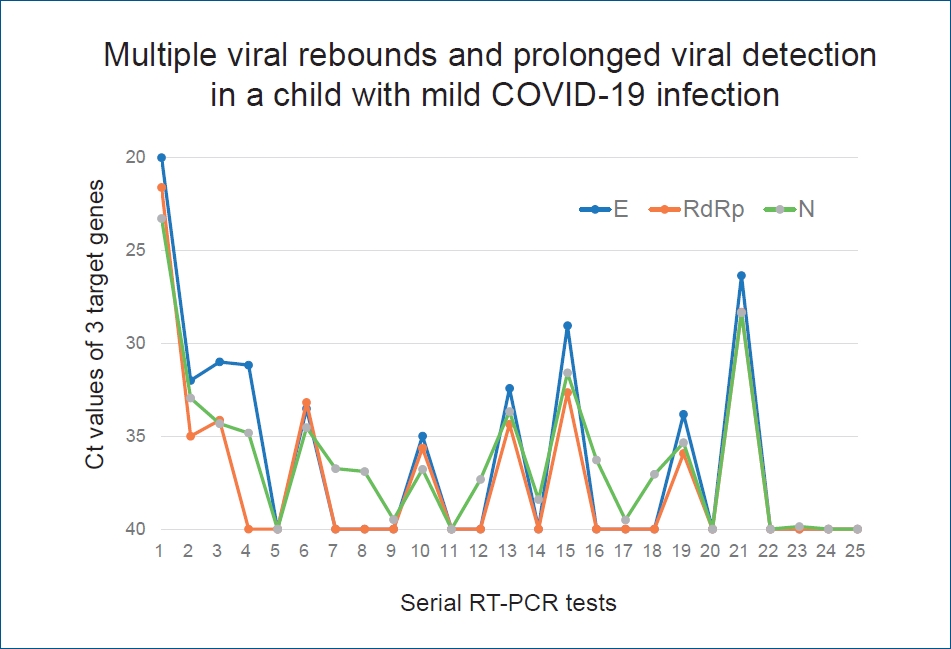
Question: What is the natural course of viral load in children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?
Finding: A significant number of patients still had a relatively high viral load once clinically asymptomatic. Nearly half of the patients experienced viral rebound, which contributed to prolonged viral detection in their respiratory specimens.
Meaning: Further studies are needed to determine the clinical significance of viral rebound in asymptomatic or mild pediatric cases of COVID-19.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Recommendation for use of diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis, inactivated poliovirus, Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate, and hepatitis B vaccine in infants
- Hye-Kyung Cho, Su Eun Park, Yae-Jean Kim, Dae Sun Jo, Yun-Kyung Kim, Byung-Wook Eun, Taek-Jin Lee, Jina Lee, Hyunju Lee, Ki Hwan Kim, Eun Young Cho, Jong Gyun Ahn, Eun Hwa Choi; The Committee on Infectious Diseases of the Korean Pediatric Society
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):602-607. Published online June 8, 2021
-
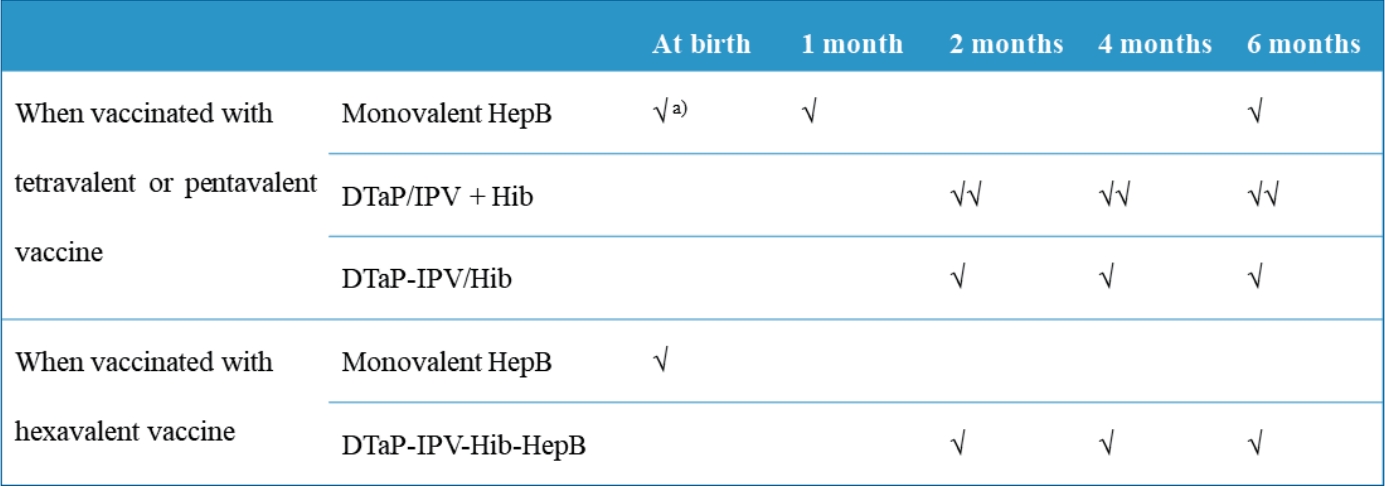
∙ Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis-inactivated poliovirus-Haemophilus influenzae type b-hepatitis B (DTaP-IPV-Hib-HepB) was licensed in Korea in April 2020.
∙ DTaP-IPV-Hib-HepB is indicated as a 3-dose primary series for infants aged 2, 4, and 6 months who received the standalone HepB vaccine at birth.
∙ Infants born to HepB surface antigen-positive mothers are currently recommended to be immunized with HepB immunoglobulin at birth and then monovalent HepB vaccine at 0, 1, and 6 months.
- Letter to the Editor
- Infection
- Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children and Kawasaki disease in infants: 2 sides of the same coin?
- Hing Cheong Kok, Dinesh Nair, Ke Juin Wong, Siew Moy Fong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):599-601. Published online October 7, 2021
-
Question: Are multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) and Kawasaki disease (KD) in infants, 2 sides of the same coin?
Finding: Here we report on a 4-month-old girl with MIS-C and signs of KD with shock. Most (83%) infants with MIS-C had features of KD, especially KD shock syndrome.
Meaning: MIS-C is similar to KD, and likely is a consequence of dysregulated immune responses secondary to sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection.
- Clinical Note
- Infection
- A neonate infected with coronavirus disease 2019 with severe symptoms suggestive of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childhood
- Fatemeh Eghbalian, Ghazal Sami, Saeid Bashirian, Ensiyeh Jenabi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):596-598. Published online September 10, 2021
-
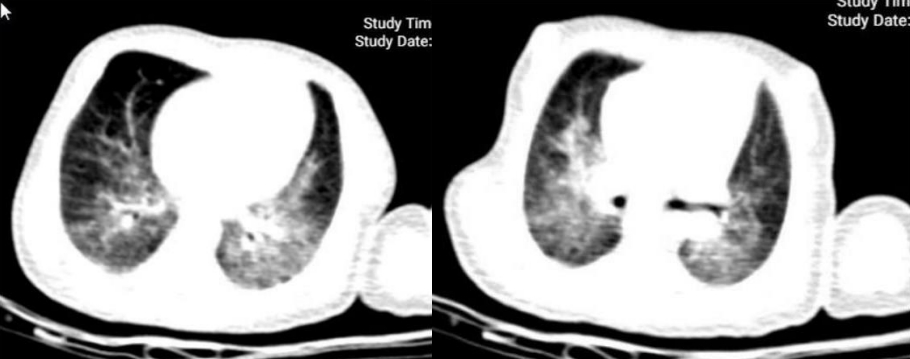
Question: Can multisystem inflammatory syndrome in childhood (MIS-C) occur in the neonate associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?
Finding: A 9-day-old neonate infected with COVID-19 had fever, respiratory distress, and gastrointestinal symptoms suggestive of MIS-C. This neonate recovered after treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG).
Meaning: IVIG successfully treated a rare case of a 9-day-old neonate with COVID-19 and severe symptoms suggestive of MIS-C.
- Original article
- Infection
- The global prevalence of Toxocara spp. in pediatrics: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Behnam Abedi, Mehran Akbari, Sahar KhodaShenas, Alireza Tabibzadeh, Ali Abedi, Reza Ghasemikhah, Marzieh Soheili, Shnoo Bayazidi, Yousef Moradi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):575-581. Published online February 5, 2021
-
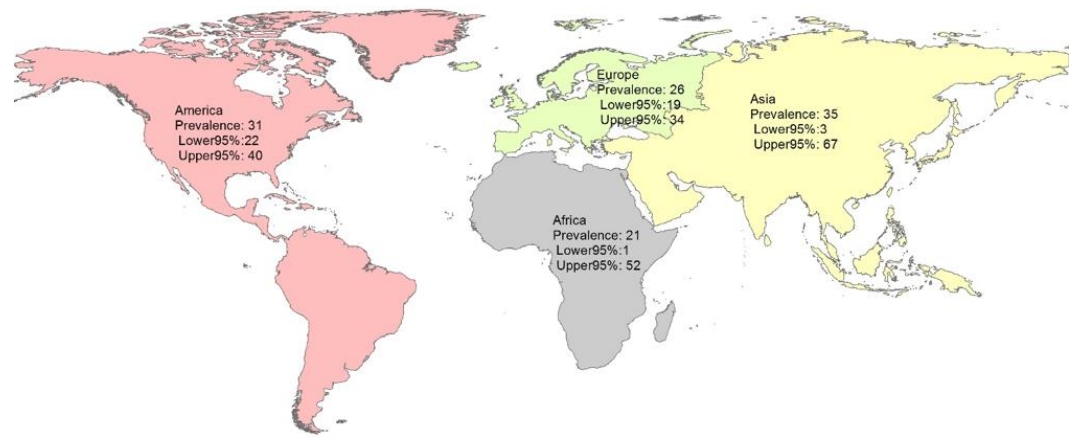
Is the global prevalence of toxocariasis high among children? The prevalence of toxocariasis is high in pediatric patients. Asian children are more susceptible to the disease than other children. Its virulence varies among different socioeconomic classes in various countries. Hand washing after soil contact, routine pet deworming, and appropriate disposal of pet feces in households with Asian pediatrics are needed to prevent toxocariasis.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Effects of nasopharyngeal microbiota in respiratory infections and allergies
- Hyun Mi Kang, Jin Han Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(11):543-551. Published online April 15, 2021
-

· The nasal microbiota varies with age and is shaped by various factors in healthy individuals.
· The pathological condition of the respiratory tract appears to be associated with reduced nasal microbiota biodiversity, while dysbiosis is involved in the pathophysiology of many respiratory diseases, including otitis, sinusitis, allergic diseases, and lower respiratory infections.
- Consideration in treatment decisions for refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia
- Hye-Kyung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(9):459-467. Published online February 10, 2021
-
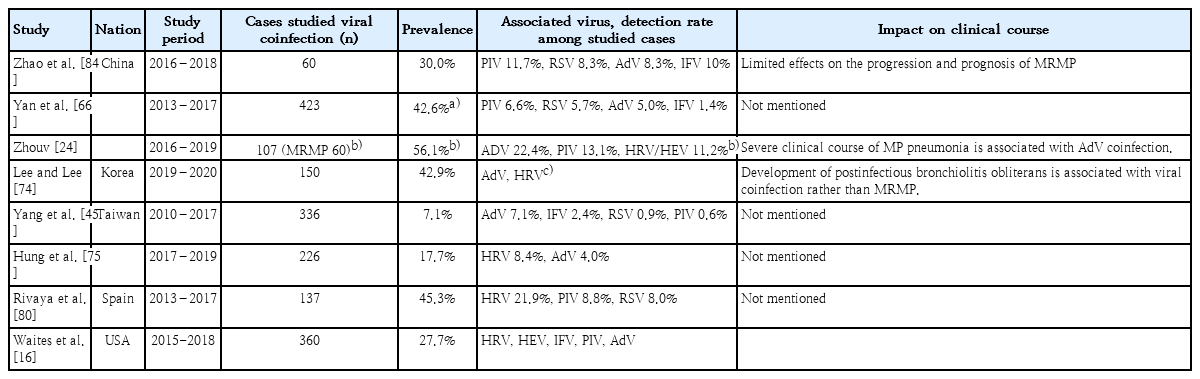
• To avoid unnecessary exposure to secondary antibiotics, it is needed to diagnose Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP) pneumonia carefully, especially when unresponsiveness to macrolide is suspected.
• Serologic and molecular tests for MP infection and excluding respiratory infection caused by other pathogens might be considered.
• It is necessary to continuously monitor antibiotic susceptibility of MP, and efforts to lower antibiotic pressure are required.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Iranian children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Farhad Sarrafzadeh, Seyed Mojtaba Sohrevardi, Hamid Abousaidi, Hossein Mirzaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(8):415-421. Published online November 20, 2020
-

The pooled prevalence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was 42% among culture-positive cases of S. aureus, 51% in hospitalized children, and 14% in healthy children. The high prevalence of MRSA in Iranian children may be due to insufficient infection control measures in hospitals, inappropriate use of methicillin, inadequate staff training, and over-prescription of antibiotics in Iran.
- Review Article
- Infection
- Updates on the coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine and consideration in children
- Hyun Mi Kang, Eun Hwa Choi, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(7):328-338. Published online June 21, 2021
-
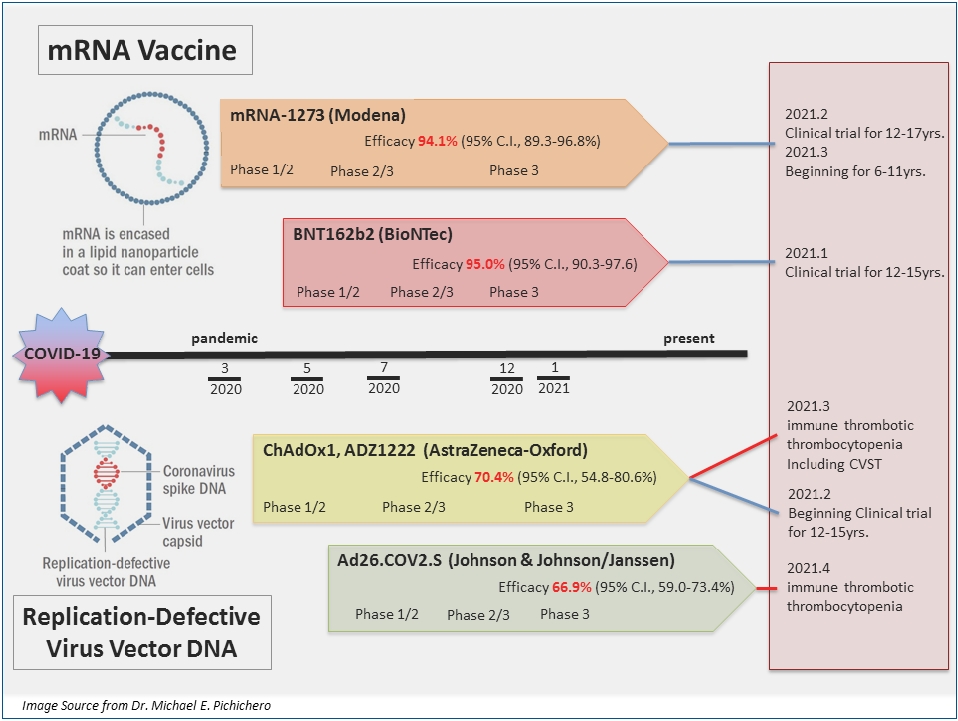
· The number of coronavirus disease 2019 cases has exponentially increased worldwide, and children ≤19 years old account for 11.0% of all confirmed cases.
· mRNA vaccines, BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273, and adenoviral vector vaccines, AZD1222 and Ad26.COV2.S, authorized for emergency use in the Emergency Use Listing of the World Health Organization are reviewed.
· Clinical trials of these vaccines have shown that they are safe and serious adverse reactions are rarely observed.
- School closures during the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak
- Eun Young Cho, Young June Choe
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(7):322-327. Published online May 31, 2021
-
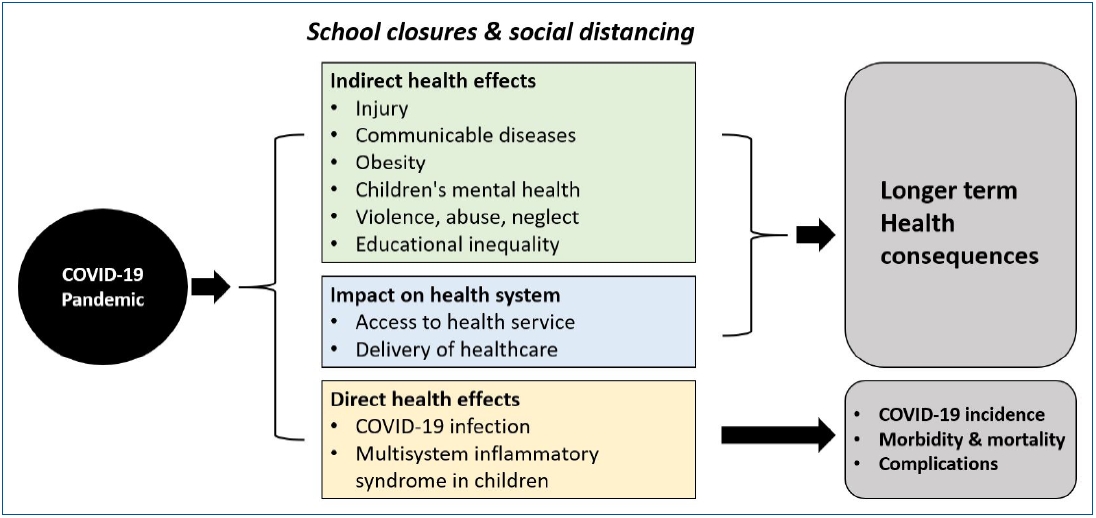
· Earlier modeling studies of the effects of school closures on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 were largely derived from the pandemic influenza model, resulting in conflicting implications.
· Observational findings suggest no clear effect of school closures on community transmission or overall mortality.
· School closures must be weighed against potential high social costs, which can also negatively affect children’s health.
- Original Article
- Infection
- Febrile urinary tract infection in children: changes in epidemiology, etiology, and antibiotic resistance patterns over a decade
- Woosuck Suh, Bi Na Kim, Hyun Mi Kang, Eun Ae Yang, Jung-Woo Rhim, Kyung-Yil Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):293-300. Published online October 14, 2020
-
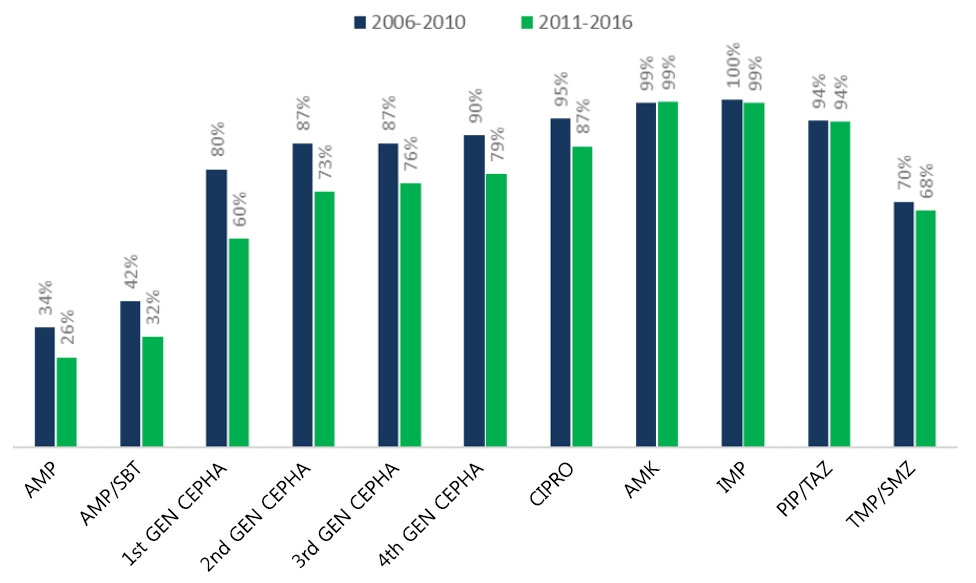
Question: How has the antibiotic susceptibility of urinary pathogens changed and what does it imply?
Finding: A yearly increase in multidrug-resistant and extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)–producing pathogens was observed. A higher recurrence rate was observed in cases of febrile urinary tract infection caused by ESBL producers in patients with underlying vesicoureteral reflux (VUR).
Meaning: The initial empirical antibiotic should reflect the changing susceptibility patterns and underlying VUR status.
- Editorial
- Infection
- Should we prescribe carbapenem for treating febrile urinary tract infection caused by extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in children with vesicoureteral reflux?
- Ji Young Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):284-285. Published online January 5, 2021
-

Recent studies are focused on the noninferiority of noncarbapenem therapy for the treatment of extended-spectrum β-lactamases producing Enterobacteriaceae infections to reduce the utilization of carbapenem.
- Babies born to mothers positive for SARS-CoV-2 – Are they in danger?
- Joon Kee Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(6):280-281. Published online May 4, 2021
-

Concerns have arisen in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic upon pregnancy and postnatal care starting from reproductive decision-making. To the utmost knowledge, reproductive decisions should not be based primarily on health-related COVID-19 concerns, as the possibility of vertical transmission is negligible and the perinatal outcome is generally not poor compared to pregnancies without COVID-19, as long as infection control measures are well kept.
- Clinical note
- Infection
- Coronavirus disease 2019 in a 13-year-old patient with acute lymphoblastic leukemia
- Seyed Kamal Eshagh Hossaini, Zahra Movahedi, Ahmad Hormati, Hosein Heydari, Seyed Jalal Eshagh Hosseini, Fatemeh Khodadust, Mahboubeh Afifian, Sajjad Ahmadpour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(5):247-250. Published online March 8, 2021
-
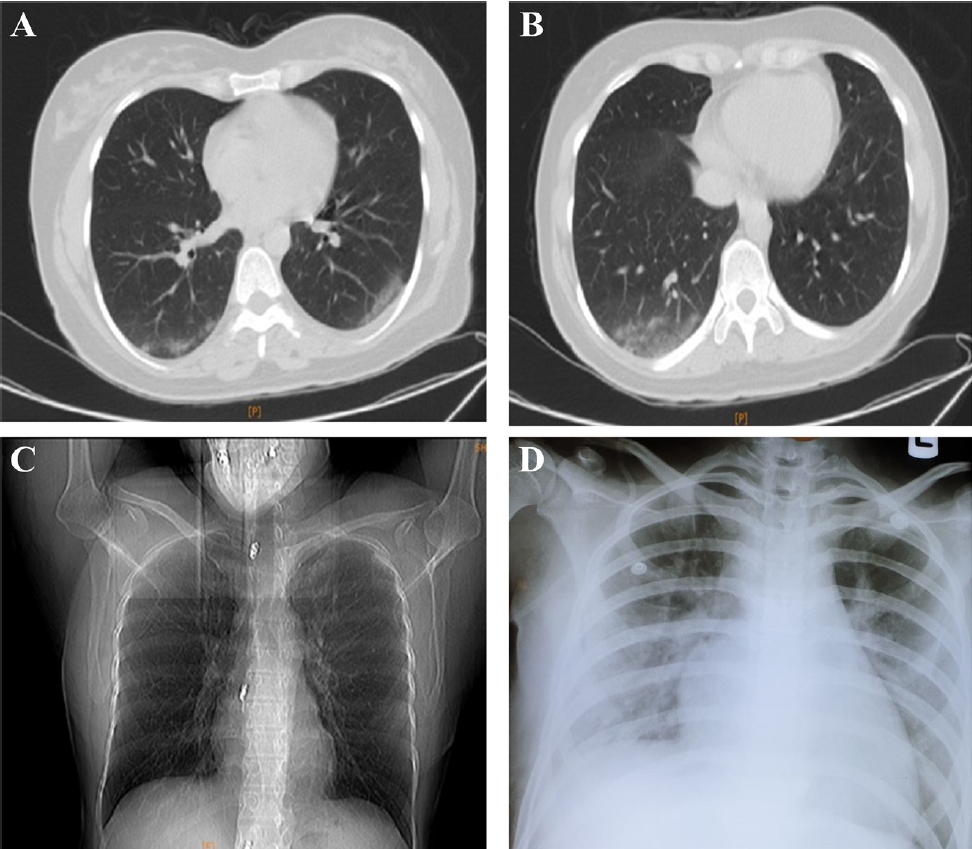
Question: What should be considered in an immunocompromised child with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?
Finding: Due to the importance of appropriately managing COVID-19 in children with cancer, the possibility of a fatal outcome should be considered in immunocompromised patients who receive chemotherapy agents.
Meaning: In all kinds of infections including COVID-19, disuse management and the development of international guidelines for children with cancer is challenging but important.
- Editorial
- Infection
- Catheter care bundle and feedback to prevent central line-associated bloodstream infections in pediatric patients
- Hye-Kyung Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(3):119-120. Published online December 8, 2020
-
• Intravascular catheter-related infection is an important cause of morbidity and mortality in children, and care bundles are effective and cost-saving in pediatric and neonatal patients.
• Providing regular feedbacks to critical care practitioners is helpful to maintain compliance to care bundle.
• Establishing a bundle policy (insertion and maintenance), monitoring compliance, and providing regular feedbacks are necessary for prevention of central line-associated bloodstream infections in pediatric patients.
- Perspective
- Infection
- Addressing children’s health amid the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic
- Young June Choe, Bilal Aurang Zeb Durrani, Stefan Swartling Peterson
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(2):46-48. Published online December 15, 2020
-
In the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, children experience heightened barriers to health and protective services. Children may also be disproportionately affected due to their reliance on the education system for daily tasks and lack of access to remote learning options. Republic of Korea findings on how vaccination coverage could be sustained in children and schools could be reopened without aggravating COVID-19 underlie the need for coordinated efforts across sectors.
- Clinical note
- Infection
- Coronavirus disease 2019 in a 2-month-old male infant: a case report from Iran
- Hosein Heydari, Seyed Kamal Eshagh Hossaini, Ahmad Hormati, Mahboubeh Afifian, Sajjad Ahmadpour
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):499-502. Published online September 21, 2020
-
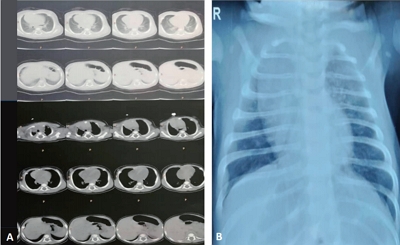
- Review Article
- Infection
- The COVID-19 pandemic: an unprecedented tragedy in the battle against childhood obesity
- Maximilian Andreas Storz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(12):477-482. Published online November 5, 2020
-

Large-scale quarantine and home confinement during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic will impose new and unfamiliar stressors on children, thereby worsening the childhood obesity epidemic. Physical, nutritional, and psychosocial factors that promote obesity in children during this special situation complementarily contribute to an unprecedented obesogenic environment. Involved stakeholders, including governments, schools, and families, must make all efforts to minimize the impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on childhood obesity.
- Editorial
- Infection
- What are considerations for neonates at risk for COVID-19?
- Soo-Han Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):359-360. Published online July 17, 2020
-

- Perspective
- Infection
- Can we get a clue for the etiology of Kawasaki disease in the COVID-19 pandemic?
- Jong-Woon Choi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(9):335-336. Published online July 13, 2020
-
A new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has been spreading globally since December 2019. Children with a Kawasaki disease (KD)-like illness related with COVID-19 have been reported in Europe and the United States. They presented with symptoms of KD with or without cardiac abnormalities or shock, showing manifestations of hyperactive proinflammatory cytokine reactions like KD. Such cases may provide the opportunity for us to learn more about the etiology and pathogenesis of KD.
- Editorial
- Infection
- Pneumococcal conjugate vaccines: choice of schedule and product development
- Jin Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(7):259-260. Published online April 27, 2020
-

-

-

-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.











