Topics
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- TOPICS
- Topics
- Topics
-
- Adolescence Medicine (4)
- Allergy (61)
- Cardiology (79)
- Critical Care Medicine (10)
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine (24)
- Emergency Medicine (5)
- Endocrinology (60)
- Gastroenterology (65)
- General Pediatrics (46)
- Genetics and Metabolism (24)
- Hematology (15)
- Immunology (15)
- Infection (73)
- Neonatology (Perinatology) (119)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary) (52)
- Neurology (94)
- Nutrition (30)
- Oncology (16)
- Neurobehavior (12)
- Pulmonology (30)
- Rheumatology (3)
- Other (36)
- Original Article
- Cardiology
- The improvement of right ventricular function after adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnea
- Dong Yeop Kim, Kyung Ok Ko, Jae Woo Lim, Jung Min Yoon, Young Hwa Song, Eun Jeong Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(12):392-396. Published online October 26, 2018
-
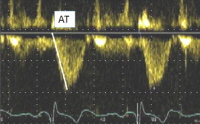
Purpose: Adenotonsillar hypertrophy (ATH) that causes upper airway obstruction might lead to chronic hypoxemic pulmonary vasoconstriction and right ventricular (RV) dysfunction. We aimed to evaluate whether adenotonsillectomy (T&A) in children suffering from obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) due to severe ATH could improve RV function. Methods: Thirty-seven children (boy:girl=21:16; mean age, 9.52±2.20 years), who underwent T&A forsleep apnea due to ATH, were...
- Neurology
- The clinical characteristics and prognosis of subgaleal hemorrhage in newborn
- Sun Jin Lee, Jin Kyu Kim, Sun Jun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(12):387-391. Published online September 16, 2018
-
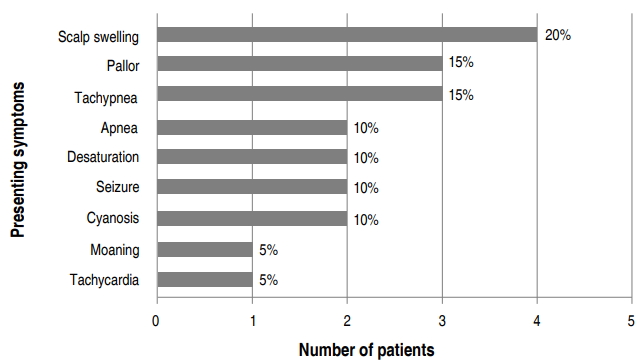
Purpose: Subgaleal hemorrhage (SGH) is a rare but potentially fatal condition in newborns; however, few studies have reported on this condition. We aimed to identify the clinical characteristics and prognostic factors of SGH. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 20 neonates diagnosed with SGH between January 2000 and June 2017. Enrolled neonates were clinically diagnosed when they had tender...
- General Pediatrics
- Current use of safety restraint systems and front seats in Korean children based on the 2008–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Seom Gim Kong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(12):381-386. Published online September 19, 2018
-

Purpose: The use of proper safety restraint systems by children is vital for the reduction of traffic accident-related injury and death. This study evaluated the rates of use of safety restraint systems and front seats by Korean children. Methods: Based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2008 to 2015, I investigated the frequencies of safety restraint...
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- The adiposity rebound in the 21st century children: meaning for what?
- Min Jae Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(12):375-380. Published online December 6, 2018
-
With the increase in the prevalence of overweight and obesity worldwide, early adiposity rebound, which is known to have a strong association with obesity, has recently been a focus of research. Early adiposity rebound is conventionally known to have a close relationship with non-communicable diseases. However, novel insights into early adiposity rebound have implied an acceleration of growth and puberty,...
- Case Report
- Infection
- Scabies mimicking graft versus host disease in a hematopoietic cell transplant recipient
- Dongsub Kim, Soo-Han Choi, Dong Youn Lee, Juyoun Kim, Eunjoo Cho, Keon Hee Yoo, Hong Hoe Koo, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(11):371-373. Published online November 9, 2018
-
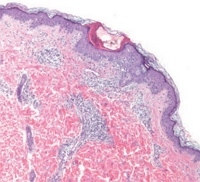
Scabies is a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the mite, Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis. Complex responses to scabies mites in the innate, humoral, and cellular immune systems can cause skin inflammation and pruritus. Diagnosis can be challenging because scabies resembles other common skin conditions. We report the first Korean case of scabies in a hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) recipient,...
- Original Article
- Infection
- A contact investigation after exposure to a child with disseminated tuberculosis mimicking inflammatory bowel disease
- Dongsub Kim, Sodam Lee, Sang-Hee Kang, Mi-Sun Park, So-Young Yoo, Tae Yeon Jeon, Joon-Sik Choi, Bora Kim, Jong Rim Choi, Sun Young Cho, Doo Ryeon Chung, Yon Ho Choe, Yae-Jean Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(11):366-370. Published online November 15, 2018
-
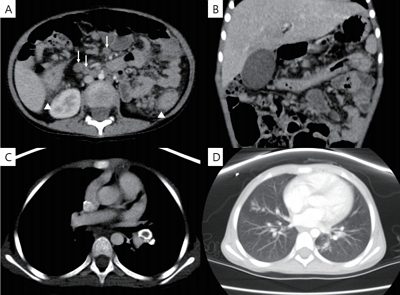
Purpose: Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the most important diseases that cause significant mortality and morbidity in young children. Data on TB transmission from an infected child are limited. Herein, we report a case of disseminated TB in a child and conducted a contact investigation among exposed individuals. Methods: A 4-year-old child without Bacille Calmette-Guérin vaccination was diagnosed as having culture-proven...
- Cardiology
- The change of QRS duration after pulmonary valve replacement in patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot and pulmonary regurgitation
- Yuni Yun, Yeo Hyang Kim, Jung Eun Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(11):362-365. Published online October 24, 2018
-
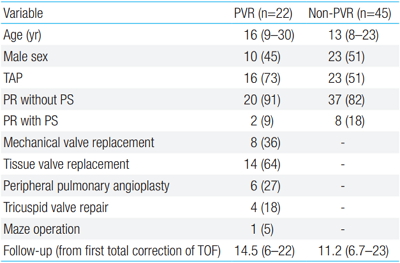
Purpose: This study aimed to analyze changes in QRS duration and cardiothoracic ratio (CTR) following pulmonary valve replacement (PVR) in patients with tetralogy of Fallot (TOF). Methods: Children and adolescents who had previously undergone total repair for TOF (n=67; median age, 16 years) who required elective PVR for pulmonary regurgitation and/or right ventricular out tract obstruction were included in this study....
- Neurology
- Clinical manifestations of headache in children younger than 7 years
- Bu Seon Kang, Jinsun Lee, Jin Hyuk Choi, Hyeok Hee Kwon, Joon Won Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(11):355-361. Published online September 16, 2018
-
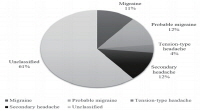
Purpose: Headache is a common symptom during childhood. It is usually persistent and requires special care. This study aimed to identify the characteristics of headache in children <7 years of age. Methods: We reviewed 3 years of clinical files on children <7 years of age with a chief complaint of headache. Results: This study included 146 children (66 males, 80 females; mean...
- Allergy
- Common features of atopic dermatitis with hypoproteinemia
- So Yoon Jo, Chan-Ho Lee, Woo-Jin Jung, Sung-Won Kim, Yoon-Ha Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(11):348-354. Published online September 16, 2018
-
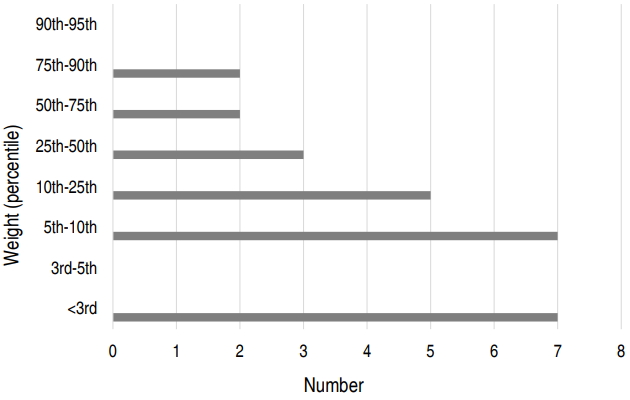
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to identify the causes, symptoms, and complications of hypoproteinemia to prevent hypoproteinemia and provide appropriate treatment to children with atopic dermatitis. Methods: Children diagnosed with atopic dermatitis with hypoproteinemia and/or hypoalbuminemia were retrospectively reviewed. The patients’ medical records, including family history, weight, symptoms, treatment, complications, and laboratory test results for allergies and skin cultures,...
- Review Article
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Acute kidney injury and continuous renal replacement therapy in children; what pediatricians need to know
- Myung Hyun Cho, Hee Gyung Kang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(11):339-347. Published online October 23, 2018
-
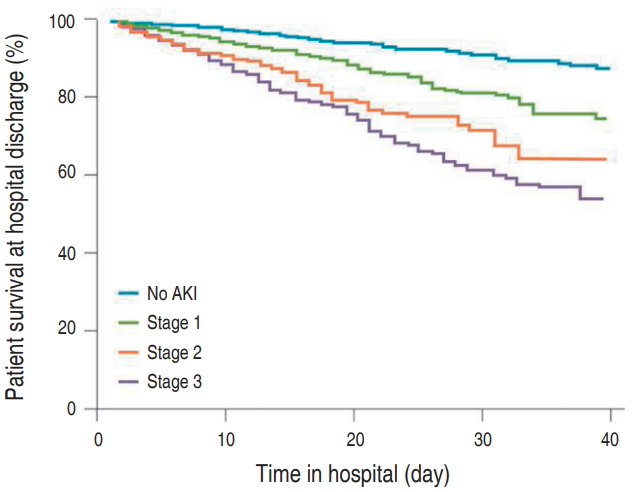
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is characterized by abrupt deterioration of renal function, and its diagnosis relies on creatinine measurements and urine output. AKI is associated with higher morbidity and mortality, and is a risk factor for development of chronic kidney disease. There is no proven medication for AKI. Therefore, prevention and early detection are important. Physicians should be aware of...
- Original Article
- Neurology
- Comparison of conservative therapy and steroid therapy for Bell’s palsy in children
- Hye Won Yoo, Lira Yoon, Hye Young Kim, Min Jung Kwak, Kyung Hee Park, Mi Hye Bae, Yunjin Lee, Sang Ook Nam, Young Mi Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):332-337. Published online September 12, 2018
-

Purpose: Bell’s palsy is characterized by sudden onset of unilateral facial weakness. The use of corticosteroids for childhood Bell’s palsy is controversial. This study aimed to identify clinical characteristics, etiology, and laboratory findings in childhood Bell’s palsy, and to evaluate the efficacy of corticosteroid treatment. Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of children under 19 years of age treated for Bell’s...
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Renal involvement in children and adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease
- Hea Min Jang, Hee Sun Baek, Jung-Eun Kim, Ju Young Kim, Yeon Hee Lee, Hee Yeon Cho, Yon Ho Choe, Ben Kang, Byung-Ho Choe, Bong Seok Choi, Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):327-331. Published online September 12, 2018
-

Purpose: The incidence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is rapidly increasing, and several reports have described the renal complications of IBD. We sought to evaluate the clinical manifestations of renal complications in children with IBD in order to enable early detection and prompt treatment of the complications. Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 456 children and adolescents aged <20...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Evaluation of prolonged pain in preterm infants with pneumothorax using heart rate variability analysis and EDIN (Échelle Douleur Inconfort Nouveau-Né, neonatal pain and discomfort scale) scores
- Mehmet Buyuktiryaki, Nurdan Uras, Nilufer Okur, Mehmet Yekta Oncel, Gulsum Kadioglu Simsek, Sehribanu Ozluer Isik, Serife Suna Oguz
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):322-326. Published online September 16, 2018
-
Purpose: The EDIN scale (Échelle Douleur Inconfort Nouveau-Né, neonatal pain and discomfort scale) and heart rate variability has been used for the evaluation of prolonged pain. The aim of our study was to assess the value of the newborn infant parasympathetic evaluation (NIPE) index and EDIN scale for the evaluation of prolonged pain in preterm infants with chest tube placement...
- Transient intubation for surfactant administration in the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in extremely premature infants
- Ji Won Koh, Jong-Wan Kim, Young Pyo Chang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):315-321. Published online September 16, 2018
-
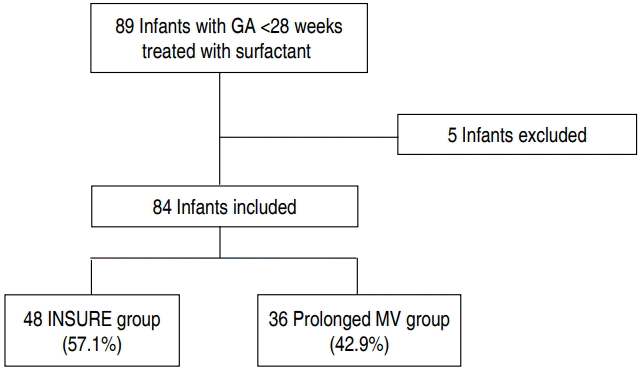
Purpose: To investigate the effectiveness of transient intubation for surfactant administration and extubated to nasal continuous positive pressure (INSURE) for treatment of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and to identify the factors associated with INSURE failure in extremely premature infants. Methods: Eighty-four infants with gestational age less than 28 weeks treated with surfactant administration for RDS for 8 years were included. Perinatal...
- Review Article
- Endocrinology
- Understanding of type 1 diabetes mellitus: what we know and where we go
- Chong Kun Cheon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(10):307-314. Published online October 4, 2018
-

The incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) in children and adolescents is increasing worldwide. Combined effects of genetic and environmental factors cause T1DM, which make it difficult to predict whether an individual will inherit the disease. Due to the level of self-care necessary in T1DM maintenance, it is crucial for pediatric settings to support achieving optimal glucose control, especially...
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- The changes of prevalence and etiology of pediatric pneumonia from National Emergency Department Information System in Korea, between 2007 and 2014
- Eun Ju Shin, Yunsun Kim, Jin-Young Jeong, Yu Mi Jung, Mi-Hee Lee, Eun Hee Chung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(9):291-300. Published online September 15, 2018
-
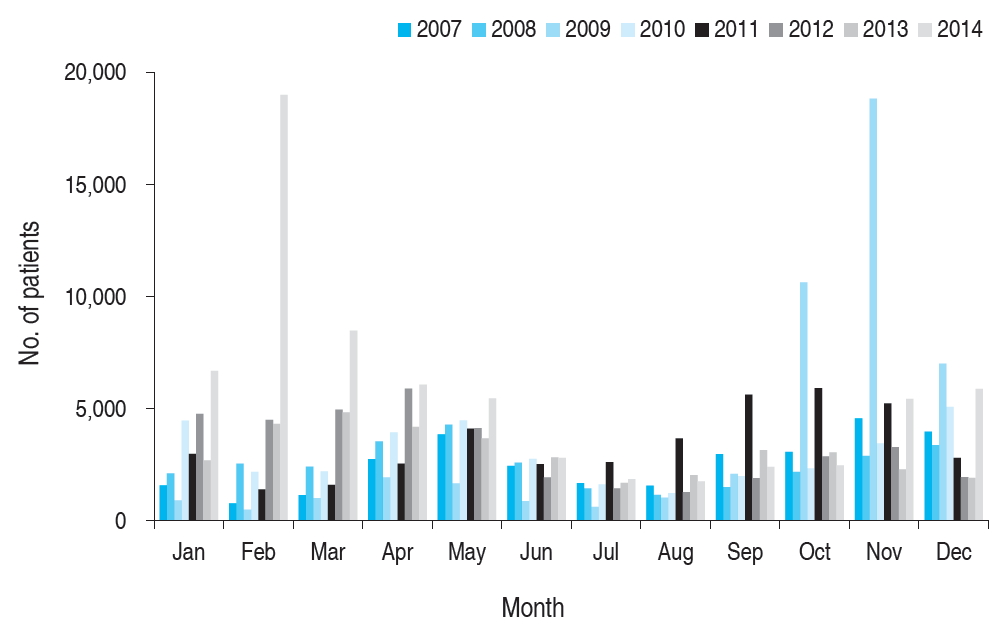
Purpose: Understanding changes in pathogen and pneumonia prevalence among pediatric pneumonia patients is important for the prevention of infectious diseases. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed data of children younger than 18 years diagnosed with pneumonia at 117 Emergency Departments in Korea between 2007 and 2014. Results: Over the study period, 329,380 pediatric cases of pneumonia were identified. The most frequent age group was...
- Infection
- Usefulness of the procalcitonin test in young febrile infants between 1 and 3 months of age
- In Sul Lee, Young Jin Park, Mi Hyeon Jin, Ji Young Park, Hae Jeong Lee, Sung Hoon Kim, Ju Suk Lee, Cheol Hong Kim, Young Don Kim, Jun Hwa Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(9):285-290. Published online September 15, 2018
-

Purpose: To study the usefulness of the procalcitonin (PCT) test in young febrile infants between 1 and 3 months of age. Methods: We evaluated the medical records of 336 febrile infants between 1 and 3 months of age who visited the Emergency Department or outpatient department of Samsung Changwon Hospital from May 2015 to February 2017, and analyzed the clinical characteristics...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Oral findings and its association with prenatal and perinatal factors in newborns
- Brenda Perez-Aguirre, Uriel Soto-Barreras, Juan Pablo Loyola-Rodriguez, Juan Francisco Reyes-Macias, Miguel Angel Santos-Diaz, Alejandra Loyola-Leyva, Obed Garcia-Cortes
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(9):279-284. Published online September 15, 2018
-
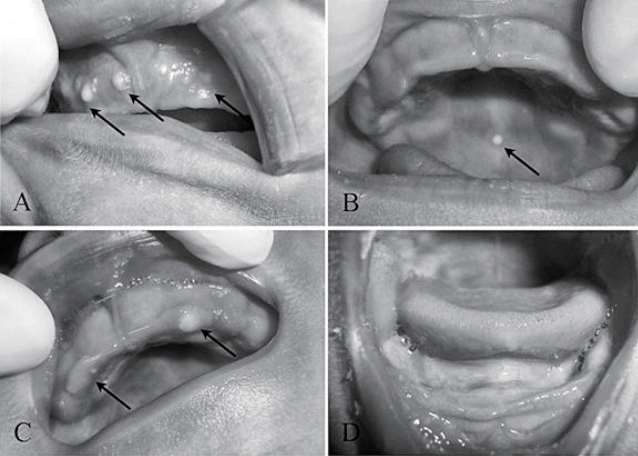
Purpose: This study aimed to determine the frequency of abnormalities in the newborn oral cavity and to evaluate the association with prenatal and perinatal factors. Methods: This cross-sectional study evaluated 2,216 newborns. Oral findings were assessed in the first 24 hours of life using visual examination. Sex, weight, length, gestational age, and medical disorders at birth were recorded. Maternal demographic and...
- Cardiology
- Change of voltage-gated potassium channel 1.7 expressions in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension rat model
- Hyeryon Lee, Kwan Chang Kim, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(9):271-278. Published online September 15, 2018
-

Purpose: Abnormal potassium channels expression affects vessel function, including vascular tone and proliferation rate. Diverse potassium channels, including voltage-gated potassium (Kv) channels, are involved in pathological changes of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Since the role of the Kv1.7 channel in PAH has not been previously studied, we investigated whether Kv1.7 channel expression changes in the lung tissue of a monocrotaline...
- Review Article
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Transfusion practice in neonates
- Do-Hyun Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(9):265-270. Published online September 6, 2018
-

Neonates, especially extremely low birth weight infants, are among the groups of patients undergoing transfusion frequently. Since they are exposed to higher specific transfusion risks compared to the patients of other age groups, there are many special aspects that must be considered for transfusion therapy in neonates. The transfusion risks in neonates include adverse outcomes specific for preterm infants as...
- Erratum
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Erratum: Pediatric kidney transplantation is different from adult kidney transplantation
- Min Hyun Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):264-264. Published online August 15, 2018
-
- Original Article
- Pulmonology
- Increased procalcitonin level is a risk factor for prolonged fever in children with Mycoplasma pneumonia
- Ji Eun Jeong, Ji Eun Soh, Ji Hee Kwak, Hye Lim Jung, Jae Won Shim, Deok Soo Kim, Moon Soo Park, Jung Yeon Shim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):258-263. Published online August 15, 2018
-
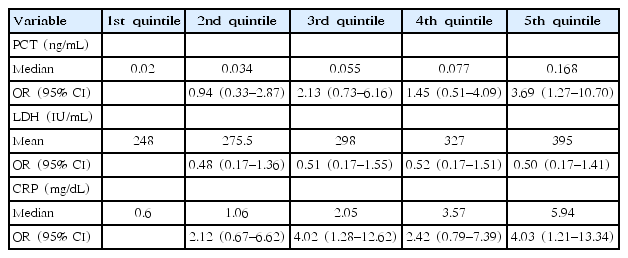
Purpose: Macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) is characterized by prolonged fever and radiological progression despite macrolide treatment. Few studies have examined serum procalcitonin (PCT) level in children with MPP. We aimed to investigate the association of acute inflammation markers including PCT with clinical parameters in children with MPP. Methods: A total of 147 children were recruited. The diagnosis of MPP...
- General Pediatrics
- Use of child safety seats during transportation of newborns
- Seon Hyuk Kim, Sung Won Park, Yeon Kyung Lee, Sun Young Ko, Son Moon Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):253-257. Published online August 15, 2018
-
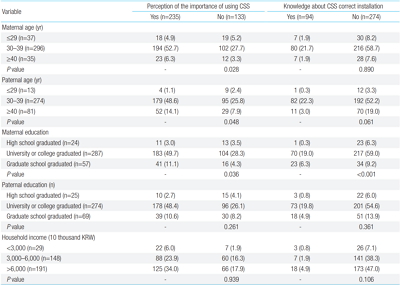
Purpose: Child safety seats (CSS) are critical for the protection of children, in case of motor vehicle accidents. Although the national legislation mandates that all newborns must be placed in an appropriately installed CSS during transportation, people often do not perceive the importance of CSS and do not use it as recommended. The purpose of this survey was to understand...
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Patterns of ischemic injury on brain images in neonatal group B Streptococcal meningitis
- Seo Yeol Choi, Jong-Wan Kim, Ji Won Ko, Young Seok Lee, Young Pyo Chang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):245-252. Published online August 15, 2018
-
Purpose: This study investigated patterns of ischemic injury observed in brain images from patients with neonatal group B Streptococcal (GBS) meningitis. Methods: Clinical findings and brain images from eight term or near-term newborn infants with GBS meningitis were reviewed. Results: GBS meningitis was confirmed in all 8 infants via cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis, and patients tested positive for GBS in both blood and CSF cultures....
- The impact of a quality improvement effort in reducing admission hypothermia in preterm infants following delivery
- Han Saem Choi, Soon Min Lee, Hoseon Eun, Minsoo Park, Kook-In Park, Ran Namgung
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):239-244. Published online August 15, 2018
-
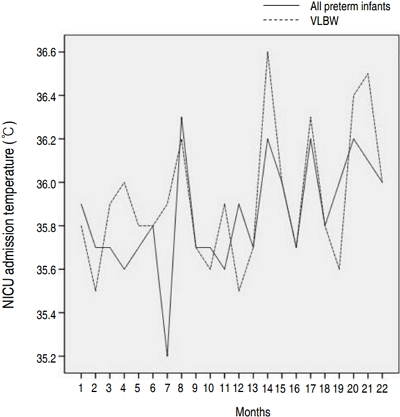
Purpose: Hypothermia at admission is associated with increased mortality and morbidity in preterm infants. We performed a quality improvement (QI) effort to determine the impact of a decrease in admission hypothermia in preterm infants. Methods: The study enrolled very low birth weight (VLBW) infants born at Gangnam Severance Hospital between January 2013 and December 2016. This multidisciplinary QI effort included the...
- Review article
- Nutrition
- Prevalence of underweight and wasting in Iranian children aged below 5 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Yousef Moradi, Fatemeh Khosravi Shadmani, Kamyar Mansori, Shiva Mansouri Hanis, Rozhin Khateri, Hossein Mirzaei
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(8):231-238. Published online August 15, 2018
-
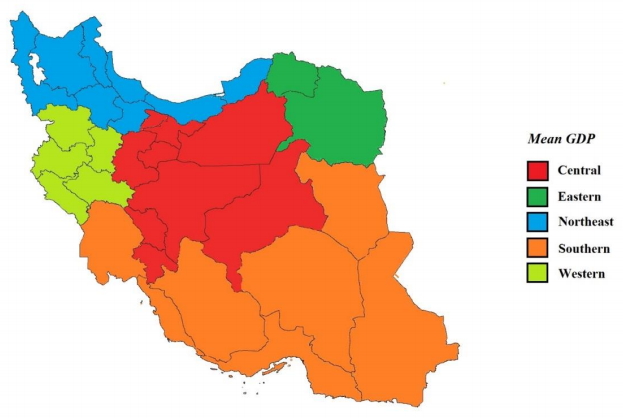
Purpose: Wasting and underweight are the 2 main indicators of children’s undernutrition. We aimed to estimate the prevalence of undernutrition at the national level in Iran. Methods: We performed a search for original articles published in international and Iranian databases including MEDLINE, Web of Science, Google Scholar, Scopus, CINHAL (Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature), Scientific Information Database, Irandoc,...
- Original Article
- Endocrinology
- Changes of the growth plate in children: 3-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging analysis
- Hyung Ho Yun, Hyun-Jung Kim, Min-Sun Jeong, Yun-Sun Choi, Ji-Young Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(7):226-230. Published online July 15, 2018
-

Purpose: This pilot study assessed changes in the growth plate and growth rates in children during a 6-month period. Methods: The study included 31 healthy children (17 boys, 14 girls) under evaluation for growth retardation. Height, weight, bone age, insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), and insulin like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGF-BP3) were measured at baseline and after 6 months....
- Final height of Korean patients with early treated congenital hypothyroidism
- Jiyun Lee, Jeongho Lee, Dong Hwan Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(7):221-225. Published online July 15, 2018
-
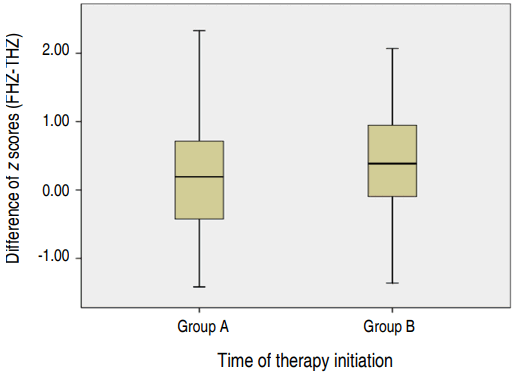
Purpose: Congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is the most common endocrine disorder in children. Thyroid hormone deprivation results not only in mental retardation but also growth retardation. This study investigates the final height (FH) in Korean patients with CH detected by newborn screening and examines factors that may affect the FH. Methods: The medical records of Korean CH patients (n=45) were reviewed. The...
- Autoimmunity and intestinal colonization by Candida albicans in patients with type 1 diabetes at the time of the diagnosis
- Semra Gürsoy, Tuba Koçkar, Sezen Ugan Atik, Zerrin Önal, Hasan Önal, Erdal Adal
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(7):217-220. Published online July 15, 2018
-
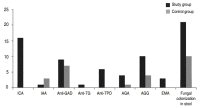
Purpose: Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is a chronic and immune-mediated disease, which is characterized by the progressive destruction of pancreatic beta cells. T1DM precipitates in genetically susceptible individuals through environmental factors. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the impact of autoimmunity and intestinal colonization of Candida albicans on the development of T1DM. Methods: Forty-two patients newly diagnosed with T1DM...
- Cardiology
- Outcome of neonatal palliative procedure for pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect or tetralogy of Fallot with severe pulmonary stenosis: experience in a single tertiary center
- Tae Kyoung Jo, Hyo Rim Suh, Bo Geum Choi, Jung Eun Kwon, Hanna Jung, Young Ok Lee, Joon Yong Cho, Yeo Hyang Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2018;61(7):210-216. Published online July 15, 2018
-

Purpose: The present study aimed to evaluate progression and prognosis according to the palliation method used in neonates and early infants aged 3 months or younger who were diagnosed with pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect (PA VSD) or tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) with severe pulmonary stenosis (PS) in a single tertiary hospital over a period of 12 years. Methods: Twenty...
-

-
-
8.02023CiteScore94th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.2
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











