Search
- Page Path
-
- HOME
- Search
- Original Article
- Global and regional burden of neonatal disorders (preterm birth, encephalopathy, jaundice, and sepsis), 1990–2021 and projections to 2050
- Yuseon Kang, Jeongseon Oh, Dongjin Yeo, Jaeyu Park, Sooji Lee, Na Yun Kim, Jungmin Park, Seung Ha Hwang, Tae Hyeong Kim, Dong Keon Yon
-
Background: Although most neonatal disorders are preventable, their global burden has not been comprehensively investigated in the context of underlying epidemiological patterns. Thus, here we conducted the first comprehensive assessment of the global burden of neonatal disorders and their 5 subtypes in 1990–2021 with projections through 2050.
Purpose: To comprehensively assess the global burden of neonatal disorders in 1990–2021 and forecast... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.01480 [Accepted]
- High-dose methylprednisolone and tocilizumab improve survival of patients with high-risk pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy
- Chaonan Fan, Fei Li, Kechun Li, Zheng Li, Yiyang Mao, Lijuan Wang, Gang Liu, Yingchao Liu, Quan Wang, Suyun Qian
-
Background: Acute necrotizing encephalopathy (ANE) is a rare but devastating neurological disorder in children that is typically triggered by viral infections such as influenza, sudden acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, and human herpesvirus-6. ANE is characterized by cytokine storm and associated with high mortality; however, optimal immunomodulatory strategies remain undefined.
Purpose: To evaluate the effectiveness of multiple immunomodulatory strategies, including high-dose methylprednisolone (MP), plasma exchange (PLEX), and tocilizumab, at reducing short-term... -
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3345/cep.2025.01431 [Accepted]
- Endocrinology
- Long-term epidemiological insights into rickets: a nationwide population-based retrospective study
- Chun-Hao Chu, Ying-Chuan Chen, Pei-Yao Liu, Chun-Chieh Hu, Yu-Lung Lin, Feng-Chih Kuo, Chieh-Hua Lu, Tzu-Ju Hsu, Yu-Tung Hung, Fuu-Jen Tsai, Chien-Ming Lin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(11):879-891. Published online August 20, 2025
-

Question: What are the nationwide trends and mortality risk factors of nutritional versus hereditary rickets among children in Asia?
Finding: In 2012–2018, the incidence of rickets steadily increased, whereas mortality rates declined. Mortality is associated with a low household income, anemia, chronic kidney disease, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and a prolonged hospital stay.
Meaning: Early diagnosis and targeted interventions addressing social and medical vulnerabilities are critical to reducing ricket-related mortality.
- Infection
- Clinical characteristics and associated factors of pediatric acute necrotizing encephalopathy: a retrospective study
- Huiling Zhang, Yilong Wang, Qianyun Ding, Xuekun Li, Sheng Ye
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2025;68(2):153-162. Published online November 11, 2024
-
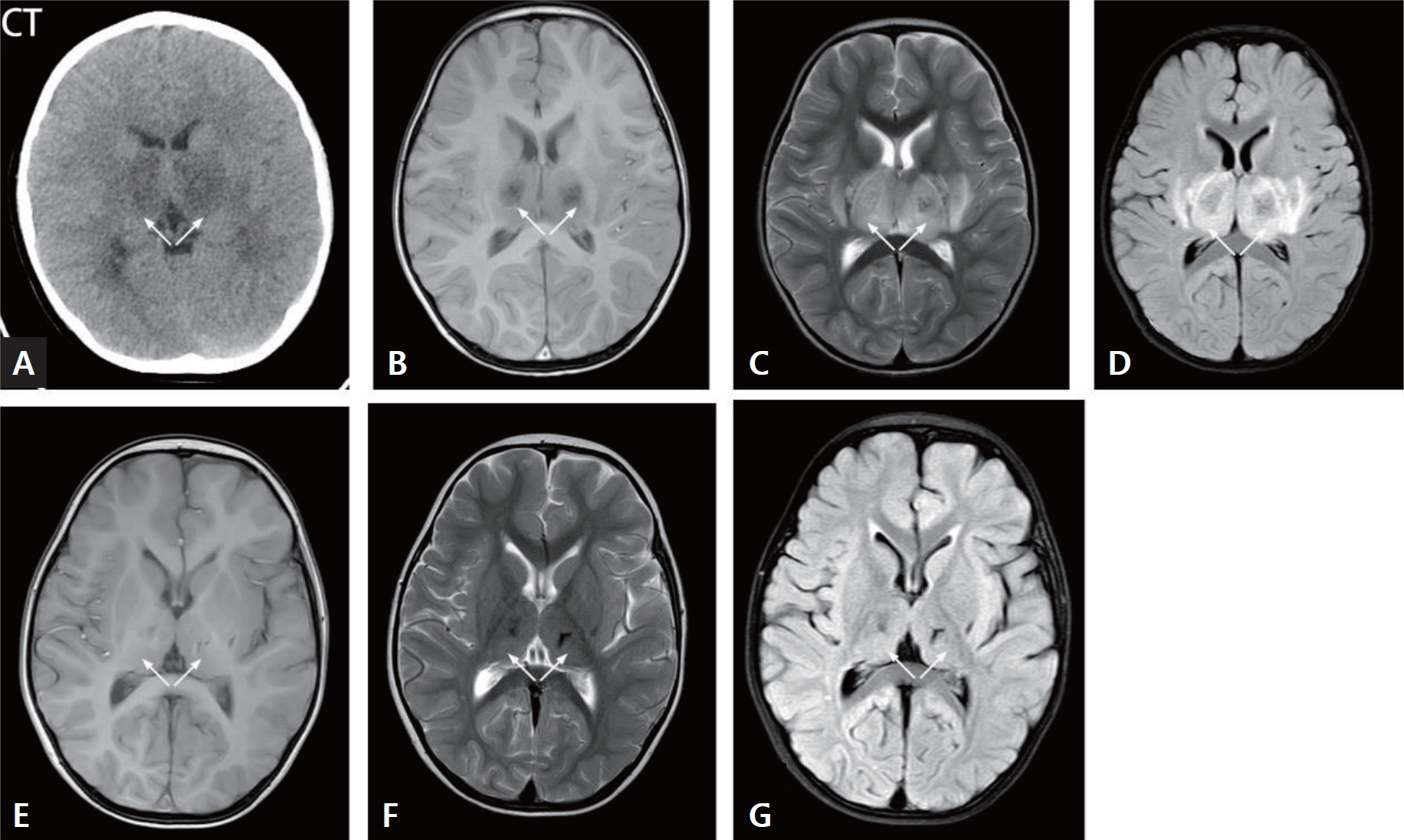
· The mortality rate of acute necrotizing encephalopathy was high.
· Laboratory tests revealed that the fatal group had higher creatinine, lactate, activated partial thromboplastin time, thrombin time, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-10, creatine kinase, and D-dimer than survivors.
· The fatal group displayed lower Glasgow Coma Scale scores and arterial pH.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Mortality of very low birth weight infants by neonatal intensive care unit workload and regional group status
- Sung-Hoon Chung, Chae Young Kim, Yong-Sung Choi, Myung Hee Lee, Jae Woo Lim, Byong Sop Lee, Ki-Soo Kim; the Korean Neonatal Network
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2024;67(11):619-627. Published online September 12, 2024
-

Question: How do structural and staffing characteristics of neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) influence the mortality rates of very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs)?
Findings: NICUs with higher staffing levels, particularly with more neonatologists, and those offering advanced care levels were associated with lower mortality rates. Additionally, regional disparities were observed, with some areas demon-strating significantly higher survival rates.
Meaning: Adequate staffing and equitable regional distribution of medical resources are crucial for improving survival outcomes in VLBWIs. Efforts to enhance NICU staffing and address regional healthcare disparities are essential for optimizing care quality and reducing mortality in this vulnerable population.
- Other
- Spatial modeling of mortality from acute lower respiratory infections in children under 5 years of age in 2000–2017: a global study
- Ali Almasi, Sohyla Reshadat, Alireza Zangeneh, Mehdi Khezeli, Raziyeh Teimouri, Samira Rahimi Naderi, Shahram Saeidi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(12):632-641. Published online March 19, 2021
-

Question: We assessed the spatial modeling of mortality from acute lower respiratory infections in children under 5 years old during 2000–2017 using a global data.
Finding: The total number of child deaths during the study period decreased, while the number of hot spots increased among countries.
Meaning: Hot spots were concentrated in Asia in 2000 but shifted toward African countries by 2017. A cold spot formed in Europe over the study period.
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- New modified version of the Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery category and mortality in premature infants with critical congenital heart disease
- Young Mi Yoon, Seong Phil Bae, Yoon-Joo Kim, Jae Gun Kwak, Woong-Han Kim, Mi Kyoung Song, Seung Han Shin, Ee-Kyung Kim, Han-Suk Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(10):395-401. Published online July 15, 2020
-
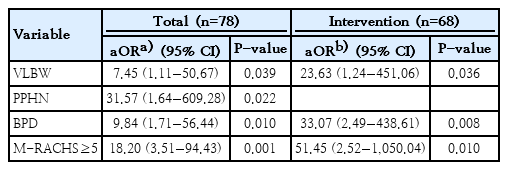
Questions: This study aimed to describe the survival of premature infants with critical congenital heart disease (CHD) and to identify the risk factors including the new modified version of the Risk Adjustment for Congenital Heart Surgery (M-RACHS) associated with mortality.
Finding: For premature infants with critical CHD, survival rate was 76.9% and very low birth weight (VLBW), persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN), bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), and M-RACHS 5 or more were associated with in-hospital mortality.
Meaning: VLBW, PPHN and BPD, as well as M-RACHS≥5, were risk factors for mortality among premature infants with critical CHD.
- Review Article
- Other
- Review of epidemiological studies on air pollution and health effects in children
- Jong-Tae Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2021;64(1):3-11. Published online June 10, 2020
-
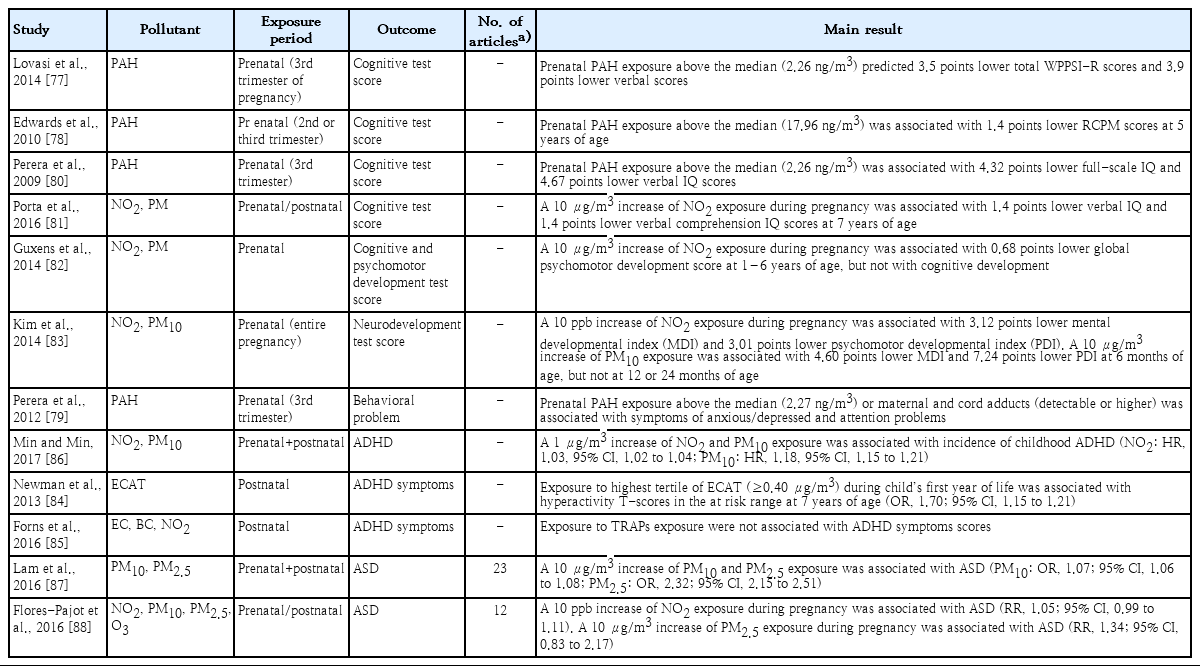
This review summarized the accumulated epidemiologic evidence with emphasis on studies conducted in Korea and heterogeneity in the literature. Based on systematic reviews and meta-analyses, there is consistent evidence on the association between exposure to ambient air pollution and children’s health, especially respiratory health and adverse birth outcomes, and growing evidence on neurodevelopmental outcomes.
- Original Article
- Critical Care Medicine
- Comparative validity of microalbuminuria versus clinical mortality scores to predict pediatric intensive care unit outcomes
- Shifa Nismath, Suchetha S. Rao, B.S. Baliga, Vaman Kulkarni, Gayatri M. Rao
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2020;63(1):20-24. Published online August 12, 2019
-

Question: Does microalbuminuria predict mortality in pediatric intensive care unit?
Finding: Positive correlation was found between albumin-creatinine ratio and pediatric intensive care unit stay, organ dysfunction and need of inotropes. Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for albumin-creatinine ratio was comparable to mortality scores.
Meaning: Microalbuminuria is a good predictor of outcome in pediatric intensive care unit and is comparable with mortality scores.
- Clinical features and surgical outcomes of complete transposition of the great arteries
- Suk Jin Hong, Hee Joung Choi, Yeo Hyang Kim, Myung Chul Hyun, Sang Bum Lee, Joon Yong Cho
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2012;55(10):377-382. Published online October 29, 2012
-
Purpose This single-center study aimed to assess the clinical features and surgical approaches and outcomes of complete transposition of the great arteries (TGA).
Methods TGA patients who had undergone surgical correction at the Kyungpook National University Hospital from January 2000 to December 2010, were retrospectively evaluated for patient characteristics, clinical manifestation, preoperative management, intraoperative findings, postoperative progress, and follow-up status.
Results Twenty-eight patients (17 boys...
- Review Article
- Changes in the neonatal and infant mortality rate and the causes of death in Korea
- Sung-Hoon Chung, Yong-Sung Choi, Chong-Woo Bae
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(11):443-455. Published online November 30, 2011
-
Neonatal mortality rate (NMR) or infant mortality rate (IMR) are the rate of deaths per 1,000 live births at which babies of either less than four weeks or of one year of age die, respectively. The NMR and IMR are commonly accepted as a measure of the general health and wellbeing of a population. Korea's NMR and IMR fell significantly...
- Original Article
- Outcomes of small for gestational age micropremies depending on how young or how small they are
- Hee Joon Yu, Eun Sun Kim, Jin Kyu Kim, Hye Soo Yoo, So Yoon Ahn, Yun Sil Chang, Won Soon Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2011;54(6):246-252. Published online June 30, 2011
-
Purpose The outcomes of small for gestational age (SGA) infants especially in extremely low birth weight infants (ELBWIs) are controversial. This study evaluated the mortality and morbidity of ELBWIs, focusing on whether or not they were also SGA.
Methods The medical records of 415 ELBWIs (birth weight <1,000 g), who were inborn and admitted to the Samsung Medical Center neonatal intensive care unit...
- An 18-year experience of tracheoesophageal fistula and esophageal atresia
- Juhee Seo, Do Yeon Kim, Ai Rhan Kim, Dae Yeon Kim, Seong Chul Kim, In Koo Kim, Ki Soo Kim, Chong Hyun Yoon, Soo Young Pi
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(6):705-710. Published online June 23, 2010
-
Purpose To determine the clinical manifestations and outcomes of patients with tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) and esophageal atresia (EA) born at a single neonatal intensive care unit.
Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted for 97 patients with confirmed TEF and EA who were admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit between 1990 and 2007.
Results The rate of prenatal diagnosis was 12%. The average gestational age...
- Effect of severe neonatal morbidities on long term outcome in extremely low birthweight infants
- Kyo Yeon Koo, Jeong Eun Kim, Soon Min Lee, Ran Namgung, Min Soo Park, Kook In Park, Chul Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(6):694-700. Published online June 23, 2010
-
Purpose To assess the validity of individual and combined prognostic effects of severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), brain injury, retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), and parenteral nutrition associated cholestasis (PNAC).
Methods We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 80 extremely low birthweight (ELBW) infants admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) of the Severance Children's Hospital, and who survived to a postmenstrual age of...
- Effect of hyperglycemia on mortality rates in critically ill children
- Seongkuk Kim, Bo Eun Kim, Eun Ju Ha, Mi Young Moon, Seong Jong Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2010;53(3):323-328. Published online March 15, 2010
-
Purpose : To verify the effect of hyperglycemia on mortality rates in critically ill children and to identify the blood glucose level that influences prognosis. Methods : From July 2006 to June 2008, a total of 206 patients who were admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) at Asan Medical Center and who survived for more than 7 days... -
- Outcome and risk factors of pediatric hemato-oncology patients admitted in pediatric intensive care unit
- Bo Eun Kim, Eun Ju Ha, Keun Wook Bae, Seongguk Kim, Ho Joon Im, Jong Jin Seo, Seong Jong Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(10):1153-1160. Published online October 15, 2009
-
Purpose : To evaluate the risk factors for mortality and prognostic factors in pediatric hemato-oncology patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU). Methods : We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of pediatric hemato-oncology patients admitted at the PICU of the Asan Medical Center between September 2005 and July 2008. Patients admitted at the PICU for perioperative or terminal... -
- Clinical features and results of recent total anomalous pulmonary venous connection : Experience in a university hospital (Clinical study of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection)
- Mi Ae Chu, Byung Ho Choi, Hee Joung Choi, Yeo Hyang Kim, Joon Yong Cho, Myung Chul Hyun, Sang Bum Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2009;52(2):194-198. Published online February 15, 2009
-
Purpose : Active perioperative intervention and improvement on surgical technique has decreased the mortality rate of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (TAPVC); however, when complicated with pulmonary venous obstruction, operative mortality is still high. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical course of TAPVC. Methods : Twenty-seven patients who were diagnosed with TAPVC (without other complex heart... -
- Performance effectiveness of pediatric index of mortality 2 (PIM2) and pediatricrisk of mortality III (PRISM III) in pediatric patients with intensive care in single institution: Retrospective study
- Hui Seung Hwang, Na Young Lee, Seung Beom Han, Ga Young Kwak, Soo Young Lee, Seung Yun Chung, Jin Han Kang, Dae Chul Jeong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(11):1158-1164. Published online November 15, 2008
-
Purpose : To investigate the discriminative ability of pediatric index of mortality 2 (PIM2) and pediatric risk of mortality III (PRISM III) in predicting mortality in children admitted into the intensive care unit (ICU). Methods : We retrospectively analyzed variables of PIM2 and PRISM III based on medical records with children cared for in a single hospital ICU from January 2003... -
- Early stress hyperglycemia as independent predictor of increased mortality in preterm infants
- Young Sun Wee, Gae Hyun Ahn, Eun Gyong Yoo, In Sook Lim, Kyu Hyung Lee
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2008;51(5):474-480. Published online May 15, 2008
-
Purpose : Stress hyperglycemia is common in critically ill adult patients. It is known as a predictor of increased mortality, and intensive insulin therapy has been shown to improve the prognosis in such patients. We have investigated the relationship between early stress hyperglycemia and clinical outcomes in preterm infants. Methods : In this study, 141 preterm infants with a gestational age... -
- Antithrombin-III as an early prognostic factor in children with acute lung injury
- Young Seung Lee, Seonguk Kim, Eun Kyeong Kang, June Dong Park
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2007;50(5):443-448. Published online May 15, 2007
-
Purpose : To evaluate the potential prognostic value of the antithrombin-III (AT-III) level in the children with acute lung injury (ALI), we analyzed several early predictive factors of death including AT-III level at the onset of ALI and compared the relative risk of them for mortality. Methods : Over a 18-month period, a total of 198 children were admitted to our... -
- Clinical significance of cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis in pediatric refractory status epilepticus
- Jung Mi Kim, Young Mi Kim, Soon Hak Kwon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2006;49(10):1086-1092. Published online October 15, 2006
-
Purpose : Refractory status epilepticus(RSE) is a serious neurological emergency in children. The mortality is high and the neurological outcome is not good. This study aimed to evaluate the clinical significance of cerebrospinal fluid(CSF) pleocytosis in refractory status epilepticus in children. Methods : From January 1999 to January 2006, 25 out of 37 children with refractory status epilepticus had... -
- A Clinical Study of the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Children
- Taek Jin, Dong Soo Kim, Dong Hwan Shin
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2003;46(1):42-50. Published online January 15, 2003
-
Purpose : The acute respiratory distress syndrome(ARDS), an acute form of severe alveolar-capillary injury evolving after a direct or indirect lung insult is thought to be a common cause of respiratory failure though not many clinical studies on the subject have been made yet. Methods : Between January 1992 and December 2001, we conducted a retrospective study on 33 children who... -
- Frequency of Platelet Transfusions and Outcome in Neonates with Thrombocytopenia
- Suk-Hwan Lim, Jin-Hwa Kook, Chang-Yee Cho, Young-Youn Choi, Tai-Ju Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2002;45(8):961-966. Published online August 15, 2002
-
Purpose : We compared the underlying or associated diseases according to the frequency of platelet transfusions in neonates with thrombocytopenia to know the factors predicting which patients will require multiple platelet transfusions. We also compared mortality. Methods : A retrospective study was performed in 72 neonates who received the platelet transfusions in neonatal intensive care unit(NICU) between August 1996 and July... -
- Long-term Clinical Study of Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
- Jin Young Song, Yong Soo Yoon
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 2000;43(2):229-235. Published online February 15, 2000
-
Purpose : Total anomalous pulmonary venous return is a rare congenital heart disease, which is fatal if untreated, especially, if the obstruction in pulmonary venous return is obstructed. With the technical development of echocardiogram, we are now able to do an early diagnosis if TAPVR and perform surgery. Accordingly, this report was aimed to evaluate patients with TAPVR as well... -
- A Nationwide Clinical Study of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Children
- Soo Jung Choi, Do Suck Jeong, Jae Won Oh, Ha Baik Lee, Im Ju Kang, Kwang Woo Kim, Kyu Earn Kim, Ki Bok Kim, Young Ho Rah, Kang Seo Park, Byong Kwan Son, Ki Young Lee, Sang Il Lee, Ji Tai Choung, Young Mi Hong
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1999;42(1):23-31. Published online January 15, 1999
-
Purpose : Acute respiratory distress syndrome(ARDS) is the final course of acute lung injury. It results from various etiological origins and pathophysiologic mechanisms, and has a mortality rate of approximately 60-70%. Although the confirmative incidence of ARDS in children is yet unknown, the increasing incidence of ARDS has been reported in Korea. In the present study, we report ARDS diagnosed... -
- Prognostic Factors for Mortality in Neonates with Respiratory Distress Syndrome After Surfactant Replacement Therapy
- Nam Soo Kang, Byung Min Choi, Young Sook Hong, Joo Won Lee, Soon Kyum Kim
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1998;41(9):1188-1197. Published online September 15, 1998
-
Purpose : To evaluate the association between neonatal mortality and the initial response to surfactant replacement therapy, and to examine the correlation between the response type and other prognostic factors. Methods : Sixty-seven neonates with respiratory distress syndrome(RDS) were divided into two groups; group I(n=51) who survived and group II(n=16) who died within the first 28 days of life after one... -
- Study on Child Mortality among Korean Children
- Beom Soo Park, Moo Song Lee, Seung Pil Jeong, Yoon Ok Ahn
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1994;37(9):1264-1272. Published online September 15, 1994
-
To estimate the child and infant mortality rates among Korean children, a mortality survey was carried out in the province of Kyongsangnam¡¤buk-do. The study popolation are the beneficiaries of Korea Medical Insurance Coorporation(KMIC), Kyongsangnam¡¤buk-do area, among which the 3,867 and 1767 deaths occurred from Januray, 1989 to December, 1990 in Kyongsangnam-do area and from January, 1991 to December, 1991 in... -
- Neonatal Mortality
- Min Jeong Kim, Eun Eui Kim, Ock Seung Jeong, Son Sang Seo
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(3):356-363. Published online March 15, 1993
-
A review of all 919 perinatal deaths occuring in Il Sin Christian Hospital From 91985 to 1989 was carried out. The results of clinical analysis were as follows : 1) The overall perinatal mortality rate was 26.30 per 1,000 birth. 2) The perinatal mortality rate was lowest in the gestation group between 37~41 week and in the weight group between 2,501~4,000gm. 3) The perinatal... -
- Surfactant Replacement Therapy in Neonates with Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Collective Evaluation of Trials from 16 Hospitals
- CW Bae, YD Kwon, SJ Ko, KS Kim, HM Kim, WS Park, SH Byun, CS Son, HS Ahn, SG Lee, YP Chang, YJ Chung, KS Cho, KH Cho, KC Choeh, MJ Chey, JH Choi, JK Yoon, CI Ahn, S Chida, T Fujiwara
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1993;36(2):244-265. Published online February 15, 1993
-
Surfactant replacement therapy in neonates with respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) has been introduced in our country since May 1990. The purpose of this study was to assess the effect and short-term outcome of surfactant replacement for neonatal RDS using collective data of uncontrolled trials from different hospitals in Korea. For the period May 1990 to Dec. 1991, a total of 68... -
- Clinical Observation of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome: Prognostic Implication of Early Meconium Suctioning
- Dae Hyun Kim, Dong Hoon Ko, Young Jong Woo, Young Youn Choi, Tae Ju Hwang
- Clin Exp Pediatr. 1992;35(4):484-491. Published online April 15, 1992
-
The authors observed the clinical findings of 36 patients with meconium aspiration syndrome(MAS) to evaluate the effect of early appropriated meconium suctioning on the morbidity and mortality of the syndrome. Patients in the study group, 20 babies born in Chonnam university Hospital, received appropriate meconium suction through endotracheal tube during and rig-ht after the delivery, while the patients in the... -
-

-
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
-
- TOPICS
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Editorial Office
-
Korean Pediatric Society
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2025 by Korean Pediatric Society.











